Week 2- Physiological Transition and Needs of the Normal Newborn
1/90
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CH 17, 18, 25 (pg 924-928 & 931 Box 25.2)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
What are the big changes the infant will experience from their intrauterine environment to their extra uterine environment?
Intrauterine is a fluid-filled, high pressure system
Extrauterine is air filled low pressure system
what is the major cardiovascular adaptation that takes place for a newborn after birth?
change from placental to pulmonary gas exchange and the switch from fetal to newborn circulation
what is the normal range for hemoglobin in a newborn?
16-18 g/dL
what is the normal range for hematocrit in a newborn?
46-68%
what is the normal range for platelets in a newborn?
150,000-350,000/ microliter
what is the normal range for red blood cells in a newborn?
4.5-7.0 (1,000,000/ microliter)
what is the normal range for white blood cells in a newborn?
10-30,000/mm3
How can nurses help babies take their first breath?
External stimuli ← usually tactile AKA vigorous rubbing
what is the role of surfactant?
surface tension reducing lipoprotein that prevents alveolar collapse
what is considered normal for a newborn respiratory assessment?
30 to 60 breaths per minute; irregular, shallow, unlabored; symmetrical chest movements
Note: apnea is defined as the absence of breathing for longer than 20 seconds (p1452).This is not normal.
What events lead to the maintenance of Respiratory Function?
Initiation of respiratory movement- Expansion of lungs, Establishment of functional residual capacity
Redistribution of cardiac output to increase pulmonary blood flow
What are the dangerous respiratory signs in an newborn?
Apnea
Tachypnea
Cyanosis
Grunting
Retractions
Nasal flaring
What are the characteristics of newborns that predispose them to heat loss? 9()
Thin skin; blood vessels close to the surface
Lack of shivering ability
limited stores of metabolic substrates (glucose, glycogen, fat)
Limited use of voluntary muscle activity
Large body surface area relative to body weight
Lack of subcutaneous fat
little ability to conserve heat by changing posture
No ability to adjust own clothing to achieve warmth
Infants cannot communicate that they are too cold or too warm
what is the normal temperature range for newborns? What is the normal route for taking a newborns temperature?
97.7-99.5F axillary
what is conduction?
transfer of heat from object to object when the two objects are in direct contact with each other
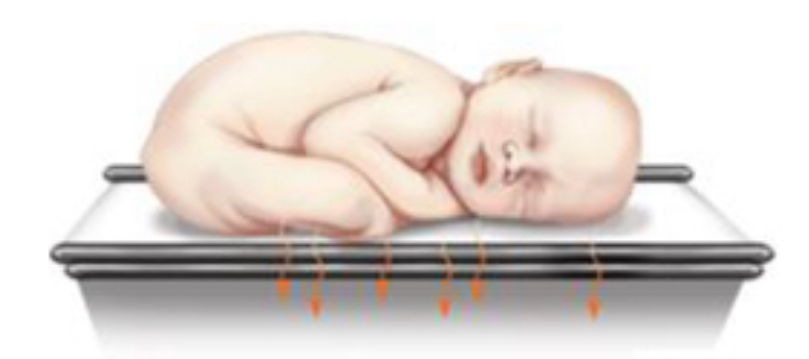
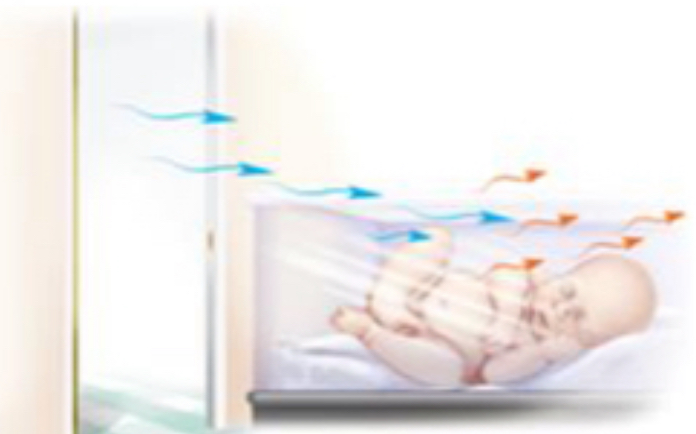
What is convection?
flow of heat from body surface to cooler surrounding air or to air circulating over a body surface

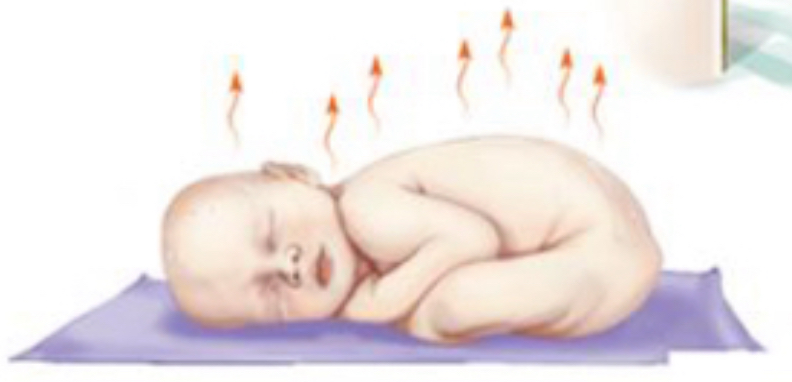
What is evaporation?
loss of heat when a liquid is converted to a vapor
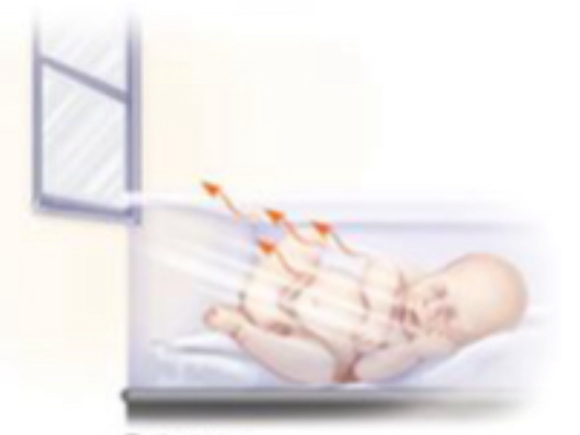
What is radiation?
loss of body heat to cooler, solid surfaces in close proximity but not in direct contact
What is the most important intervention for cold stress?
PREVENTION! Don’t let baby get cold!
How does bilirubin accumulate in pathological jaundice?
overproduction
How does bilirubin accumulate in physiological jaundice?
decreased conjugation
How does bilirubin accumulate in biliary duct issues?
impaired excretion
how much weight do infants lose in the first few days after birth?
5-10% of body weight
Why are babies susceptible to regurgitation?
stomach nervous control and cardiac sphincter control are immature which causes regurgitation and uncoordinated peristaltic activity
what is meconium?
1st stool; tar-like, sticky, black stool
what does the stool of breast-fed newborns look like?
yellow-gold, loose, stringy to pasty, sour-smelling but less odorous than other kind (almost sweet smelling)
what does the stool of formula-fed newborns look like?
yellow to yellow-green, loose, pasty, or formed, unpleasant odor
how long should it take for an infant to pass their first stool?
within the first 24 hours is ideal but can take up to 48 hours
How many voids should the baby have per day?
6-8
What is natural immunity?
physical barriers, chemical barriers, and resident nonpathologic organisms
what is acquired immunity?
development of circulating immunoglobulins; formation of activated lymphocytes
what is a good source of acquired immunity for newborns?
Breastmilk
What are the main functions of the skin? (3)
Protection (harmful agents, physical trauma, water loss)
Thermoregulation
Fat storage
what is the least developed sense when babies are first born?
vision
What patterns does neurological development take place in?
cephalocaudal and proximal-distal patterns
What occurs during the first period of reactivity?
newborn is alert, moving, may appear hungry
Good time to breast feed and golden hour for skin to skin
when does the first period of reactivity take place?
birth to 30mins to 2hrs after birth
When does the period of decreased responsiveness take place?
30-120 minutes old
what takes place during the period of decreased activity?
Sleep, decreased activity
When does the second period of reactivity take place?
2-8 hrs after birth
What occurs during the second period of reactivity?
newborn awakens and shows an interest in stimuli
Feeding #2 takes place now
what is orientation? (Newborn behavioral response)
Response to stimuli
what is habituation? (Newborn behavioral response)
Ability to process and respond to auditory and visual stimuli; ability to block out external stimuli after the newborn has become used to activity
What are the social behaviors of a newborn?
Cuddling and snuggling
What are the critical adaptations that take place in the transition from fetus to newborn?
Initiation of independent respirations
Circulatory changes- closure of fetal shunts
Thermoregulation and glucose stabilization
Establishing feeding, elimination, and physiologic homeostasis
what are the nursing priorities during the newborn transitional phase? (5)
ABC’s
Temperature regulation
Early bonding
Feeding
Prevention of complications
what are the nursing priorities in the care of a newborn? (3)
Establish airway
Provide warmth
Assess frequently
Respiratory Status
Activity- flexed? Mvmt?
Perfusion
Position/time
how do nurses provide warmth to infants?
Drying infant
Place on mom’s abdomen/chest “skin to skin”
Wrap the baby in a warm blanket
Place a cap on the baby’s head
If using a radiant warmer, no clothes on infant- decrease barriers
What are some signs that indicate a problem for the infant?
Nasal flaring
Chest retractions
Grunting on exhalation
Labored breathing
Generalized cyanosis
Flaccid body posture
Abnormal breath sounds
Abnormal respiratory rates
Abnormal heart rates- too high = initial compensation; too low = fatigue from efforts to compensate
Abnormal newborn size
What does APGAR stand for?
Appearance (color)
Pulse/HR
Grimace (reflex irritability)
Activity (muscle tone)
Respiratory effort
what is the purpose of the APGAR score? (2)
standardized, quick method to determine the newborn’s physiologic status
Does not guide resuscitation
Allows objective communication amongst providers
What is a normal newborn temperature?
97.7-99.5 degrees F
What is a normal newborn HR?
110-160 bpm
Can increase with crying
Can decrease with sleep
What is a normal newborn RR?
30-60 breaths/min
Can increase with crying
What is a normal newborn BP?
50-75 systolic
30-45 diastolic
what is a preterm or premature gestational age (in weeks)?
prior to 37 weeks gestation exactly
what is a term gestational age (in weeks)?
38-42 weeks gestation
what is a post-term or post-dates gestational age (in weeks)?
after 42 weeks gestation
what is a postmature gestational age (in weeks)?
after week 42 of gestation with signs of placental aging
Often are induced before this point
what is small for gestational age (SGA)?
less than 10th percentile for gestational age or less than 5lb 5oz
what is appropriate for gestational age (AGA)?
About 7.5lbs on average
5lbs 5oz < baby < 9lbs or 90th percentile for gestational age
what is large for gestational age (LGA)?
greater than 9lbs or higher than 90th percentile for gestational age
Often diabetic
What are the priority nursing interventions for the immediate newborn period?
Maintaining airway patency
Ensuring proper identification
Maintaining thermoregulation
Administering prescribed medications
Vitamin K
Eye prophylaxis - usually erythromycin
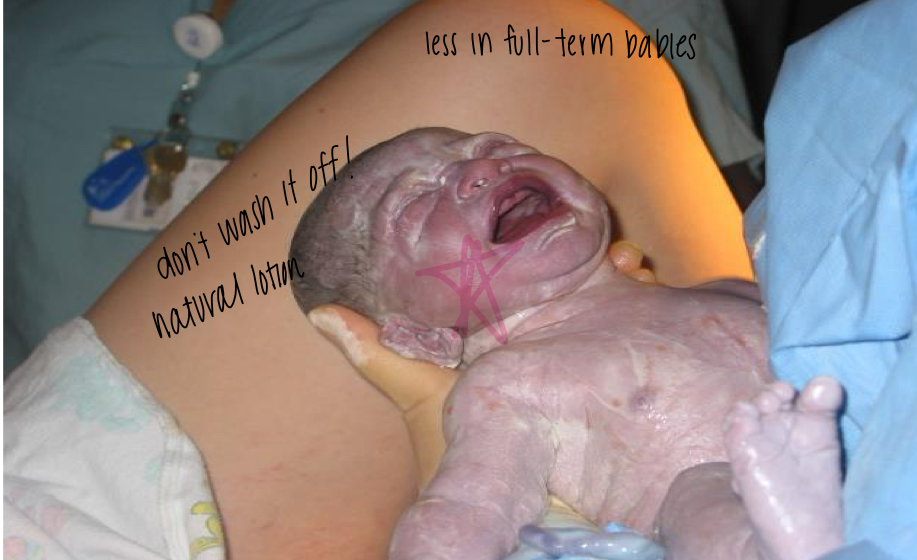
what is vernix caseosa?
Cottage cheese like substance
What is lanugo?
peach fuzz
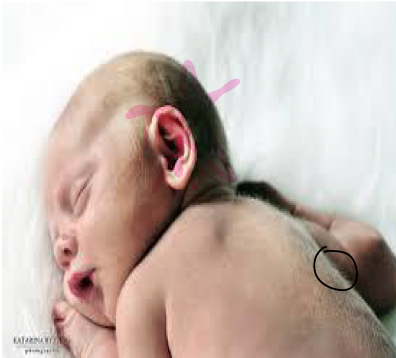
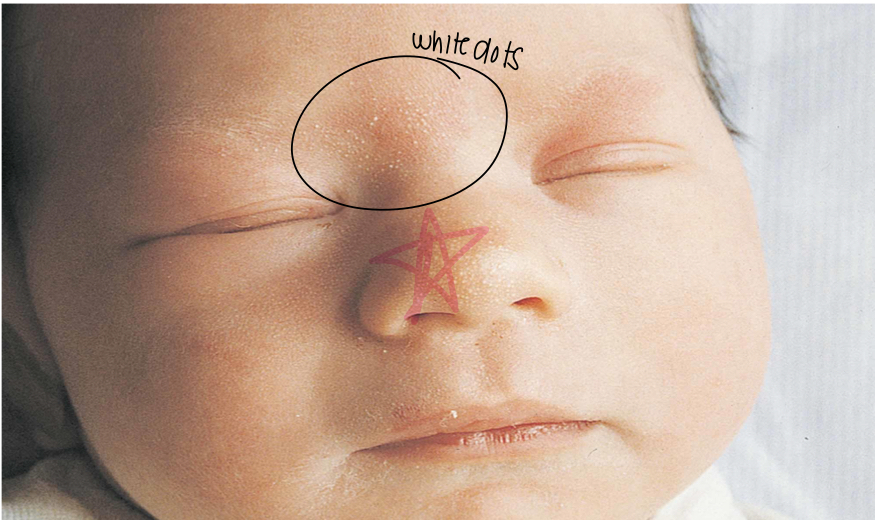
what is milia?
Newborn acne
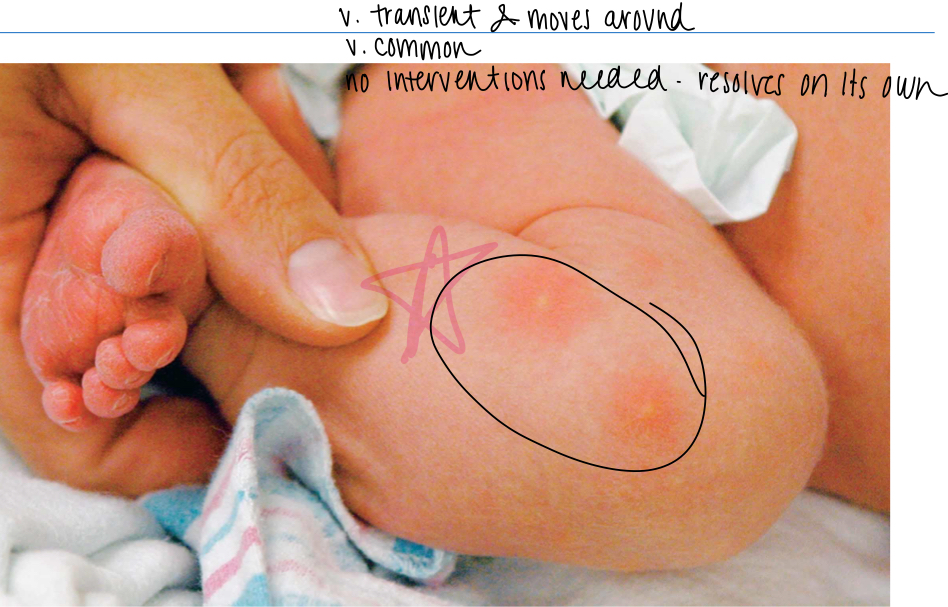
What is erythema toxicum?
newborn rash
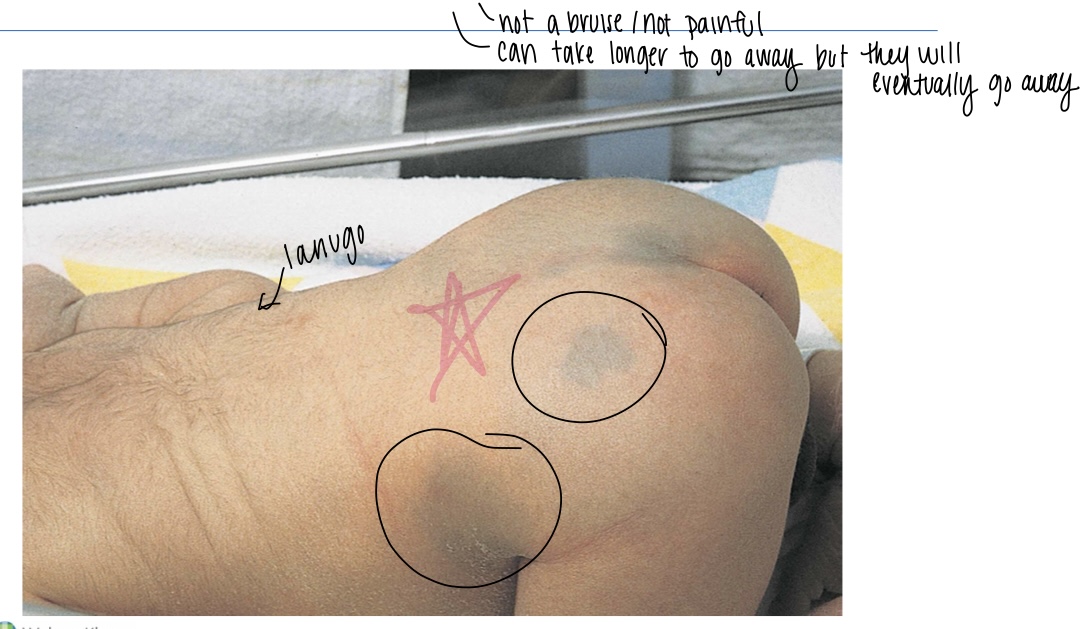
What are Mongolian spots?
Bruise like spots
What is molding?
”conehead” that occurs as a result of passing through the pelvis
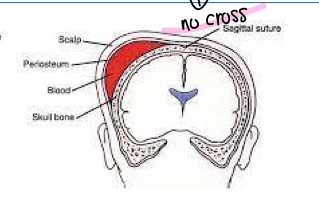
What is caput succedaneum?
Edema in scalp
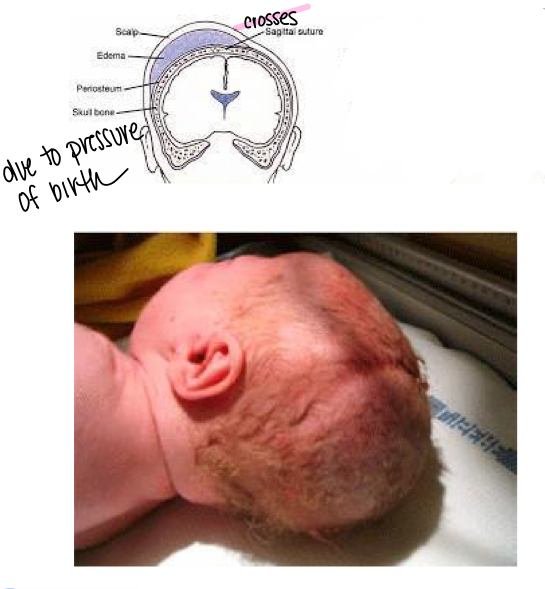
what is a cephalohematoma?
accumulation of fluid and blood
what is microcephaly?
small headW
What is macrocephaly?
large head
what can bulging fontanelles indicate?
increased ICP
what can sunken fontanelles indicate?
dehydration
what is torticollis?
an abnormality in which the newborn’s head is not midline with the rest of the body
when can bowel sounds first be auscultated in a newborn?
1-2 hr after birth maximum; note: if the infant passed meconium stool in utero bowel sounds can be heard during first assessments directly after birth
What does post-circumcision care entail? (6)
Applying Vaseline gauze to prevent adherence to the diaper
Assess bleeding q30min for at least 2hr
Assess for and document first voiding post-op
Pain management
Observe for s&s of infection- REEDA
Assess for swelling ← risk for urinary obstruction
How is pain management achieved in newborns for circumcisions? ()
Swaddling
Nursing
Emla cream
Sucking on oral glucose (ex. Sweetums)
Penile nerve block
what is the rooting and sucking reflex?
upon touching or stroking their cheek or the corner of their mouth, the infant turns their head toward the stimulus and opens their mouth, preparing to feed
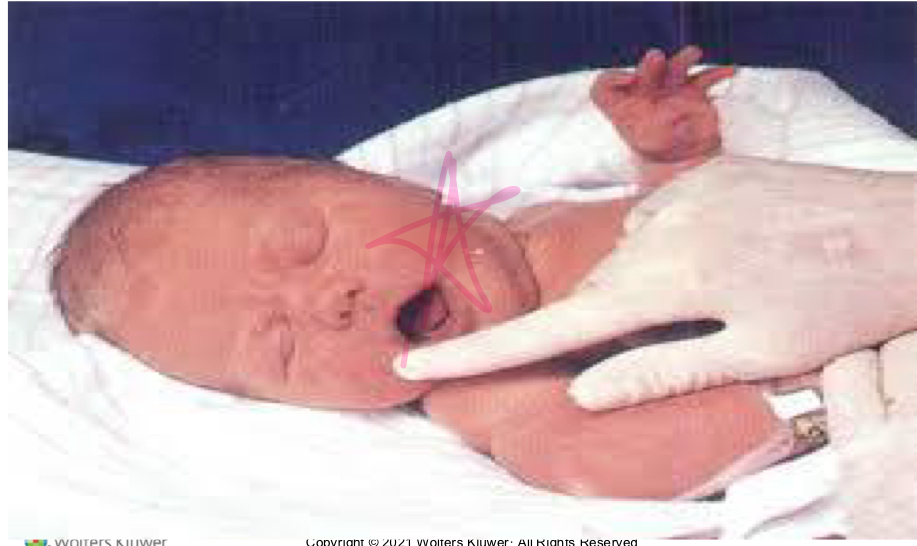
What is the Moro/startle reflex?
an involuntary reaction in newborns where they suddenly extend their arms and legs, spread their fingers, and then quickly bring their arms and legs back to their body, often accompanied by a cry
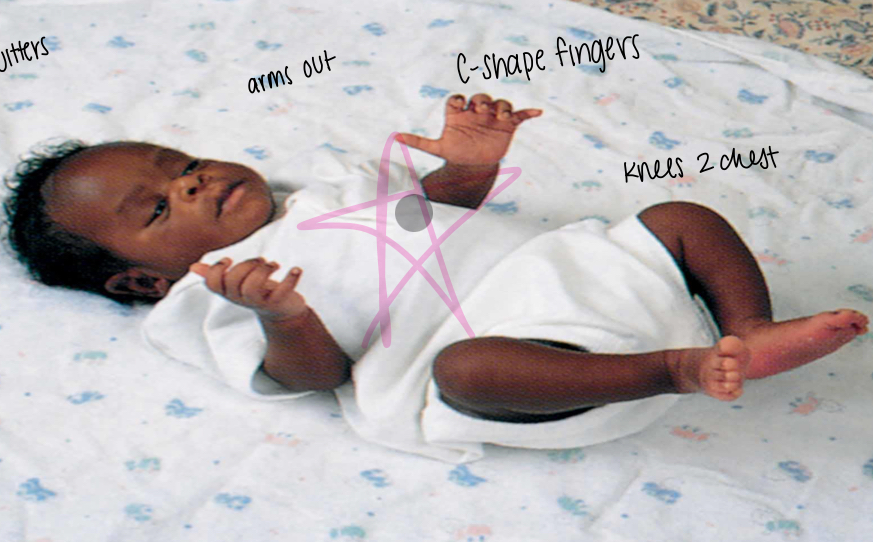
what is the tonic neck reflex?
head and arm extends to go in the same direction
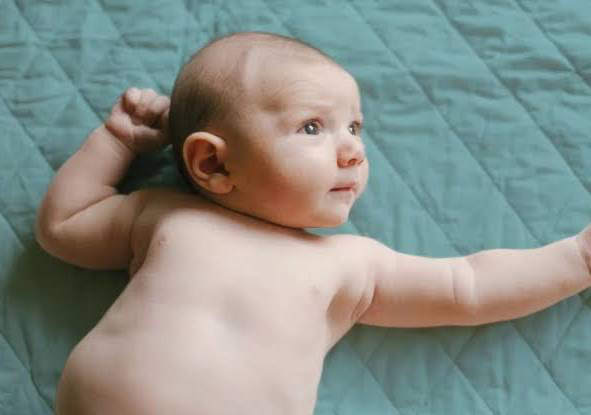

what is the fencing reflex?
flexion of opposite arm that occurs during the tonic neck reflex?
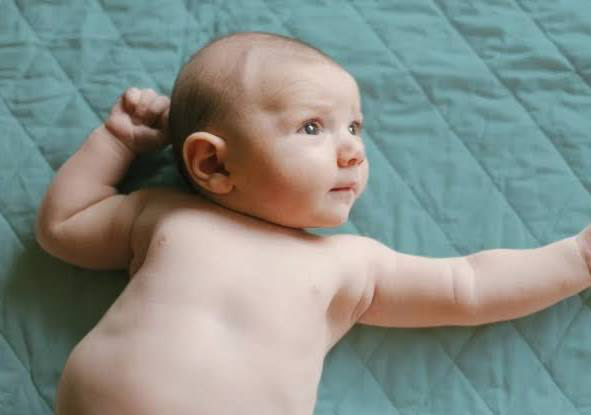

What is the palmar reflex?
a newborn's involuntary response to an object in its palm, causing the fingers to close in a grasp
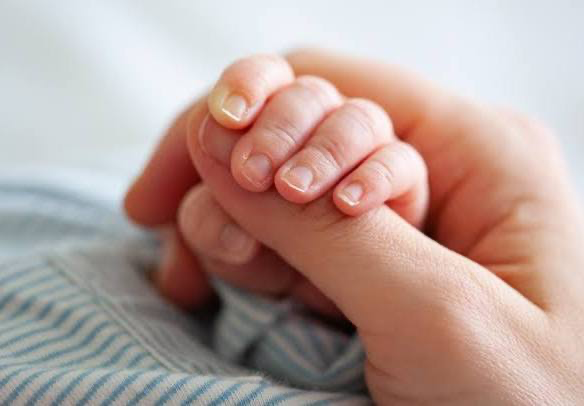

what is the babinski/plantar reflex?
a normal, primitive reflex in infants where the big toe moves upward (dorsiflexion) and the other toes fan out when the sole of the foot is stroked
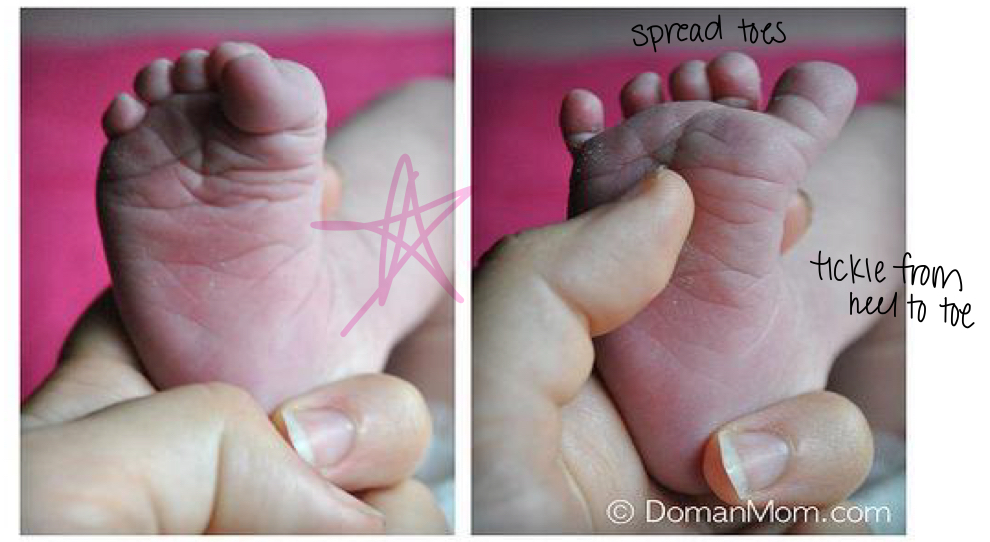
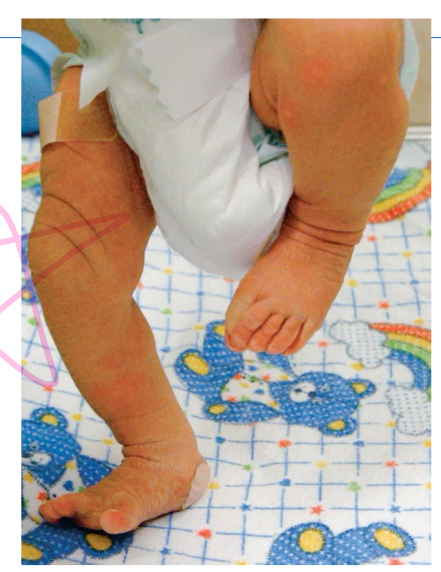
what is the stepping reflex?
an instinctive response that makes a baby appear to walk when held upright with their feet on a flat surface
what are the Barlow and ortolani maneuvers used for?
Checking for hip problems
what is syndactyly?
2 or more digits that are fused together
Can be fingers or toes
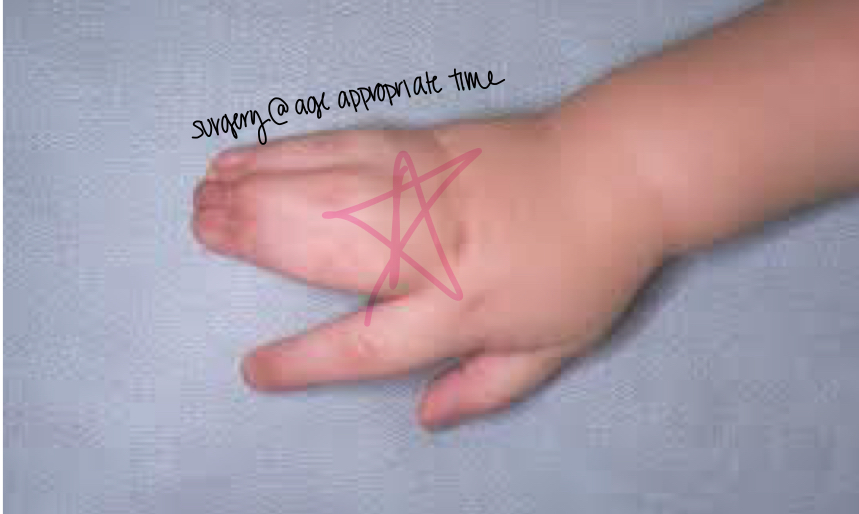

What is polydactyly?
extra digits
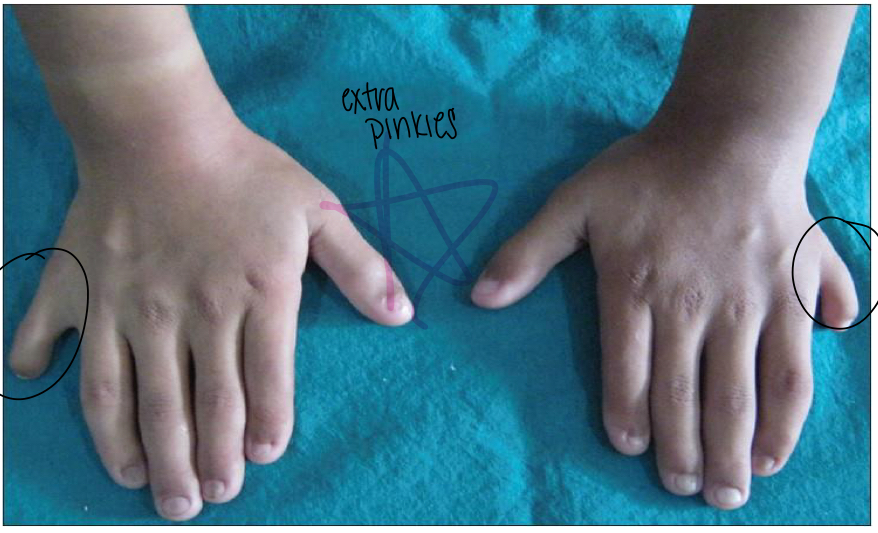
what should be done if polydactyly is observed? Outcomes?
Assess for bones!
If present- extra digits must be surgically removed
If not present- digits are sutured around to cut of blood supply and then necrosis takes place and the digit will fall off on its own