Forscenics- Fiber/Trace Evidence
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Trace Evidence
Evidence that is man made or natural, that is tiny or small in scale.
Class Evidence
Evidence that belongs to a large group of people
Not helpful for identifying the specific suspect, but helps narrowing it down
EX: Hair color, Shoe size, Blood type ( Just the type of blood, not actual blood)
Individual evidence
Evidence that can only belong to one person
Very helpful in identifying suspect
EX: DNA, Fingerprints, Bite marks
Locard Principle ( unlikely on test)
The principle that states: Any two objects that come in contact with each other, will leave some kind of trace (whether we can see this trace , depends)
Types of Trace Evidence
Hair
Fiber ( ex: carpet fur ,clothing materials )
Blood
Prints
Glass
Paint
Morphology
The study of strucutre/form of objects and organisms (SPECIFICALLY HAIR/FIBER)
This study includes: Shape,Structure,Color, Patterns
HAIR IS MADE OF THE PROTEIN KERATIN.
Hair as a piece of evidence
Hair is abundant
Time cannot change hair
Can be easily lost
Used mostly for Sexual/violent Assault cases
Parts of Hair
SHAFT
Part of the hair that sticks out
ROOT
The part that lies beneath the skin (Extension of the shaft)
FOLLICLE
Organ from which the hair itself grows from
POSSIBLE SOURCE OF DNA, IF CONTAINS FOLLICULAR TAG

Hair Root
Roots are the part in the hair that is beneath the skin
It has the possibility to contain the Fonicular Tag
Fonicular Tag
TISSUE (CONTAINS DNA) THAT SURROUNDS the root when the hair is forcibly removed

Hair Growth Stage- Anagen
Hair that is still in the process of growing
Has a flame shaped appearance
may have the follicular tag
note: image contains follicular tag

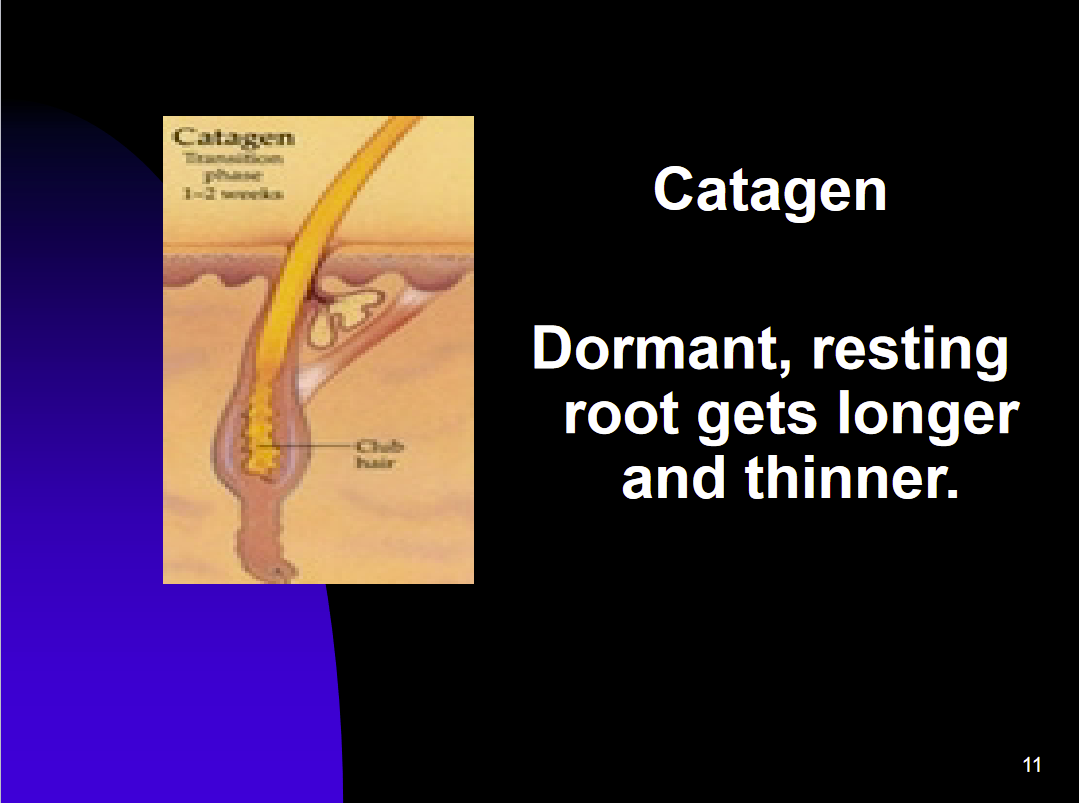
Hair Growth Stage - Catagen
The Transition between growth and rest
Hair still grows , but at a slower rate
more elongated appearance
Hair Growth Stage-Telogen
Hair Growth has stopped
Has a club shaped appearance

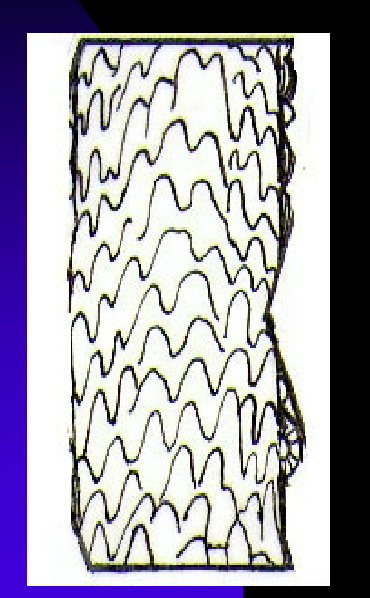
Parts of the hair-Cuticle
Cuticle: The outermost hair
Covered with Scales
Scales ALWAYS POINT TOWARDS TIP OF THE HAIR

Scale Type- Mosiac
This Scale type is mainly Cats
The appearance is akin the Scales of a fish, that are jagged

Scale Type - Chevron
This Scale type mainly belongs to rodents/rabbits
Appearance is akin to wood grain
Can be mistaken for petal, but can be distinguished by its sharper/taller, and longer upside down U’s

Scale Type- Imbricate
This Scale type IS ONLY HUMANS
Appearance is akin to lots of lines, that are jagged or long and stretched

Scale Type- Petal
This Scale type is usually for dogs
Appearance can be akin to mountain tops - small,short U’s with few sketches on the hair
CAN BE MISTAKEN FOR CHEVRON
Hair Part- Cortex
The cortex is made of cortical cells- the thing that gives the hair its shape
Melanin- Pigment that gives the hair color
Cortical fusi— The air spaces that is found all thought the shaft and the root.
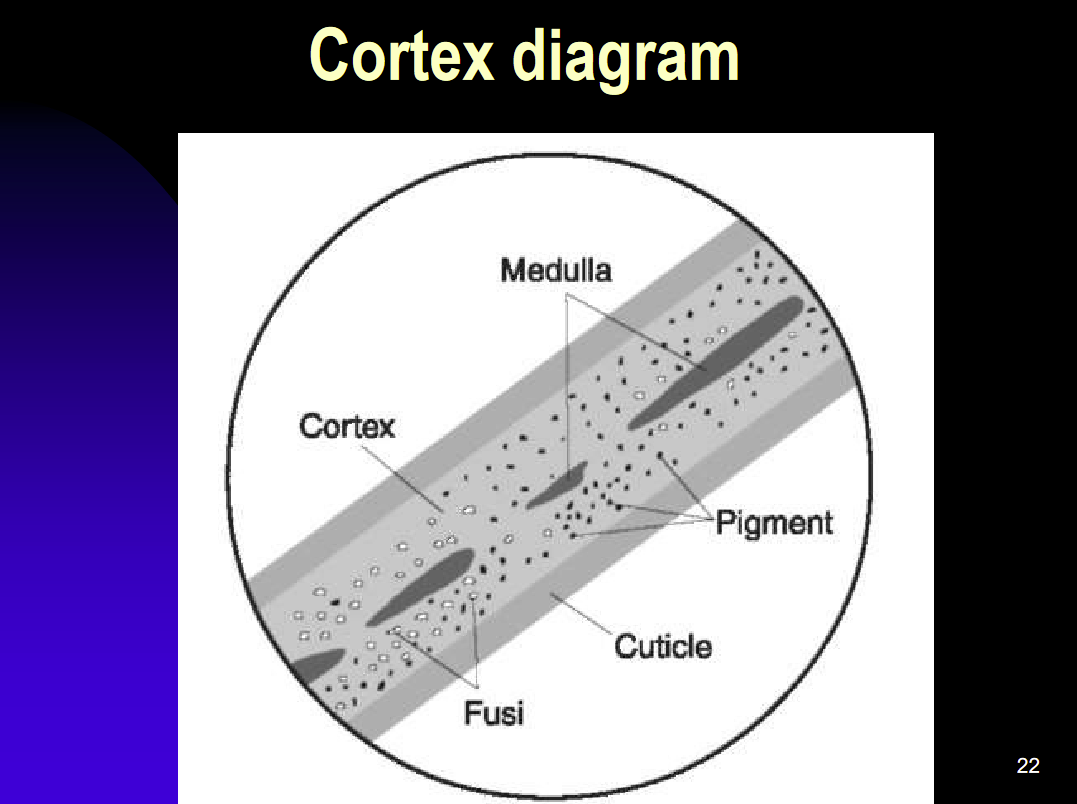
Hair Part- Medulla
The medulla is the center Canal running through the hair
ALL OF THIS ARE ONLY FOR HUMAN
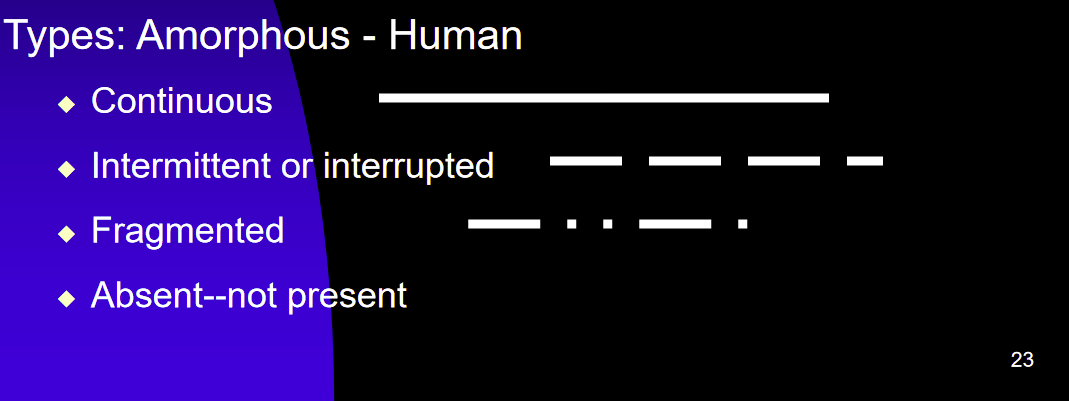
There are Several types of medullas
Continuous :
A long line of medulla that is unbroken
Intermittent:
Medulla that occasionally has breaks in between similar shaped parts
Fragmented:
Medulla that has parts that are broken up, that have different sizes
Absent:
Not present
Medullary index:
The comparison of the diameter of the hair shaft, to the diameter of the medulla
Medullary Index for humans: usually less than 1/3
Medullary Index for animals: usually greater than 1/2
Characteristics of medulla
Terminal hair (Coarse):
Hair that is most common. Basically the hair on your head right now
Vellus (fine)
Hair that is very fine and tiny, like peach fuzz
Medulla origins:
Blonde hair usually doesn’t have medulla
Asian and African Hair will likely have continuous medulla
European Hair will likely have absent,fragmented, or interrupted Medulla
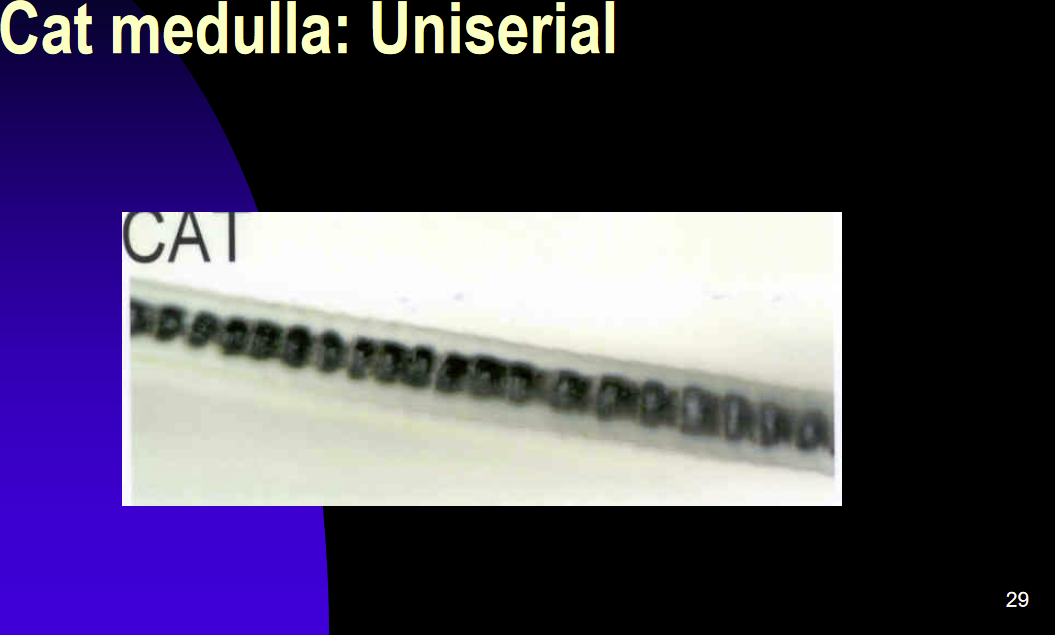
Hair Medulla- Uniserial
Uniserial: a single row, of uniform/similar shaped medulla
Hair part-Medulla-MULTI SERIAL
Multi serial: MORE THAN ONE, rows of similar sized medulla

Hair part-Medulla- Vacuolated
Vaculoated: Medulla that has odd shapes as its medulla
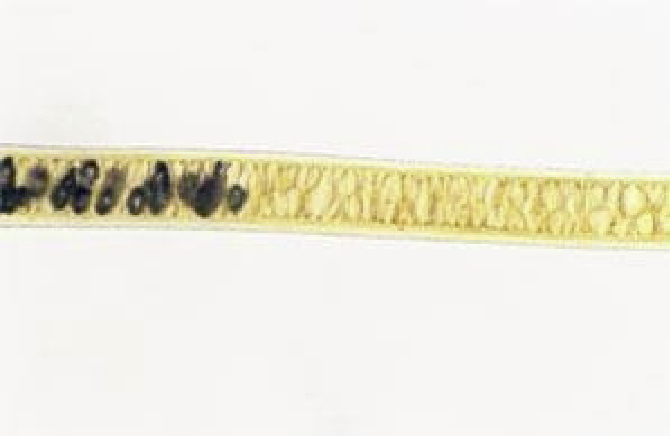

Hair part-Medulla-Lattice
Lattice: Medulla that has rows of circles as its medulla

What can Hair help you determine
Human or animal
Race
Origin ( where it came from on the body)
Manner in which the hair was removed
Treated/Bleached hair
Drugs recently ingested
Age
sex
Main two determinants between Human and Animals
Scale
Medulla Type
Hair Changes
Dyed hair still keeps the same color it had originally, all in the cuticle and cortex
Bleaching out rights removes the pigment and gives the hair a yellow tint
Tips of hair
The tips of hair depending on circumstances:
Blunt: Recently cut
rounded: previously cut and allowed to regrow
Blackend/frayed: Burnt
Broken: Irregular looking tip

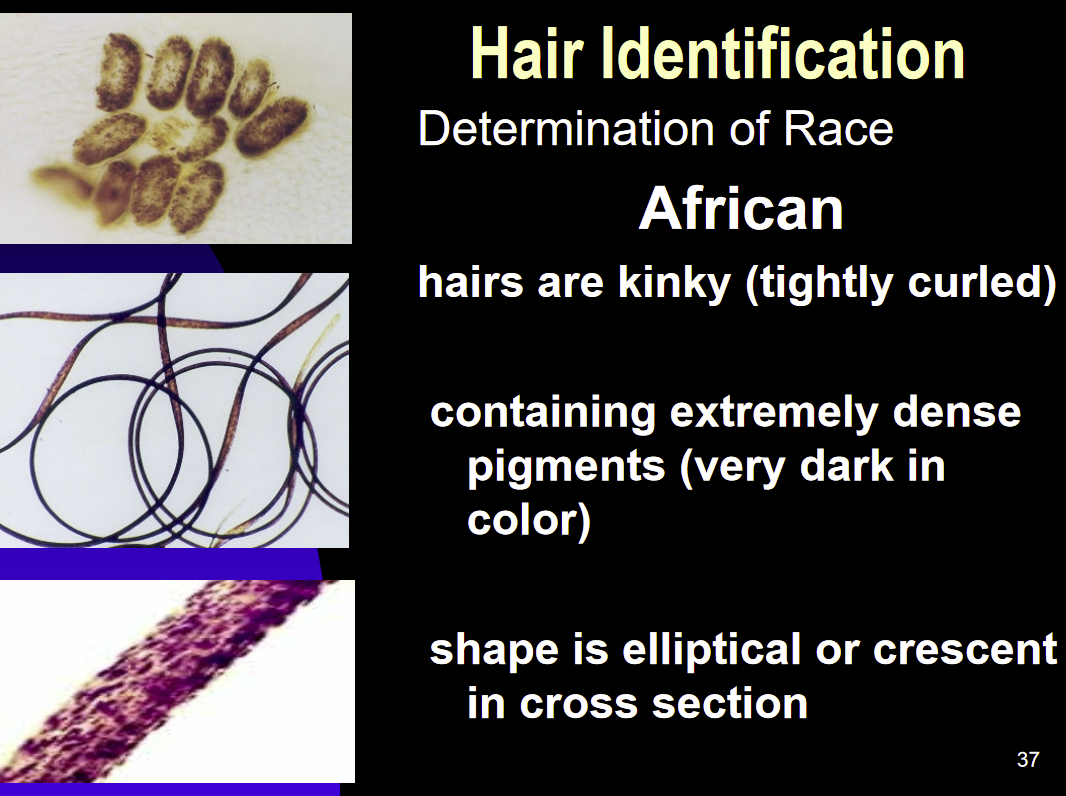
Hair Identification-African
Tightly Curled
Cotains extremly dense pigment/color
cross section Shape is elliptical/oval
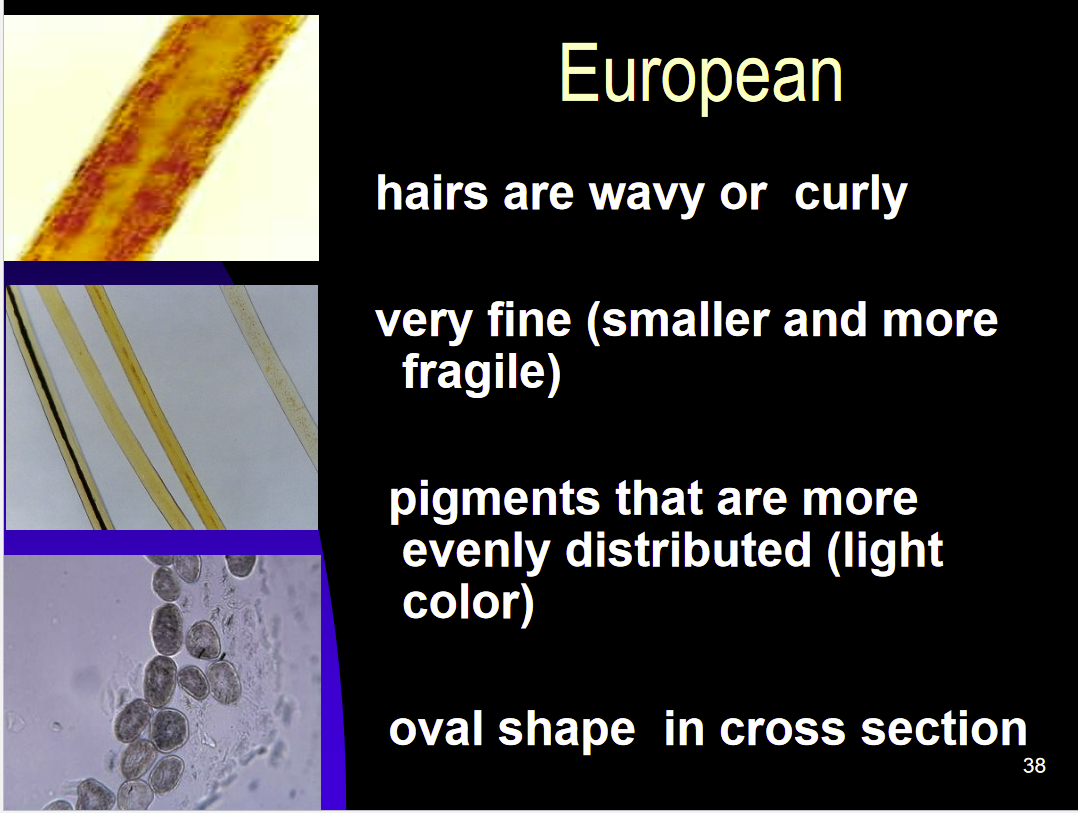
Hair Identification-European
hair is wavy or curly
very fine (small and fragile)
Pigment is light and evenly disturbed across the hair
Cross section is oval
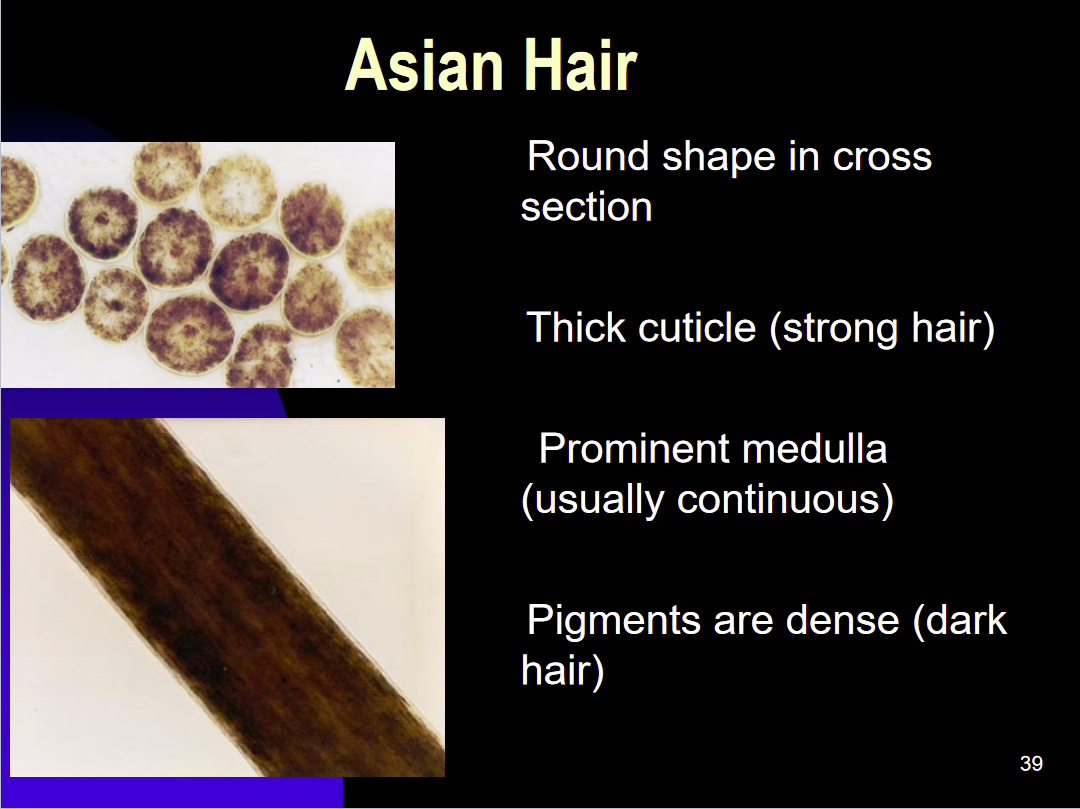
Hair Identification-Asian
Thick cuticle (Strong)
Prominent medulla (Usually continuous)
Pigments are dense/ and dark
Round shape in cross section
Collection of hair evidence
Crime Scene hairs must have these criteria
Be from the Victim, possible suspects, and any other hairs deposited at the Scene
50 full-length hairs
24 full-length pubic hairs.
Ways of collecting:
Using tape for exposed skin
Using tweezers, or vacuum
ALL MUST BE PUT INTO A BINDLE
Pattern or Transfer of Evidence
When direct contact occurs between two objects or a object an a person, that leaves a trace.
Types of transfers: Biological, chemical, impression
Physical evidence
Physical: Items that can be collected or measured for examination
ex:
Fingerprints
Footprints
Shoe prints
Handwriting
Firearms
etc
Conditional: Evidence
Conditional: Evidence that tells a story
Examples include:Locaiton of injuries or wounds
Bloodstains
Vechicles
Weapon cartdiges
Broken glass
Body position
ANYTHING THAT TELLS A STORY OF WHAT HAPPEND
Transient/temporary evidence
Transient/Temporary Evidence: Evidence that has a limited life span. Examples include: odor,temperature,foot-prints,etc.
Biological evidence
Evidence that comes from humans or organisms
Blood
Semen
Saliva
Sweat/tears
Hair
Bone
Urine
etc
Chemical evidence
Any evidence that has a chemical composition, and not living
Fibers
Glass
Soil
gunpowder
metal
Drugs
Paper
Ink
etc
Fibers
Any small elongated pieces of material used to manufacture cloth,carpet,paper,cardboard,etc
Fiber production
Fibers are the individual pieces
Multiple fibers make threads/yarns
Multiple threads/yarns make fabric, which are then woven or kniotted
Weave Terminogloy
Warp- A lengthwise yarn (LEFT TO RIGHT)
Weft-Crosswise yarn (UP AND DOWN)
Blend- a fabric made up of two different types of fiber (
Plain Weave
the most used and simplete weave pattern
similar to a checkerboard, the warp and weft go over and under, each other alternating
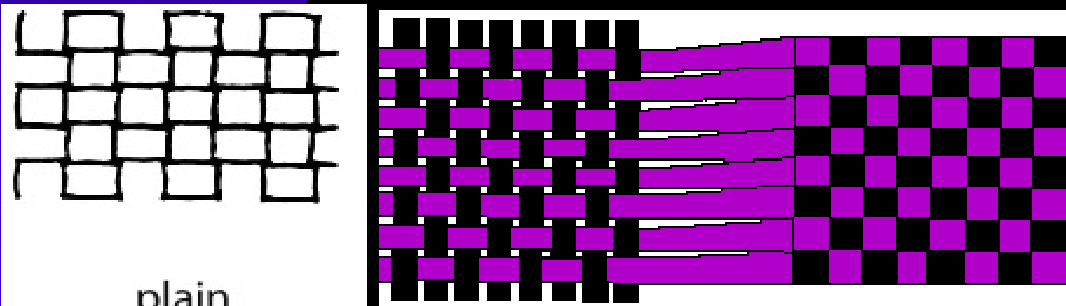
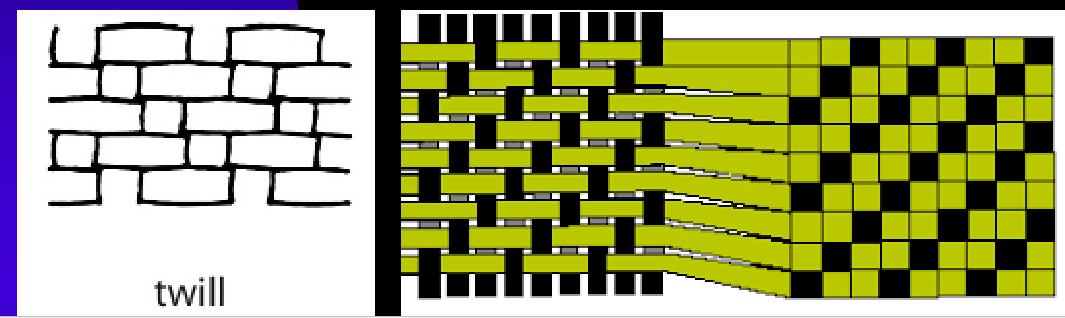
Twill Weave
The Warp yarn is passed over the weft, forms a diagonal pattern
Resemblers stairs or a
MAINLY USED FOR DENIM
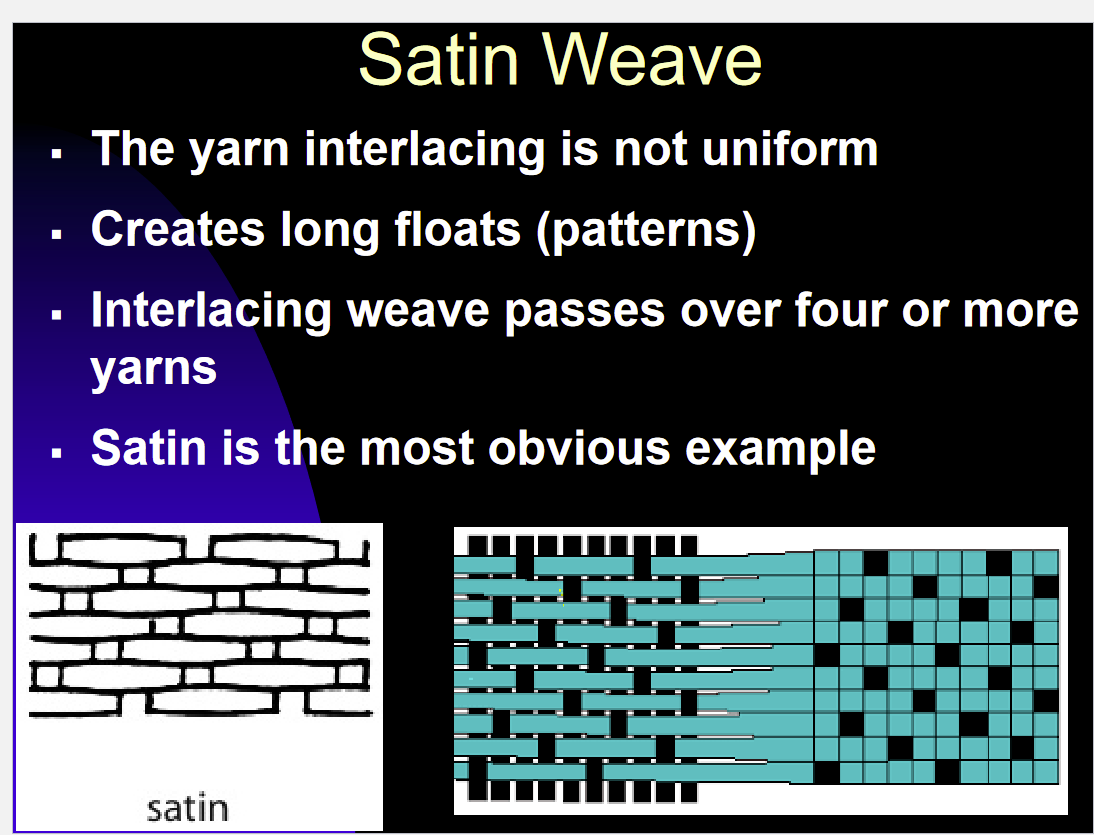
Satin Weave
Yarn interlacing must be over four or more yarns
Creates long floats patterns
Satin is the most obvious example
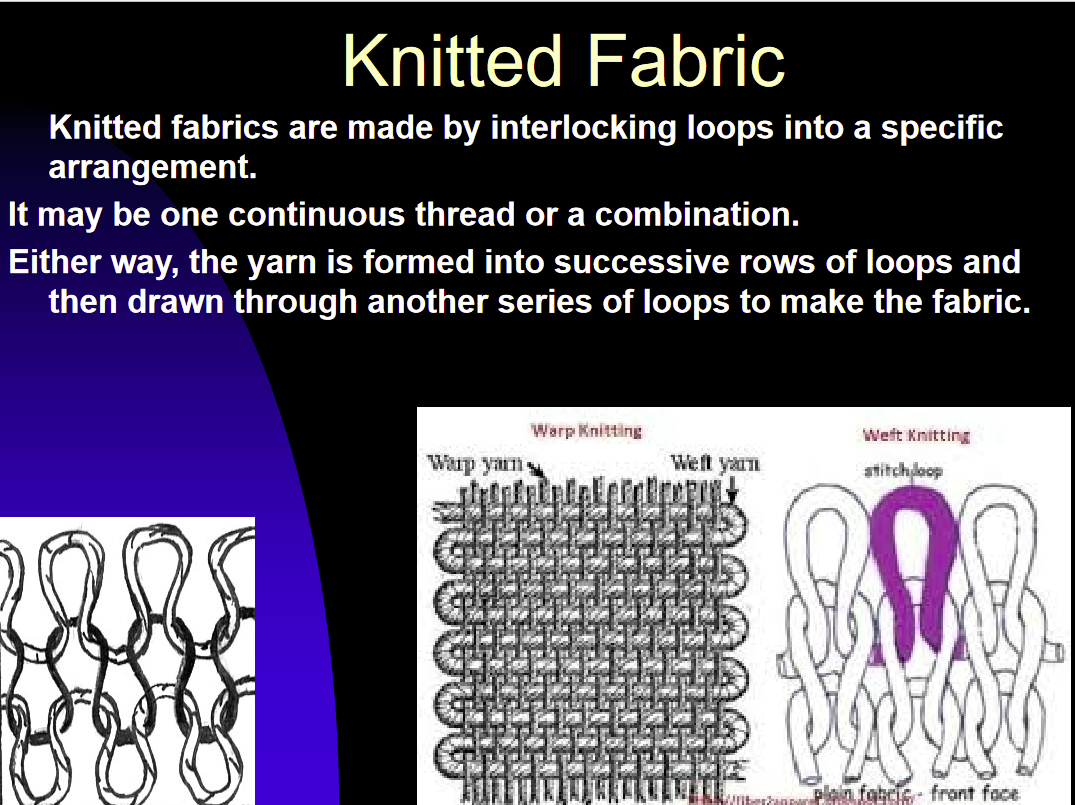
Knitted Fabric
Interlocking loops of yarn into a specfici arangment
rows of loops that are drawn through more rows of loops to make the fabric
Type of fiber: Animal/protein (Natural)
All animal hairs are described as protein hair
Ex: Sheep,Goats,camels,llamas,etc
Type of fiber: Plants/cellulose (Natural)
Natrually occuring fibers that occur in plants
Cotton is the most prevalent example
Its worthly to note cotton twists like a thread
Type of fiber: Excrement (Natural)
Very few examples exist, Excrement that comes from the silk worm is the most promient example
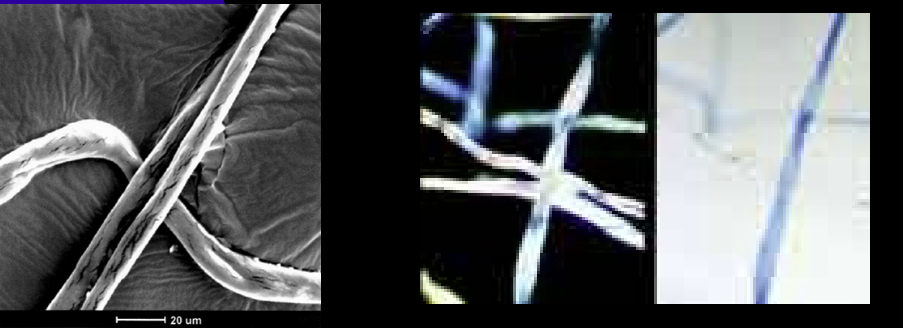
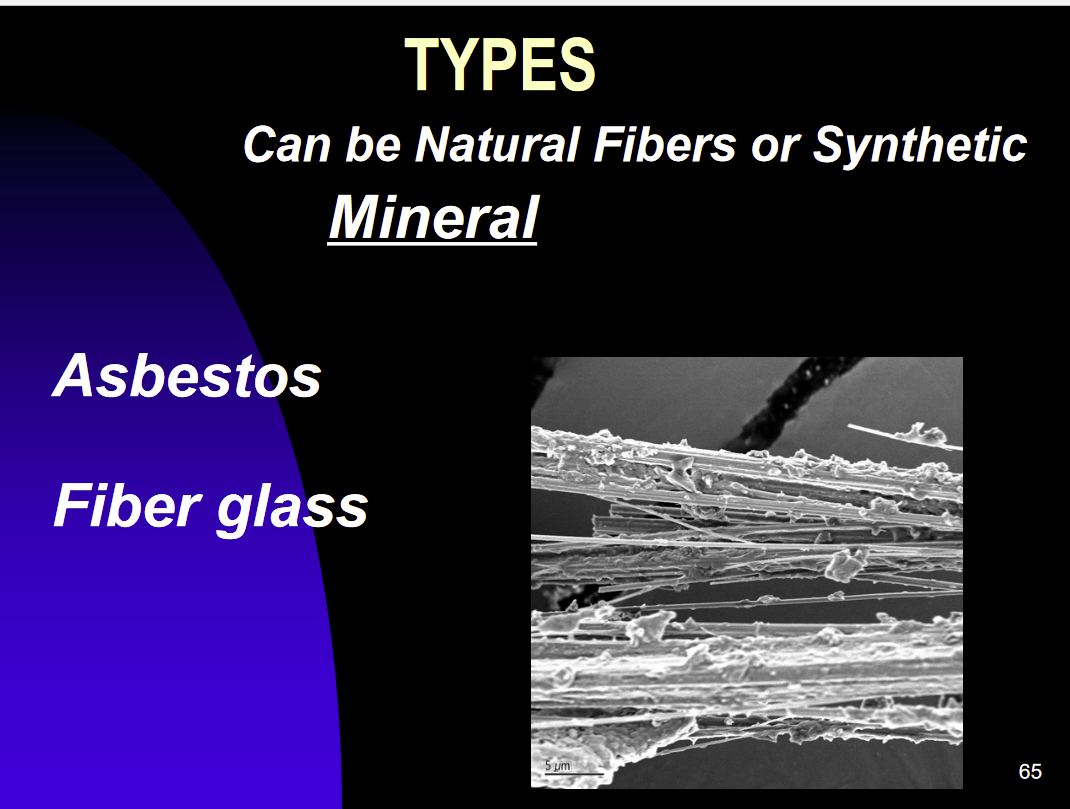
Type of fiber: Mineral (Natural and/or synthetic)
Anything that has a jagged appearance to it, or it comes from minerals
Ex: Asbestos, Fiber glass
Type of fiber: Petroleum Plastics (Man made)
Plastic made from coal, natrual gas/oil
examples incluide:
Nylon: Most duarble, manmade fabric
Polyester: Widley used
Acrylic: Provides warmth, soft and resilient
Spandex: Extreme elastic properties
ALL ARE NOT BIOGEGRADABLE
Type of fiber: Regenerated Fibers (Man made)
Made from a base of cellulose. the chemical process involves dissolving the cellulose, forcing it through a spinneret( filter), and then solidifies into a fiber to later be used to make a fabric
Examples: Rayon
Type of fiber: Synthetic fibers (Man made)
Fibers produce from synthetic chemicals.
All surface quality are identical
We can only differentiate the synthetic fibers through microscope
ex: Teflon, Dacron

Polymers
Polymers are chemical substances of chained together molecules
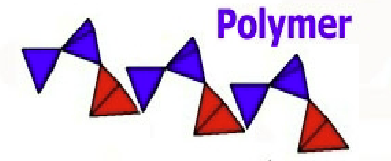
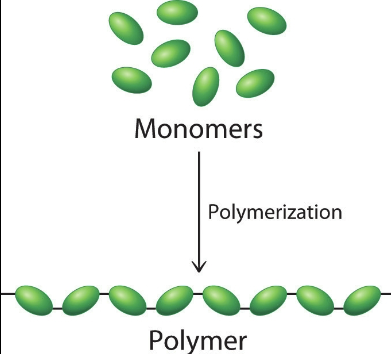
Monomers
a molecule that can be bonded to other identical molecules to form a polymer.

Types of polymers
Natural: Built by linking amino acids together
Ex: Cotton and starch
Synthetic: Created through man made means
Polymerization
the selection of specfic monomers and linking them together to form a polymer
note: changing the order of the monomers can affect the quality of the fiber (soft,strecthy, stain resitant,etc)
Testing what type of fiber
Burning: Observing how the fiber burns, odor, time of burn, color, smoke, and residue left
Thermal decomposition: More equivalent of a oven; heating up the fiber till it breaks down to its original monomers
Chemical tests: Solubility and decomposition
Density: the mass divided by volume of the object
Florescence: Used for comparing and spotting the fibers
Infrared Spectroscopy: The best technique to identify and compare fibers
Uses three characteristics: Reflection, absorption, and emission
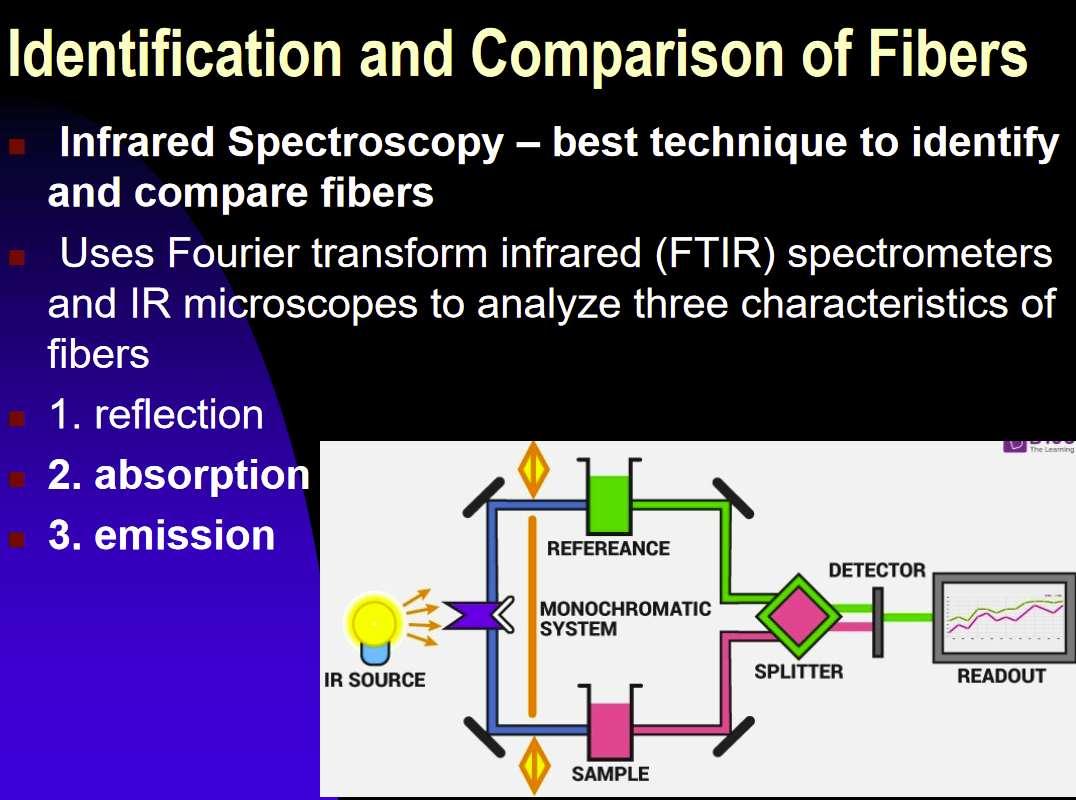
Microscopic examination of fibers
Examination of fibers under the microscope
Micrspectrophotmeter: Used to compare fiber colors through patterns
Chromatography: A more detailed comparison of the color/dye
What fibers can give you
Location: where on the body
Construction: How the fibers were constructed
Nature of contact: If the contact was violent or brief contact
Me after going through 92 SLIDES OF HAIR!!!!
