Muscular System Review
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
Smooth, Skeletal, Cardiac.
What are the characteristics of skeletal muscles?
Skeletal muscles are striated, voluntary, and attached to bones.
Define 'Origin' in muscle anatomy.
The origin is the fixed attachment point of a muscle.
Define 'Insertion' in muscle anatomy.
The insertion is the movable attachment point of a muscle.
What is the difference between the origin and insertion points?
The origin is stationary while the insertion moves towards the origin during contraction.
What is an Agonist muscle?
The agonist is the primary muscle responsible for movement.
What are Synergists in muscle function?
Synergists are muscles that assist the agonist in performing a movement.
What are Antagonists in muscle function?
Antagonists are muscles that oppose the action of the agonist.
What is a Fixator muscle?
A fixator stabilizes the origin of the agonist muscle.
Identify the agonist, synergists, antagonists, and fixator in a bicep curl.
Agonist: Biceps brachii; Synergists: Brachialis, Brachioradialis; Antagonist: Triceps brachii; Fixator: Muscles of the shoulder.
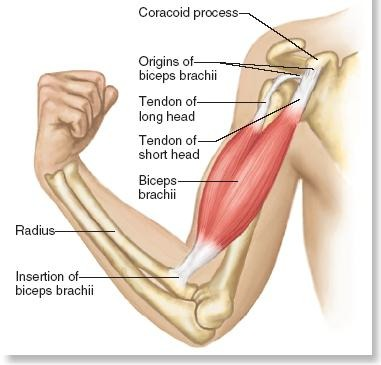
What are the two types of muscle contractions?
Isotonic and Isometric.
What is an Isotonic contraction?
An isotonic contraction involves muscle shortening and movement, such as lifting a weight.
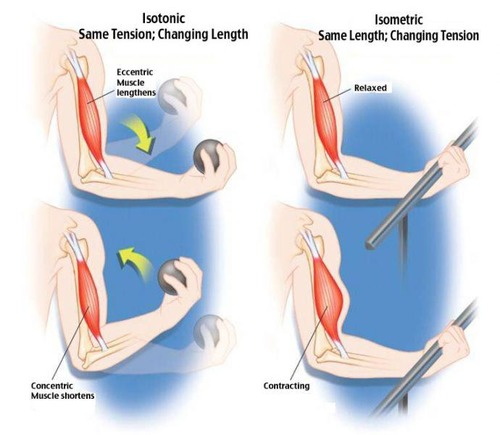
What is an Isometric contraction?
An isometric contraction involves muscle tension without movement, such as holding a weight steady.
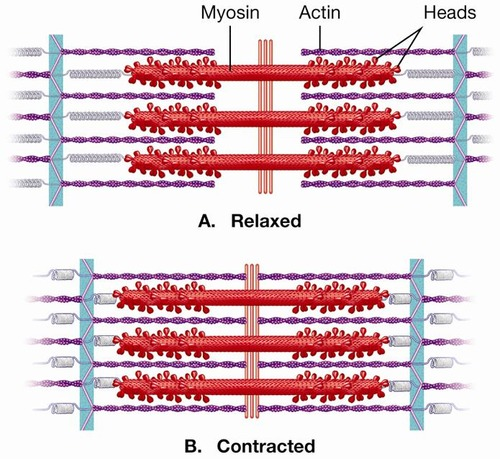
What is a sarcomere?
A sarcomere is the basic contractile unit of a muscle fiber.
What is the largest muscle in the human body?
The gluteus maximus.
What is the longest muscle in the human body?
The sartorius.
What is the smallest muscle in the human body?
The stapedius.
How many skeletal muscles are in the human body?
About 600 skeletal muscles.
How many muscles are needed to smile?
Approximately 17 muscles.
How many muscles are needed to frown?
Approximately 43 muscles.
What percentage of body weight do skeletal muscles make up?
Skeletal muscles make up about 40% of body weight.
What percentage of body heat comes from muscle contractions?
About 85% of body heat comes from muscle contractions.
Which muscles make up the hamstrings?
Biceps femoris, Semitendinosus, Semimembranosus.
Which muscles make up the quadriceps?
Rectus femoris, Vastus lateralis, Vastus medialis, Vastus intermedius.
Which muscles make up the groin?
Adductor longus, Adductor brevis, Adductor magnus.
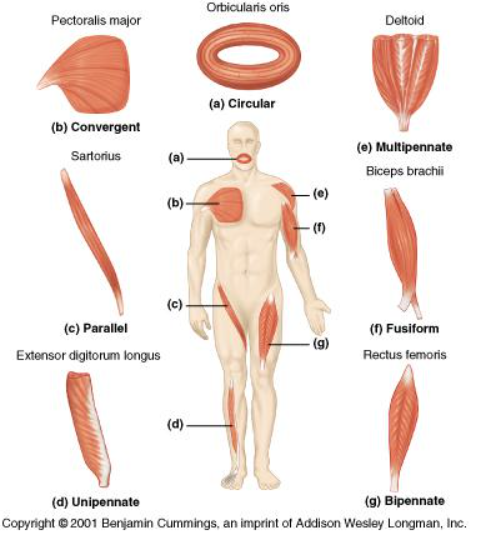
Parallel Fiber arrangements
Fusiform, bundled, triangular
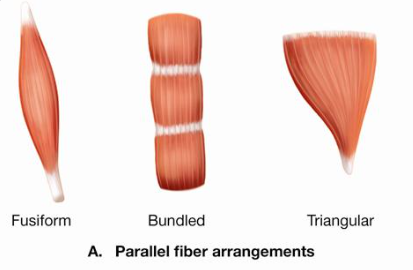
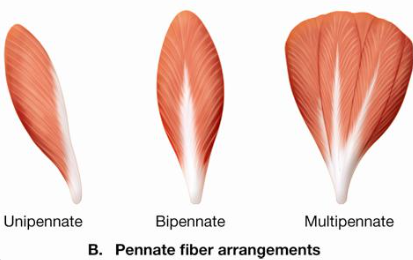
Pennate fiber arrangements
Label parts of a sarcomere in order
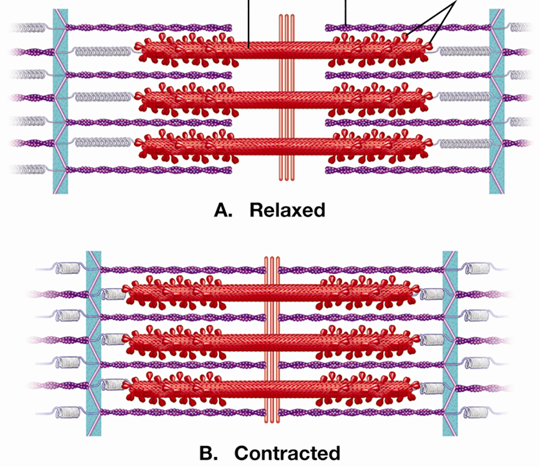
Myosin, actin, heads
Location of fusiform
Biceps brachii
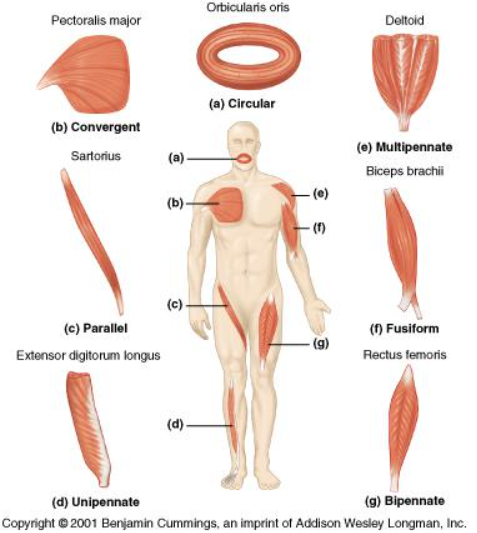
location of unipennate
Extensor digitorum longus
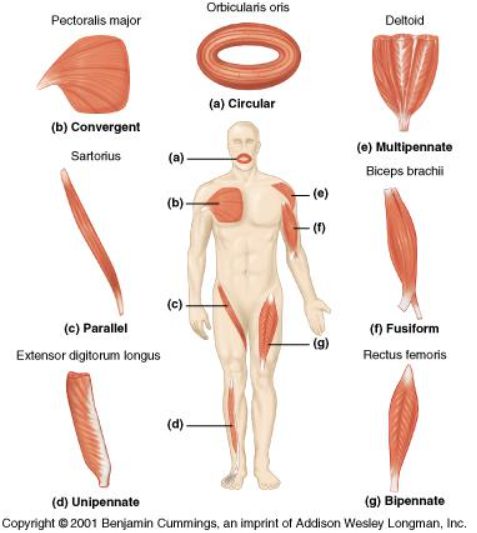
location of bipennate
rectus femoris
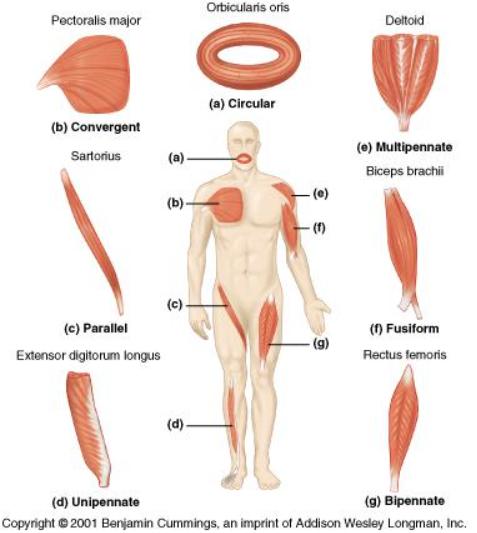
location of multipennate
deltoid muscle
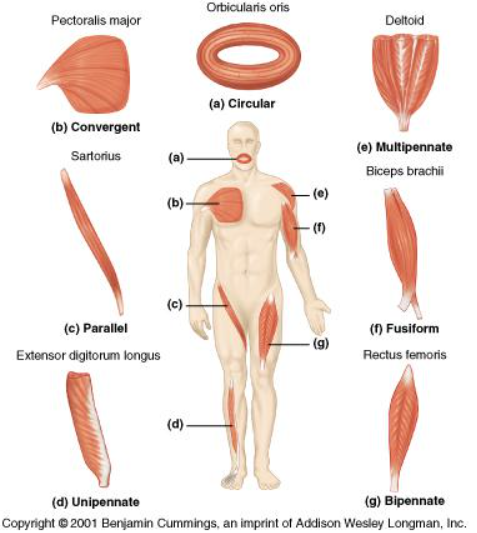
location of circular
orbicularis oris
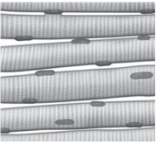
What muscle tissue is this?
Cardiac muscle
What muscle tissue is this?
Skeletal muscle
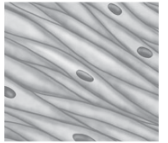
What muscle tissue is this?
Smooth muscle
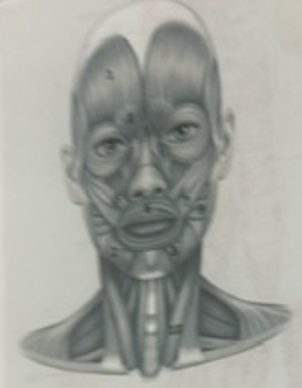
What muscle is 1?
Frontalis
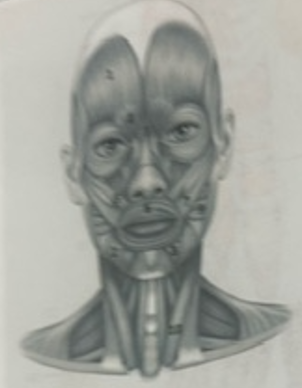
What muscle is 2?
Depressor anguli oris
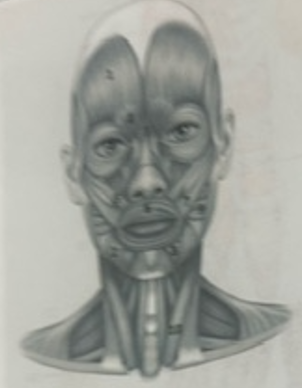
What muscle is 3?
Depressor labili inferioris
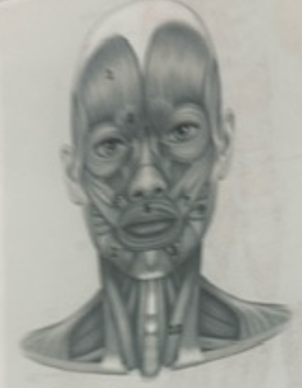
What muscle is 4?
Corrugator supercili
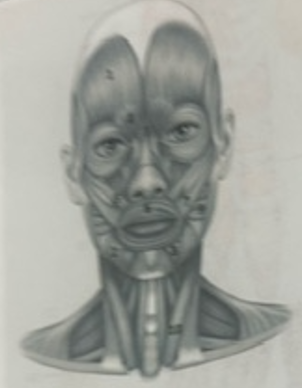
What muscle is 5?
Orbicularis oris

What muscle is 6?
Zygomaticus minor
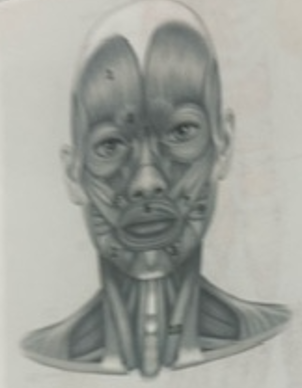
What muscle is 7?
Zygomaticus major
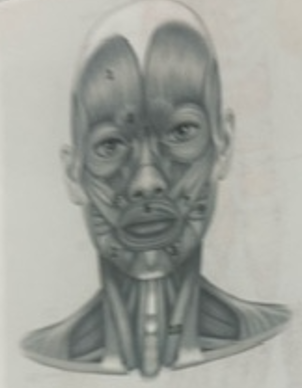
What muscle is 9?
Buccinator
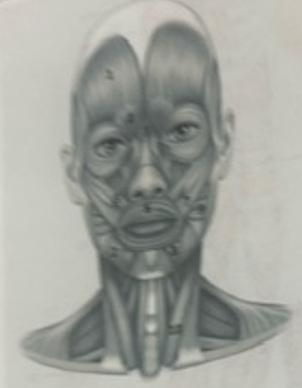
What muscle is 10?
Sternocleidmastoid
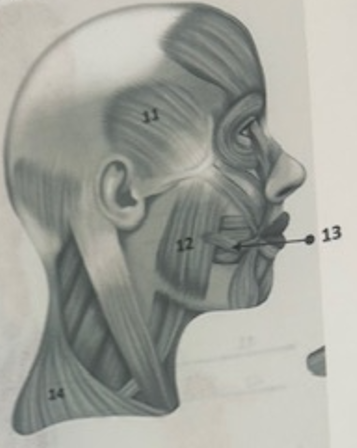
What muscle is 11?
Temporalis
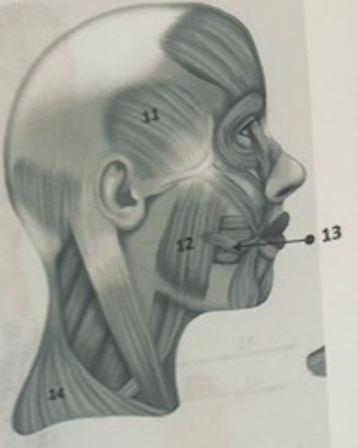
What muscle is 12?
Masseter
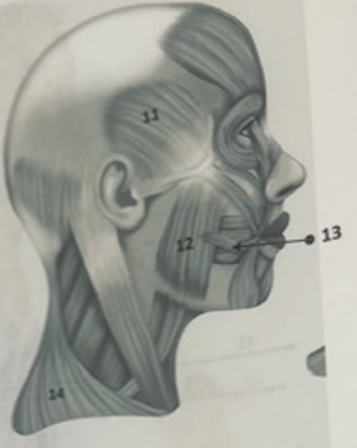
What muscle is 13?
Risorius
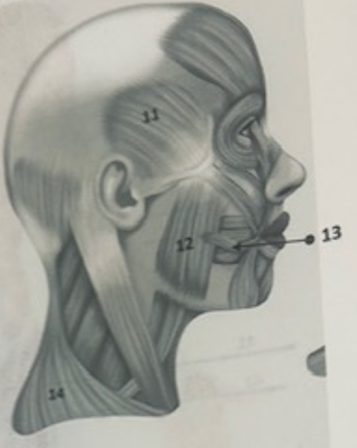
What muscle is 14?
Trapezius
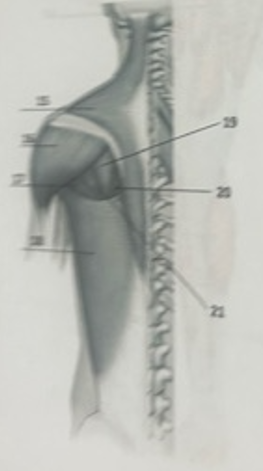
What muscle is 15?
TrapeziusW
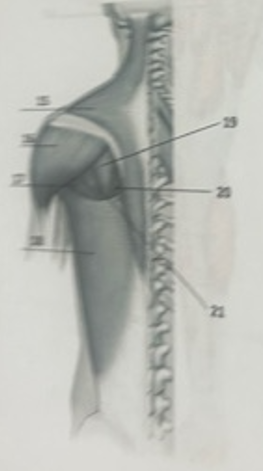
What muscle is 16?
DeltoidWhat
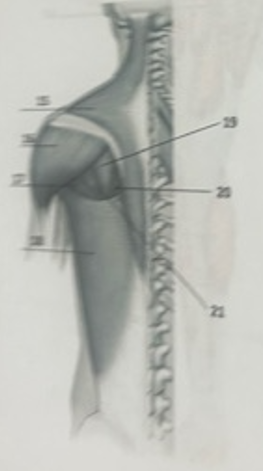
What muscle is 17?
Teres majorW
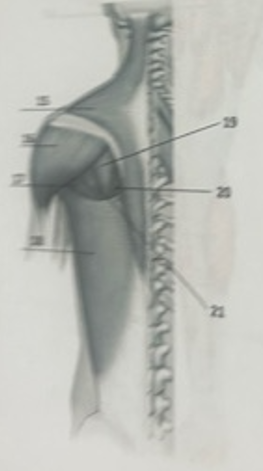
What muscle is 18?
Latissimus dorsiW
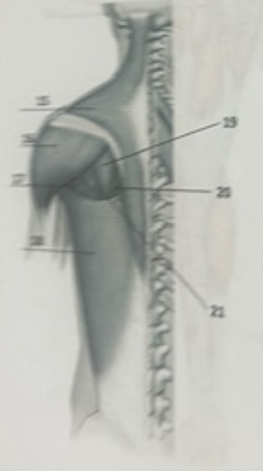
What muscle is 19?
Infraspinatus
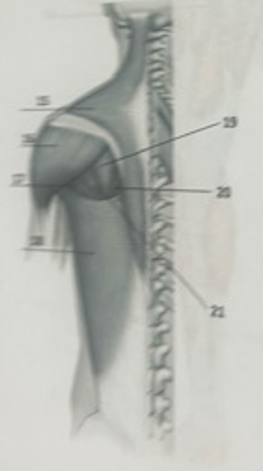
What muscle is 20?
Rhomboid
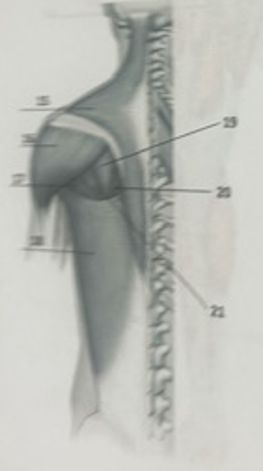
What muscle is 21?
Teres minor
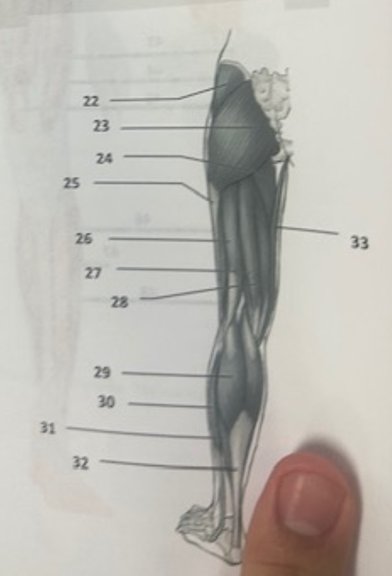
What muscle is 22?
Gluteus medius
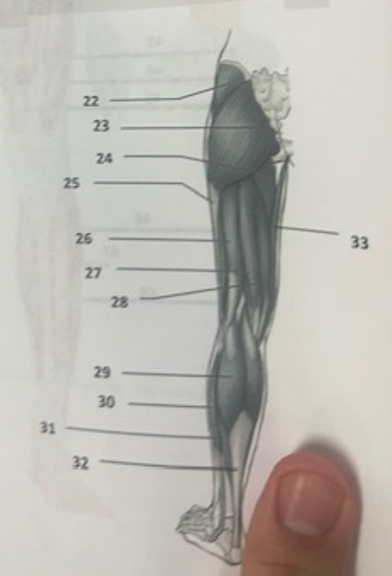
What muscle is 23?
Gluteus maximus
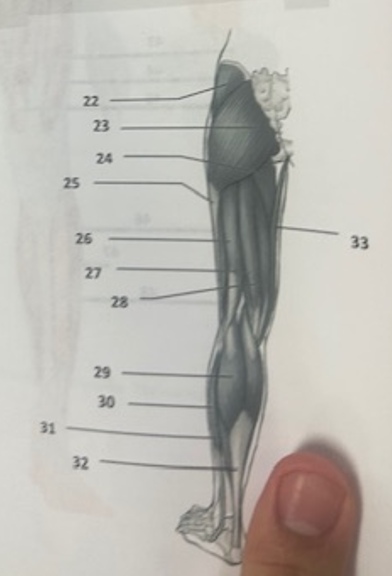
What muscle is 24?
Adductor magnus
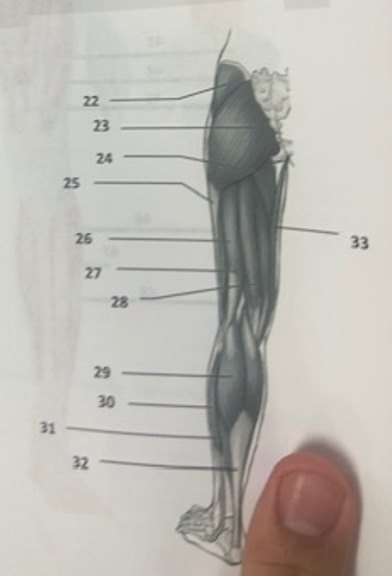
What muscle is 25?
Illiotibal band
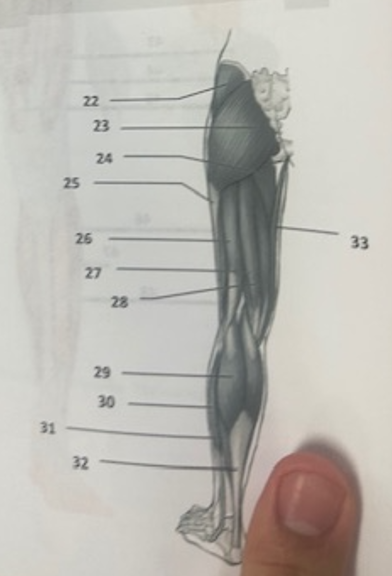
What muscle is 26?
Biceps femoris
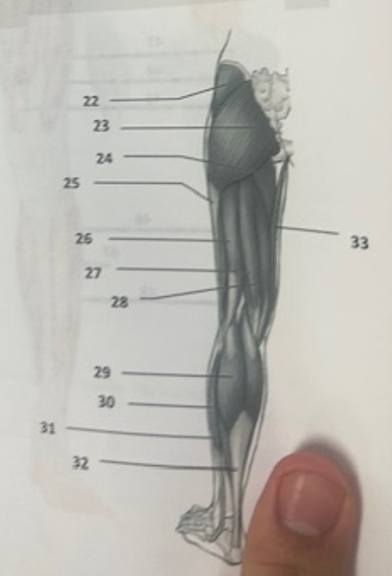
What muscle is 27?
Semitendinosus
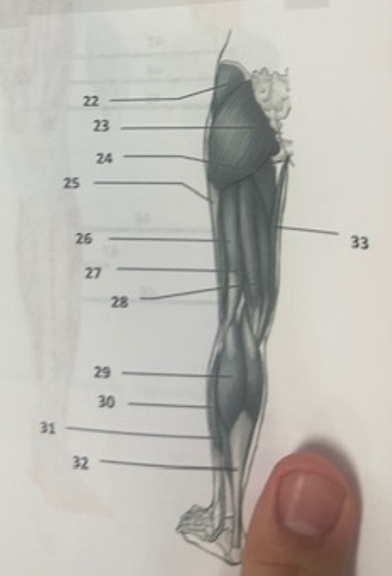
What muscle is 28?
Semimembranosus
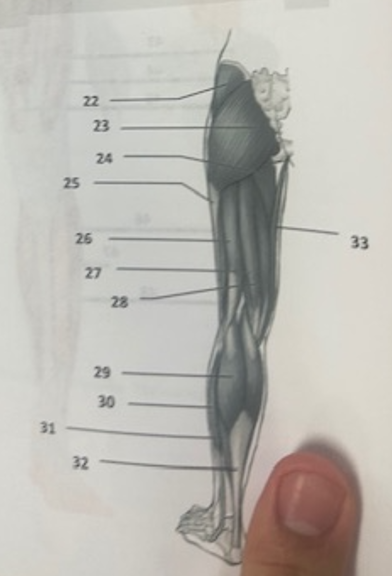
What muscle is 29?
Gastrocnemius
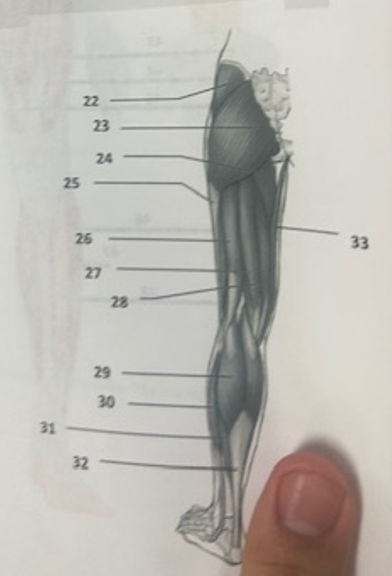
What muscle is 30?
Peroneus longusWh
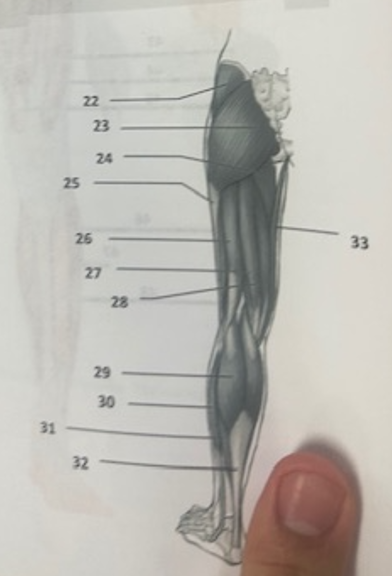
What muscle is 31?
Soleus
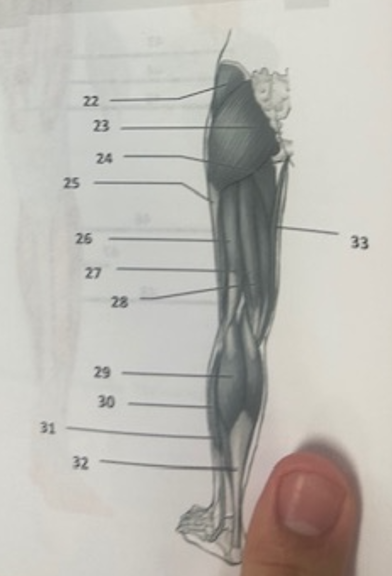
What muscle is 32?
Achilles tendon
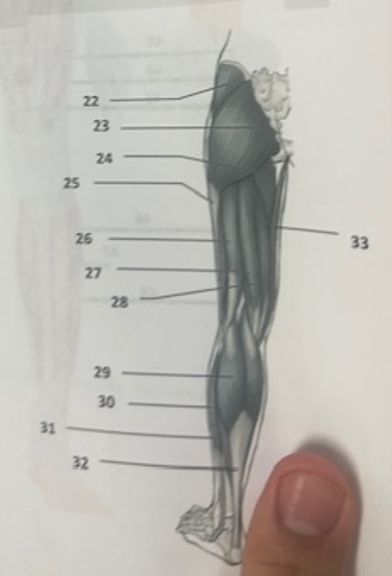
What muscle is 33?
Gracilis
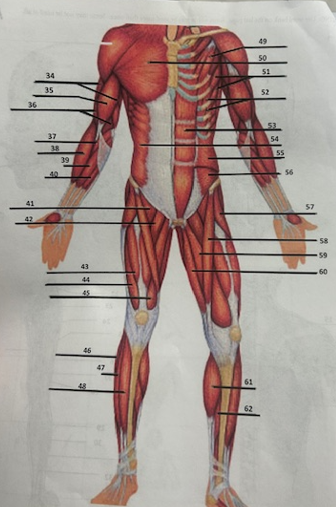
What muscle is 34?
Triceps brachii
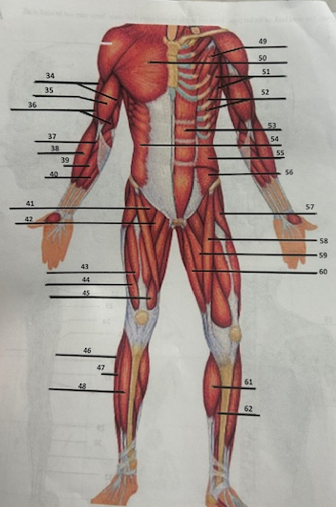
What muscle is 35?
Biceps brachii
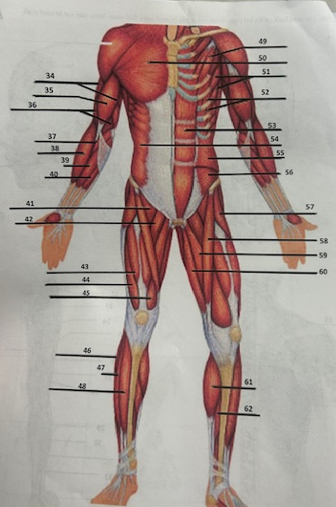
What muscle is 36?
Brachialis
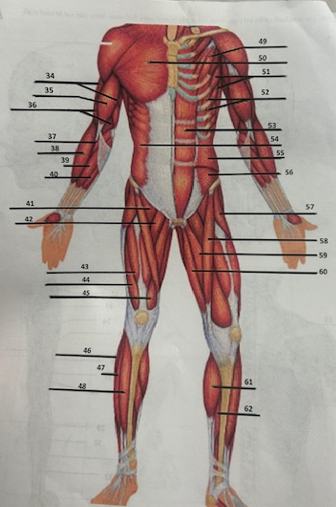
What muscle is 37?
Pronator teres
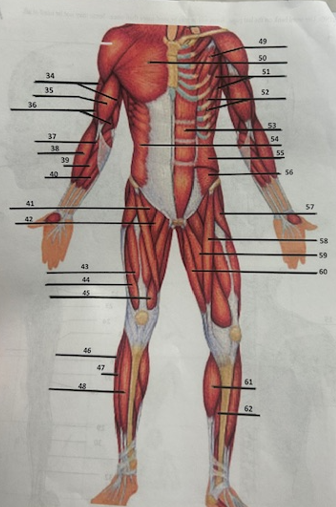
What muscle is 38?
Brachioradialis
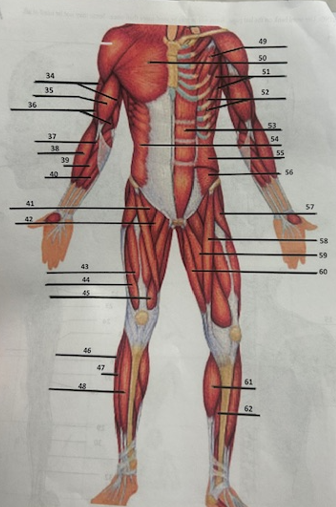
What muscle is 39?
Flexor
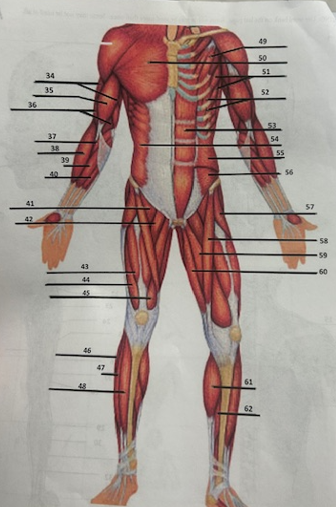
What muscle is 40?
Palmaris longus
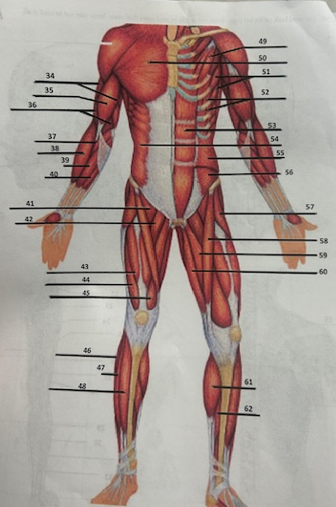
What muscle is 41?
Pectineus
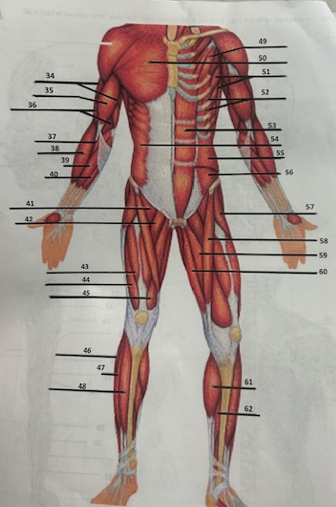
What muscle is 42?
Adductor longusW
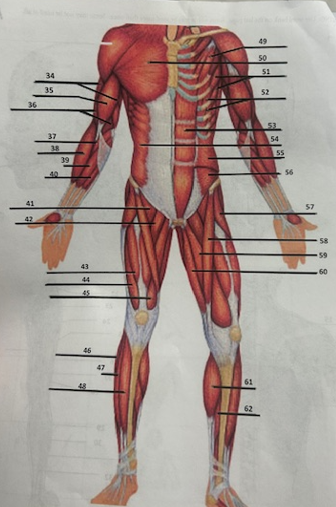
What muscle is 43?
Rectus femoris
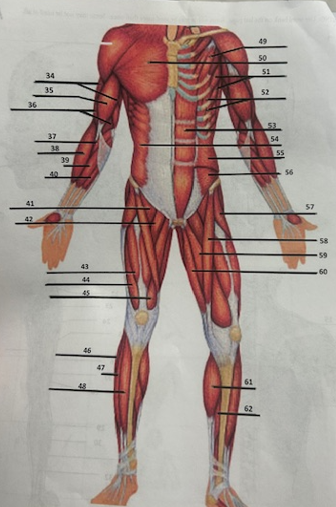
What muscle is 44?
Vastus lateralis
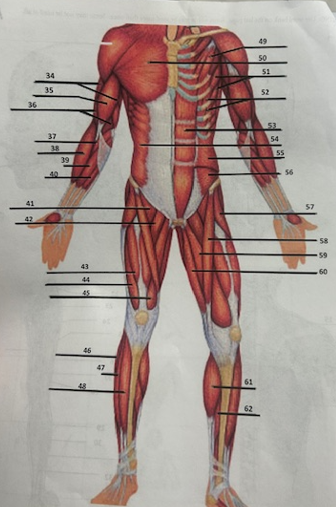
What muscle is 45?
Vastus medialis
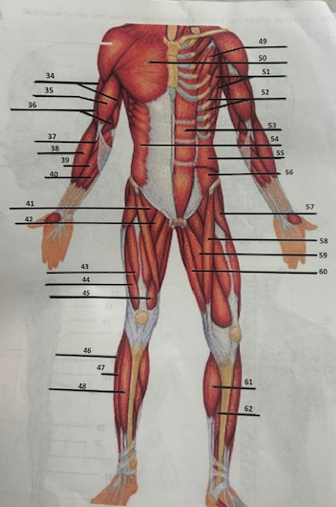
What muscle is 46?
Peroneus longus
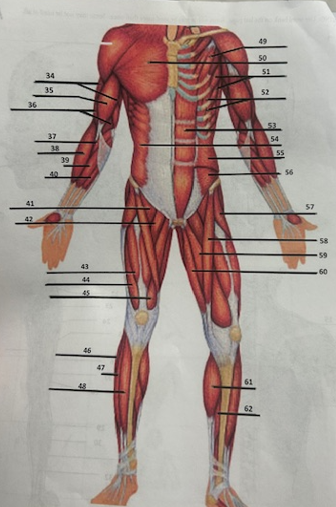
What muscle is 47?
Fibularis longus
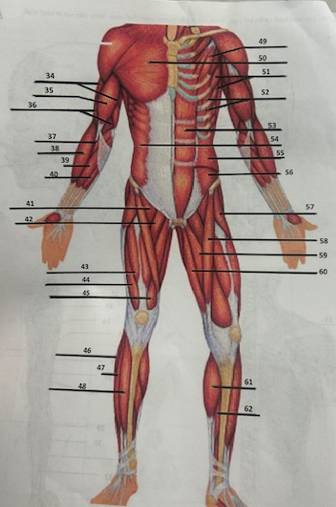
What muscle is 48?
Tibialis anterior
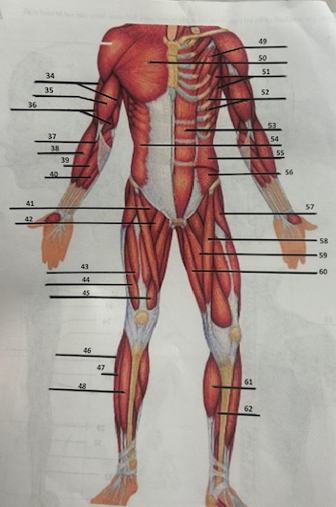
What muscle is 49?
Pectoralis minor
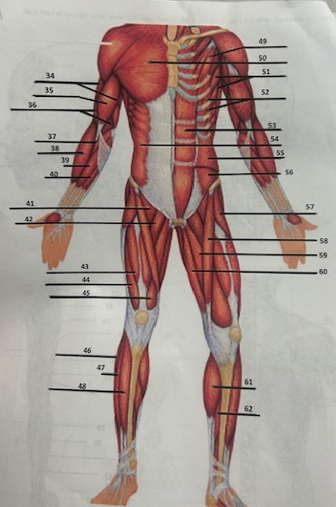
What muscle is 50?
Pectoralis major
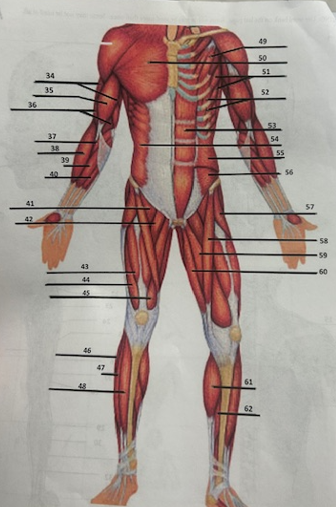
What muscle is 51?
Serratus anterior
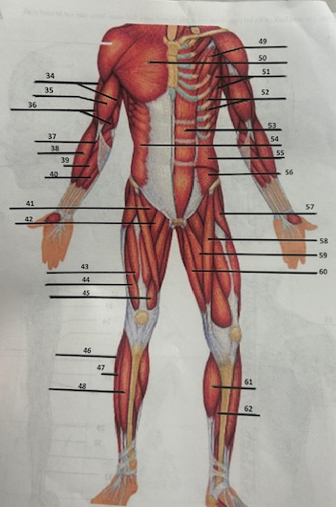
What muscle is 52?
Intercostals
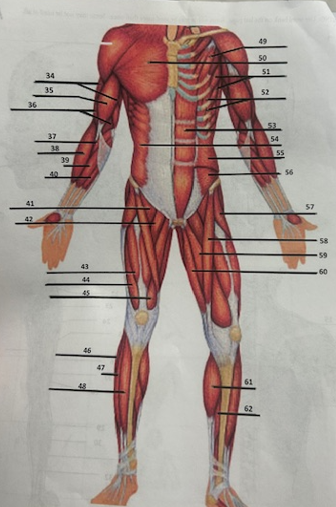
What muscle is 53?
Rectus abdominis
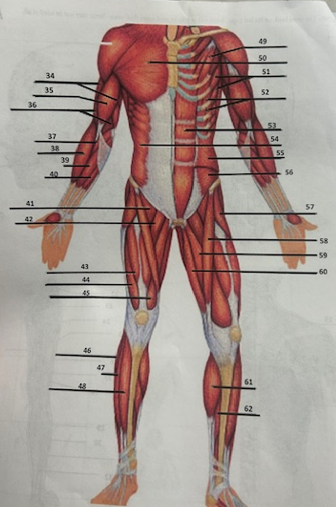
What muscle is 54?
External oblique
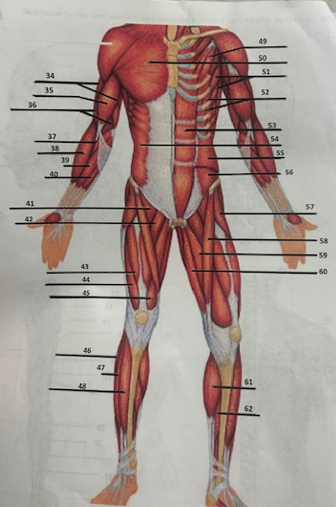
What muscle is 55?
Internal oblique
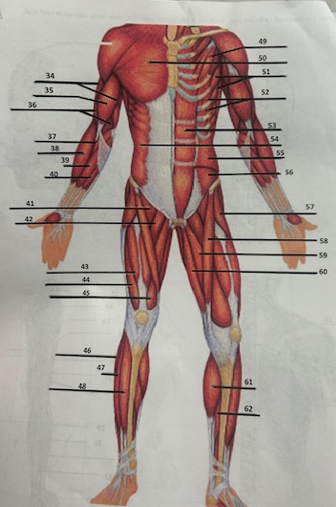
What muscle is 56?
Transverse oblique
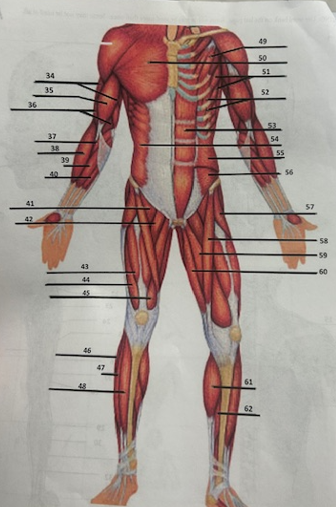
What muscle is 57?
Tensor fasciae latae
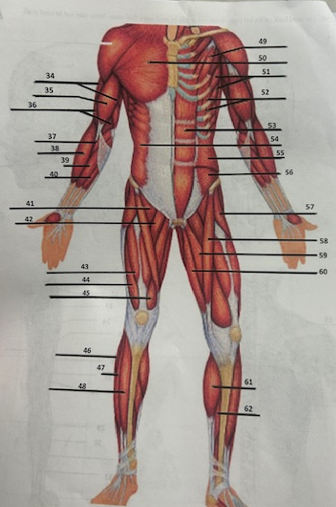
What muscle is 58?
Sartorius
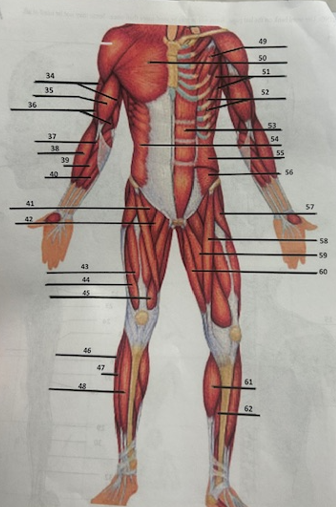
What muscle is 59?
adductor brevis
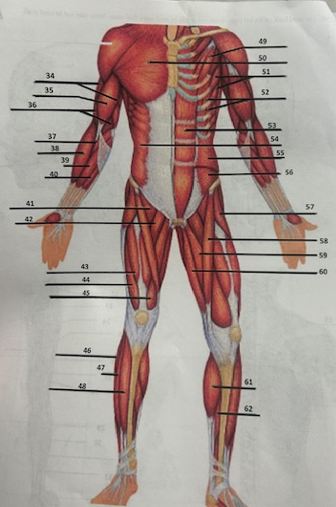
What muscle is 60?
Adductor magnus
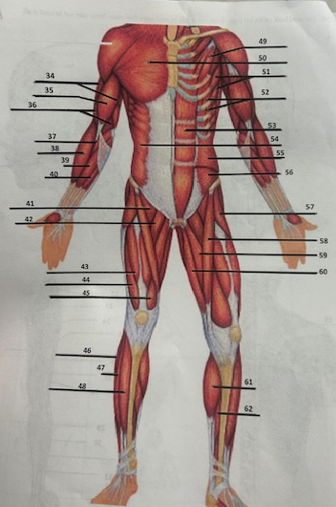
What muscle is 61?
Gastrocnemius
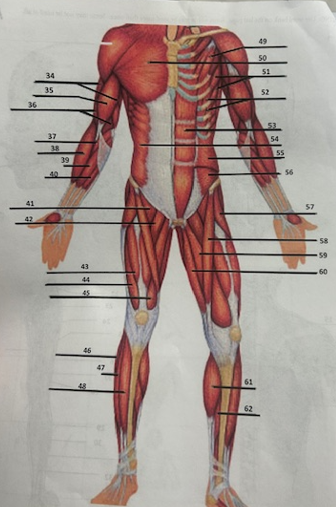
What muscle is 62?
Soleus