measuring and forecasting weather
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ccc 2nd year geography
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
what is weather
state of the atmosphere at any given time
what is a weather station
a facility that uses equipment and instruments to measure and observe the weather
how weather is gathered
through satellites and weather stations
what data is gathered
atmospheric pressure
temperature
precipitation
wind direction and speed
humidity
sunshine
what is atmospheric pressure measured by
weight of the atmosphere pushing down on the earth, measured in millibars(mb) by a barometer
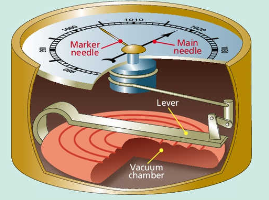
barometer
a very sensitive vacuum chamber inside the barometer responds to atmospheric pressure
the the main needle on the face moves clockwise when pressure increases and anticlockwise when it decreases
the second needle is used as a marker to check back and see what the atmospheric pressure was later
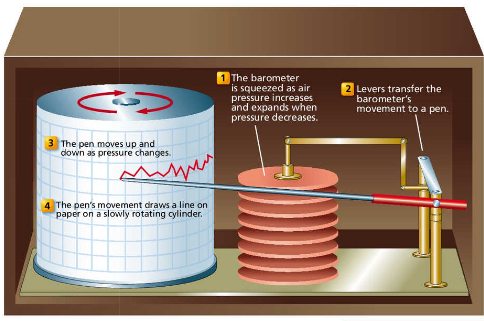
barograph
a barometer that records its readings on a moving graph used in weather stations
the barometer is squeezed as air pressure increases and expands when pressure decreases
levers transfer its movements to a pen which draws on the paper
isobars
lines on map that measure atmospheric pressure
H = high atmospheric pressure
L = low atmospheric pressure
Low atmospheric pressure
wind is quite strong
significant cloud cover
high levels of precipitation
High atmospheric pressure
light wind
little cloud cover
little or no precipitation
what is temperature measured with
degrees celsius/centigrade using a thermometer - maximum and minimum thermometer
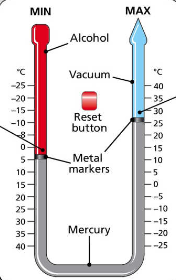
maximum and minimum thermometer
u shaped glass tube
alcohol is on the minimum side and empty space on the maximum side with mercury in between
metal makers on either side of the mercury
when temp. decreases alcohol contracts causing the metal marker to go up on min. side
when temp increases alcohol expands causing metal marker to go up on max. side
what is precipitation measured with
milimeters measured using a rain gauge
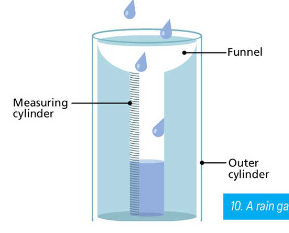
rain gauge
an outer cylinder and a funnel that directs water into a measuring cylinder, is partially buried in ground
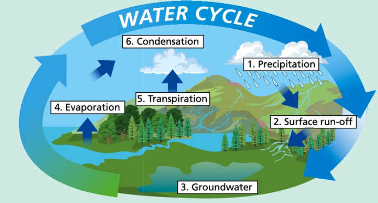
water cycle
precipitation
surface run off
groundwater
evaporation
transpiration
condensation
types of rain
relief
convectional
frontal
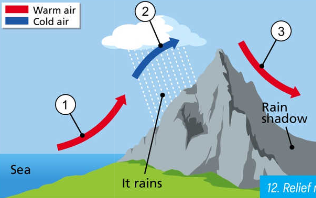
relief rain
warm moist air travels over a large body of water
it reaches a mountain, rises and cools and condenses forming clouds and bringing rain
once it passes over the mountain the air begins to dry up again and forms a rain shadow
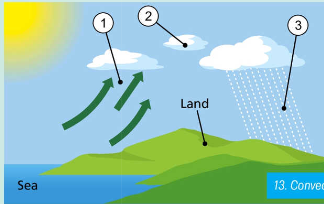
convectional rain
occurs during warm weather when land is heated
this creates warm air which rises which is known as a convection current
as warm air rises it cools and condenses forming large clouds
frontal rain
this rain occurs when a warm front of air meets a cold front
the heavier cold air will sink to the ground and the warm air will rise above it
when the air rises it cools and condenses
clouds form bringing rain
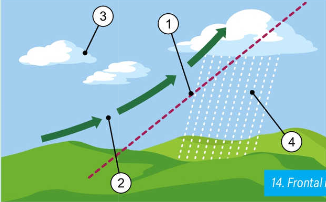
what is a front
a boundary between two different types of air
rainfall on maps
lighter shade of blue = less rain
darker shade of rain = more rain
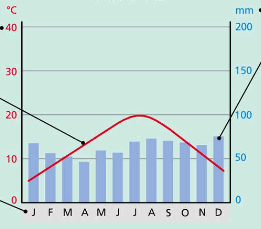
climate graphs
used to illustrate avg. temp. and precipitation of an area over 12 months of the year
line shows the temperature
bars show precipitation
cloud types
cirrus
cumulus
stratus
cirrus
above 8000m
thin and wispy
tiny ice crystals not water droplets
cumulus
below 5000m
base is flat rounded top
white = fair weather
black = heavy rain
stratus
below 200m
large thick heavy grey
long spells of precipitation
what is wind direction measured with
a wind vane
what is wind speed measured with
km/h with anemometer
wind vane

anemometer
three cups rotate when the wind blows
stronger wind = faster they move

beufort scale
scale used to measure wind force
what is humidity measured with
amount of water vapour in the air using a hygrometer shows relative humidity
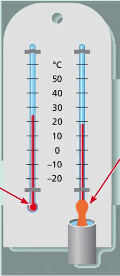
wet and dry hygrometer
one thermometer measures the air temp.
the other bulb is kept wet by a cloth that is dipped in water
the difference between the two indicates relative humidity
what is sunshine measured with
a campbell-stokes recorder
campbell-stokes recorder
a solid glass ball concentrates the suns ray onto a removable strip of card which is placed behind the ball
the card is marked at hourly intervals as the sun shines through the ball it scorches a mark on the paper
