QE 4th
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Diffusion
Movement of substances from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration without assistance.
Osmosis
The diffusion of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane.
Facilitated Transport
Transport of substances across a membrane with the help of transport proteins, typically for hydrophilic molecules and charged ions.
Active Transport
Movement of substances against their concentration gradient, requiring ATP.
Passive Transport
Movement of substances across a membrane without the use of ATP; includes diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated transport.
Hypertonic
A solution with a higher concentration of solutes compared to the cell, causing the cell to lose water and shrink.
Hypotonic
A solution with a lower concentration of solutes compared to the cell, causing the cell to gain water and swell.
Isotonic
A solution with equal concentrations of solutes inside and outside the cell, resulting in no net movement of water.
Endocytosis
The process by which materials are brought into a cell.
Exocytosis
The process by which materials are expelled from a cell.
PHAGOCYTOSIS
Engulfs food or cell
PINOCYTOSIS
Vesicles form around a liquid
RECEPTOR-MEDIATED
Receptors for substances
Enzymes
Organic catalysts made up of proteins that speed up chemical reactions.
Emil Fischer
Creator of the Lock and Key Model in 1894
Substrate
The substance upon which an enzyme acts.
Lock and Key Model
A model that describes the specific interaction between an enzyme and its substrate.
Optimum Temperature
The temperature at which an enzyme is most active, generally between 30⁰C and 40⁰C.
pH Level
A measure of acidity or alkalinity; any change in pH can lead to enzyme inactivity.
Redox Reactions
Chemical reactions involving electron transfer, crucial for biological processes like photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
Oxidation
The process of losing electrons.
Reduction
The process of gaining electrons.
Reducing Agent
A molecule that loses electrons in a redox reaction.
Oxidizing Agent
A molecule that gains electrons in a redox reaction.
Proteases
Enzymes that break down proteins into amino acids.
Carbohydrases
Enzymes that break down carbohydrates into simple sugars.
Lipases
Enzymes that break down fats or lipids into fatty acids and glycerol.
Nucleases
Enzymes that break down nucleic acids into nucleotides.
Factors affecting Enzyme Activity
Temperature, pH levels, and type of substrate are key factors influencing enzyme function.
Activation Energy
The energy required to start a chemical reaction; can be lowered by enzymes.
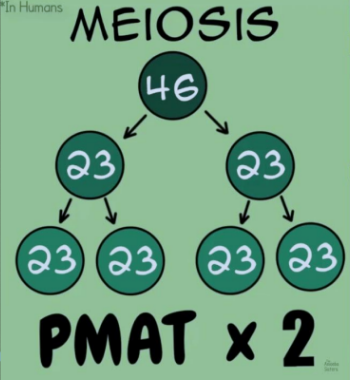
Meiosis
The process of producing haploid cells from diploid cells through two rounds of division.
Meiosis Pmat of humans
Haploid
A cell that has half the number of chromosomes, denoted as n.
Diploid
A cell that has two complete sets of chromosomes, typically denoted as 2n.
Prophase I
The first stage of meiosis I where homologous chromosomes pair and crossing-over occurs.
Metaphase I
The stage in meiosis I where homologous chromosomes align at the metaphase plate.
Anaphase I
The stage in meiosis I where homologous chromosomes are pulled apart to opposite poles.
Telophase I
The stage in meiosis I where the nuclear envelope reappears around two haploid daughter cells.
Meiosis II
The second round of meiotic division where sister chromatids are separated, leading to four unique haploid cells.
Crossing-over
The exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during prophase I.
Cytokinesis
The final stage of cell division where the cytoplasm divides, resulting in two new daughter cells.
Prophase II
Centrioles doubled and move to opposite ends
Metaphase II
Centrioles release spindle fibers
Anaphase II
Chromosomes are separated from each other
Telophase II
Spindle fibers are gone
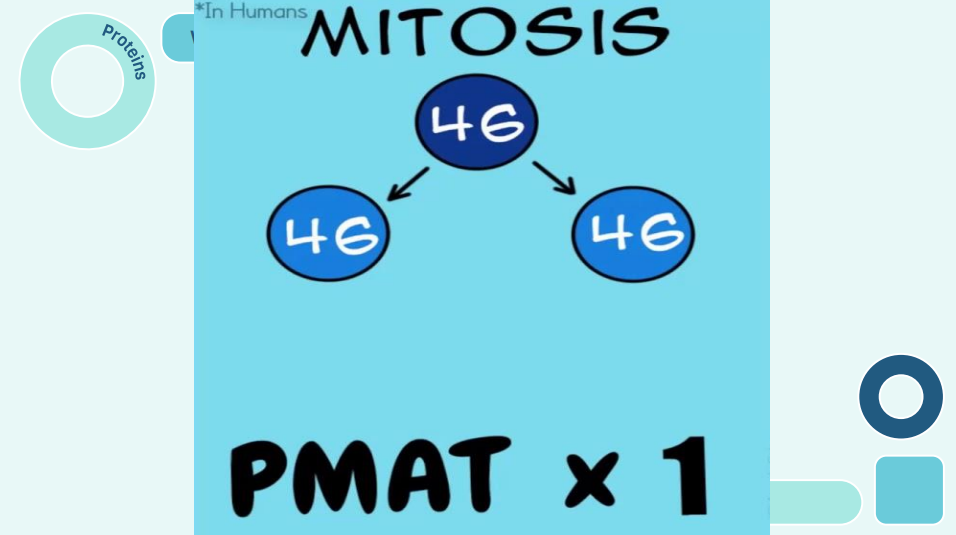
Mitosis
The process of cell division where each daughter cell receives a diploid complement of chromosomes identical to its parent cell.
Interphase
The longest phase of the cell cycle where the cell performs its normal functions and prepares for division.
G1 Phase
The first phase of interphase where the cell grows and performs its work with unduplicated chromosomes.
S Phase
The synthesis phase of interphase where DNA replication occurs.
G2 Phase
The third phase of interphase involving final preparations for mitosis, where some conditions may cause the cell to enter G0 or apoptosis.
Prophase
The phase of mitosis characterized by the preparation of chromosomes, the doubling of centrioles, and the disappearance of the nucleolus.
Metaphase
The phase of mitosis where chromosomes align at the metaphase plate and the nucleus disappears.
Anaphase
The shortest phase of mitosis where sister chromatids are separated from each other.
Telophase
The phase of mitosis where chromosomes arrive at opposite poles, decondense, and are surrounded by new nuclear envelopes.
Cytokinesis
The process that occurs after mitosis where the cytoplasm divides, resulting in two daughter cells.
Chromosome
The most condensed structure of a DNA molecule, composed of DNA and proteins.
Gene
A sequence of DNA or RNA that codes for a molecule with a function, acting as a locus on a chromosome.
Diploid
A cell with paired chromosomes; in humans, this includes 46 chromosomes.
Meiosis
A type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, producing gametes.
46
How many chromosomes do humans have?
44
The amount of homologous humans have
2
The amount of nonhomologous (sex chromosomes) in humans
Genome
Prokaryotes & eukaryotes
Checkpoints
G1 Phase, S Phase, G2 Phase, and M Phase
RNA
Adenine
Guanine
Cytosine
Uracil
DNA
Adenine
Guanine
Cytosine
Thymine
Mitosis Phase
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Mitosis Pmat of humans