Atomic Structure and Bonding
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
An atoms consists of a dense ________ charged nucleus
positively
What surrounds the nucleus of an atom?
Negatively charged electrons at different energy levels at relatively large distances
What subatomic particles of an atom is found in the nucleus?
Protons - positively charged
Neutrons - electrically neutral
Electron
symbol, charge, mass (g) , relative mass
e-
-1
9.109 × 10-28
1
Proton
symbol, charge, mass (g) , relative mass
p
+1
1.673 × 10-24
1839
Neutron
symbol, charge, mass (g), relative mass
n
0
1.675 × 10-24
1839
Atomic number (Z)
Number of protons in the atom’s nucleus- equal to the sum if electrons present in a neutral atom
Mass number (A)
The sum of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus
Number of neutrons?
mass number - number of protons
What is an isotope?
Atoms of an element with the same atomic number but different mass number.
Same number of protons but can differ in the number of neutrons
Relative atomic mass (Ar)
Average mass of its atoms compared to 1/12th the mass of an atom of carbon-12.
Molecular weight
The sum of the atomic weights of all atoms in the molecule
Relative molecular mass (Mr)
Average mass of a molecule compared to 1/12th the mass of an atom of carbon-12
According to the quantum model, electrons behave as _____
Waves
The behaviour of a specific electron in an atom is described by mathematical expression called a _________
Wave equation
What is the term for the solution of a wave equation?
Wave function (psi)
What is (psi)²?
The probability of finding an electron at a particular point.
The atomic orbital
What is the atomic orbital defined by?
Three quantum numbers:
Principle quantum number, n
Orbital angular momentum quantum number, l
Magnetic quantum number, m
The principal quantum number, n
Different value of n divided orbitals into groups of similar energies called shells
n can take whole number values
Describes the energy of the orbitals
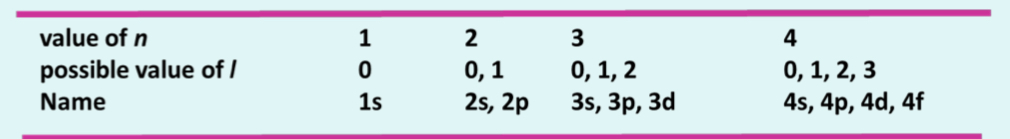
The orbital angular momentum quantum number, l
Depends on values of n: such that l= 0, 1, 2, …, n-1
Gives information about sub-shells and the shape of an orbital in the subshell
Different possible values are given letters rather than numbers, namely, s, p, d and f
The magnetic quantum number, m
determines the spatial orientation of the angular momentum
determines where orbitals are in space
values range from -l to +l
Possible ml values of the 2p subshell and their names
+1, 0, -1
2px, 2py, 2pz
What is the spin quantum number ms
describes the spin of the electron with respect to an external magnetic field
can take values +1/2 or -1/2
Shape of s orbital?
Spherical
Nucleus at the centre
Shape of p orbital?
Dumbbell shaped
Nucleus at the middle
What is an electron shell?
A group of an atom’s electrons with the same principal quantum number
Ground state electron configuration
Most stable, lowest-energy electron configuration of an ion or an atom
Aufbau principle
Electrons fill the lowest energy orbitals first
Pauli Exclusion Principle
Only two electrons of opposite spins can occupy an orbital
Hund’s rule
Electrons fill degenerate orbitals singly with parallel spins before pairing
Why do atoms from bonds?
To become more stable and lower their energy due to attraction between oppositely charged ions, nuclei and shared electrons
Octet rule
Atoms gain, lose or sharer electrons to achieve eight electrons in their valence shellWh
What is an ionic bond?
Electrostatic force of attraction between two oppositely charged ions formed as a result of an electron transfer
Alkali metals in group 1 in ionic bonding…
loses single s electron from their valence to form a cation
Halogens in group 7 in ionic bonding…
gain a p electron to fill their valence shell.], forming an anion
What is a covalent bond?
A shared pair of atoms between electrons
Lewis structures
Electron-dot structure
What are lone pairs?
Valence electrons not involved in bonding. The can act as nucleophiles
Problems with the octet rule:
applies only to first row and roughly p block compounds
fails for PCl5, NO, BF3
does not predict the strength of bonds