29. Diseases of the intervertebral disc. Diseases of the thoraco- lumbar vertebrae. Discospondylitis Spondylosis deformans. DISH. Fractures, luxation and neoplasia. Aetiology, symptoms, diagnosis and therapy.
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
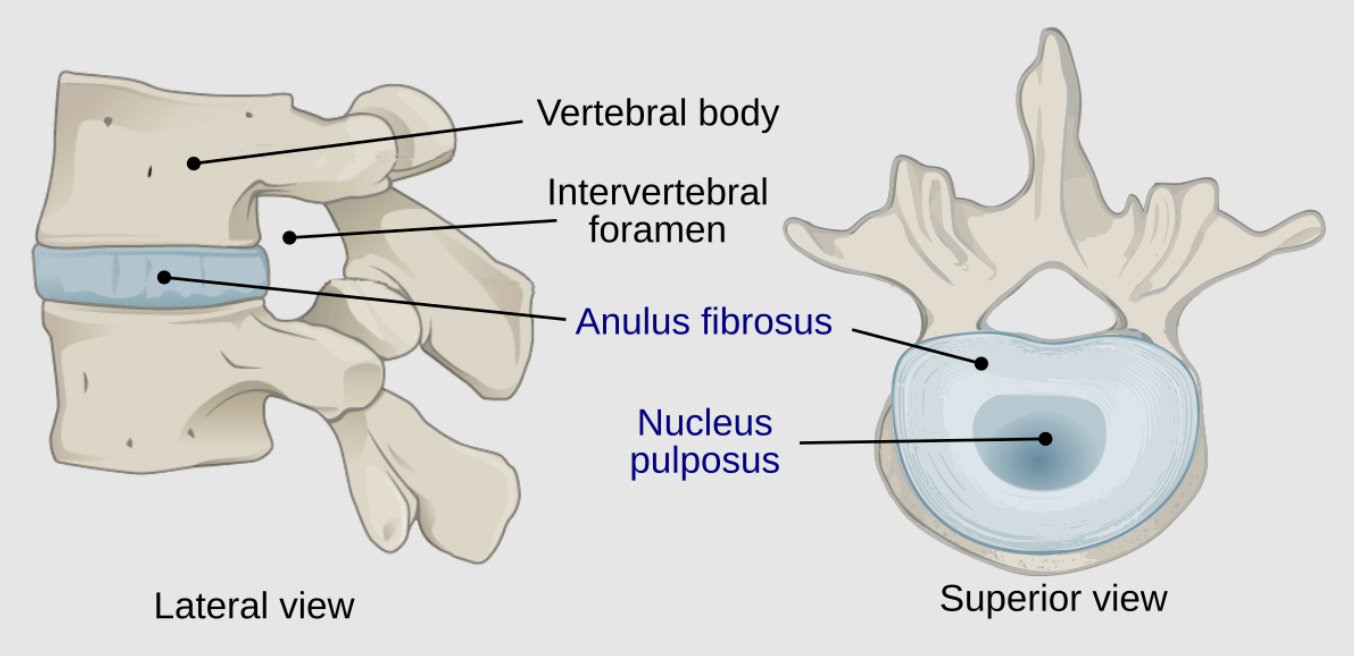
What is the main disease of the intervertebral discs?
Intervertebral Disc Disease (IVDD)
Degeneration and herniation, leading to spinal cord/nerve/nerve root compression
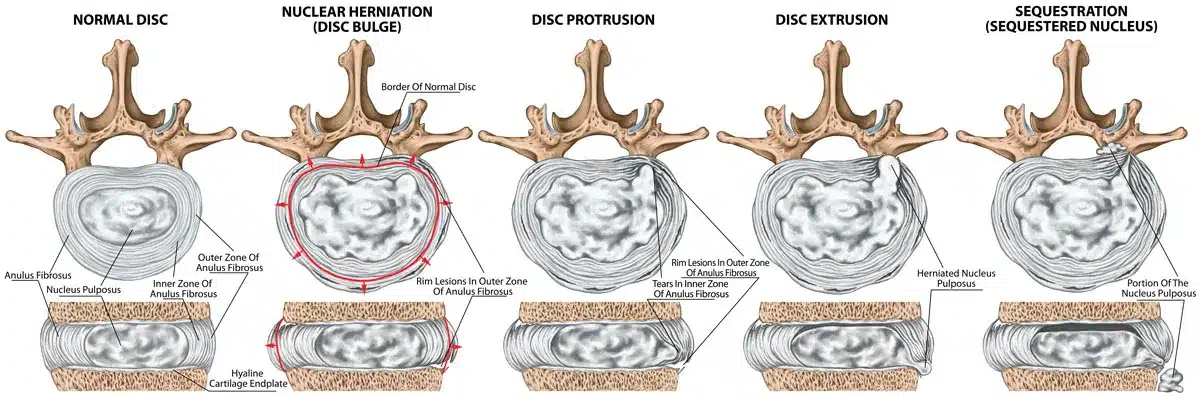
Bulging: nucleus pulposus causes a bulge by stretching intact annulus fibrosus. No herniation
Protrusion/Prolapse: discal mass bulges into vertebral canal; herniation. Annulus and nucleus remain intact
Extrusion: nucleus has broken through the annulus into the epidural space. Herniation
Sequestration: part of the nucleus pulposus is discontinuous with the native disc
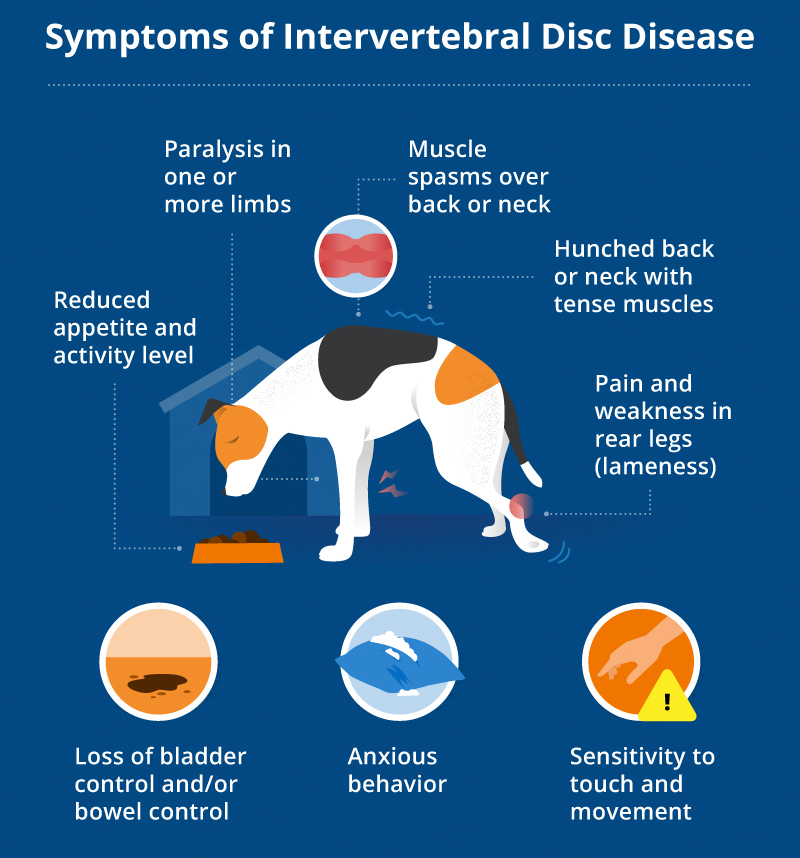
Depends on the location
Cervical
severe neck pain, altered stiff gait, lowered head carriage, neck/muscle shoulder spasms, neuropathic pain in forelimb, paresis/paralysis (worse in hind limbs)
Thoracolumbar
neck and back pain, “sawhorse” back, hindlimb paresis with altered proprioception, with/out urinary incontinence
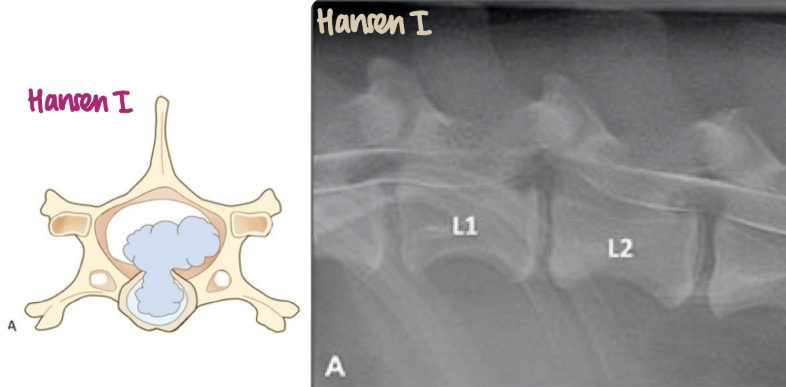
Chondrodystrophic breeds (Dachshund, Beagle). Young.
What is the pathogenesis of Hansen I IVDD?
Dehydration of the disc → granulation and mineralisation of the nucleus pulposus → annulus fibrosus degenerates & loses its capacity to contain nucleus → extrusion → acute spinal cord compression → severe neurological signs (paralysis of extremities)
Soft tissue radiopacity (mineralisation) in the nucleus pulposus (instead of radiolucent). Can be focal (central zone of nucleus), Ring-like (periphery of nucleus) or involve whole nucleus.
Older, non-chondrodystrophic breeds (Doberman) and cats
What is the pathogenesis of Hansen II IVDD?
Desiccation of nucleus pulposus → fibrous nuclear material, usually not mineralised → protrusion/prolapse of disc into the spinal canal → spinal cord compression
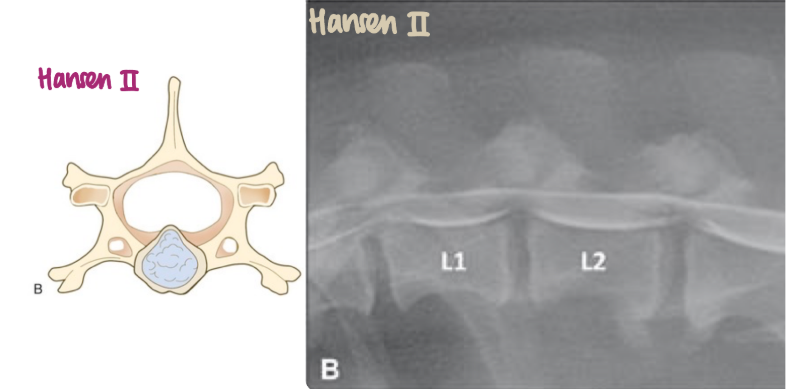
Conservative: strict confinement, pain relief (not NSAIDs), muscle relaxer, rehab
Surgical: Fenestration (removal of nucleus pulposus, not extruded disc material) or Decompression by ventral slot or hemilaminectomy (removal of extruded disc material from vertebral canal)
Narrowing of disc space and articular process joint space
Small IV foramen
Increased opacity of IV foramen
Extruded, mineralised disc material within vertebral canal.
Mineralisation of IVD
What are examples of diseases of the thoraco-lumbar vertebrae?
Discospondylitis
Spondylosis deformans
Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperosteosis (DISH)
Fractures
Luxation
Neoplasia
Bacterial infection of the intervertebral disc, vertebral endplates, and vertebral bodies → progressive bone lysis & proliferation occurring ventral & lateral to IV spaces
Where does the infection in discospondylitis originate?
Spread from another system (urinary, prostate)
Local infection in disc space
Progressive, non-specific; back/neck pain, reluctance to walk, stiff gait, proprioceptive deficits, lethargy, pyrexia, inappetence, lameness
Conservative: Long-term antibiotics, pain relief (codeine), cage rest, physiotherapy
Surgery: remove affected bone (if deteriorating neurologically)
Presence of osteophytes along the edges of vertebral bodies, forming bridges
X-ray, spinal MRI
Often asymptomatic; reduced spinal flexibility → decreased agility/mobility, rarely painful nerve compression
NSAIDs/corticosteroids, analgesics, surgery (severe cases to reduce nerve compression)
Abnormal spinal alignment, narrowed IV disc space, distorted shape
Smaller and more radiopaque vertebrae
Displacement of a bone from a joint with or without fracture
Myelography. May not be visible on every view.
What are examples of neuroepithelial tumours?
Astrocytoma, oligodendroglioma
What are examples of secondary tumours of the spine?
Nephroblastoma, osteosarcoma, fibrosarcoma, peripheral nerve sheath tumours
Vary depending on progression, size, and location. Pain and myelopathy
X-ray, CT, MRI, scintigraphy, biopsy
What are differential diagnoses of spinal neoplasia?
IVDD, discospondylitis, meningomyelitis, fibrocartilaginous embolism
Surgical removal, radiation, chemotherapy
How and why does spondylosis form on the spine?
Spondylosis forms as a degenerative response to instability in the spine, with the body creating bone spurs to stabilize and limit movement between vertebrae.