[PT13] Thoracoabdominoinguinal, Spine & Back, Hip & Thigh
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/80
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
1
New cards
Which of the following muscles DOES NOT originate from the ischial tuberosity?
a. Semitendinosus
b. Semimembranosus
c. Biceps femoris short head
d. Adductor magnus
a. Semitendinosus
b. Semimembranosus
c. Biceps femoris short head
d. Adductor magnus
Biceps femoris short head. It attaches to the Linea Aspera.
2
New cards
The following structures are contained within the femoral sheath, EXCEPT:
a. Branch of genitofemoral nerve
b. Femoral nerve
c. Femoral artery and vein
d. Lymphatics
a. Branch of genitofemoral nerve
b. Femoral nerve
c. Femoral artery and vein
d. Lymphatics
Femoral nerve
3
New cards
Which of the following positions of the hip and knee stretches the hamstrings?
a. Hip flexion with knee extension
b. Hip extension with knee flexion
c. Hip flexion with knee flexion
d. Hip extension with knee extension
a. Hip flexion with knee extension
b. Hip extension with knee flexion
c. Hip flexion with knee flexion
d. Hip extension with knee extension
Hip flexion with knee extension
4
New cards
The following muscles laterally rotates the thigh at the hip joint, EXCEPT:
a. Gluteus maximus
b. Tensor fasciae latae
c. Sartorius
d. Quadratus femoris
a. Gluteus maximus
b. Tensor fasciae latae
c. Sartorius
d. Quadratus femoris
Tensor fasciae latae = FAbIR
5
New cards
The following are categorized as muscles of the pelvic walls and floor, EXCEPT:
a. Piriformis
b. Coccygeus
c. Levator ani
d. Obturator externus
a. Piriformis
b. Coccygeus
c. Levator ani
d. Obturator externus
Obturator externus
6
New cards
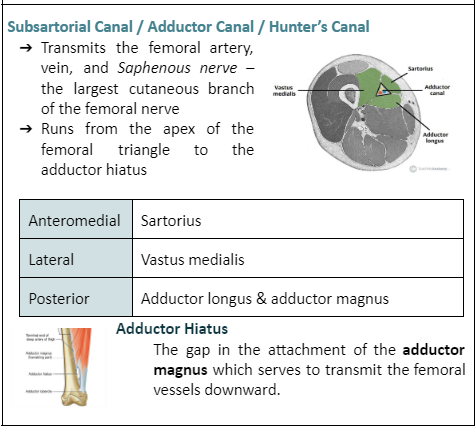
The lateral wall of the subsartorial canal is formed by the:
a. Vastus medialis
b. Adductor longus and magnus
c. Sartorius
d. Adductor brevis
a. Vastus medialis
b. Adductor longus and magnus
c. Sartorius
d. Adductor brevis
Vastus medialis
7
New cards
The Y-ligament of Bigelow is otherwise known as:
a. Inguinal ligament
b. Pubofemoral
c. Iliofemoral
d. Ischiofemoral
a. Inguinal ligament
b. Pubofemoral
c. Iliofemoral
d. Ischiofemoral
Iliofemoral
8
New cards
Which of the following muscles is innervated by both femoral and obturator nerve?
a. Piriformis
b. Pectineus
c. Biceps femoris
d. Adductor magnus
a. Piriformis
b. Pectineus
c. Biceps femoris
d. Adductor magnus
Pectineus
9
New cards
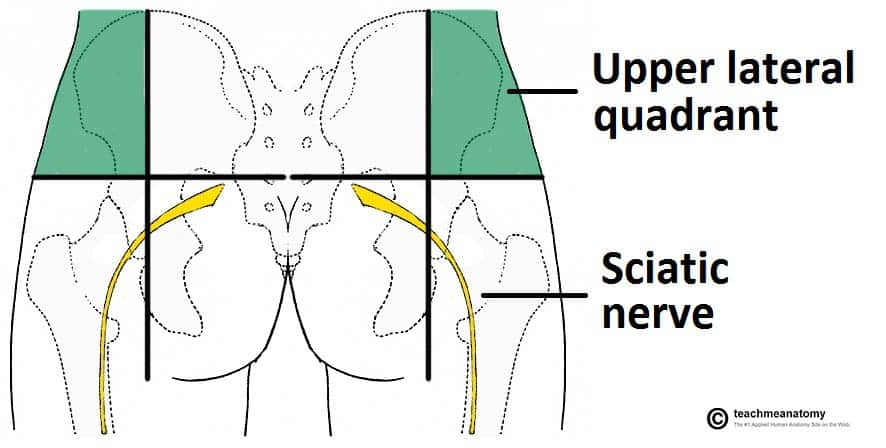
The safest area for gluteal intramuscular injections is the:
a. Upper outer quadrant
b. Upper inner quadrant
c. Lower outer quadrant
d. Lower inner quadrant
a. Upper outer quadrant
b. Upper inner quadrant
c. Lower outer quadrant
d. Lower inner quadrant
Upper outer quadrant
10
New cards
The following muscles insert on the pes anserine tendon, EXCEPT:
a. Semitendinosus
b. Semimembranosus
c. Gracilis
d. Sartorius
a. Semitendinosus
b. Semimembranosus
c. Gracilis
d. Sartorius
Semimembranosus
11
New cards
The piriformis muscle exits the pelvic cavity via:
a. Obturator foramen
b. Greater sciatic foramen
c. Lesser sciatic foramen
d. Femoral ring
a. Obturator foramen
b. Greater sciatic foramen
c. Lesser sciatic foramen
d. Femoral ring
Greater sciatic foramen
12
New cards
An increase in the neck – shaft angle of the femur is otherwise known as:
a. Coxa valga
b. Coxa vara
c. Genu valga
d. Genu vara
a. Coxa valga
b. Coxa vara
c. Genu valga
d. Genu vara
Coxa valga
13
New cards
The following muscles are supplied by the obturator nerve, EXCEPT:
a. Gracilis
b. Adductor brevis
c. Pectineus
d. Obturator internus
a. Gracilis
b. Adductor brevis
c. Pectineus
d. Obturator internus
Obturator internus. It is instead supplied by the nerve to obturator internus in the sacral plexus.
14
New cards
The femoral triangle is bounded by the following structures, EXCEPT:
a. Inguinal ligament
b. Sartorius
c. Adductor longus
d. Gracilis
a. Inguinal ligament
b. Sartorius
c. Adductor longus
d. Gracilis
Gracilis
15
New cards
The ligament that divides the sciatic notch into greater and lesser foramen is the:
a. Sacroiliac ligament
b. Sacrospinous ligament
c. Sacrococcygeal ligament
d. Iliolumbar ligament
a. Sacroiliac ligament
b. Sacrospinous ligament
c. Sacrococcygeal ligament
d. Iliolumbar ligament
Sacrospinous ligament
16
New cards
Trendelenburg sign is an indication of weakness of this muscle:
a. Gluteus medius
b. Piriformis
c. Adductor magnus
d. Sartorius
a. Gluteus medius
b. Piriformis
c. Adductor magnus
d. Sartorius
Gluteus Medius
17
New cards
The anterior superior iliac spine is the proximal attachment of this muscle:
a. Sartorius
b. Rectus femoris
c. Vastus intermedius
d. Iliopsoas
a. Sartorius
b. Rectus femoris
c. Vastus intermedius
d. Iliopsoas
Sartorius
18
New cards
The skin dimpling just above the intergluteal cleft is the surface landmark of:
a. Iliac crest
b. Posterior superior iliac spine
c. Coccyx
d. Posterior inferior iliac spine
a. Iliac crest
b. Posterior superior iliac spine
c. Coccyx
d. Posterior inferior iliac spine
Posterior superior iliac spine
19
New cards
Which of the following muscles DO NOT have attachment on the greater trochanter?
a. Gluteus medius
b. Iliopsoas
c. Obturator externus
d. Piriformis
a. Gluteus medius
b. Iliopsoas
c. Obturator externus
d. Piriformis
Iliopsoas. It attaches distally to the lesser trochanter.
20
New cards
The following muscle abducts the thigh at the hip joint, EXCEPT:
a. Sartorius
b. Tensor fasciae latae
c. Gluteus medius
d. Quadratus femoris
a. Sartorius
b. Tensor fasciae latae
c. Gluteus medius
d. Quadratus femoris
Quadratus femoris
21
New cards
The anterior inferior iliac spine is the proximal attachment of this muscle:
a. Sartorius
b. Rectus femoris
c. Vastus intermedius
d. Iliopsoas
a. Sartorius
b. Rectus femoris
c. Vastus intermedius
d. Iliopsoas
Rectus femoris
22
New cards
The posterior pelvic wall is formed by the following structures, EXCEPT:
a. Sacrum
b. Coccyx
c. Piriformis
d. Pubis
a. Sacrum
b. Coccyx
c. Piriformis
d. Pubis
Pubis
23
New cards
The obturator internus muscle exits the pelvic cavity via:
a. Obturator foramen
b. Lesser sciatic foramen
c. Greater sciatic foramen
d. Femoral ring
a. Obturator foramen
b. Lesser sciatic foramen
c. Greater sciatic foramen
d. Femoral ring
Lesser sciatic foramen
24
New cards
The adductor hiatus is formed by the attachment of this muscle in the femur:
a. Sartorius
b. Adductor magnus
c. Gracilis
d. Adductor longus
a. Sartorius
b. Adductor magnus
c. Gracilis
d. Adductor longus
Adductor magnus
25
New cards
The common action of the muscles inserted on the pes anserine tendon is:
a. Hip flexion
b. Hip extension
c. Knee flexion
d. Knee extension
a. Hip flexion
b. Hip extension
c. Knee flexion
d. Knee extension
Knee flexion
26
New cards
The following muscles are dually innervated, EXCEPT:
a. Pectineus
b. Adductor magnus
c. Biceps femoris
d. Piriformis
a. Pectineus
b. Adductor magnus
c. Biceps femoris
d. Piriformis
Piriformis
27
New cards
Which of the following muscles is innervated by both obturator and sciatic nerve?
a. Adductor magnus
b. Pectineus
c. Biceps femoris
d. Quadratus femoris
a. Adductor magnus
b. Pectineus
c. Biceps femoris
d. Quadratus femoris
Adductor magnus
28
New cards
The muscle that can flex, abduct and internally rotate the hip is:
a. Sartorius
b. Tensor fasciae latae
c. Gluteus medius
d. Iliopsoas
a. Sartorius
b. Tensor fasciae latae
c. Gluteus medius
d. Iliopsoas
Tensor fasciae latae
29
New cards
Which part of the quadriceps muscle keeps track the position of the patella in the anterior surface of the knee joint?
a. Rectus femoris
b. Vastus lateralis
c. Vastus intermedius
d. Vastus medialis
a. Rectus femoris
b. Vastus lateralis
c. Vastus intermedius
d. Vastus medialis
Vastus medialis
30
New cards
The common peroneal nerve come from this spinal roots:
a. L2 – L4
b. L4 – S1
c. L4 – S2
d. L4 – S3
a. L2 – L4
b. L4 – S1
c. L4 – S2
d. L4 – S3
L4 - S2
31
New cards
Which adductor muscle of the thigh is capable of flexing the knee joint?
a. Gracilis
b. Adductor magnus
c. Adductor longus
d. Adductor brevis
a. Gracilis
b. Adductor magnus
c. Adductor longus
d. Adductor brevis
Gracilis
32
New cards
The femoral artery is best palpated midway between ASIS and symphysis pubis especially when pressed against which muscle of the anterior compartment?
a. Psoas
b. Pectineus
c. Sartorius
d. Rectus femoris
a. Psoas
b. Pectineus
c. Sartorius
d. Rectus femoris
Pectineus
33
New cards
The following structures are easily palpable in the gluteal region, EXCEPT:
a. Iliac crests
b. ASIS
c. PIIS
d. Ischial tuberosity
a. Iliac crests
b. ASIS
c. PIIS
d. Ischial tuberosity
PIIS
34
New cards
The following structures belong to the anterior pillar of the spine, EXCEPT:
a. IV discs
b. Vertebral body
c. Anterior longitudinal ligament
d. Supraspinous ligament
a. IV discs
b. Vertebral body
c. Anterior longitudinal ligament
d. Supraspinous ligament
Supraspinous ligament
35
New cards
Rotation of the vertebral bodies lead to this condition:
a. Kyphosis
b. Lordosis
c. Scoliosis
d. Swayback
a. Kyphosis
b. Lordosis
c. Scoliosis
d. Swayback
Scoliosis
36
New cards
The ligament of the spine that connects adjacent laminae is the:
a. Ligamentum flavum
b. Intertransverse ligament
c. Interspinous ligament
d. Supraspinous ligament
a. Ligamentum flavum
b. Intertransverse ligament
c. Interspinous ligament
d. Supraspinous ligament
Ligamentum flavum
37
New cards
Abdominal flexion with rotation towards the left is accomplished by:
a. Left internal oblique, right external oblique and right transversus abdominis
b. Right internal oblique, left external oblique and left transversus abdominis
c. Left external and internal obliques, right transversus abdominis
d. Right external and internal obliques, left transversus abdominis
a. Left internal oblique, right external oblique and right transversus abdominis
b. Right internal oblique, left external oblique and left transversus abdominis
c. Left external and internal obliques, right transversus abdominis
d. Right external and internal obliques, left transversus abdominis
Left internal oblique, right external oblique and right transversus abdominis.
\
Ipsilateral Rotation - Internal Oblique
Contralateral Rotation - External Oblique & Transversus Abdominis
\
Ipsilateral Rotation - Internal Oblique
Contralateral Rotation - External Oblique & Transversus Abdominis
38
New cards
The following muscles of the anterior thoracic wall elevate the ribs, EXCEPT:
a. External intercostal
b. Levator costarum
c. Subcostal
d. Transversus thoracis
a. External intercostal
b. Levator costarum
c. Subcostal
d. Transversus thoracis
Transversus thoracis
39
New cards
The roof of the vertebral arch is formed by the:
a. Vertebral body
b. Pedicle
c. Lamina
d. Transverse process
a. Vertebral body
b. Pedicle
c. Lamina
d. Transverse process
Lamina
40
New cards
Which of the following vertebra has a heart-shaped body?
a. Cervical
b. Thoracic
c. Lumbar
d. Sacral
a. Cervical
b. Thoracic
c. Lumbar
d. Sacral
Thoracic
41
New cards
The ligament of the spine that limits hyperextension:
a. Anterior longitudinal ligament
b. Posterior longitudinal ligament
c. Supraspinous ligament
d. Ligamentum flavum
a. Anterior longitudinal ligament
b. Posterior longitudinal ligament
c. Supraspinous ligament
d. Ligamentum flavum
Anterior longitudinal ligament
42
New cards
The following are intrinsic muscles of the back, EXCEPT:
a. Spinalis
b. Semispinales
c. Splenius cervicis
d. Serratus posterior inferior
a. Spinalis
b. Semispinales
c. Splenius cervicis
d. Serratus posterior inferior
Serratus posterior inferior
43
New cards
Flexion of the thoracic spine is accomplished by the following muscles, EXCEPT:
a. Rectus abdominis
b. External abdominal oblique
c. Internal abdominal oblique
d. Transversus abdominis
a. Rectus abdominis
b. External abdominal oblique
c. Internal abdominal oblique
d. Transversus abdominis
Transversus abdominis
44
New cards
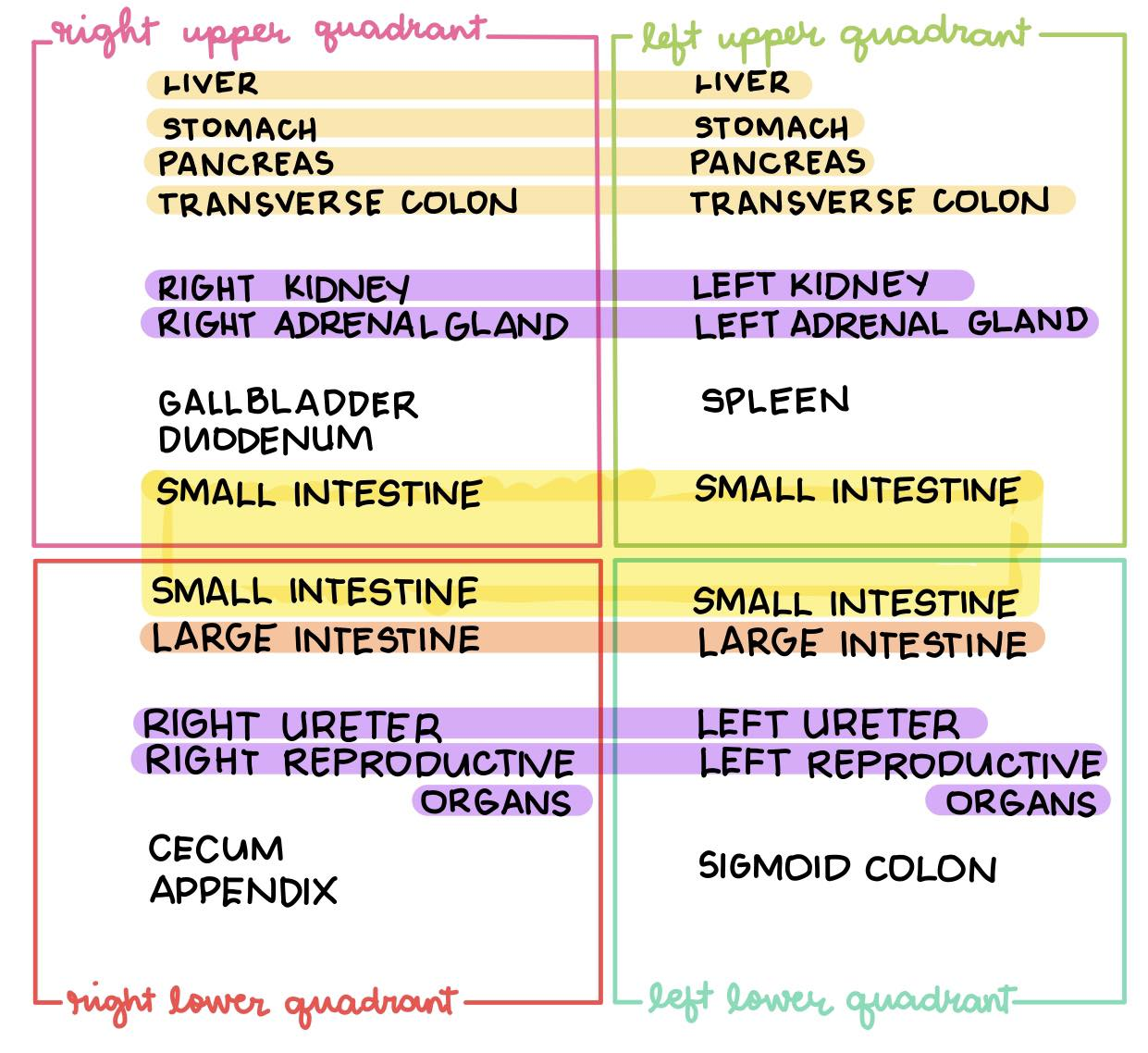
The median and transumbilical planes divide the abdomen into four quadrants. Which quadrant is the appendix located?
a. Right upper quadrant
b. Right lower quadrant
c. Left upper quadrant
d. Left lower quadrant
a. Right upper quadrant
b. Right lower quadrant
c. Left upper quadrant
d. Left lower quadrant
Right lower quadrant
45
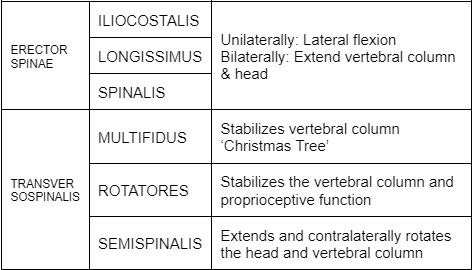
New cards
Which of the following DOES NOT belong as a major muscle group of the erector spinae?
a. Spinalis
b. Semispinalis
c. Iliocostalis
d. Longissimus
a. Spinalis
b. Semispinalis
c. Iliocostalis
d. Longissimus
Semispinalis
46
New cards
What important artery passes through the transverse foramina of C1-C6?
a. Spinal artery
b. Vertebral artery
c. Jugular artery
d. Subclavian artery
a. Spinal artery
b. Vertebral artery
c. Jugular artery
d. Subclavian artery
Vertebral artery
47
New cards
Herniated intervertebral discs often occur in this area:
a. Cervical
b. Thoracic
c. Lumbar
d. Sacral
a. Cervical
b. Thoracic
c. Lumbar
d. Sacral
Lumbar
48
New cards
Which dermatome overlies the umbilicus?
a. T4
b. T7
c. T10
d. T12
a. T4
b. T7
c. T10
d. T12
T10
49
New cards
Which of the following vertebras has a bifid spine?
a. Cervical
b. Thoracic
c. Lumbar
d. Sacral
a. Cervical
b. Thoracic
c. Lumbar
d. Sacral
Cervical
50
New cards
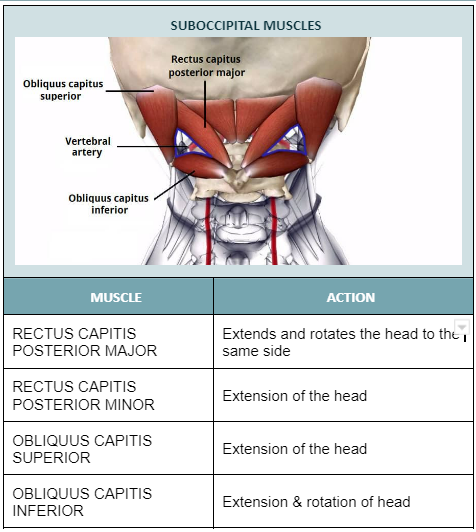
Which suboccipital muscle extends the head and rotates it to the same side?
a. Rectus capitis posterior major
b. Rectus capitis posterior minor
c. Obliquus capitis superior
d. Obliquus capitis inferior
a. Rectus capitis posterior major
b. Rectus capitis posterior minor
c. Obliquus capitis superior
d. Obliquus capitis inferior
Rectus capitis posterior major
51
New cards
The muscles that primarily adduct the thigh at the hip joint is located in:
a. Anterior fascial compartment
b. Posterior fascial compartment
c. Medial fascial compartment
d. Lateral thigh
a. Anterior fascial compartment
b. Posterior fascial compartment
c. Medial fascial compartment
d. Lateral thigh
Medial fascial compartment
52
New cards
Which spinal nerve root does the superior gluteal nerve come from?
a. L3 – L4
b. L2 – S3
c. L4 – S1
d. L5 – S2
a. L3 – L4
b. L2 – S3
c. L4 – S1
d. L5 – S2
L4 -S1
53
New cards
Which structure separates the true and false pelvis?
a. Inguinal ligament
b. Pelvic brim
c. Sacrospinous ligament
d. Ischial tuberosity
a. Inguinal ligament
b. Pelvic brim
c. Sacrospinous ligament
d. Ischial tuberosity
Pelvic brim
54
New cards
The following are categorized as muscles of the pelvic walls and floor, EXCEPT:
a. Piriformis
b. Coccygeus
c. Levator ani
d. Obturator externus
a. Piriformis
b. Coccygeus
c. Levator ani
d. Obturator externus
Obturator externus
55
New cards
The muscle capable of hip flexion, abduction and external rotation is the:
a. Sartorius
b. Tensor fasciae latae
c. Iliopsoas
d. Pectineus
a. Sartorius
b. Tensor fasciae latae
c. Iliopsoas
d. Pectineus
Sartorius.
\
FAbER - Sartorius
FAbIR - Tensor Fasciae Latae
\
FAbER - Sartorius
FAbIR - Tensor Fasciae Latae
56
New cards
The saphenous nerve is a branch of:
a. Femoral nerve
b. Obturator nerve
c. Tibial nerve
d. Common peroneal nerve
a. Femoral nerve
b. Obturator nerve
c. Tibial nerve
d. Common peroneal nerve
Femoral nerve
57
New cards
The following branches of the lumbosacral plexus comes from the ventral division, EXCEPT:
a. Internal pudendal nerve
b. Tibial nerve
c. Femoral nerve
d. Obturator nerve
a. Internal pudendal nerve
b. Tibial nerve
c. Femoral nerve
d. Obturator nerve
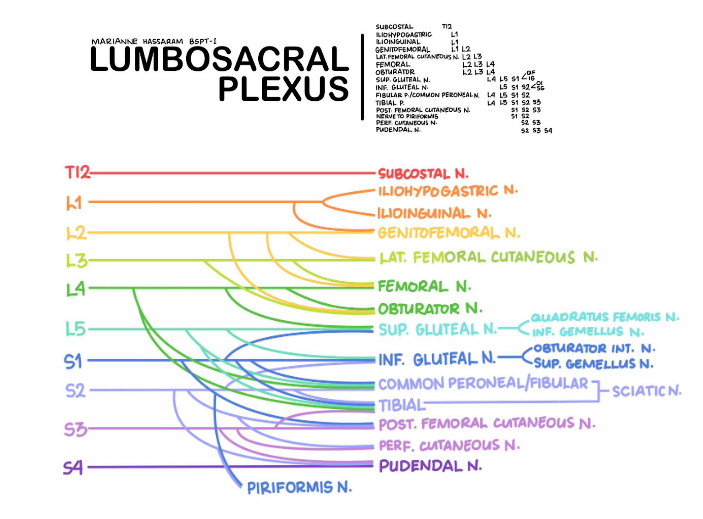
Femoral nerve

58
New cards
The nerve to obturator internus also supply this muscle:
a. Obturator externus
b. Superior gemellus
c. Inferior gemellus
d. Piriformis
a. Obturator externus
b. Superior gemellus
c. Inferior gemellus
d. Piriformis
Superior gemellus
59
New cards
The following muscles medially rotate the knee against the femur, EXCEPT:
a. Semitendinosus
b. Semimembranosus
c. Sartorius
d. Biceps femoris
a. Semitendinosus
b. Semimembranosus
c. Sartorius
d. Biceps femoris
Biceps femoris.
Long head - flexes & laterally rotates leg at knee joint
Short head - extends thigh at hip joint
\
Internal Rotators of KNEE are the 3S = Semitendinosus, Semimembranosus, & Sartorius
Long head - flexes & laterally rotates leg at knee joint
Short head - extends thigh at hip joint
\
Internal Rotators of KNEE are the 3S = Semitendinosus, Semimembranosus, & Sartorius
60
New cards
The superior gluteal nerve supply the following muscles, EXCEPT:
a. Gluteus maximus
b. Gluteus medius
c. Gluteus minimus
d. Tensor fasciae latae
a. Gluteus maximus
b. Gluteus medius
c. Gluteus minimus
d. Tensor fasciae latae
Gluteus maximus
61
New cards
The iliac crest corresponds to this level:
a. L2 vertebra
b. L3 vertebra
c. L4 vertebra
d. L5 vertebra
a. L2 vertebra
b. L3 vertebra
c. L4 vertebra
d. L5 vertebra
L4 vertebra
62
New cards
Which of the following adductor muscles is innervated by the femoral nerve?
a. Gracilis
b. Adductor magnus
c. Adductor brevis
d. Pectineus
a. Gracilis
b. Adductor magnus
c. Adductor brevis
d. Pectineus
Pectineus. It is dually innervated by the femoral and obturator nerve.
63
New cards
The nerve to quadratus femoris also supply this muscle:
a. Inferior gemellus
b. Superior gemellus
c. Piriformis
d. Obturator externus
a. Inferior gemellus
b. Superior gemellus
c. Piriformis
d. Obturator externus
Inferior gemellus
64
New cards
The cutaneous nerve that supplies the skin of the lateral thigh comes from which root?
a. L1
b. L2-L3
c. L3-L4
d. L5
a. L1
b. L2-L3
c. L3-L4
d. L5
L2-L3
65
New cards
The following structures attach on the outer surface of the ilium, EXCEPT:
a. Gluteus maximus
b. Gluteus medius
c. Gluteus minimus
d. Iliacus
a. Gluteus maximus
b. Gluteus medius
c. Gluteus minimus
d. Iliacus
Iliacus. It attaches to the iliac fossa.
66
New cards
The ilioinguinal and iliohypogastric nerves come from which spinal root?
a. L1
b. L2
c. L3
d. T12
a. L1
b. L2
c. L3
d. T12
L1
67
New cards
**Dimples above intergluteal cleft also known as ‘Dimples of Venus’ are at what level?**
a. L5
b. S1
c. L4
d. S2
a. L5
b. S1
c. L4
d. S2
S2
68
New cards
The ligament of the spine that connects adjacent transverse processes is the:
Select one or more:
a. Supraspinous ligament
b. Ligamentum flavum
c. Intertransverse ligament
d. Interspinous ligament
Select one or more:
a. Supraspinous ligament
b. Ligamentum flavum
c. Intertransverse ligament
d. Interspinous ligament
Intertransverse ligament
69
New cards
Which of the following muscles DOES NOT form part of the pelvic floor and walls?
Select one or more:
a. Obturator externus
b. Piriformis
c. Levator ani
d. Coccygeus
Select one or more:
a. Obturator externus
b. Piriformis
c. Levator ani
d. Coccygeus
Obturator externus
70
New cards
Which of the following muscles DOES NOT externally rotate the thigh at the hip joint? Select one or more:
a. Sartorius
b. Gluteus medius
c. Gluteus maximus
d. Quadratus femoris
a. Sartorius
b. Gluteus medius
c. Gluteus maximus
d. Quadratus femoris
Gluteus Medius
71
New cards
The tibial nerve comes from the spinal roots:
Select one or more:
a. L2-L4
b. L4-S1
c. L4-S2
d. L4-S3
Select one or more:
a. L2-L4
b. L4-S1
c. L4-S2
d. L4-S3
L4-S3
72
New cards
Which of the following muscles is NOT supplied by the obturator nerve?
Select one or more:
a. Obturator externus
b. Superior gemellus
c. Pectineus
d. Adductor magnus
Select one or more:
a. Obturator externus
b. Superior gemellus
c. Pectineus
d. Adductor magnus
Superior gemellus
73
New cards
Which of the following positions of the hip and knee stretches the rectus femoris?
Select one or more:
a.
Hip flexion with knee flexion
b.
Hip extension with knee flexion
c.
Hip flexion with knee extension
d.
Hip extension with knee extension
Select one or more:
a.
Hip flexion with knee flexion
b.
Hip extension with knee flexion
c.
Hip flexion with knee extension
d.
Hip extension with knee extension
Hip extension with knee flexion
74
New cards
The piriformis muscle exits the pelvic cavity via:
Select one or more:
a. Femoral ring
b. Greater sciatic foramen
c. Obturator foramen
d. Lesser sciatic foramen
Select one or more:
a. Femoral ring
b. Greater sciatic foramen
c. Obturator foramen
d. Lesser sciatic foramen
Greater sciatic foramen
75
New cards
A decrease in the neck-shaft angle of the femur is otherwise known as:
Select one or more:
a.
Coxa valga
b.
Talipes equinovara
c.
Coxa vara
d.
Genu vara
Select one or more:
a.
Coxa valga
b.
Talipes equinovara
c.
Coxa vara
d.
Genu vara
Coxa vara
76
New cards
Trendelenburg sign is pathognomonic for lesion of the:
Select one or more:
a. Superior gluteal nerve
b. Femoral nerve
c. Inferior gluteal nerve
d. Obturator nerve
Select one or more:
a. Superior gluteal nerve
b. Femoral nerve
c. Inferior gluteal nerve
d. Obturator nerve
Superior gluteal nerve
77
New cards
Which of the following nerves is being avoided for damage during gluteal intramuscular injection at the upper outer quadrant?
Select one or more:
a. Obturator nerve
b. Inferior gluteal nerve
c. Sciatic nerve
d. Superior gluteal nerve
Select one or more:
a. Obturator nerve
b. Inferior gluteal nerve
c. Sciatic nerve
d. Superior gluteal nerve
Sciatic nerve
78
New cards
Which of the following structure forms the anteromedial wall of the Hunter's canal?
Select one or more:
a. Adductor longus and magnus
b. Adductor brevis
c. Sartorius
d. Vastus medialis
Select one or more:
a. Adductor longus and magnus
b. Adductor brevis
c. Sartorius
d. Vastus medialis
Sartorius
79
New cards
Which of the following muscles distally attach to the lesser trochanter?
Select one or more:
a. Piriformis
b. Iliopsoas
c. Obturator externus
d. Gluteus medius
Select one or more:
a. Piriformis
b. Iliopsoas
c. Obturator externus
d. Gluteus medius
Iliopsoas
80
New cards
Which of the quadriceps muscles is the workhorse of knee extension?
Select one or more:
a. Vastus medialis
b. Vastus lateralis
c. Vastus intermedius
d. Rectus femoris
Select one or more:
a. Vastus medialis
b. Vastus lateralis
c. Vastus intermedius
d. Rectus femoris
Rectus femoris
81
New cards
Which of the following ligaments is located posterior to the hip joint and contributes to its stability posteriorly?
Select one or more:
a. Iliofemoral ligament
b. Inguinal ligament
c. Pubofemoral ligament
d. Ischiofemoral ligament
Select one or more:
a. Iliofemoral ligament
b. Inguinal ligament
c. Pubofemoral ligament
d. Ischiofemoral ligament
Ischiofemoral ligament