Fin 3461 exam 2 workbook problems
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
What are the two main sources of equity return?
Price change (capital gains) + dividends.
What is the formula for total return?
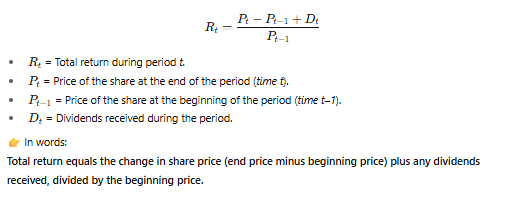
What is the third source of return for foreign shares/ADRs?
Foreign exchange gains or losses.
Why do growth-stage companies rarely pay dividends?
They reinvest earnings to finance growth.
Why do mature companies often pay dividends?
Fewer growth opportunities, so excess cash is returned to investors.
What is the impact of reinvested dividends long-term?
Significantly higher compounded returns compared to price appreciation alone.
How is equity risk defined?
Uncertainty of expected total return (price + dividends).
What metric is most often used to measure risk?
Standard deviation of returns.
What are two ways to estimate expected return and risk?
Historical averages OR probability-based future scenarios.
Why are preference shares less risky than common shares?
Fixed dividends, priority in dividends and liquidation, more predictable cash flows.
Why are common shares riskier than preference shares?
Dividends are uncertain, returns depend on price appreciation, last in liquidation.
Which typically has higher expected returns: common or preferred?
Common shares.
Putable shares — more or less risky? Why?
Less risky (investor can sell back at a preset price); lower dividends.
Callable shares — more or less risky? Why?
More risky (issuer can redeem, capping upside); higher dividends.
Cumulative preference shares — more or less risky? Why?
Less risky (unpaid dividends accumulate until paid).
Non-cumulative preference shares — more or less risky? Why?
More risky (missed dividends are lost).
Why do companies issue equity securities?
To raise capital, increase liquidity, fund expansion, R&D, acquisitions, and sometimes to meet regulatory or debt requirements.
What additional uses do companies have for equity besides raising capital?
Equity can be used as a “currency” for acquisitions and to provide stock option-based incentives to employees.
What is management’s ultimate goal when issuing equity?
To increase the book value of equity and maximize the market value of equity.
How is the book value of equity defined?
Total assets minus total liabilities; increases when net income is retained.
What does book value reflect?
Historical management decisions and accounting choices
How can management directly affect book value?
By increasing net income, retaining earnings, or issuing/buying back shares.
How is market value of equity calculated?
Market price per share × number of shares outstanding.
What does market value of equity reflect?
Investor expectations about the company’s future cash flows (amount, timing, and risk).
Why do book value and market value usually differ?
Book value is backward-looking (historical), while market value reflects future expectations.
What does the price-to-book ratio indicate?
Investor expectations about future growth and profitability; higher ratios signal stronger expected opportunities.
What is intrinsic value?
The present value of future cash flows that can be taken out of the business.
What does return on equity (ROE) measure?
How effectively management uses shareholders’ equity to generate profits.
How is ROE calculated?
Net income available to common shareholders ÷ average (or beginning) book value of equity.
What are two limitations of using ROE?
It can be distorted by accounting methods or by changes in leverage.
What is the cost of equity?
The minimum return a company must offer to attract and retain equity investors.
How is the cost of equity different from cost of debt?
Debt has a contractual interest rate, while equity’s cost is uncertain and estimated.
What models are commonly used to estimate cost of equity?
Dividend Discount Model (DDM) and Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM).
What is an investor’s required rate of return on equity?
The minimum expected return based on future cash flows, which are uncertain and vary across investors.
How do cost of equity and required return relate to each other?
Cost of equity is the company’s perspective; required return is the investor’s perspective.
How do cost of equity and ROE differ?
Cost of equity is the return the company must provide to raise capital, while ROE is the actual accounting return generated for shareholders.
How do forecasting approaches vary by analyst type?
External analysts focus on quarterly forecasts for revenue and EPS accuracy, while private company investors can build detailed multi-year or multi-decade forecasts using more internal information.
How does the business model affect forecasting?
Forecast models differ by industry (e.g., banks vs. oil & gas) because each has unique financial dynamics and key metrics.
What are the four common forecast objects?
Drivers of financial statement lines (e.g., net sales = # of stores × sales per store).
Individual financial statement lines (e.g., amortization, other non-current assets).
Summary measures (e.g., free cash flow, EPS, total assets).
Ad hoc objects (e.g., legal losses, regulatory actions, natural disasters).
Why is forecasting drivers often preferred?
Forecasting drivers improves explanatory value and accuracy because line items can have multiple underlying factors.
When might an analyst forecast individual line items directly?
For less material items, lines without clear drivers, or when management estimates are available.
What is the advantage of forecasting summary measures?
Efficiency—requires fewer inputs.
What is the disadvantage?
Less transparency and harder to audit forecasts.
Which data should analysts focus on?
Objects that are regularly disclosed or can be calculated from regularly disclosed data (e.g., net sales, store count).
Why should overly complex models be avoided?
They require more forecasts, take longer to update, and often do not improve accuracy.
What is the historical results approach?
Uses past observed values as forecasts.
Pros: Simple, plausible.
Cons: May not reflect future changes; less suitable for cyclical or restructuring companies.
What is the historical base rates and convergence approach?
Assumes company metrics will converge to long-term industry or peer averages.
Pros: Good for established industries and smaller companies maturing toward peers.
Cons: Less suitable for unique, cyclical, or dominant companies.
What is the management guidance approach?
Uses targets or ranges provided by company management (e.g., sales growth, capex, free cash flow).
Pros: Forward-looking; management has detailed company knowledge.
Cons: Less reliable in high-uncertainty periods or for macro-sensitive items.
What are analyst discretionary forecasts?
Forecasts based on judgment, surveys, scenarios, or unique events (e.g., new product adoption).
Use case: Cyclical industries, companies without comparables, no guidance, or undergoing structural changes.
What factors determine the forecast horizon?
Investment strategy (long-term: 3–5 years, short-term: 1–2 quarters).
Industry cyclicality (forecast should cover full cycle).
Company-specific events (e.g., acquisitions, restructurings).
Employer-specified parameters.
A company discloses financial results by geographic area, and the economic exposure of each geographic area is similar. Explain why an analyst should or should not develop forecasts by geographic area and aggregate the results.
An analyst should not develop forecasts by geographic area, because each area has similar economic exposure. Developing forecasts for each geographic area would require more time to develop and update, without a significant improvement in accuracy over an aggregate forecast.
Which approach is most appropriate for an analyst to use to forecast revenue for an industry leader in a mature, non-cyclical industry?
A. Historical results
B. Analyst’s discretionary forecast
C. Historical base rates and convergence
Historical results
Which of the following statements about management guidance is most accurate?
A. The availability of guidance increases during periods of high uncertainty.
B. The midpoint of guidance best represents management’s “true” expectations.
C. Understanding the assumptions behind the guidance is critical to assessing the guidance.
C. Understanding the assumptions behind the guidance is critical to assessing the guidance.
Which of the following is an example of an ad hoc forecast object?
A. Amortization expense
B. Average sales per store
C. Pending legal proceedings
C. Pending legal proceedings
At initiation, what is the value of a forward contract?
0 (ignoring costs/credit risk).
How is the forward price of an asset (no costs/benefits) calculated?
It equals today’s spot price grown at the risk-free rate over the life of the contract.
What is the value of a long forward contract at maturity?
The value equals the final spot price minus the forward price that was agreed at the start.
What is the value of a forward contract during its life?
It equals the current spot price minus the present value of the forward price.
How do costs and benefits affect the forward price?
Costs (like storage or carrying costs) increase the forward price.
Benefits (like dividends or income from the asset) decrease the forward price.
What is the value of a forward contract with costs or benefits during its life?
It equals the current spot price (adjusted for benefits and costs) minus the present value of the forward price.
What is the payoff for long and short positions at expiration?
Long position: Final spot price minus the forward price.
Short position: Forward price minus the final spot price.
In foreign exchange forwards, how is the forward rate determined?
It is based on the current spot exchange rate adjusted for the difference in interest rates between the two currencies.
In foreign exchange forwards, which currency trades at a forward premium?
The currency with the lower interest rate trades at a premium.
The currency with the higher interest rate trades at a discount.
What is a zero rate?
It is the yield on a zero-coupon bond for a given maturity.
What is a discount factor?
It is the present value of one dollar received in the future, based on the zero rate for that maturity.
How are zero rates usually obtained from coupon bond prices?
By a process called bootstrapping, which solves for zero rates step by step using available bond prices.
What is a forward rate?
It is the breakeven interest rate that links two zero-coupon yields. It tells us what interest rate must hold in the future to prevent arbitrage.
What does “two-year three-year” forward rate mean?
It is a contract made today for an interest rate that will start in two years and last for three years (ending in five years).
What does “three-month six-month” forward rate mean?
It is the six-month interest rate beginning in three months from now.
Why are forward rates important?
They prevent arbitrage between rolling over short-term investments versus investing long-term, and they are used to price interest rate forwards, swaps, and futures.
How do models like CAPM and DDM help in valuing equity securities?
They estimate the required return for an investment, which is used to determine the present value of expected cash flows, helping investors assess a stock’s fair value.
Why is the cost of equity sensitive to changes in interest rates and market risk premium?
Because increases in interest rates or market risk premiums raise the required return, lowering valuation multiples like the P/E ratio and reducing stock prices.
What factors are considered when forecasting a company’s future earnings?
Analysts examine financial statements, industry trends, and overall economic conditions to project performance and estimate fair value for investment decisions.
How does an accurate forecast affect investment decisions?
It helps determine a company’s fair value, guiding investors on whether to buy, hold, or sell a stock.
What is a forward contract?
It is an agreement between two parties to buy or sell an asset at a specific price on a future date, customized to the needs of the parties.
How is the value of a forward contract determined?
By adjusting for the risk-free rate and market factors, and considering changes in the underlying asset’s price, which affects its potential use in hedging or speculation.
How does financial analysis help evaluate company performance?
By calculating key ratios like ROE and ROI, and considering risk-adjusted returns, analysts gain insights into profitability and investment quality.
How do derivatives like forwards and futures assist in risk management?
They hedge against price fluctuations and currency risks, helping companies stabilize cash flows and reduce exposure to financial uncertainty.
What happens to the cost of equity when interest rates increase, assuming other factors remain constant?
A. It decreases
B. It remains the same
C. It increases
D. It fluctuates based on market risk
Answer: C. It increases. An increase in interest rates raises the risk-free rate, which increases the cost of equity due to the increased required return.
A company has a P/E ratio of 18, expected dividend of $4, and an expected growth rate of 5%. What is the expected price of the stock based on the Dividend Discount Model?
A. $72
B. $80
C. $84
D. $90
Answer: A. $72. Price = Dividend / (Cost of equity - Growth rate) = $4 / (0.10 - 0.05) = $72
Explain why increasing leverage (debt) might increase the risk of a company.
Answer: Increasing leverage amplifies both potential returns and losses, increasing
financial risk. More debt means higher fixed interest payments, which reduces financial
flexibility and raises the likelihood of default during adverse conditions.
If the risk-free rate increases, how does it affect the expected return on equity according to the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM)?
A. It decreases
B. It increases
C. It stays the same
D. It depends on the beta
Answer: B. It increases. The CAPM formula incorporates the risk-free rate, so an increase directly increases the expected return on equity.
A company has a debt-to-equity ratio of 2:1. If its ROE is 10%, what is its Return on Assets (ROA)?
A. 5%
B. 6%
C. 8%
D. 10%
Answer: A. 5%. ROA = ROE / (1 + Debt-to-equity ratio) = 10% / 3 = 5%
A firm's beta increased from 1.2 to 1.4 due to an expansion into international markets. What would most likely happen to its required return?
A. It will decrease
B. It will remain the same
C. It will increase
D. It is impossible to determine
Answer: C. It will increase. An increase in beta indicates higher systematic risk, which raises the required return according to CAPM.
Given that the current spot price of an asset is $50 and the risk-free rate is 4%, calculate the 1-year forward price assuming no dividends.
A. $51.50
B. $52.00
C. $52.04
D. $53.00
Answer: C. $52.04. Forward price = Spot e^(Risk-free rate Time) = $50 e^(0.04 1) =$52.04
An investor has the following data for two stocks: Stock A (Beta = 1.2) and Stock B (Beta =0.8). Assuming the market risk premium is 7%, calculate the required return for Stock A using CAPM. Assume rf =0.04
A. 10.4%
B. 12.4%
C. 14.4%
D. 16.4%
Answer: B. 12.4%. Required return = Risk-free rate + Beta * Market risk premium = 4% +1.2 * 7% = 12.4%
Explain how forward contracts differ from futures contracts
Forward contracts are customizable, traded OTC, and settled at maturity,
while futures contracts are standardized, traded on exchanges, and settled daily with margin requirements.
A company has a ROE of 15%, assets of $3 million, and liabilities of $1.5 million. What is its equity?
A. $1.5 million
B. $2 million
C. $2.5 million
D. $3 million
Answer: B. $2 million. Equity = Assets - Liabilities = $3 million - $1.5 million = $2 million
Given the following data, calculate the firm's ROE: Net income = $500,000, Assets = $5 million, Liabilities = $2 million.
A. 10%
B. 12%
C. 15%
D. 18%
Answer: C. 15%. ROE = Net income / Equity = $500,000 / ($5 million - $2 million) = 15%
What is the impact on the forward price of a commodity if the convenience yield increases?
A. The forward price decreases
B. The forward price increases
C. The forward price remains the same
D. The impact cannot be determined
Answer: A. The forward price decreases. Higher convenience yield implies a greater benefitto holding the physical asset, reducing the incentive to lock in future prices through a forward contract.
In a scenario where the spot rate of EUR/USD is 1.12 and the 3-month forward rate is
1.10, what does this indicate about EUR/USD?
Answer: A. EUR is at a forward premium
B. EUR is at a forward discount
C. USD is at a forward premium
D. USD is at a forward discount
Answer: B. EUR is at a forward discount. The forward rate is lower than the spot rate, indicating EUR is expected to depreciate against USD
Which of the following is most likely to result in a short position in a forward contract?
Answer: A. Buying an asset with the expectation that its price will rise
B. Selling an asset with the expectation that its price will fall
Answer: B. Selling an asset with the expectation that its price will fall.