Atomic spectroscopy and the hydrogen atom
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
atomic emissions/ rydberg formula/ ionisation energies/ selection rules
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
1
New cards
Atomic emission
* when atoms heat they glow
* dispersing this light through a prism produces an emission spectrum
* each atom emits light at characteristic and well defined wavelengths
* dispersing this light through a prism produces an emission spectrum
* each atom emits light at characteristic and well defined wavelengths
2
New cards
in an atomic emission spectrum, classical mechanics predicts that all wavelengths of light (white light) should be _____
emitted
3
New cards
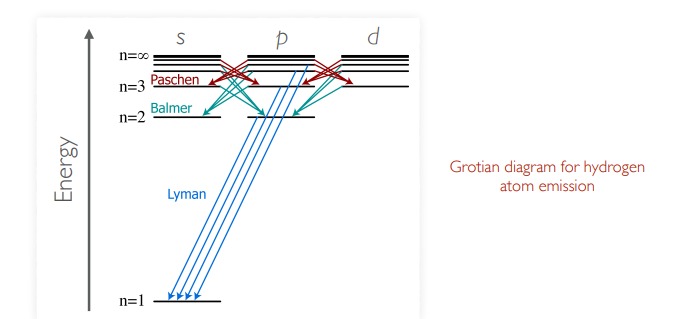
Hydrogen atom emission
* hydrogen, the simplest atom, has the simplest spectrum
* emission spectrum of atomic H consists of several series of sharp lines.
* lines of each series get closer together at high energy - the series limit
* emission spectrum of atomic H consists of several series of sharp lines.
* lines of each series get closer together at high energy - the series limit
4
New cards
The Rydberg formula
* an empirical formula able to accurately predict the wavenumber value of all H-atom lines

5
New cards
Lymann series
n1 = 1
thus n2 = 2,3,4
UV light
thus n2 = 2,3,4
UV light
6
New cards
Balmer series
n1 = 2
n2 - 3,4,5…
visible light
n2 - 3,4,5…
visible light
7
New cards
Paschen series
n1 = 3
n2 = 4,5,6…
IR spectroscopy
n2 = 4,5,6…
IR spectroscopy
8
New cards
Why are all Rydberg formula for hydrogen atom care so much about integers?
* shows atoms can only have certain discrete energies - energy is quantised
9
New cards
By absorbing or emitting light, atoms can ‘hop’ between energy levels ….
Transitions have to terminate on another energy level
10
New cards
What is the link between energy levels and spectra?
because energy levels of atoms are quantised, EM radiation can only be absorbed or emitted at certain discrete energies
11
New cards
What does the spectra tell us?
spacing between energy levels
12
New cards
What does the spectra not tell us?
the absolute energies of energy levels
13
New cards
Energy levels and spectroscopy
* atoms have many energy levels, giving rise to numerous possible transitions
* the energies of these transitions contribute to the spectrum of the atom
* the spectrum of each atom is unique (an atomic ‘fingerprint’)
* the energies of these transitions contribute to the spectrum of the atom
* the spectrum of each atom is unique (an atomic ‘fingerprint’)
14
New cards
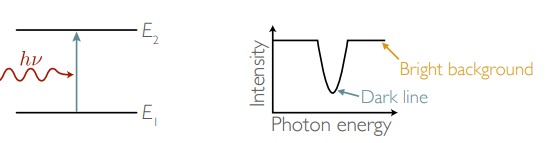
When a photon is absorbed, atoms ____ energy
gains
15
New cards
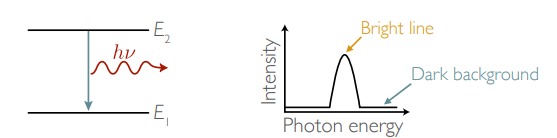
When photons are emitted atoms ____ energy
lose
16
New cards
Emission and absorption spectra give the same information about ____________
Energy level separations
17
New cards
What does the difference in energy between the initial and final energy levels determine?
The frequency of the photon absorbed or emitted
18
New cards
The Bohr frequency condition
Difference in energy = E2 - E1 = hv
19
New cards
If we can derive theoretical expressions for energy levels (quantum mechanics) then we can predict ______
the energies of lights absorbed/emitted (spectroscopy)
20
New cards
Niels Bohr - allowed energy levels of the H atom are

21
New cards
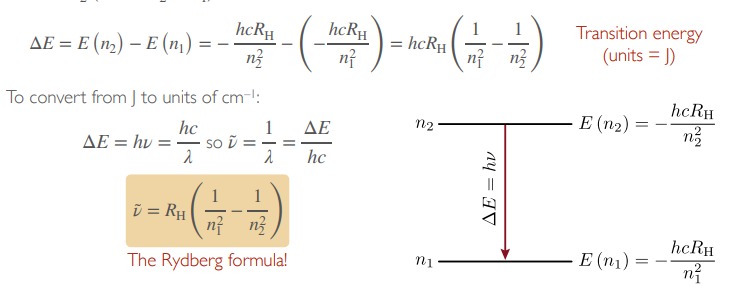
The energy spacing between a level with a principal quantum number n1 and a level with quantum number n2 is :
22
New cards
What does the Bohr’s equation demonstrate?
that the observed transitions are between different electronic energy levels of the H atom
23
New cards
What does the Bohr’s model of the H atom predicts?
that the energy levels get closer together as n → infinity
as a consequence the lines in each spectral series converge to a series limit at high energy
as a consequence the lines in each spectral series converge to a series limit at high energy
24
New cards
Lowest state is the…
ground state
25
New cards
Anything abut the ground state is the …
Excited state
26
New cards
when n = infinity…
it is ionised
27
New cards
What does the Rydberg formula predicts the __?__
wavenumber and the wavelength of any line in the H atom spectrum
28
New cards
Example: calculate the wavenumber of the first line in the Balmer series
15233 cm-1
29
New cards
What is the ionisation energy?
the minimum energy required to remove an electron completely from an atom
30
New cards
Example: calculate the ionisation energy (in joules) of ground-state H atoms
2\.179 x 10-18 J
31
New cards
Wavenumber to Joules
Wavenumber = difference in energy/ planck’s constant x speed of light
32
New cards
Orbitals is an H atom are…
electronic wavefunctions
33
New cards
orbitals in a H atom are described using…
three quantum numbers
34
New cards
What are the quantum numbers which describe the orbitals in an H atom?
* principle quantum number (n)
* orbital angular momentum (l)
* magnetic quantum number(ml)
* orbital angular momentum (l)
* magnetic quantum number(ml)
35
New cards
Principle quantum number
determines energy and size
n = 1,2,3 …..
n = 1,2,3 …..
36
New cards
Orbital angular momentum
orbital type (s,p,d,f)
l = 0,1,2 … n-1
l = 0,1,2 … n-1
37
New cards
Magnetic quantum number
orientation of orbital
ml = -l to +l
ml = -l to +l
38
New cards
for hydrogen atoms, energy is only dependent on
the principle quantum number
39
New cards
When an H atom undergoes a spectroscopic transition, the electron _____
jumps between orbitals
40
New cards
In a physical process, there are three fundamental quantities which must be conserved:
1. momentum
2. energy
3. angular momentum
41
New cards
In spectroscopy, the conservation of energy accounted for by?
the Bohr frequency condition
difference in energy = E2 - E1 = hv
difference in energy = E2 - E1 = hv
42
New cards
In addition to an energy (E = hv) photons also have an ____
intrinsic angular momentum, s=1
43
New cards
what must change in order to compensate, when a photon is observed or emitted?
the angular momentum (l) of the electron in the H atom
44
New cards
What are the forbidden transitions:
1. an electron in a d-orbital (l=2) cannot make a transition to an s-orbital (l=0) - *change in two units of momentum*
2. an electron in as s- orbital cannot make a transition to another s-orbital - *no change in the angular momentum*
45
New cards
The allowed change in angular momentum
if change in l = +- 1, then the transition is allowed
46
New cards
What is a selection rule?
a statement about which spectroscopic transitions are allowed
47
New cards
What are the selection rules for hydrogen (and other 1-electron atoms) ?
/\\n = any value
/\\l = +- 1 (laporte selectrion rule)
/\\ml = 0, +- 1
/\\l = +- 1 (laporte selectrion rule)
/\\ml = 0, +- 1
48
New cards
Grotrian diagrams
* energy of atomic states and the allowed spectroscopic transitions are summarised using grotrian diagrams