APEX Breathing Circuits
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
What are the 4 classifications of breathing circuits?
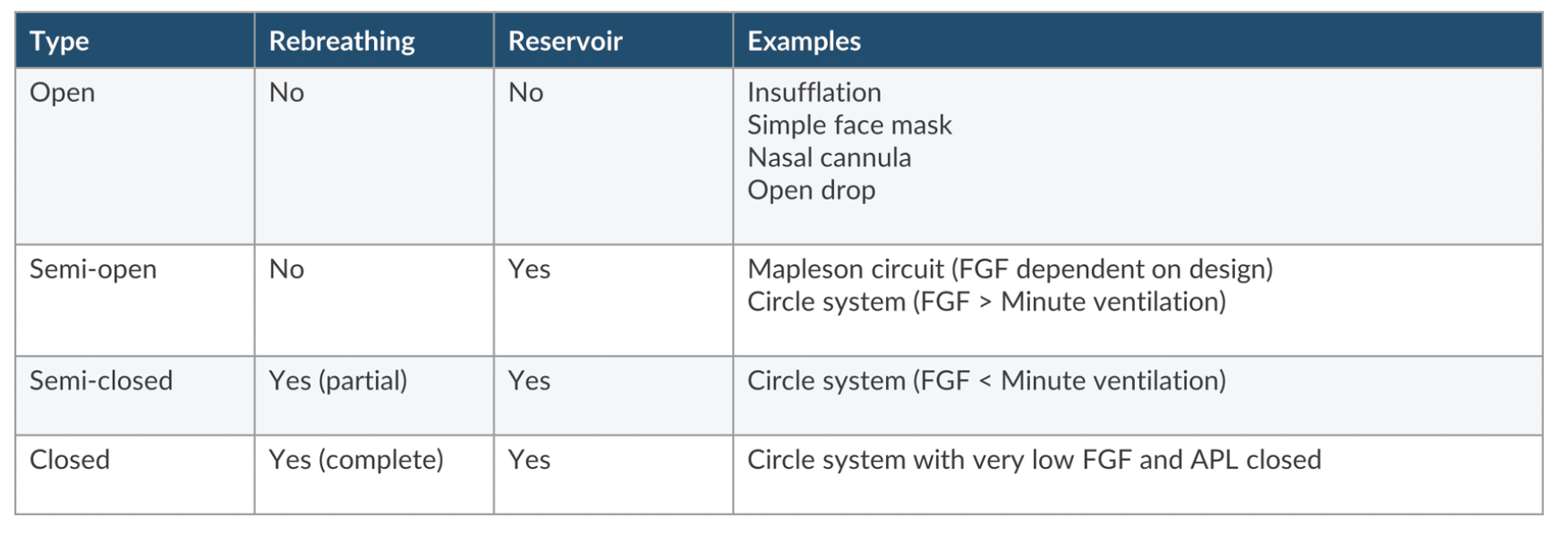
Open
Semi-open
Semi-closed
Closed
This type of breathing circuit is a non contained system where the patient exchanges gas with the atmosphere
Open
In this type of breathing circuit, FGF is greater than the patient's minute ventilation
Semi-open
T/F: there is no rebreathing of exhaled gas in a semi-open circuit
T
In this type of breathing circuit, FGF is less than the patient's minute ventilation
Semi-closed
T/F: semi-closed breathing circuits don't allow rebreathing of exhaled gas
F
In a semi-closed breathing circuit, what effect do unidirectional valves have on airway resistance?
Increase it
This type of breathing circuit uses a very low FGF so there is complete rebreathing of exhaled gas
Closed
In a closed breathing circuit, the amount of gas that needs to be replaced is the sum of what?
Patient's O2 consumption + amount of anesthetic agent that's absorbed by the patient
In a closed breathing circuit, why isn't gas able to exit the scavenger?
The volumes of inspired and expired gases are equally matched
In a closed breathing circuit, is the APL valve open or closed
Closed
In a closed breathing circuit, is the change in gas concentration fast or slow?
Slow d/t low FGF
Which type of breathing circuit does not contain a reservoir?
Open
What breathing circuit configurations can a circle system take on? How can it do this
Based on how you set the FGF and APL the circle system can be either semi-open, semi-closed, or closed
Give examples of open, semi-open, semi-closed, and closed breathing circuits
Open: simple face mask, nasal cannula
Semi-open: Mapleson circuit (FGF dependent on design) or circle system if FGF > minute ventilation
Semi-closed: Circle system (if FGF < minute ventilation)
Closed: Circle system with very low FGF and APL closed
A circle system contains how many unidirectional valves to ensure that gas only travels in 1 direction
2
What type of circuit are you creating if you use 10L/min flow during anesthetic induction?
Semi-open
What type of circuit are you creating if you use 2L/min flow for anesthetic maintenance?
Semi-closed
What are 5 advantages and 3 disadvantages to a circle system
Advantages:
1. Consistent inspired gas concentrations
2. Maintains heat and humidity
3. Low resistance (not as low as Mapleson)
4. Can be used as semi-open, semi-close, or closed systems
5. Minimizes OR pollution
Disadvantages:
1. Multiple places where disconnection can occur
2. Less portable than non-rebreathing cirucits
3. Unidirectional valves can malfunction
Purpose of co2 absorber in circle system
removes exhaled co2 a dallows patient to rebreathe exhaled gas
What happens if the unidirectional valve on a circle system is stuck open? Stuck closed?
Open: rebreathing
Closed: airway obstruction
What are 2 benefits of the reservoir bag in a circle system?
1. Exhaled gas accumulates inside the bag during exhalation. This gas is returned to the patient during the next breath. This allows rebreathing and the use of lower FGF
2. It allows you to deliver positive pressure to deliver assisted or controlled ventilation
What is the most distensible component of the breathing system?
Reservoir bag
The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) requires that pressure inside an adult-sized (3L) reservoir bag does not exceed an internal pressure of _____cm H2O if the bag is inflated up to ____x's its size
60cm H2O
4x's
The adjustable pressure limiting valve (APL)
determines how much pressure can be generated inside breathing ciruit when bag mode is selected
Recommended APL completely open during spontanous ventialtion and partially closed when providing assisted or manual controlled ventialtion
Closing APL valve during mask ventialtion is sueful when theres a leak around mask
T/F: the APL valve is completely bypassed when the ventilator is on vent mode
T
Where is the most common site of circuit disconnect?
Y-piece
When the unidirectional valves are working properly, where does dead space begin and end?
Begins at Y-piece
Ends at terminal bronchioles
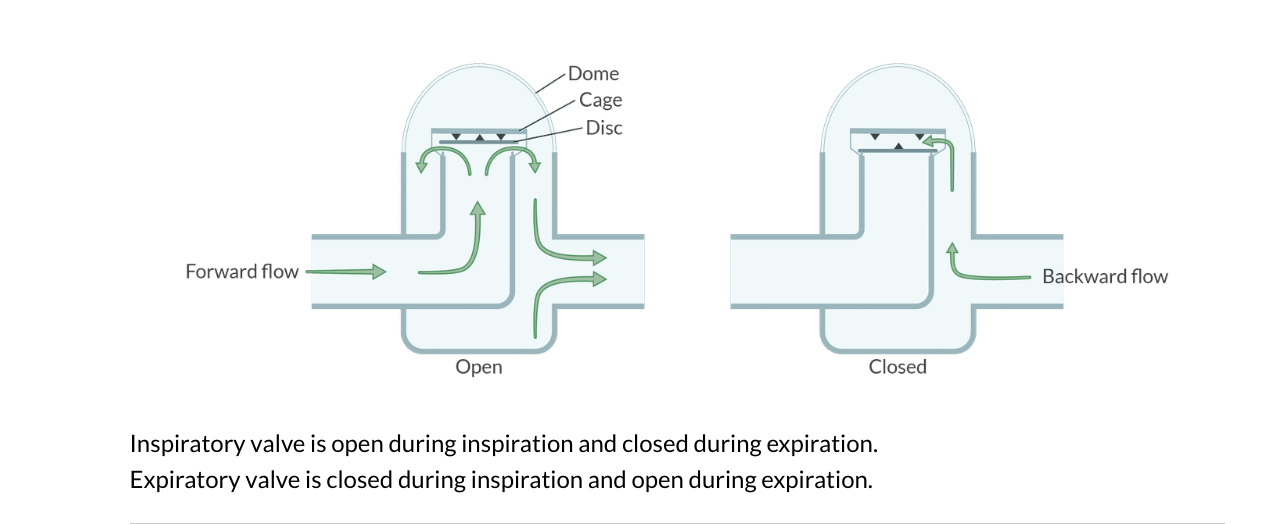
The inspiratory valve is _____ during inspiration and ____ during expiration
The expiratory valve is ___ during inspiration and ____ during expiration
Inspiratory: open during inspiration. Closed during expiration
Expiratory: Closed during inspiration. Open during expiration
What are the 2 most common conditions related to the breathing circuit that increase inspired CO2 concentration?
1. Incompetent unidirectional valve
2. Exhausted CO2 absorber
If a unidirectional valve becomes incompetent, the corresponding limb is converted to _____ which means what?
Dead space
The patient will rebreathe exhaled CO2
The definitive treatment for an incompetent unidirectional valve is to fix the valve. If this cannot be done, what should you do?
A closed or semi-closed circuit should be converted to semi-open
If your CO2 absorber exhausts during a procedure, what are 2 things you can do?
1. Convert a closed or semi-closed circuit to semi-open by increasing FGF to 5-8L/min
2. Change absorbent but risky in case you cannot get it in place
If your patients CO2 is increasing during a procedure and you believe it's the result of exhausted soda lime but increasing FGF doesn't fix the problem, what is the likely problem?
Incompetent unidirectional valve
T/f: if your CO2 absorber exhausts during a procedure, you can increase the patients minute ventilation to decrease the EtCO2
F
The patient will continue to rebreath exhaled CO2
This structure on the anesthesia machine determines how much gas remains in the circuit and how much gas is directed to the scavenger
APL valve
How mnay configurations do Mapelson circuit have?
6; A-F
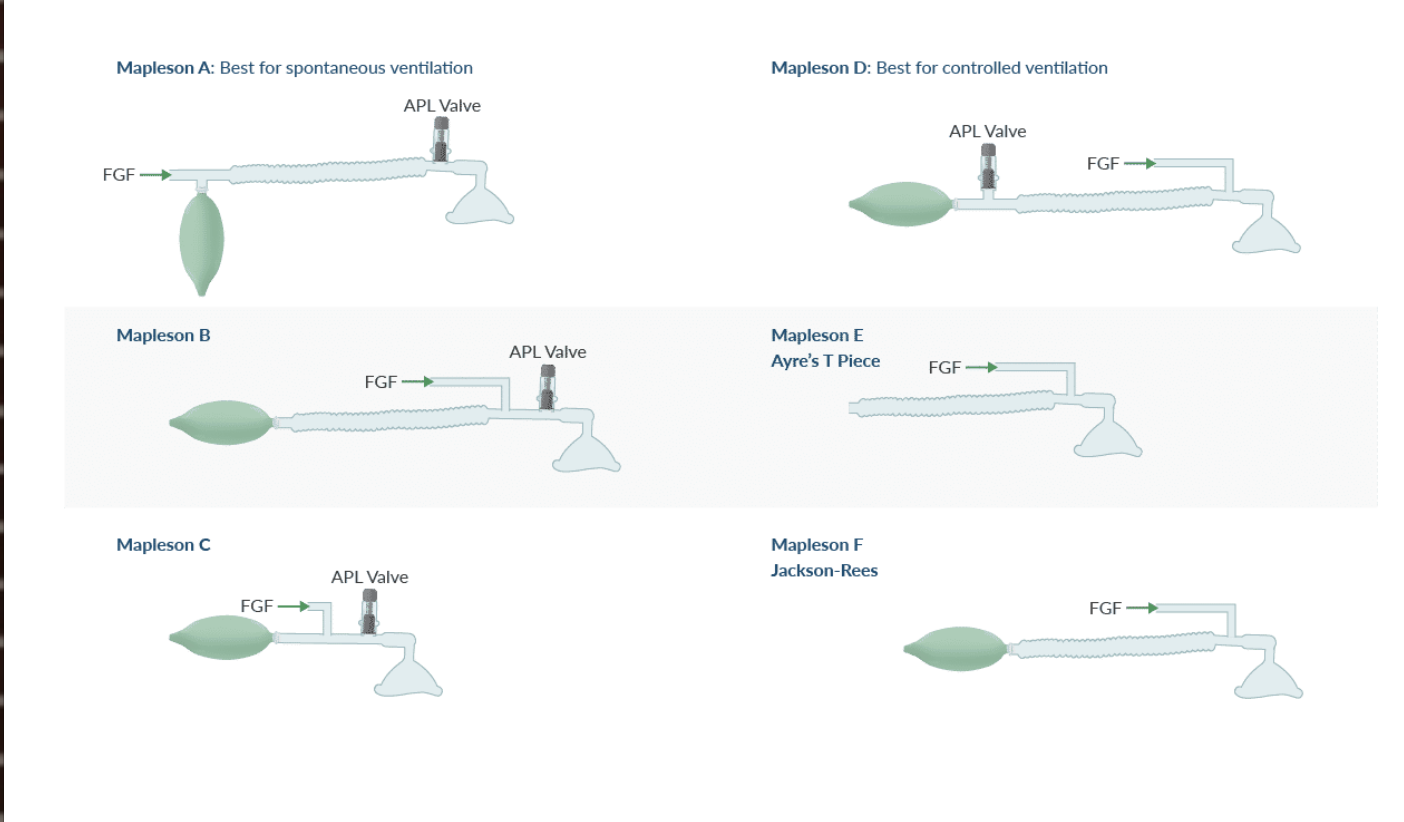
What type of breathing circuit are Mapleson circuits classified as?
Semi-open non-rebreathing circuits
What 5 components are present in a Mapleson circuit?
What 2 components are not present?
Present:
Reservoir bag
Fresh gas inlet
Corrugated circuit tubing
APL valve (Mapleson E does not have an APL valve or reservoir bag)
Mask
Not present:
Unidirectional valves
CO2 absorber
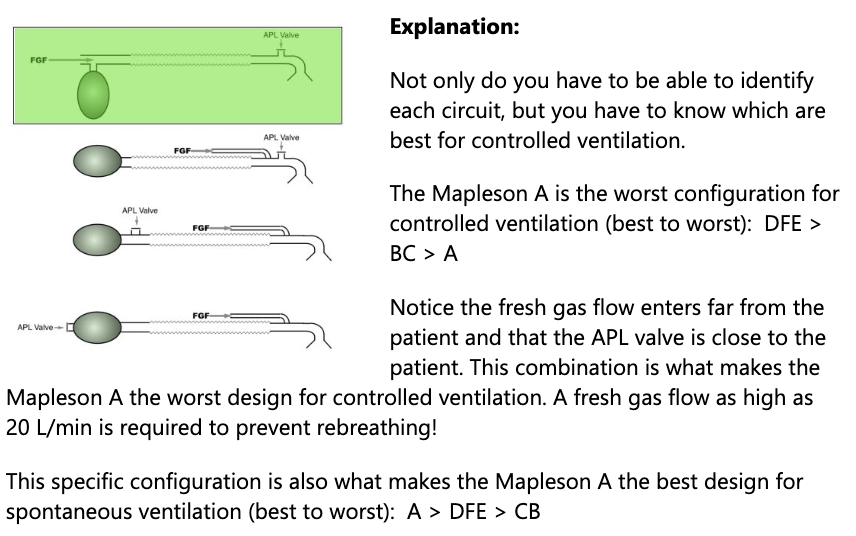
For all Mapleson circuits, the fresh gas inlet location is near the patient except for 1 circuit. Which circuit is it? Where is it located?
Mapleson A
Near the bag
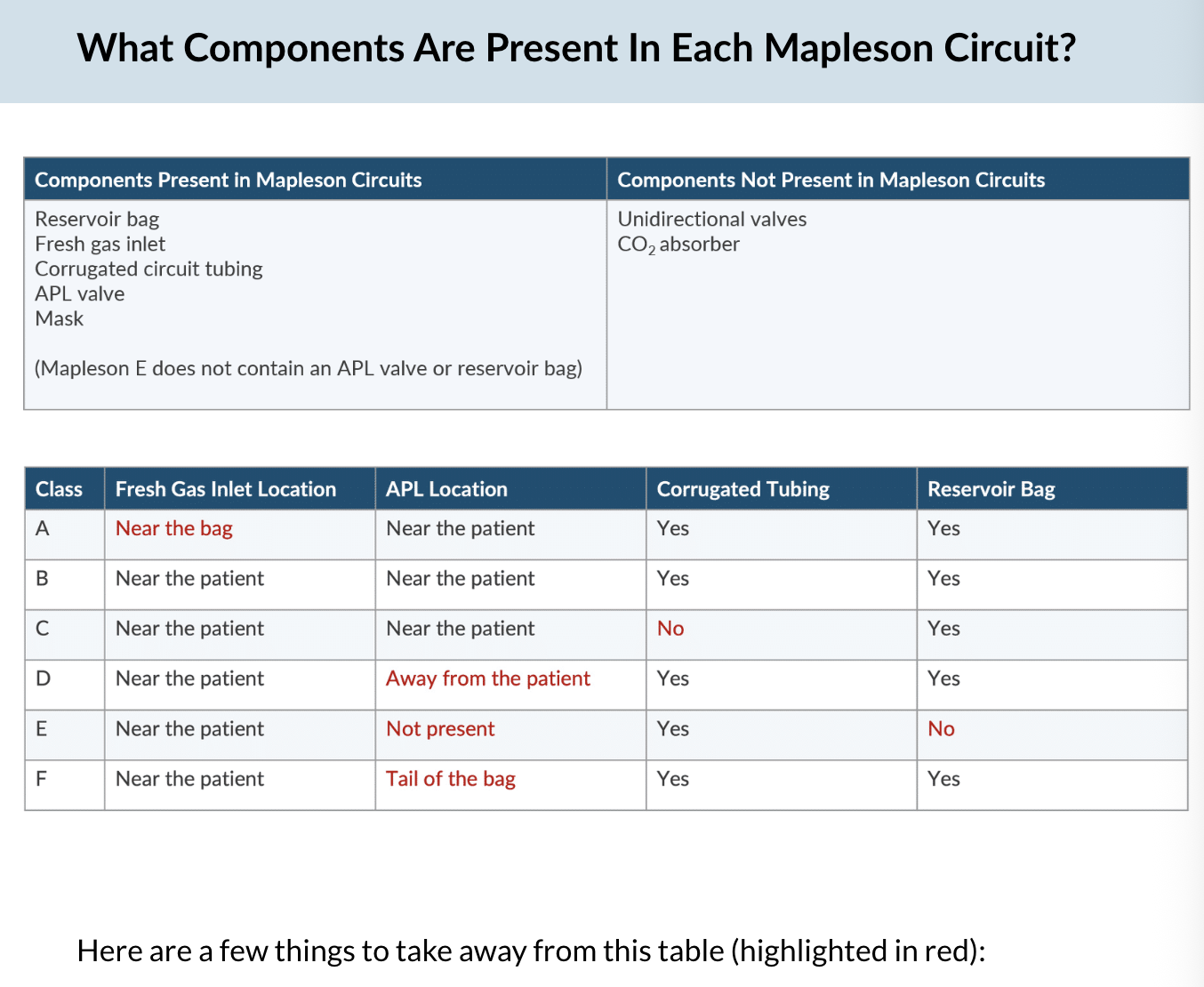
Which mapelson design is best design for spontanous ventilation
A (B is the worst)
Which Mapleson circuit is the only one with the APL valve away from the patient?
D
Which Mapleson circuit does not contain an APL valve?
E
Which Mapleson circuit does not contain corrugated tubing?
C
Which Mapleson circuit contains the APL valve at the tail of the bag?
F
Which Mapleson circuit does not contain a reservoir bag?
E
How do Mapleson circuits work?
-During expiration, gas containing CO2 enters the corrugated tubing and travels away from patient
-After expiration but before the next inspiration, FGF washes out exhaled gas left inside the corrugated tubing
-During inhalation the patient breathes in fresh gas. If the fresh gas is inadequate, the patient will also rebreathe exhaled gas left over in the corrugated tubing
What 3 ways can you minimize rebreathing with a Mapleson circuit
Higher FGF
Smaller tidal volume
Longer expiratory time
What is the best method for determining the amount of FGF required to prevent rebreathing with a Mapleson circuit
End-tidal CO2 monitoring (look at baseline of capnograph)
What are 4 advantages and 6 disadvantages of a Mapleson circuit?
Advantage:
1. Less airway resistance (good for peds)
2. Convenient
3. Easily scavenged
4. Bain circuit prevents heat loss
Disadvantage:
1. Increased apparatus dead space
2. Requires high FGF to prevent rebreathing
3. Loss of heat and humidity (except for Bain)
4. Inefficient use of inhaled anesthetics
5. Risk of environmental pollution
6. Unrecognized kinking of fresh gas hose in Bain circuit
Which Mapleson circuit is the best and worst for spontaneous ventilation? What about for controlled ventilation?
Spontaneous:
Best: A
Worse: B
pneumonic: All Dogs Bite (A > DFE > CB)
Controlled:
Best: D
Worst: A
pneumonic: Don't Be Arrogant (DFE > BC > A)
With the Mapleson circuits, it's impossible to know exactly how much FGF is required to prevent rebreathing. As a general rule, FGF should be _____x's the patient's minute ventilation
What circuit is the exception to this? What should FGF be during controlled ventilation with this circuit?
2.5x's
Mapleson A
FGF should be 20L/min
Mapleson circuits are semi-open non-rebreathing circuits but rebreathing can still occur. Why is this? How do you prevent it?
Because the inhaled and exhaled gases travel through the same tubing
Increase FGF to 2.5x's patients minute ventilation
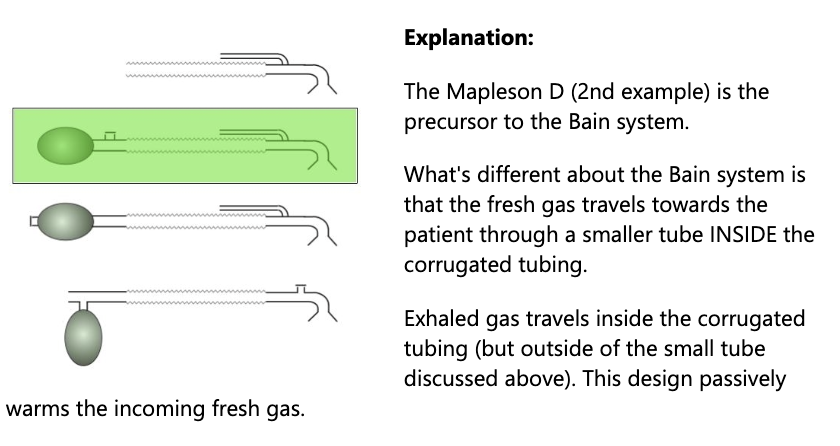
The Bain system is a modified _____
Mapleson D
In the Bain system, fresh gas enters the circuit through the _____ tubing and exhaled gas exits via the ____ tubing
Enters through inner tubing
Exits through outer corrugated tubing
T/F: the Bain system prevents heat loss
T
How does the Bain system prevent heat and humidity loss.
Since the inhaled tubing is inside the exhaled tubing, the exhaled gas warms and humidifies incoming fresh gas
With the Bain system, to prevent rebreathing what should FGF be set at?
2.5x's patients minute ventilation
What is the number 1 pitfall of the Bain circuit?
The inner tubing can become kinked or disconnected and is hard to see since it's inside the outer tubing. This converts all of the corrugated tubing to dead space putting the patient at risk for hypercarbia
What test should be performed prior to each procedure when using a Bain circuit?
What steps are involved in this test?
Explain how to interpret results
Pethick test
1. Occlude the elbow at the end of the circuit
2. Close APL valve
3. Use O2 flush valve to fill the circuit
4. Remove the occlusion at the elbow when flushing the circuit
Results:
-If inner tubing is patent, the Venturi effect will cause reservoir bag to collapse. The circuit is safe to use
-If inner tubing is occluded, the reservoir bag will remain inflated. The circuit is not safe to use
T/F: The Bain circuit is useful for spontaneous and controlled ventilation
T
Rebreathing with the circle system is primarily influenced by what 3 factors?
FGF
Arrangement of components in the circle system
Properly functioning unidirectional valves
What are 2 benefits of using low FGF in a circle system
1. Increased humidity in the system
2. Slower reduction in body temp
Which component in the circle system protects the patient from excessive airway pressure during spontaneous ventilation
Reservoir bag
If you close the APL valve and run fresh gas through the circuit, the pressure inside the circuit won't exceed 60 cm H2O until the reservoir bag inflates to at least _____ L
12 L (4x's the size of the bag which is usually 3L for adults)
For spontaneous ventilation, which circuit is best and which circuit is worst?
All Dogs Bite, A>DFE>CB;
Best: Mapelson A
Worst: Mapelson B
For controlled ventilation, which circuit is best and worst?
“Don’t Be Arrogant”
Best: Mapelson D
Worst: Mapelson A
Which Mapelson circuit is most likely to cause Hypercarbia when receiving controlled ventilation w/ FGF of 5 L/min?
Mapelson A-FGF of at least 20 L/min is required
Which circuit contains a reservoir bag but does not allow rebreathing of exhaled gases?
semi-open circuits (Nonrebreathing circuits)
What components are absent in a Mapelson D?
Unidirectional Valves
CO2 absorbent
A circle system with a fresh gas flow of 3L/min is an example of a/an
Semi-closed
Which Mapelson circuits are MOST likely to be encountered in modern anesthetic practice?
D, E, F (T-piece group)
What are the 4 steps of the Pethick test when performing a pre-anesthetic check on Bain circuit?
1. Occlude the elbow at the patient end of the circuit
2. Close the APL valve
3. Use the oxygen flush valve to fill the circuit
4. Remove the occlusion at the elbow while flushing the circuit
Which circuit does not contain dead space?
Open b/c it's open to atmosphere
Between the simple face mask, T-piece, nasal cannula, and Bain system, all allow fresh gas to escape into the atmosphere except which one?
Bain System-b/c it's semi-open
The Mapleson D is an example of
A. Semi open circuit
B. Semi closed circuit
C. Open circuit
D. Closed circuit
A. Semi open circuit
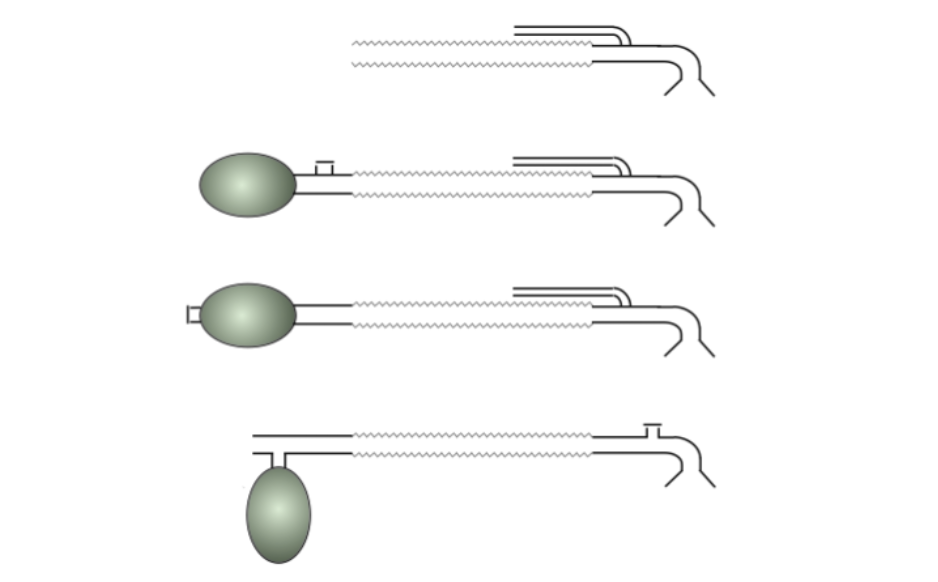
What circuit is the predecessor to the bain system?
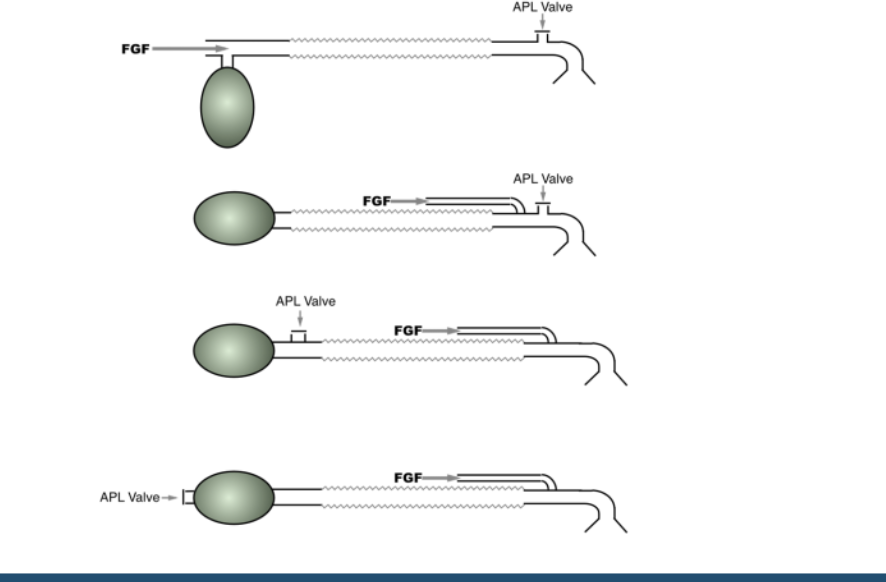
A patinet is receiving controlled ventilation with a fresh gas flow of 5L/min. Click on the cuir tthat is MOST likely to cause hypercarbia