Lymphatic System
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Lymphatic system
Circulate bodily fluid called lymph
Transport fluid away from interstitial spaces
Launch attacks against foreign substances, protects against disease
Lacteals
Special lymphatic capillaries → absorb digested fats and transport to venous circulation
Location: lining of small intestine
Lymphatic capillaries
Microscopic, close-ended tubes, extend into interstitial spaces, everywhere w/blood capillaries
Walls have a single layer of squamous epithelial cells → allow interstitial fluid to enter
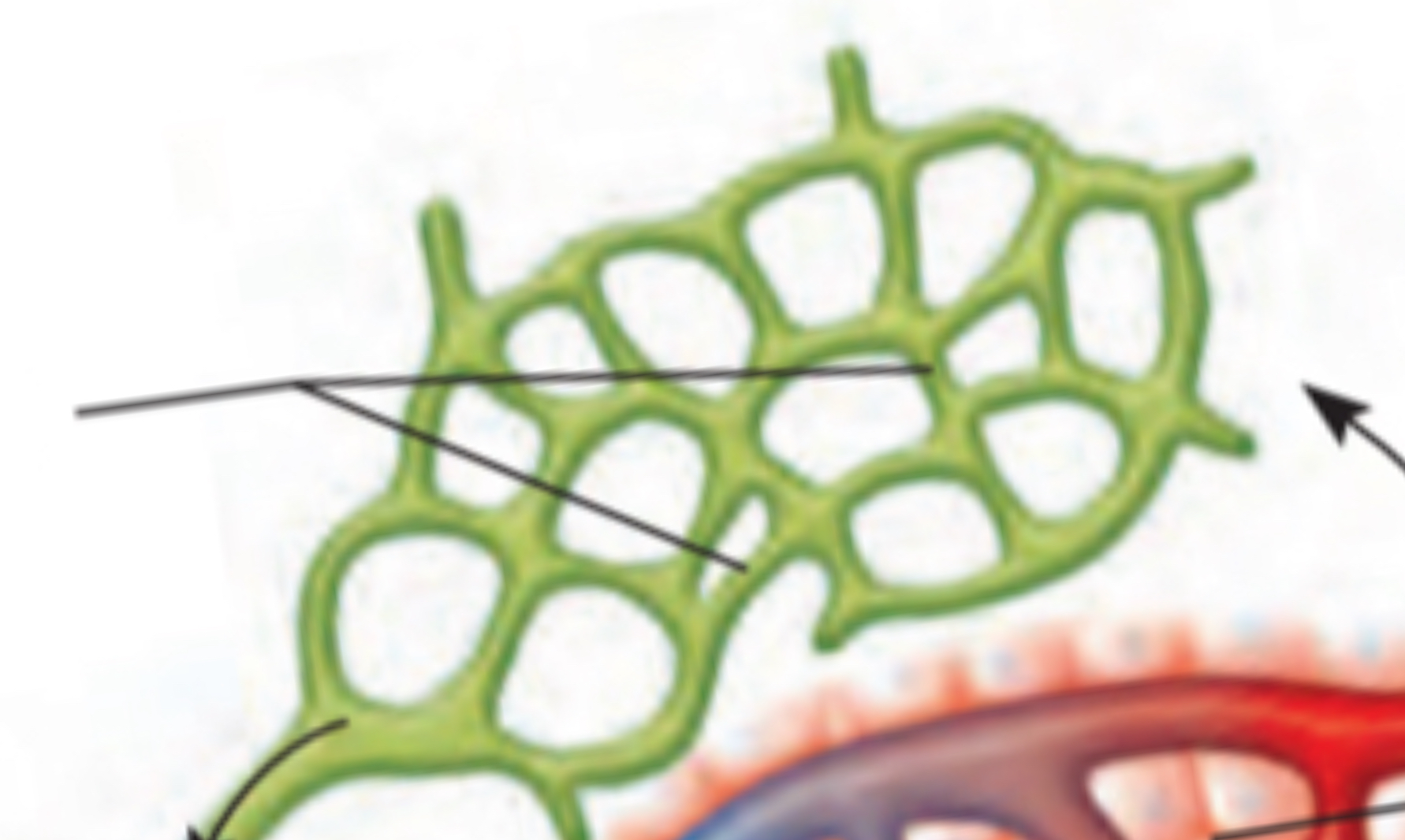
Lymph
Fluid inside lymphatic capillaries
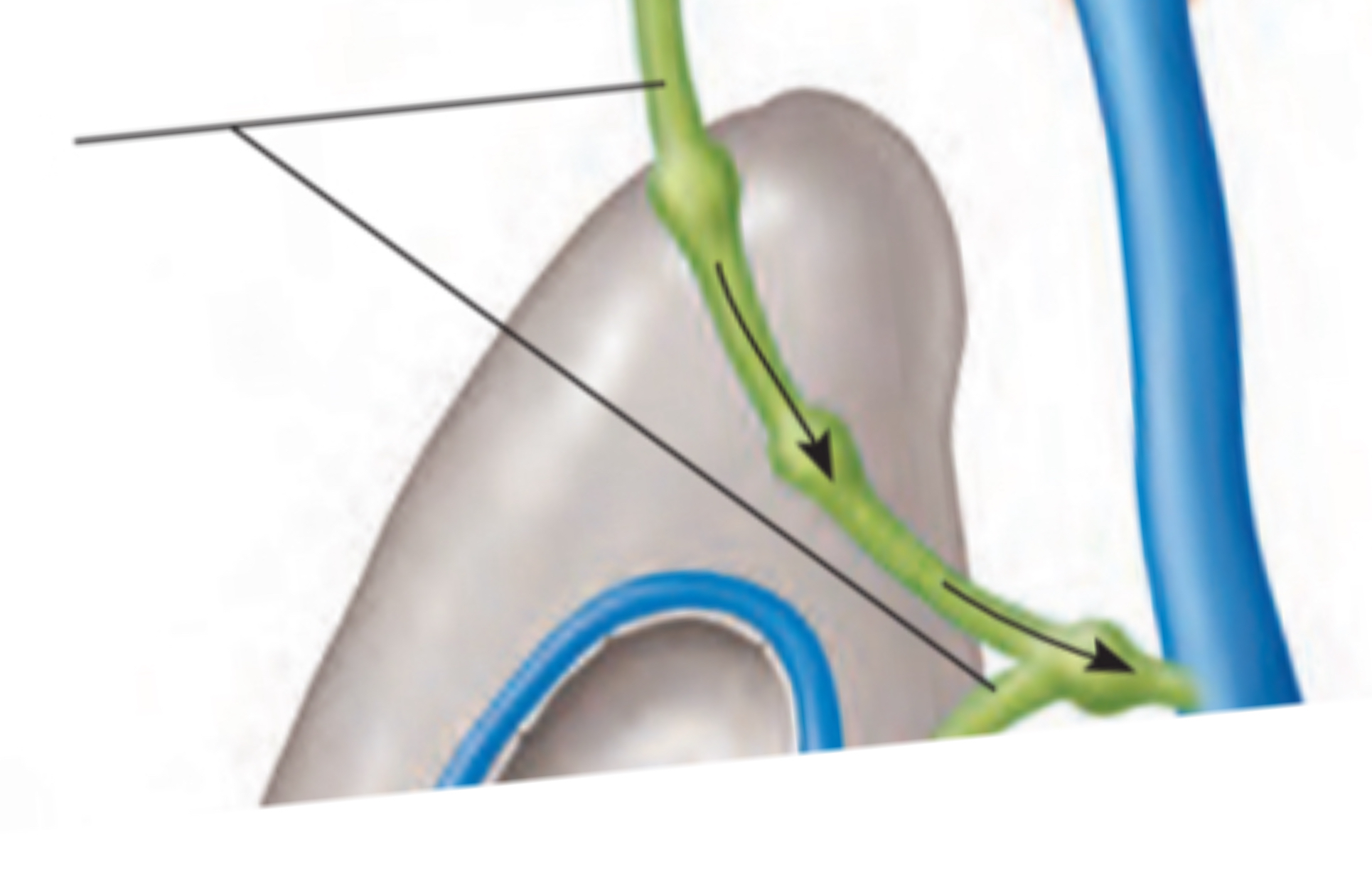
Lymphatic vessels
Have flaplike valves → prevent backflow of lymph
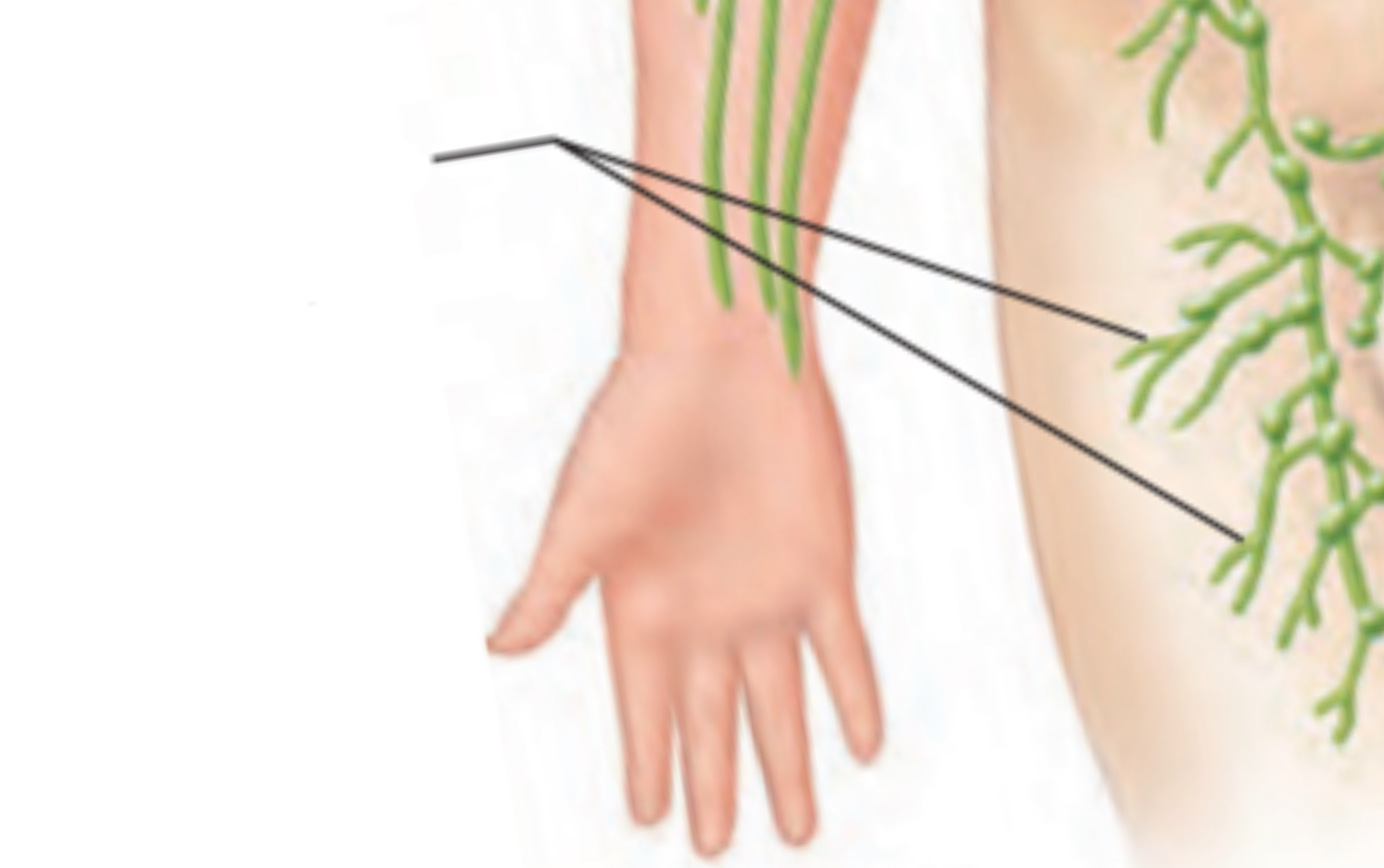
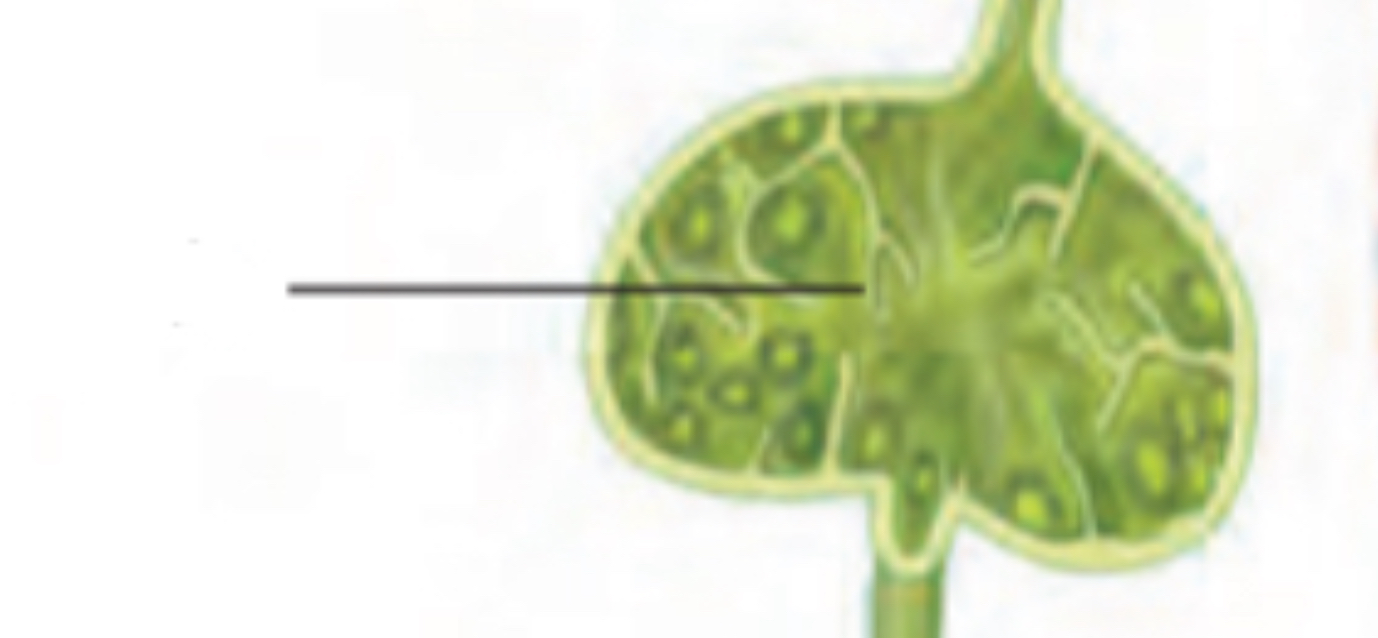
Lymph nodes
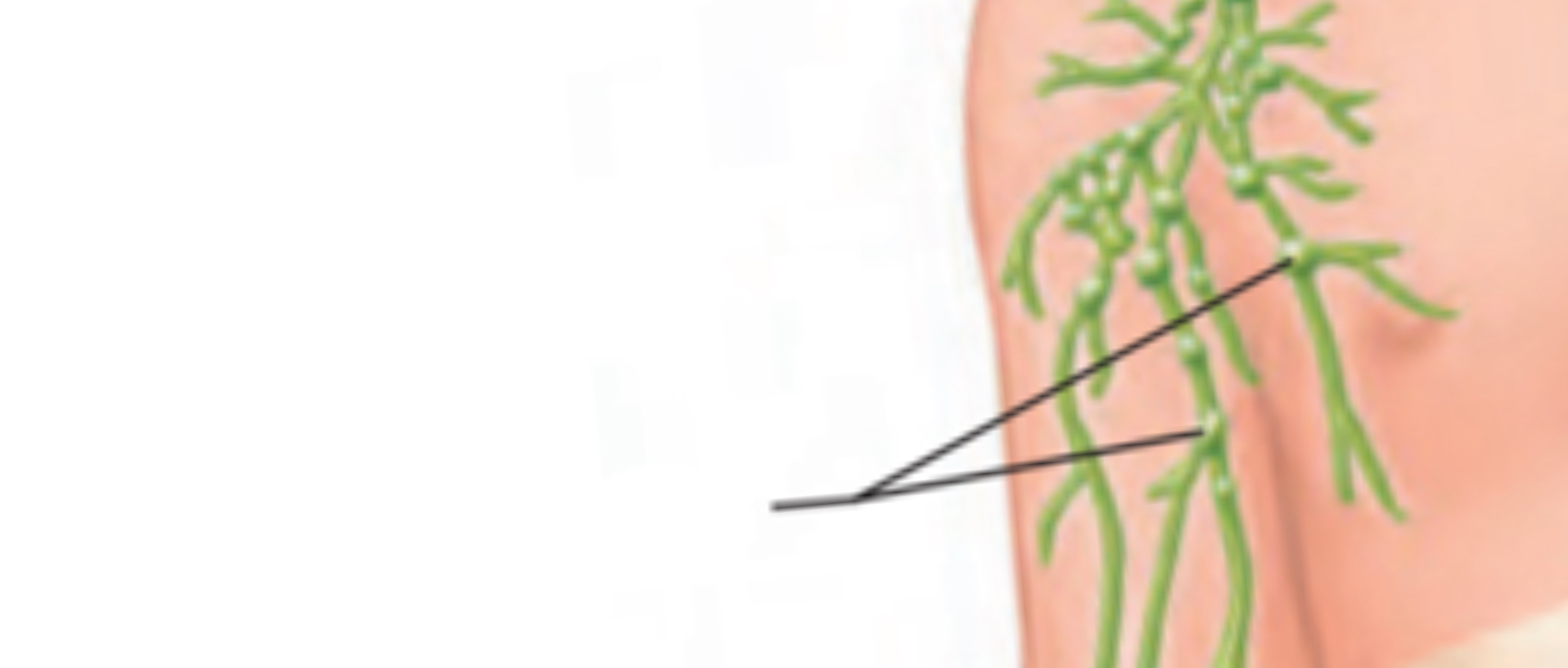
Lymphatic trunks
Drain lymph from vessels
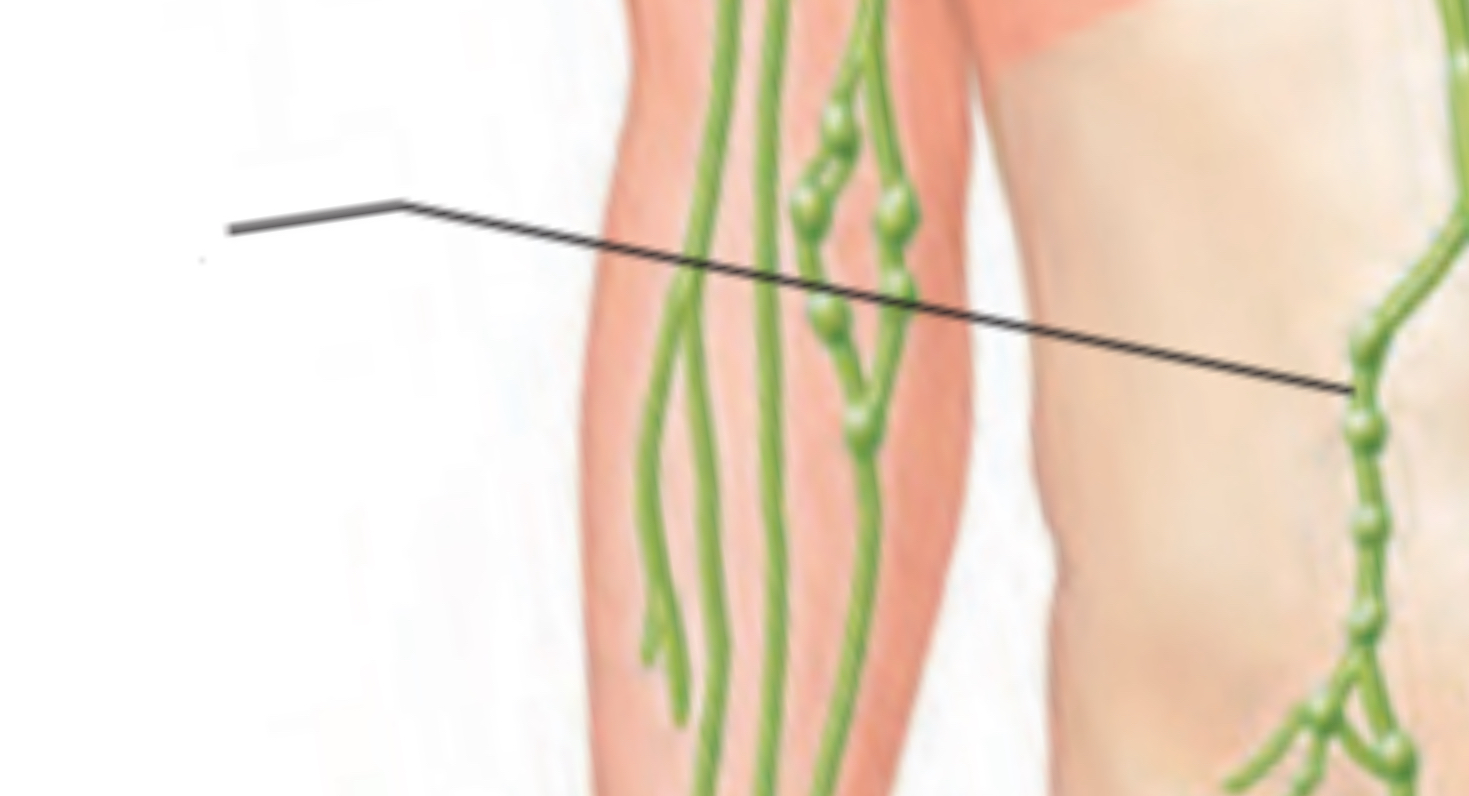
Thoracic duct
Wider and longer collecting duct → receives lymph from:
Lower limbs
Abdominal regions
Left upper limb
Left side of thorax, head & / neck
Empties into left subdavian vein
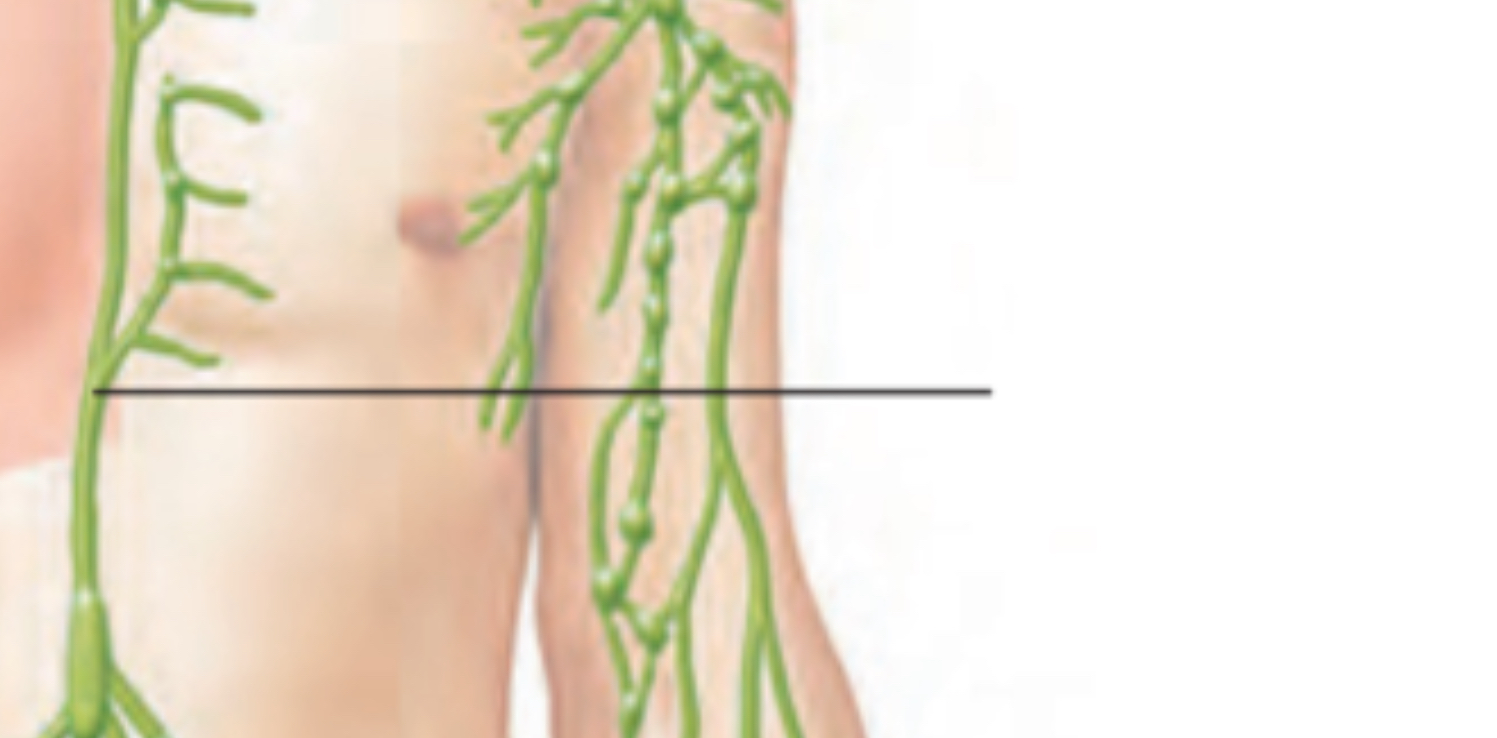
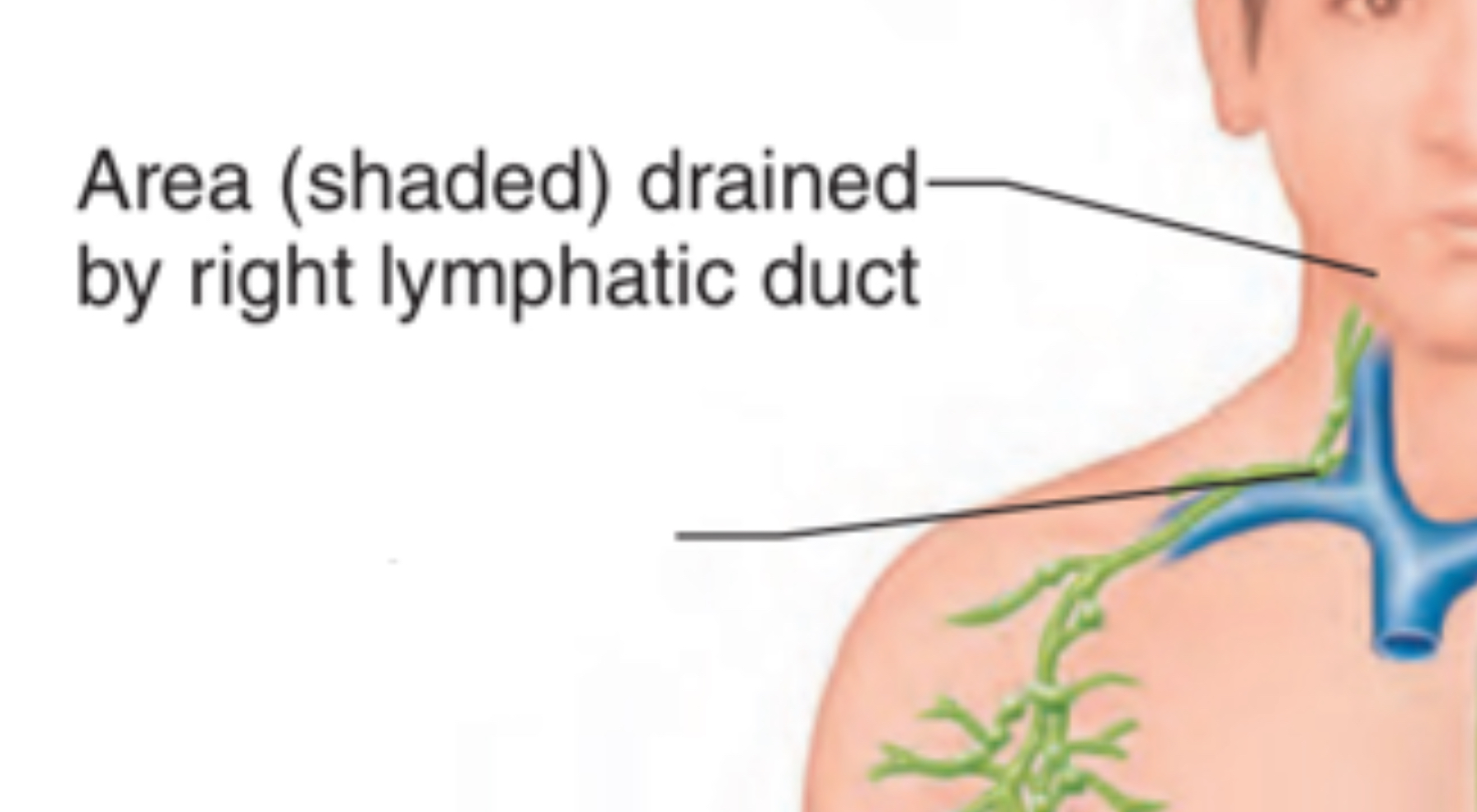
Right lymphatic duct
Receives lymph from: the right side of the head/neck + right upper limb + right thorax
Complies into right subclavian vein
Tissue Fluid Formation
tissue fluid originates from blood plasma → composed of water and dissolved substances that leave blood capillaries by filtration
plasma colloid osmotic pressure
osmotic effect of plasma proteins → helps draw fluid back into the capillaries by osmosis
lymph formation
filtration from plasma proteins exceeds reabsorption → net formation of tissue fluid
increases tissue fluid hydrostatic pressure → moves tissue fluid into lymphatic capillaries
lymph function
returns small proteins that the blood capillaries filtered to the BLOODSTREAM
transports foreign particles to lymph nodes
muscular activity
largely influnces the movement of lymph through the lymphatic vessels
because lymph is usually under low hydrostatic pressure → may not flow easily through lymphatic vessels
contraction of smooth muscles in the walls of lymphatic trunks
contraction of skeletal muscles
contraction of skeletal muscles
compresses lymphatic vessels directly, moves lymph inside vessels
valves in these vessels prevent backflow
contraction of smooth muscle
in the walls of larger lymphatic trunks → contracts rhythmically and compresses the lymph inside → forcing the fluid onward
breathing
creates a relatively low pressure in the thoracic cavity during inhalation
contracting diaphragm increases the pressure in the abdominal cavity
lymph is squeezed out of the abdominal vessels and forced into thoracic vessels, and valves prevent backflow
Edema
When tissue fluid accumulates within interstitial spaces
swelling