Chem - Topic - Core Practicals
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/50
Last updated 8:56 PM on 11/16/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
1
New cards
NEUTRALISATION:
What are the main errors in this experiment?
Explain one way to improve the accuracy of the experiment.
What are the main errors in this experiment?
Explain one way to improve the accuracy of the experiment.
Using the universal indicator paper
Use a pH meter or probe which will digitally record the pH.
Use a pH meter or probe which will digitally record the pH.
2
New cards
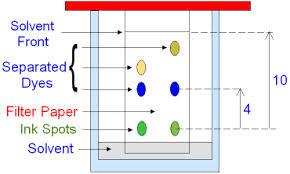
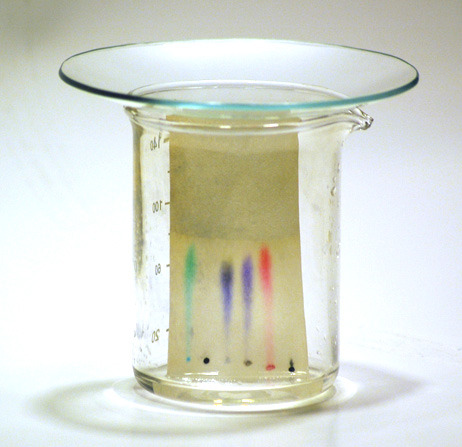
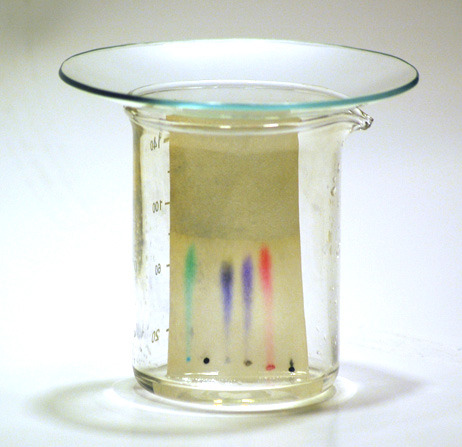
SEPARATION OF INKS:
Why is it important to draw the lines and write labels on the chromatography paper in pencil and not in ink?
Why is it important to draw the lines and write labels on the chromatography paper in pencil and not in ink?
Pencil is insoluble in the solvent
3
New cards
SEPARATION OF INKS:
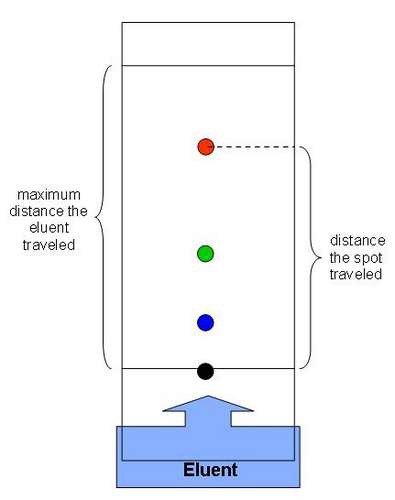
Why should the spots of ink be above the level of the solvent in the beaker?
Why should the spots of ink be above the level of the solvent in the beaker?
So the ink doesn't dissolve
4
New cards
SEPARATION OF INKS:
What is meant by the term 'solvent front'?
What is meant by the term 'solvent front'?
The level that solvent rises to/distance moved by solvent
5
New cards
SEPARATION OF INKS:
What is the mobile phase?
What is the mobile phase?
Solvent

6
New cards
SEPARATION OF INKS:
What is the stationary phase?
What is the stationary phase?
Paper

7
New cards
SEPARATION OF INKS:
Where do the insoluble substances reside on the chromatogram?
Where do the insoluble substances reside on the chromatogram?
On the baseline

8
New cards
SEPARATION OF INKS:
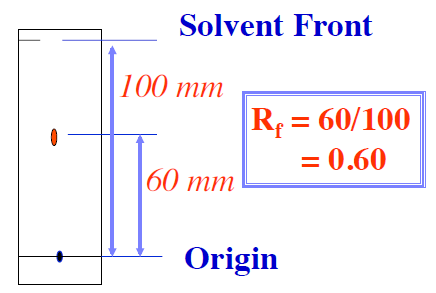
What change could you make to the experiment in order to determine an Rf value of an insoluble food colouring?
What change could you make to the experiment in order to determine an Rf value of an insoluble food colouring?
Change the solvent
9
New cards
SEPARATION OF INKS:
What process takes place when a liquid turns into a gas?
What process takes place when a liquid turns into a gas?
Evaporation

10
New cards
SEPARATION OF INKS:
What process takes place when a gas turns into a liquid?
What process takes place when a gas turns into a liquid?
Condensation

11
New cards
SEPARATION OF INKS:
What will liquid will be collected first:
Liquid A 100⁰C or Liquid B at 65⁰C?
What will liquid will be collected first:
Liquid A 100⁰C or Liquid B at 65⁰C?
Liquid B
12
New cards
SEPARATION OF INKS:
What is the purpose of the crushed ice?
What is the purpose of the crushed ice?
Speed up the process of condensation
13
New cards
SEPARATION OF INKS:
What is the temperature on the thermometer when the water is distilling off?
What is the temperature on the thermometer when the water is distilling off?
100⁰C
14
New cards
SEPARATION OF INKS:
What is the difference between simple and fractional distillation?
What is the difference between simple and fractional distillation?
The difference between simple and fractional distillation is that simple is mainly used for two liquids with two different melting points and fractional is used for multiple liquids with different boiling points
15
New cards
SEPARATION OF INKS:
What is a temperature gradient found in the fractional distillation column?
What is a temperature gradient found in the fractional distillation column?
As the column heats up, it will be hottest at the bottom and the temperature will drop towards the top.
16
New cards
SEPARATION OF INKS:
What method would be used to separate crude oil and saltwater?
What method would be used to separate crude oil and saltwater?
Crude oil - fractional distillation (more than 2 liquids)
Salt water - simple distillation (1 soluble compound and 1 liquid)
Salt water - simple distillation (1 soluble compound and 1 liquid)
17
New cards
NEUTRALISATION:
What is the best piece of apparatus to measure the volume of hydrochloric acid? Why is that the best piece of apparatus?
What is the best piece of apparatus to measure the volume of hydrochloric acid? Why is that the best piece of apparatus?
Measuring cylinder (1 mark). It has an appropriate scale on the size to measure out volume correctly
18
New cards
NEUTRALISATION:
How do you use universal indicator paper to measure the pH of the solution?
How do you use universal indicator paper to measure the pH of the solution?
Remove a sample using a glass rod and add to the paper.
Then use the pH scale to compare the colours
Then use the pH scale to compare the colours
19
New cards
NEUTRALISATION:
How do you know when the hydrochloric acid is exactly neutralised?
How do you know when the hydrochloric acid is exactly neutralised?
To ensure all the hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions react
20
New cards
NEUTRALISATION:
What colour and pH is neutral when using universal indicator?
What colour and pH is neutral when using universal indicator?
Green/pH 7
21
New cards
FORMATION OF A SOLUBLE SALT FROM AN INSOLUBLE BASE:
What is meant by the filtrate and residue?
What is meant by the filtrate and residue?
Filtrate (through the filter paper) residue in filter paper
22
New cards
FORMATION OF A SOLUBLE SALT FROM AN INSOLUBLE BASE:
What colour was the copper sulfate solution
that formed?
What colour was the copper sulfate solution
that formed?
Blue
23
New cards
FORMATION OF A SOLUBLE SALT FROM AN INSOLUBLE BASE:
Why should the acid solution be warmed slightly?
Why should the acid solution be warmed slightly?
To speed up the reaction
24
New cards
FORMATION OF A SOLUBLE SALT FROM AN INSOLUBLE BASE:
Why is the metal oxide added in excess?
Why is the metal oxide added in excess?
To ensure all the acid has reacted
25
New cards
FORMATION OF A SOLUBLE SALT FROM AN INSOLUBLE BASE:
How did you know when the copper oxide was present in excess?
How did you know when the copper oxide was present in excess?
It was insoluble (copper oxide is insoluble in water)
26
New cards
FORMATION OF A SOLUBLE SALT FROM AN INSOLUBLE BASE:
Why is the mixture filtered?
Why is the mixture filtered?
To remove the excess metal oxide
27
New cards
FORMATION OF A SOLUBLE SALT FROM AN INSOLUBLE BASE:
Why should a water bath be used rather than a Bunsen burner?
Why should a water bath be used rather than a Bunsen burner?
It is safer and equal distribution of heat
28
New cards
ELECTROLYSIS OF COPPER SULFATE SOLUTION WITH COPPER ELECTRODES
What safety precautions should you take when carrying out this experiment and why?
What safety precautions should you take when carrying out this experiment and why?
Propanone is an irritant and highly flammable
29
New cards
ELECTROLYSIS OF COPPER SULFATE SOLUTION WITH COPPER ELECTRODES
Why is it necessary to clean the copper electrodes with emery paper before using them?
Why is it necessary to clean the copper electrodes with emery paper before using them?
Clean the copper electrodes - to reduce the amount of sludge that will form under the anode or to remove all grease present on the electrodes
30
New cards
ELECTROLYSIS OF COPPER SULFATE SOLUTION WITH COPPER ELECTRODES
Which factors should be kept the same during the electrolysis?
Which factors should be kept the same during the electrolysis?
The key control variables are the concentration of the electrolyte, the time of electrolysis and the volume of copper sulphate used
31
New cards
ELECTROLYSIS OF COPPER SULFATE SOLUTION WITH COPPER ELECTRODES
How do you wash and dry the electrodes at the end of the electrolysis?
How do you wash and dry the electrodes at the end of the electrolysis?
Propanone has a higher evaporation point than water and can quickly dry the electrodes. These are washed with propanone and then this evaporates quickly.
The electrodes should be dry as any liquid left on them will increase the mass.
The electrodes should be dry as any liquid left on them will increase the mass.
32
New cards
ELECTROLYSIS OF COPPER SULFATE SOLUTION WITH COPPER ELECTRODES
Why is there a difference in the change in mass of the anode and the change in mass of the cathode?
Why is there a difference in the change in mass of the anode and the change in mass of the cathode?
The copper atoms in the anode lose electrons to become copper ions.
These dissolve in the solution and migrate to the cathode, where they are deposited as pure copper.
These dissolve in the solution and migrate to the cathode, where they are deposited as pure copper.
33
New cards
ELECTROLYSIS OF COPPER SULFATE SOLUTION WITH INERT ELECTRODES
State and explain one safety precaution
State and explain one safety precaution
Wear goggles - be careful using liquid around a live current/ the electrodes will become hot if a high current is used
34
New cards
ELECTROLYSIS OF COPPER SULFATE SOLUTION WITH INERT ELECTRODES
What did you observe at the anode?
What did you observe at the anode?
Non metal produced - oxygen gas given off
35
New cards
ELECTROLYSIS OF COPPER SULFATE SOLUTION WITH INERT ELECTRODES
What did you observe at the cathode?
What did you observe at the cathode?
Metal produced at the cathode - pure copper
36
New cards
ELECTROLYSIS OF COPPER SULFATE SOLUTION WITH INERT ELECTRODES
How do you explain the formation of the product at the anode?
How do you explain the formation of the product at the anode?
Oxygen negative charged and more reactive therefore it will migrate towards the positive electrode and therefore oxygen gas with form
37
New cards
ELECTROLYSIS OF COPPER SULFATE SOLUTION WITH INERT ELECTRODES
How do you explain the formation of the product at the cathode?
How do you explain the formation of the product at the cathode?
Copper is positively charged and therefore will migrate towards the negative electrode and therefore copper metal will be produced at the negative electrode
38
New cards
ELECTROLYSIS OF COPPER SULFATE SOLUTION WITH INERT ELECTRODES
What happens to the blue colour of the copper sulfate solution?
What happens to the blue colour of the copper sulfate solution?
When Copper(II) sulphate is electrolysed with graphite electrodes the copper from solution migrates towards the negative electrodes, reduces and therefore is removed from solution.
Therefore over time the solution will loose the blue colour.
Therefore over time the solution will loose the blue colour.
39
New cards
ELECTROLYSIS OF COPPER SULFATE SOLUTION WITH INERT ELECTRODES
Explain why a different product is formed at the anode when copper sulfate solution is electrolysed using graphite electrodes rather than copper electrodes.
Explain why a different product is formed at the anode when copper sulfate solution is electrolysed using graphite electrodes rather than copper electrodes.
The copper anode is preferentially oxidised to discharge Cu²⁺ copper ions.
Oxygen gas is formed at the positive electrode, an oxidation reaction (electron loss)
Oxygen gas is formed at the positive electrode, an oxidation reaction (electron loss)
40
New cards
ELECTROLYSIS OF COPPER SULFATE SOLUTION WITH INERT ELECTRODES
If the electrolysis is continued for a long time, what will be left in the solution?
If the electrolysis is continued for a long time, what will be left in the solution?
H₂SO₄ (H⁺ and SO₄²⁻) and water (H⁺+OH⁻)
41
New cards
RATE OF REACTION - COLLECTING A GAS
What is the best practical method to determine the rate of this reaction and why?
What is the best practical method to determine the rate of this reaction and why?
To collect the gas over 5 minutes using a gas syringe.
Air tight system so no gas escapes/closed system
Air tight system so no gas escapes/closed system
42
New cards
RATE OF REACTION - COLLECTING A GAS
What are two different methods of collecting and measuring the volume of gas produced?
What are two different methods of collecting and measuring the volume of gas produced?
The volume of gas given off/ the change in mass
43
New cards
RATE OF REACTION - COLLECTING A GAS
Increasing surface area will do what to the production of the gas?
Increasing surface area will do what to the production of the gas?
Speeds up the production of gas
44
New cards
RATE OF REACTION - COLLECTING A GAS
How can you explain the graphs of volume of gas plotted against time for two different sizes of marble chips?
How can you explain the graphs of volume of gas plotted against time for two different sizes of marble chips?
The graph for the small pieces of marble chips is steeper- larger surface area- faster rate of reaction (steeper the gradient)
45
New cards
RATE OF REACTION - COLLECTING A GAS
What needs to be kept the same when you repeat the first experiment but use different size marble chips?
What needs to be kept the same when you repeat the first experiment but use different size marble chips?
Same volume, Same amount of calcium carbonate, same concentration of acid, same length of time for reactions
46
New cards
RATE OF REACTION - COLLECTING A GAS
How can you calculate the rate of reaction from a graph
How can you calculate the rate of reaction from a graph
Gradient = change in y/change in x
47
New cards
RATE OF REACTION - CHANGE IN TEMPERATURE
What is seen when sodium thiosulfate solution reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid?
What is seen when sodium thiosulfate solution reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid?
A cloudy precipitate is formed
48
New cards
RATE OF REACTION - CHANGE IN TEMPERATURE
What safety precautions should you take in this investigation?
What safety precautions should you take in this investigation?
Increasing the temperature can cause burns
49
New cards
RATE OF REACTION - CHANGE IN TEMPERATURE
What is the best practical method to determine the rate of this reaction and why?
What is the best practical method to determine the rate of this reaction and why?
The cross disappears quicker as the rate of reaction increases
50
New cards
RATE OF REACTION - CHANGE IN TEMPERATURE
What happens to the time taken for the reaction to occur as the temperature increases?
What happens to the time taken for the reaction to occur as the temperature increases?
The time taken decreased as the temperature increases
51
New cards
RATE OF REACTION - CHANGE IN TEMPERATURE
How do you explain this change in terms of the energy of the particles and collisions?
How do you explain this change in terms of the energy of the particles and collisions?
When the temperature is increased the particles move quicker, they will have more collisions
Higher temperatures also increase the energy of the collisions, since the particles are moving faster. Reactions only happen if the particles collide with enough energy.
At higher temperatures there are more successful collisions (more particles will collide with enough energy to react).
Increasing the temperature increases the rate of reaction
Higher temperatures also increase the energy of the collisions, since the particles are moving faster. Reactions only happen if the particles collide with enough energy.
At higher temperatures there are more successful collisions (more particles will collide with enough energy to react).
Increasing the temperature increases the rate of reaction