CH2 - Atomic Structure
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms

Behaviour of beam of subatomic particles in an electric field.


Behaviour of beam of subatomic particles in an electric field.

The proton determines the identity of the element. True of False?
True
What does “the orbital becomes more diffuse” mean?
The orbital becomes larger in size.
How many electrons can each orbital accommodate?
2
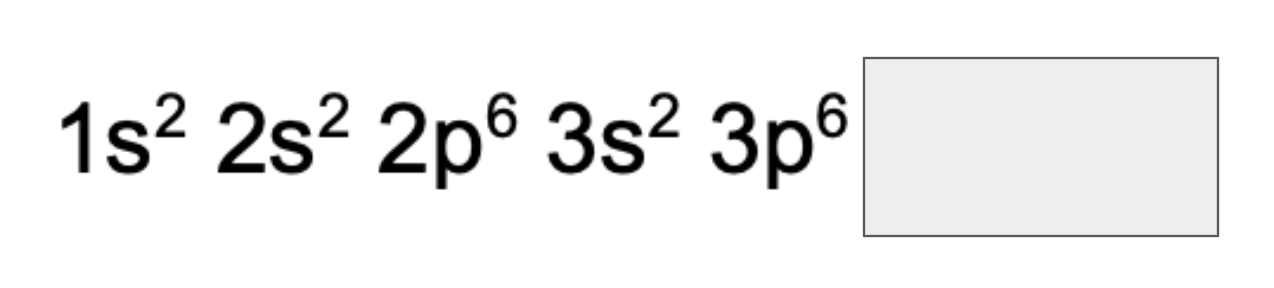
What is the electronic configuration of 24Cr

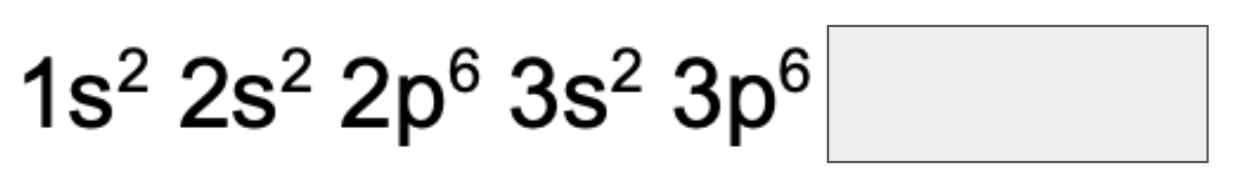
What is the electronic configuration of 29Cu?
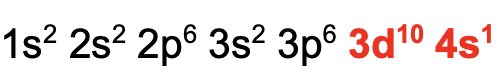
An atom is in the ground state when it is overall at the lowest energy level. (i.e. they have the most stable electronic configurations)
Most atoms are not in their ground state at room temperature. True of False?
False.
Most atoms are in their ground state at room temperature.
An atom is in the excited state when one or more electrons release energy and are demoted to a lower energy level. True of False?
False.
An atom is in the excited state when one or more electrons absorb energy and are promoted to a higher energy level. Excited atoms are unstable and can emit energy to return to the ground state.
What are isoelectronic species?
Isoelectronic species are species with the same total number of electrons.
What are the 3 main factors that affect the strength of the electrostatic attraction between the nucleus and electrons?
Number of electron shells
Nuclear charge
Shielding effect by electrons
What is atomic radius?
Atomic radius is defined as half the shortest inter-nuclear distance found in the structure of the element. This observed ‘radius’ of the atom depends upon how the atom bonds or interacts with its neighbours.
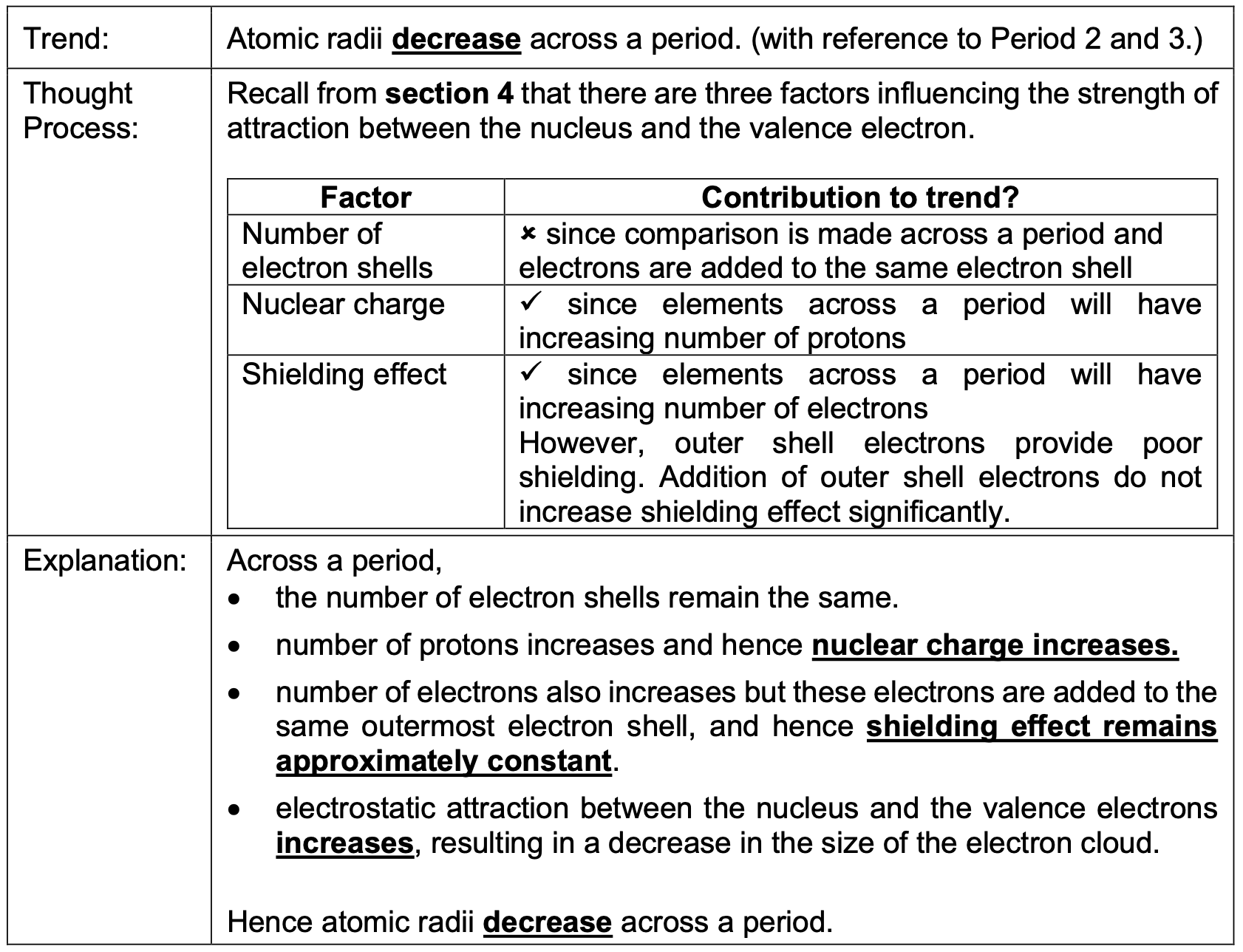
Atomic radii decrease across a period. True or False?
Think in terms of the 3 main factors and craft an answer before checking.
True.
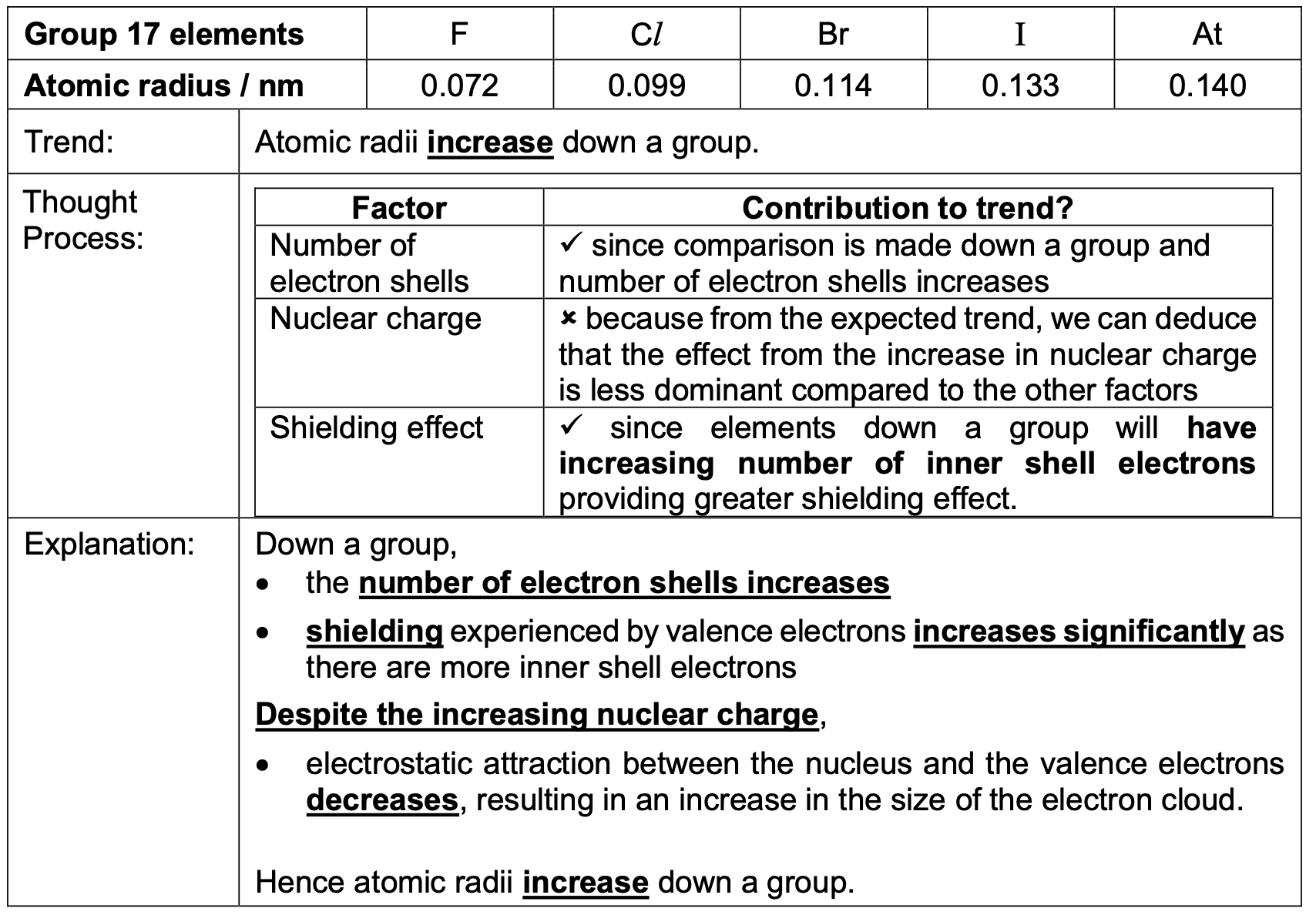
Atomic radii increase down a group. Why?
The radius of a cation is always smaller than that of the parent atom. Why?

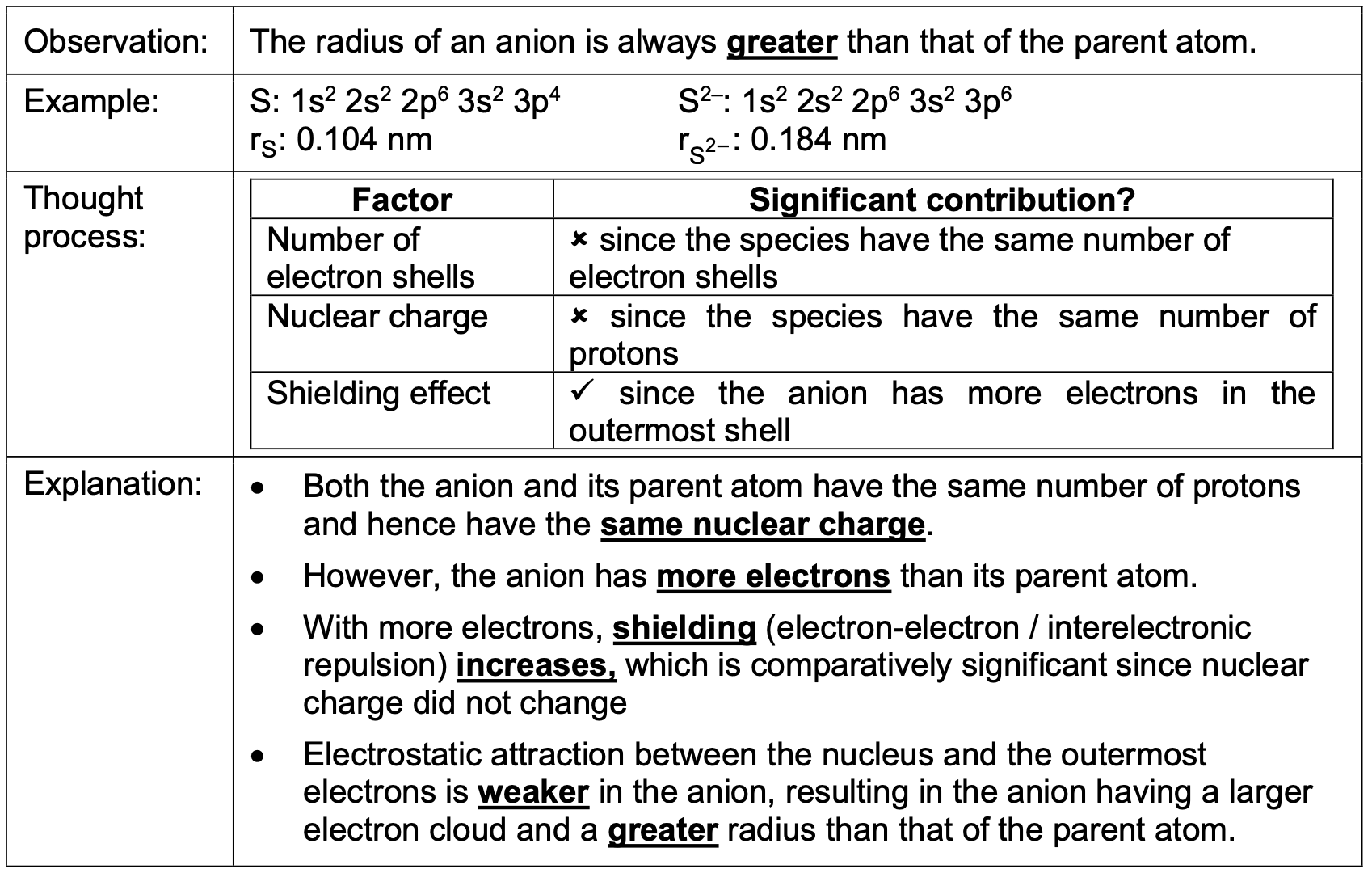
The radius of an anion is always greater than that of the parent atom. Why?
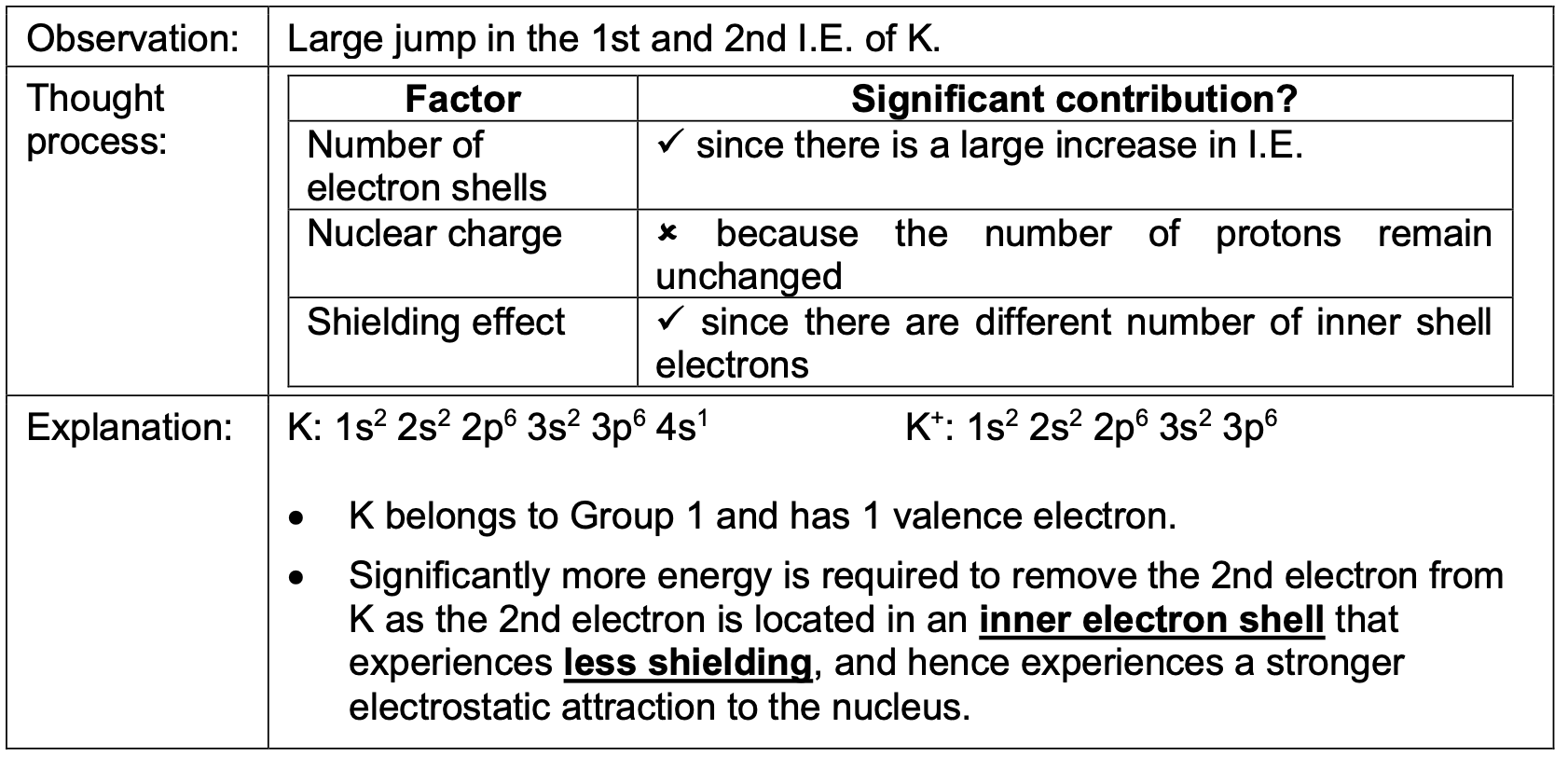
What is the first ionisation energy?
The first ionisation energy of an element M is the energy required to remove 1 mole of electrons from 1 mole of gaseous M atoms to form 1 mole of gaseous M+ ions.
What is the second ionisation energy?
The second ionisation energy of an element M is the energy required to remove 1 mole of electrons from 1 mole of gaseous M+ ions to form 1 mole of gaseous M2+ ions.
Ionisation is an exothermic process. True of False?
False. Ionisation is an endothermic process and ionisation energies are positive values since energy is absorbed during ionisation to overcome the attraction between the electron and the nucleus.
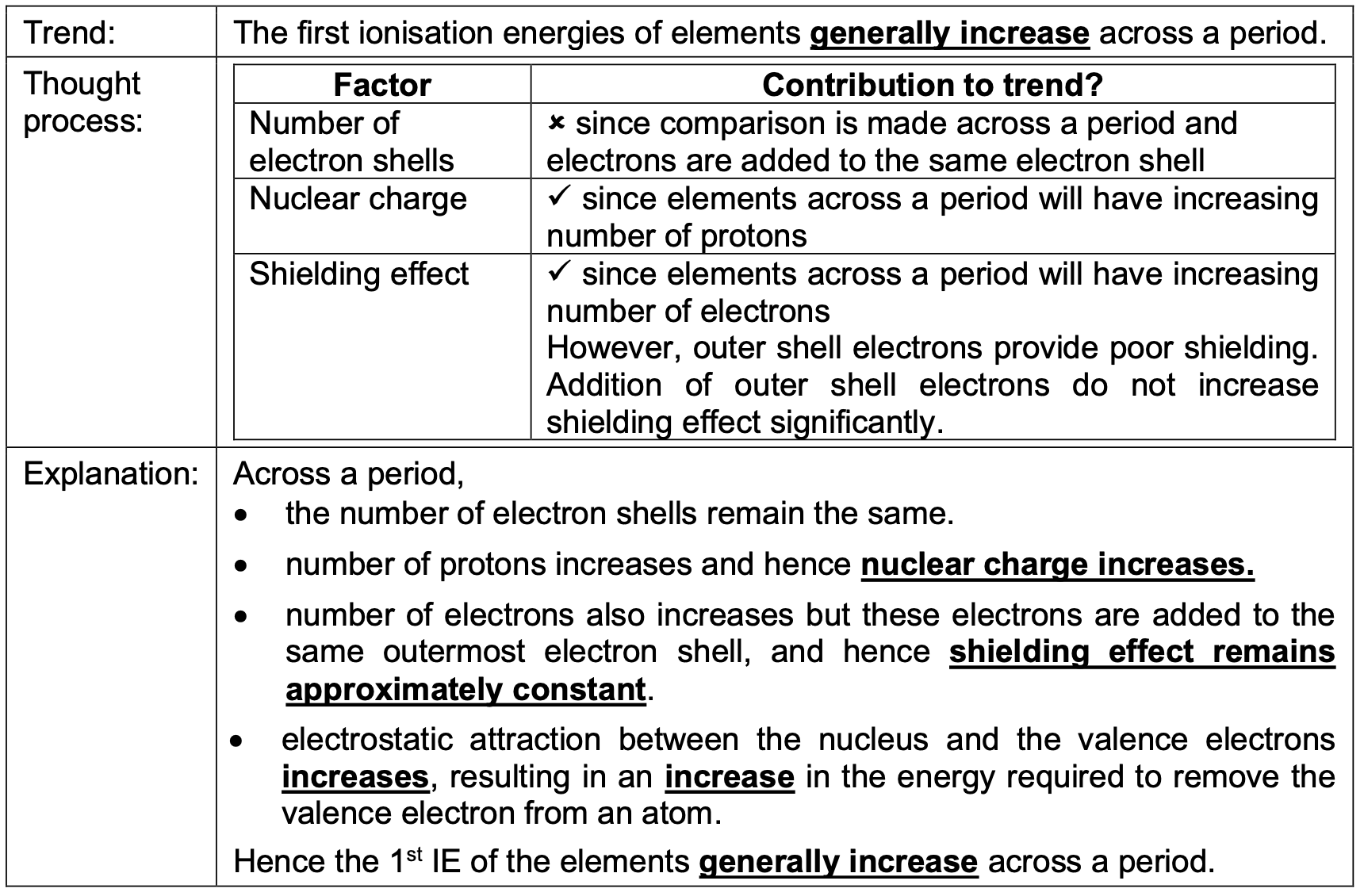
The first ionisation energies of elements generally increase across a period. Why?
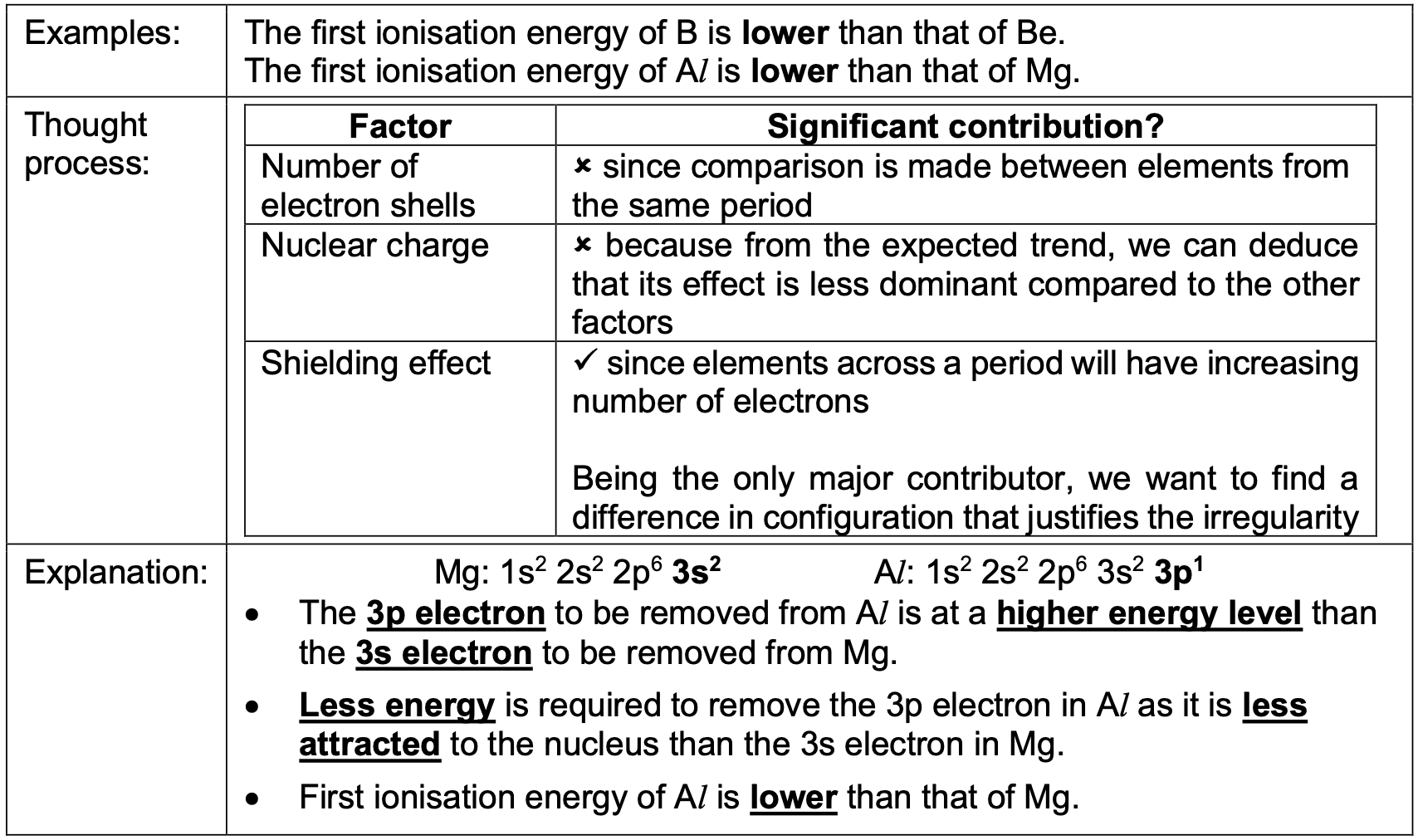
Why is the first ionisation energy of B (group 13) lower than that of Be (group 2)?
Hint: Check the electronic configuration of each atom
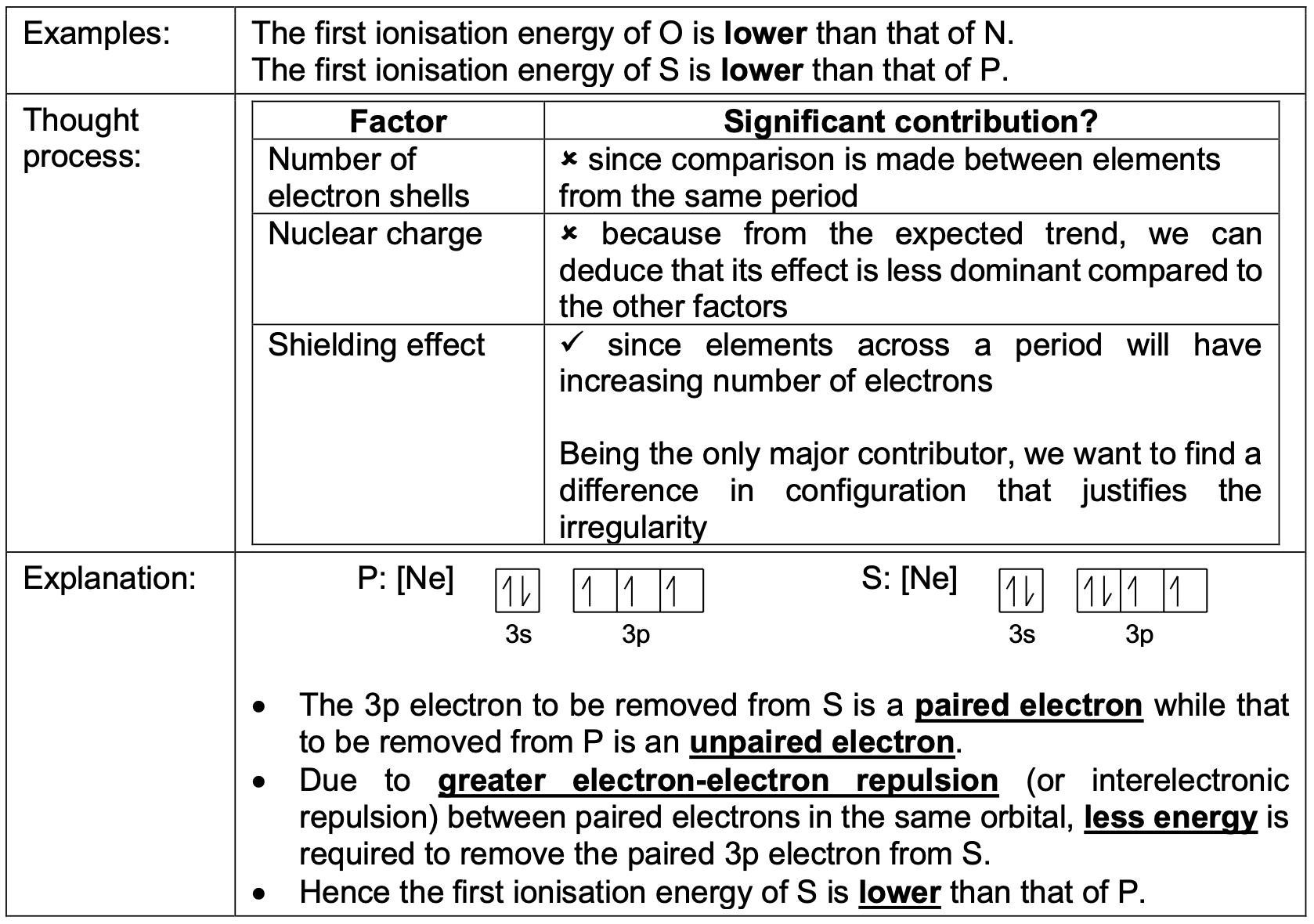
Why is the first ionisation energy of O (group 16) lower than that of N (group 15)?
Hint: check the electronic configuration of each atom
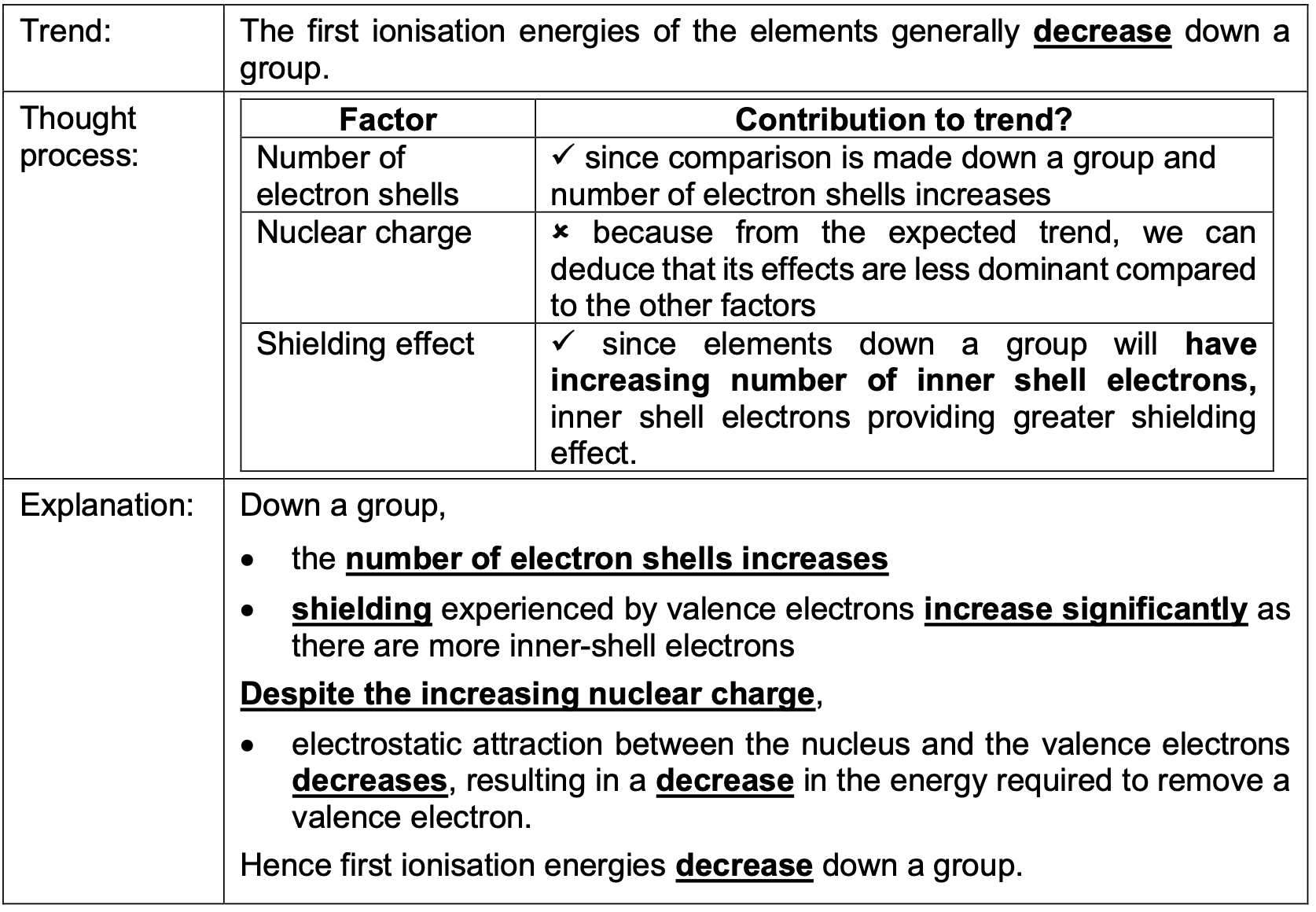
The first ionisation energies of the elements generally decrease down a group. Why?
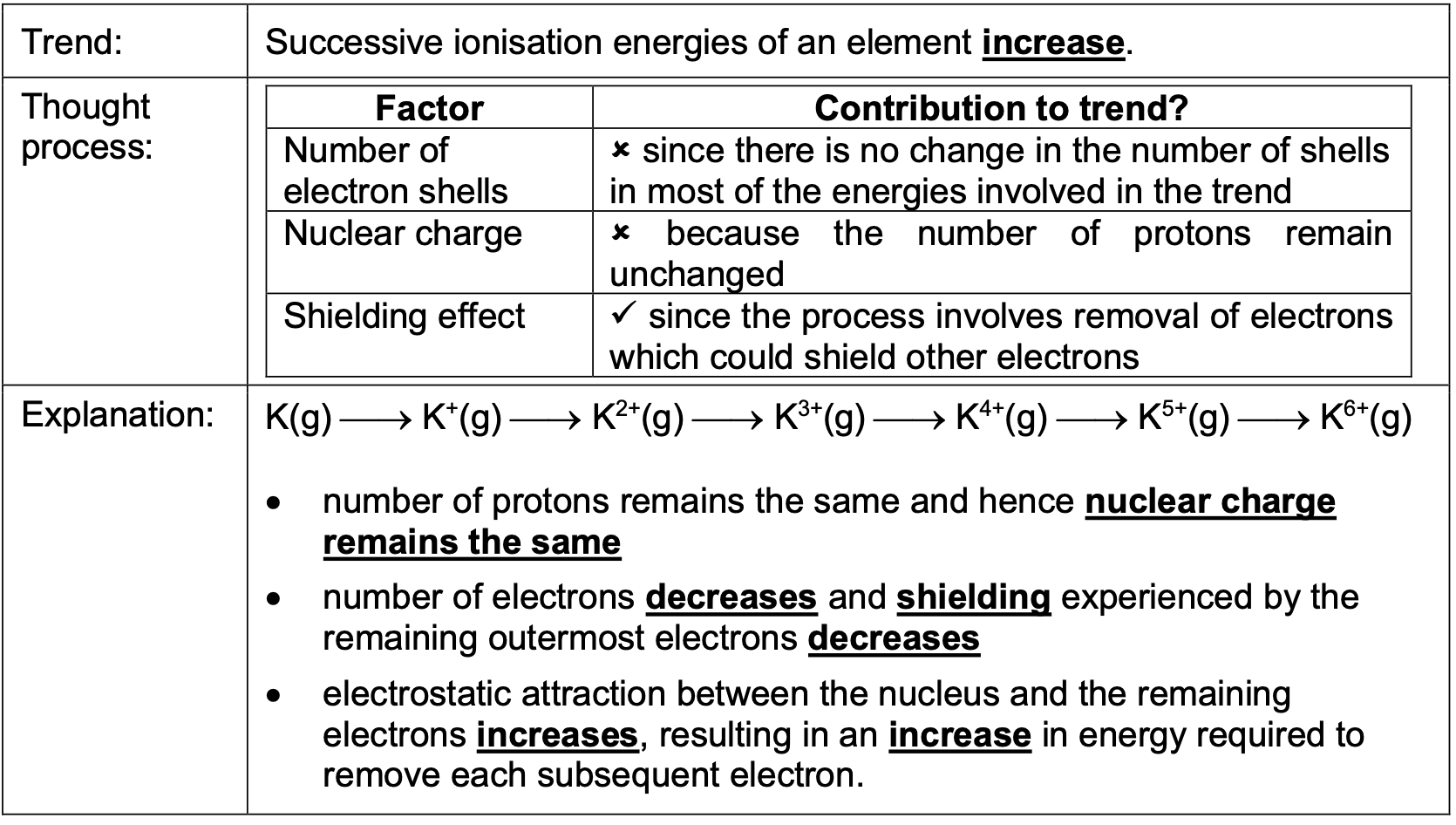
Successive ionisation energies of an element increase. Why?
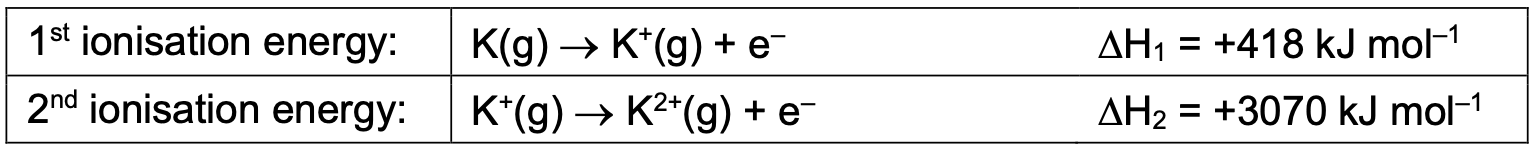
How to deduce group number from successive ionisation data?
The _____ of an atom in a molecule is a relative measure of its ability to attract bonding electrons.
The electronegativity of an atom in a molecule is a relative measure of its ability to attract bonding electrons.
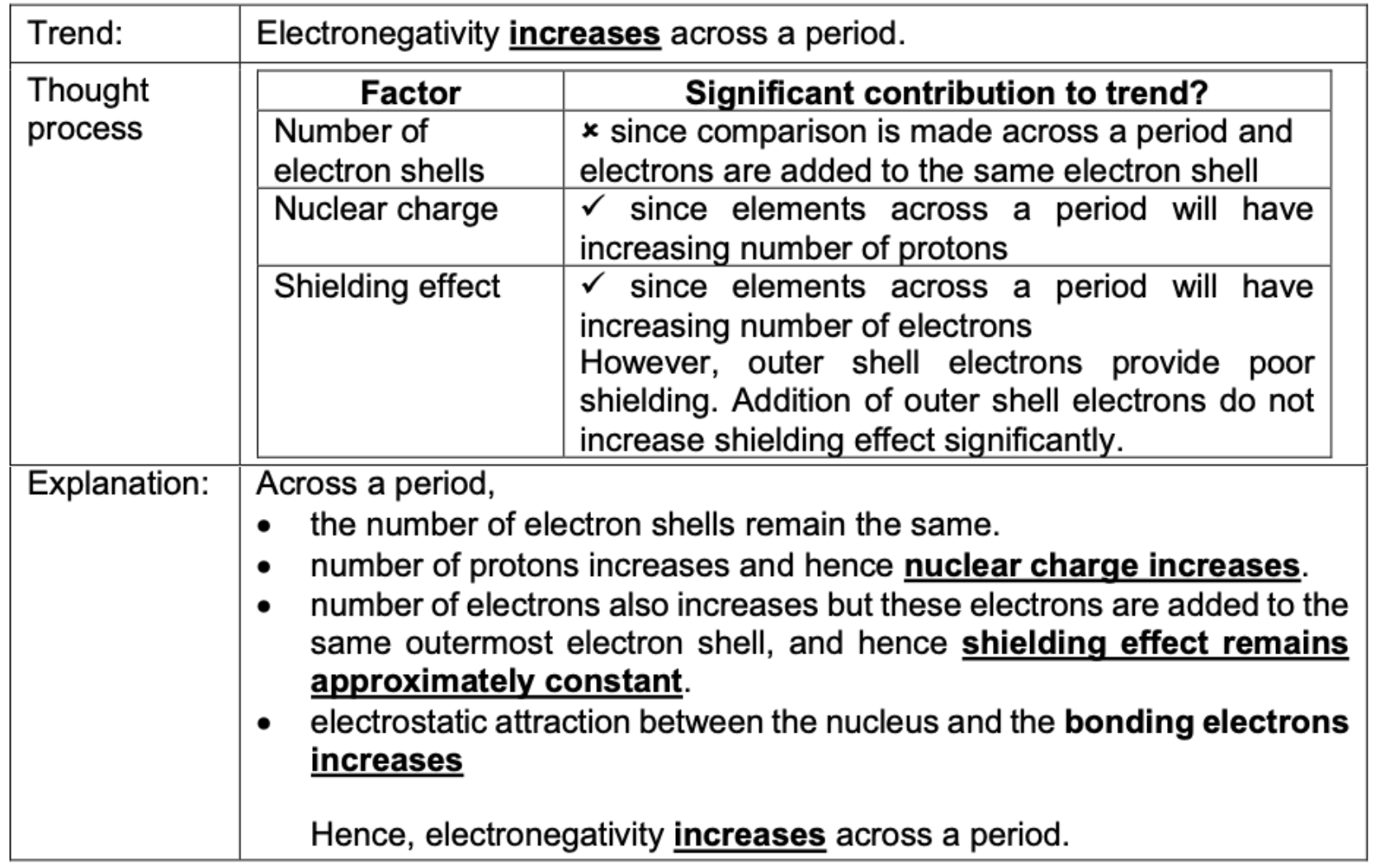
Electronegativity increases across a period. Explain why.
Electronegativity decreases down a group. Explain why.