BY 124L Quiz 7 Flashcards
1/195
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
196 Terms
Reproductive system
Responsible for producing gametes that fuse together with the opposite sex
Sperm
Male Sex Cells
Egg
Female sex cells
Reproductive system
responsible for the hormones being produced for development
Scrotum
houses the testes in males
Testes
Sperm production is in the ______
Cremaster muscles
retract the testes closer to the body to be warmer
2 degrees Celsius
Temperature is important (needs to be cooler)- Human testes are _____ cooler
Cremasteric Pouches
Testes are enclosed in the ____________ _______
Spermatic Cord
Cranially connected to the testes is the _________ ____
Spermatic Cord
Contains the vas deferens, spermatic artery and vein, nerves, and lymphatic vessels
Epididymis
coiled to the side of each teste
Seminiferous tubules
Sperm production is within the ________ ______ (be specific)
Epididymis
Sperm is stored in the ___________
leave the epididymis, into the vas deferens, and towards the urethra
Sperm ejaculation pathway
Yes
Do both woman and men have a urethra?
Vagina
Sperm are highly alkaline to fight the high acidity of the _______
Bulbourethral Glands and Preputial Gland
The 2 glands that produce the alkaline secretions that keep Sperm basic
Seminal vesicles
secrete a viscous fluid to keep the sperm from drying out
Vas deferens and urethra
Seminal vesicles are located at the junction of what 2 features?
Seminal vesicles
Fluid contains Fructose for energy and hormones to promote sperm motility in the female
Testicle

Epididymis

Sperm pathway/Vas deferens

Bladder

Seminal vesicle

Prostate

Penis
Female Reproductive System
Ovaries are paired, and located caudal to the kidneys
Oviduct
coiled “communications” to each ovary
Oocytes (eggs)
What does the oviduct carry during ovulation?
Oviduct
No physical connection; use “finger-like” projections to sweep eggs into the oviduct
Fertilization
occurs in the upper third of the oviduct
Implantation
occurs further in the Uterus
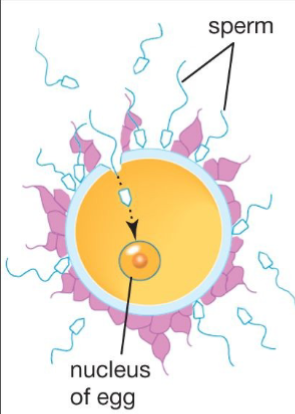
Nucleus

Egg
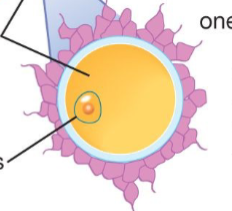
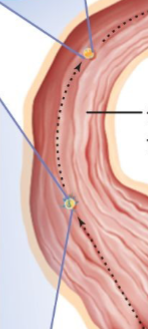
Egg leaves ovary and enters fallopian tube
Step 1
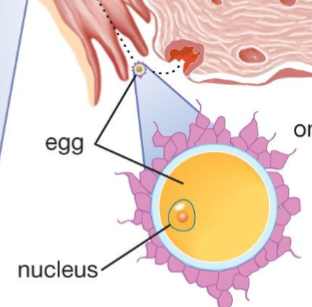
Ovary
Sperm enters egg and unites with nucleus
Step 2
Fallopian tube
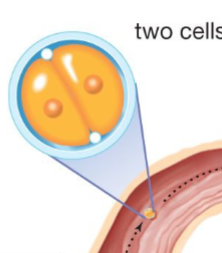
Fertilized egg divides
Step 3
Uterus
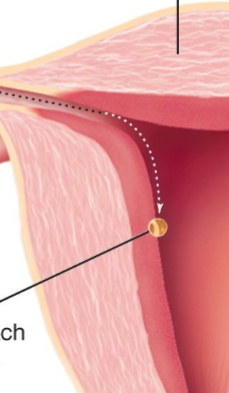
Cells attach to uterus
Step 4
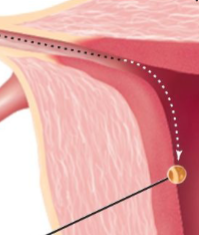
Uterine Horns
In Pigs, the Uterus is divided into ___________ ____, where embryonic development of the fetus occurs
Uterine Body
In pigs, where the Uterine Horns converge on the cervix
Uterine Horns
In humans, the ______ _____ reduced and the zygote implants and develop in the body of the Uterus
Cervix
construction of semi- cartilaginous tissue
Vagina
extends caudally from the Cervix
Urethra
Vagina and Cervix are joined by the _______
Urogenital Sinus
Vagina and Urethra open up to a common chamber called the
Urogenital sinus
Handles both reproductive and urinary systems
Opens to the outside of the body through the Urogenital Opening
Humans will NOT have a single opening, they are separate, but they are in proximity of each other
Fimbriae

Uterine Tube
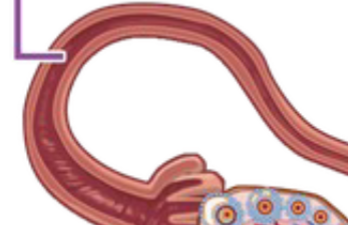
Fundus

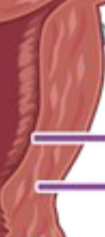
Endometrium
Inside wall

Myometrium
Outside wall
Cervix

Vagina
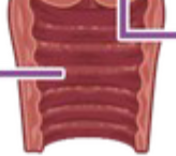
Ovary
Genital Papilla
On the fetus, the finger-like projection outside the body
Genital Papilla
Like the male penis
Sends sensations to the brain
Covers the Urogenital Opening
Penis

Preputial gland

Bulbourethral gland

Seminal vesicles

Urethra

Vas deferens

Epididymis

Testes

Ovary

Oviduct

Uterine horns

Urethra

Vagina

Urogenital Sinus

Genital pappila

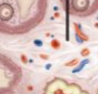
Ovaries
will be swollen due to hormone sinuses. Scars from released eggs can be seen
Infundibulum
Opening of the oviduct that receives eggs from the ovary
Mesosalpinx
Holds the coils of the oviduct and contains the blood vessels for the oviduct tissues
grow in size
Uterine Horns can and will _____ ____ ____ to accommodate the embryos developing
14
Pigs have a litter of __ (larger than humans)
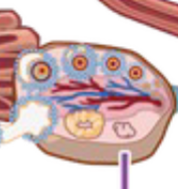
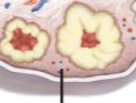
Ovarian medulla
Ovarian cortex
Ampulla
Isthmus
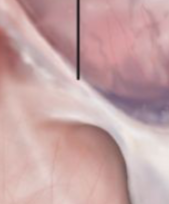
Intramural
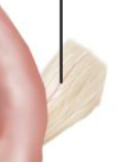
Ligament of ovary
Suspensory ligament of ovary
Mesovarium

Mesometrium
Round ligament of uterus
Mesosalpinx
Mesometrium, Mesosalpinx, Mesovarium
Makes up broad ligament of uterus- 3 parts
Uterosacral ligament
Chorionic Vesicle
Each Fetus is enclosed within a ______ _____
Placenta
where the Chorionic Vesicle and Uterine Lining come together
Placenta
Food, Gases, and Waste diffuse here
2 extra-embryonic membranes
Fetus is composed of ___ _____-________ ________
Chorion
Fetus outer membrane
Allantois
Fetus Inner Membrane, houses fetal metabolic wastes