administration, scoring, and interpretation of selected tests
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
maximum muscular _____ (low-speed strength) is related to the _____ a muscle or muscle group can exert in one maximal effort; it’s generally tested via _____ in a particular lift
strength; force; 1 repetition maximum (1RM)
_____ or maximum muscular _____ (high speed strength) is related to the ability of muscle tissue to exert high _____ while _____ at a high speed (also called maximal aerobic muscular power or anaerobic power); it may include vertical jump height and time to sprint up a staircase
anaerobic; power; force; contracting
most maximum muscular _____ tests use relatively slow movement speeds and therefore reflect low speed strength
strength
assessment of high speed muscular strength can involve measuring 1RM for _____ resistance training exercises of the _____ of a vertical jump
explosive; height
_____ capacity is the maximal rate of energy production by combined phosphagen and _____ glycolytic energy systems for moderate duration activities
anaerobic; anaerobic
local muscular _____ is the ability of certain muscles or muscle groups to perform repeated contractions against a submaximal resistance
endurance
_____ capacity is the maximum rate at which an athlete can produce energy through oxidation of energy resources (carbs, fats, and proteins); it’s usually expressed as volume of oxygen consumed per kg of body weight per minute; also called _____ power
aerobic; aerobic
_____ is the ability to change direction or speed of the whole body in response to a sport specific stimulus; it’s generally confined to physical capacity testing such as change of direction speed of cognitive components such as anticipation
agility
_____ is movement distance per unit time, typically quantified as the time taken to cover a fixed distance
speed
_____ is range of motion about body joint
flexibility
_____ is the ability to maintain static and dynamic equilibrium
balance
_____ is the ability to return to a desired position following a disturbance to the system
stability
_____ are relative proportions by weight of fat and lean tissue
body composition
_____ is the science of measurement applied to the human body; it generally includes measurements of height, weight, and selected body girths
anthropometry
to maximize the reliability of tests, conditions should be as _____ as possible for all athletes tested and from test to retest of the same athlete
similar
_____ and _____, _____, and type of _____ should be consistent
temperature; humidity; surface; equipment
athletes should not be tested when _____ - they should arrive for testing normally _____ and with standard _____ (no supplements)
fatigued; hydrated; nutrition
warm-up for the tests should be _____
standardized
common 1RM tests include:
bench _____
bench _____
_____
_____
*coaches should aim to find 1RM within _____ to _____ attempts after their warm up and be given _____ minutes between sets
press; pull; back squat; power clean; 3; 5; 5
_____ jump: athlete stands with toes just behind starting line and performed counter-movement jump as far forward as possible; athlete must land on feet in order for the jump to be scored; distance is measured from the back edge of the athlete’s rearmost heel
standing long
_____ jump (using wall and chalk): tester rubs chalk on athlete’s dominant hand and athlete stands about _____ inches from wall and places a mark on the wall with the dominant arm as high as possible keeping both feet flat on the floor; athlete then performance countermovement jump and places second chalk mark as high as possible on the wall
vertical; 6
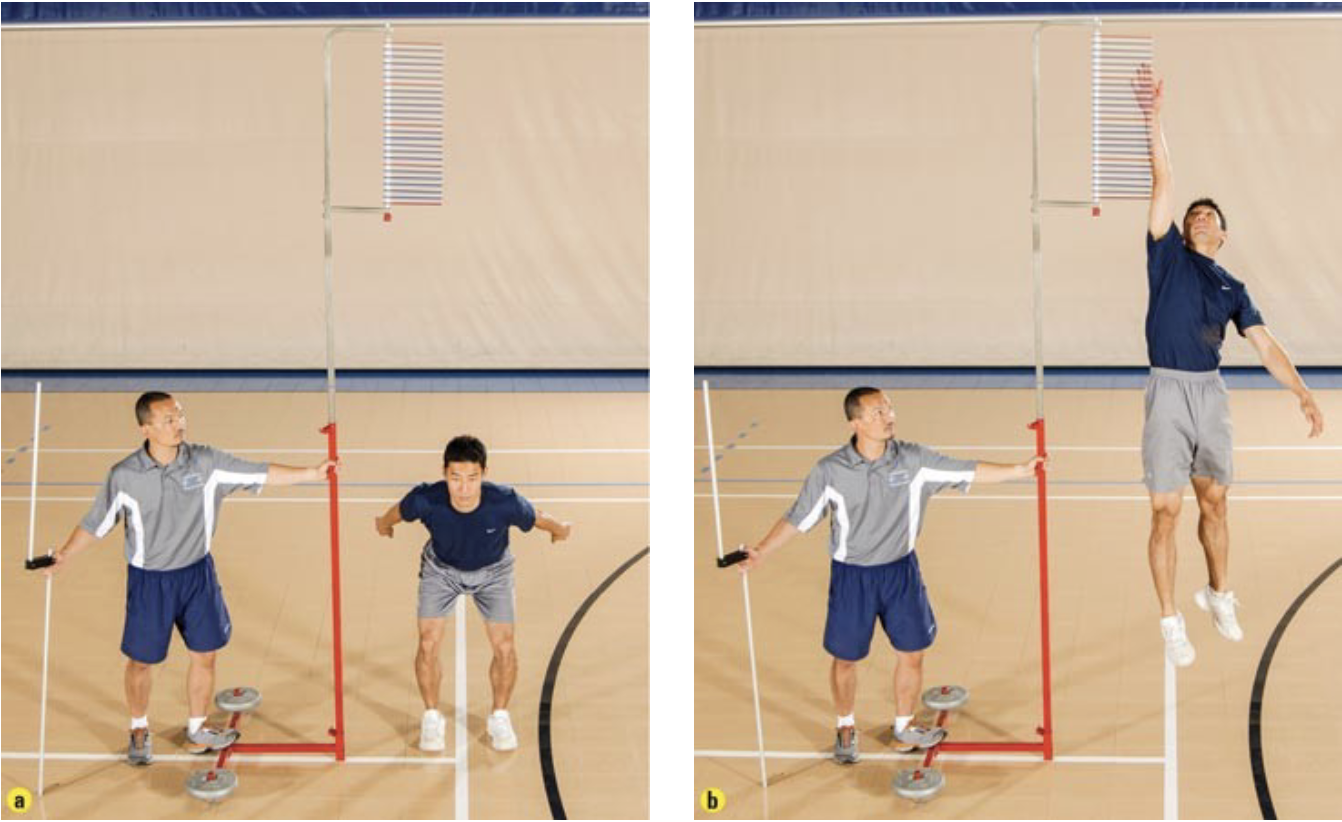

this is the _____ jump using a commercial vertec device
vertical
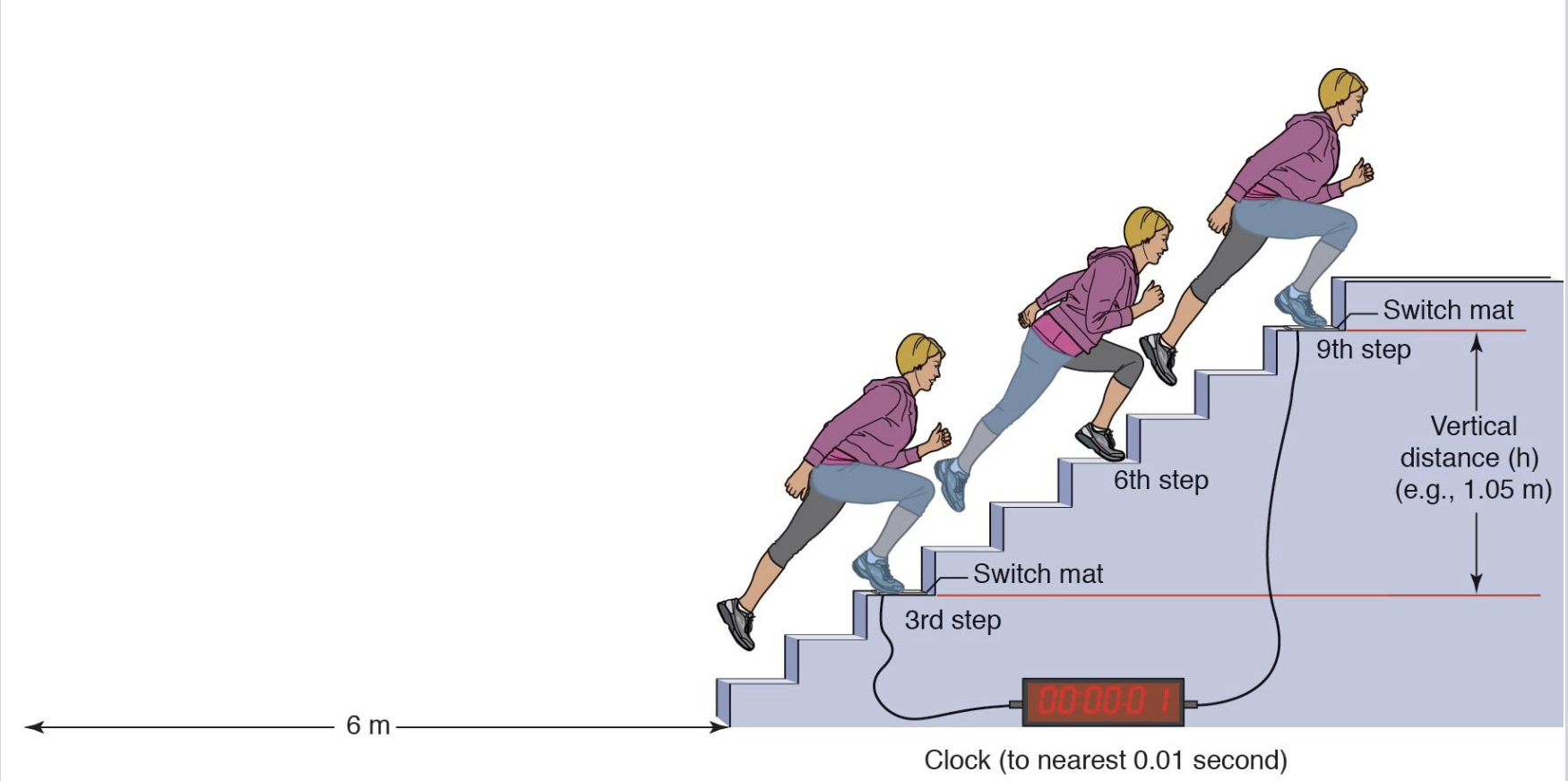
_____ test (stair spring test): athlete sprints toward stairs from a standing start 20 feet (6m) from base of stairs then up staircase three steps at a time
_____ in watts is calculated as the athlete’s weight (w) in Newtons x height (h) in meters from the 3rd step to the 9th step divided by measured time interval (t) in seconds: P = (w x h) / t
margaria-kalamen; power
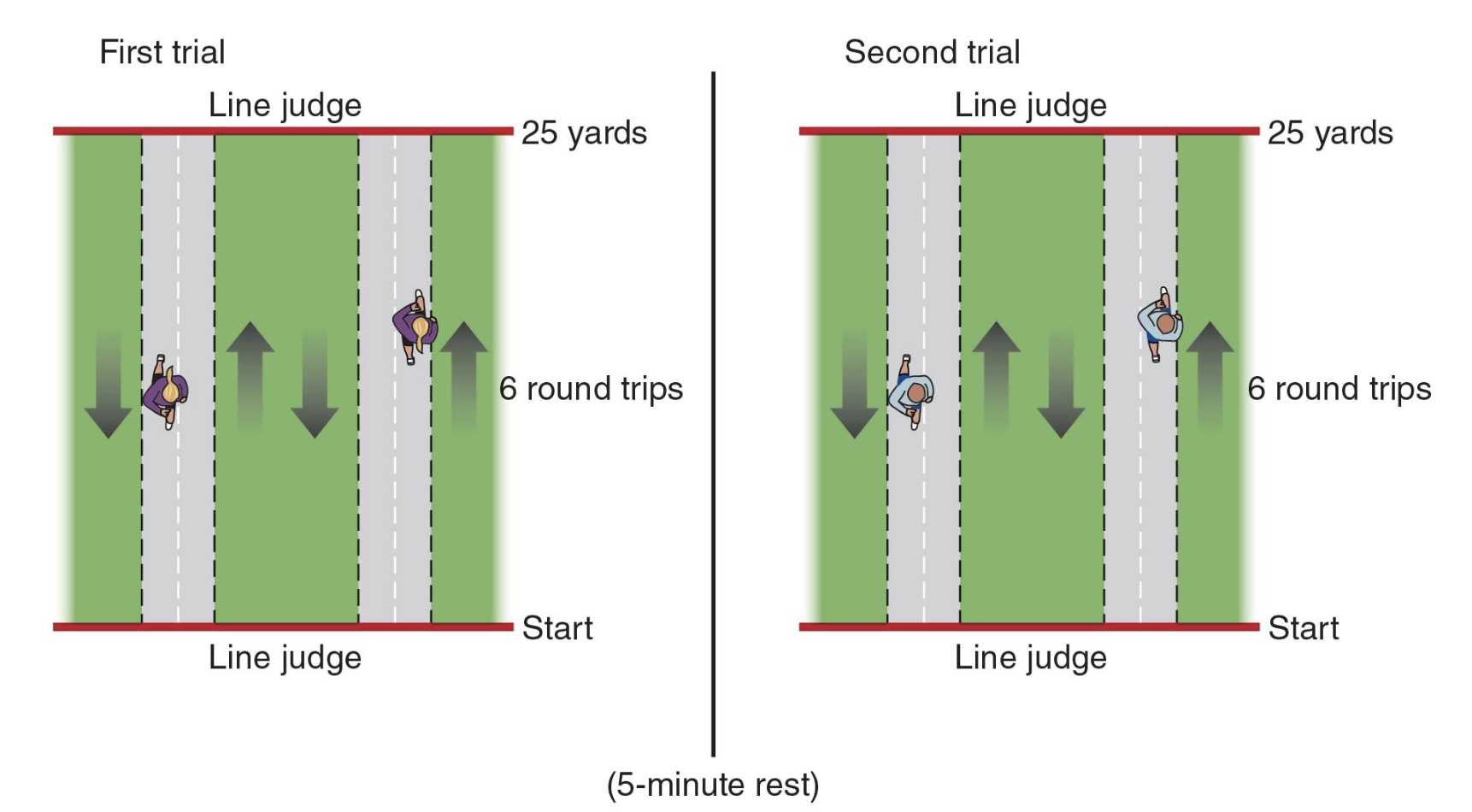
_____ shuttle is an _____ test where a pair of athletes of similar ability sprint 25 yards away, then immediately sprint back to the start line for 6 trips; goal is to run as fast as possible without stopping and the average of two trials is recorded to the nearest 1.0 second
300-yard; aerobic
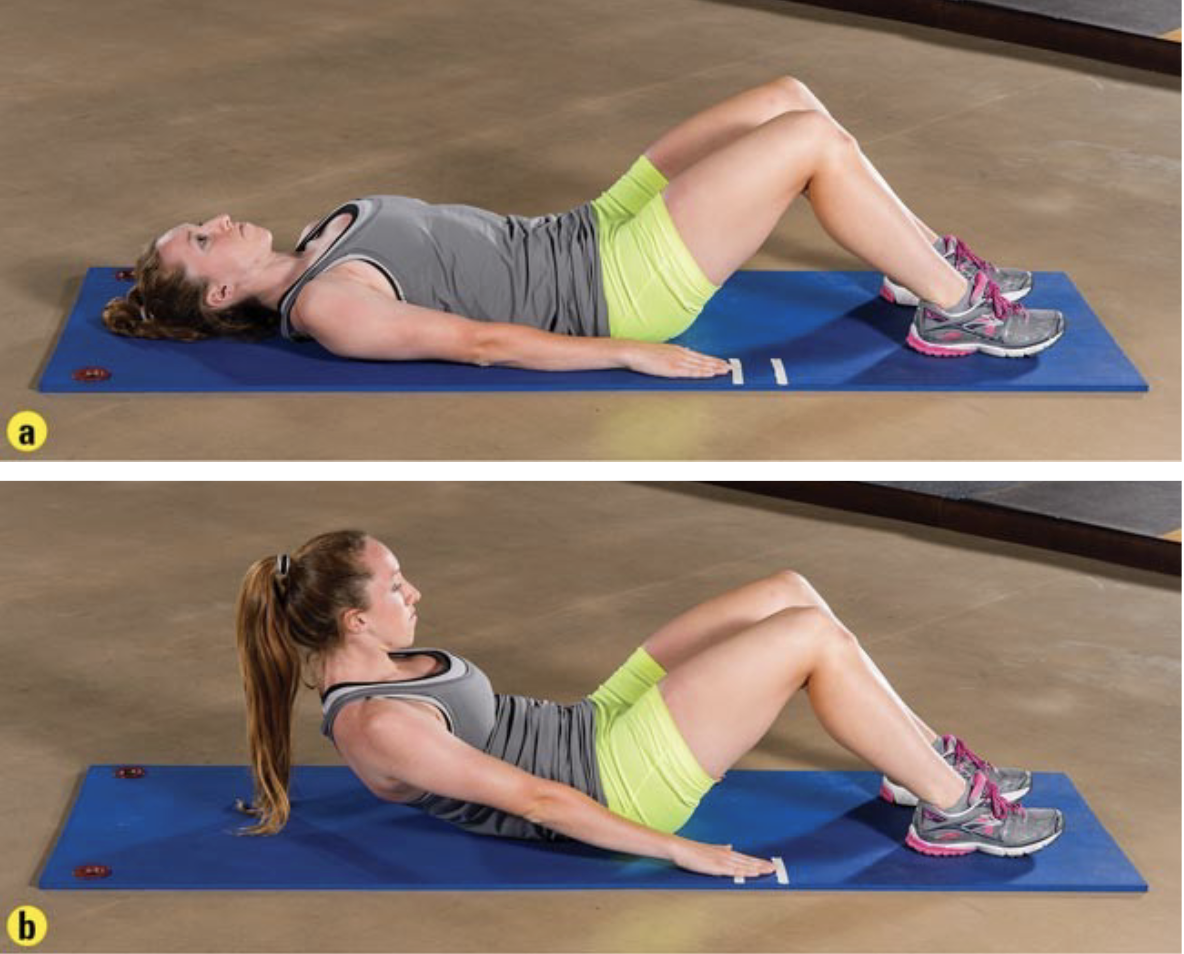

_____ test involves setting a metronome to _____ beats per minute and having the individual do slow, controlled, curl-ups to lift the shoulder blades off the mat in time with metronome; upper back must touch floor before each curl-up; athlete should perform as many as possible without pausing to a maximum of 75
partial curl-up; 40
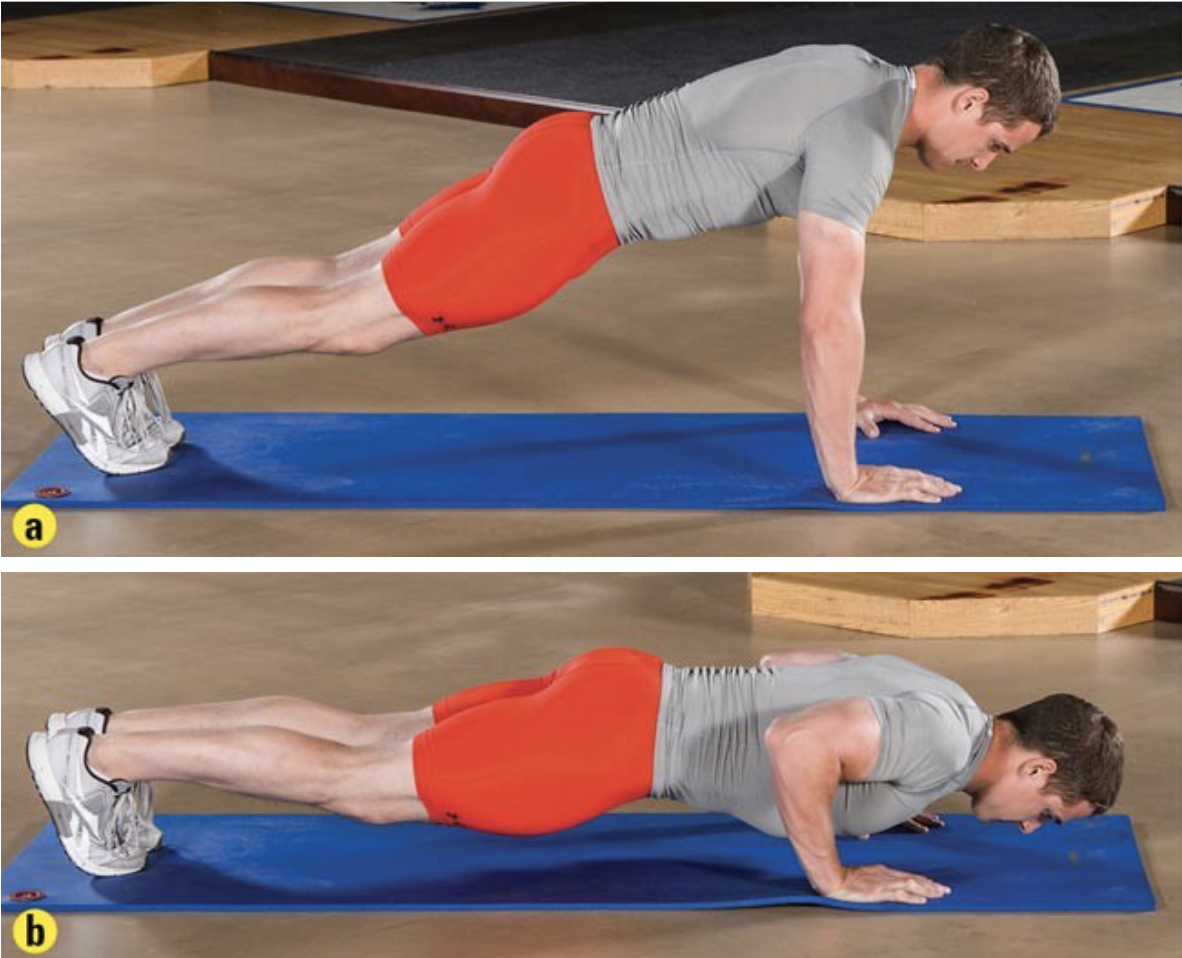

push up test according to army standard is as many reps as possible within _____ minute time period
2
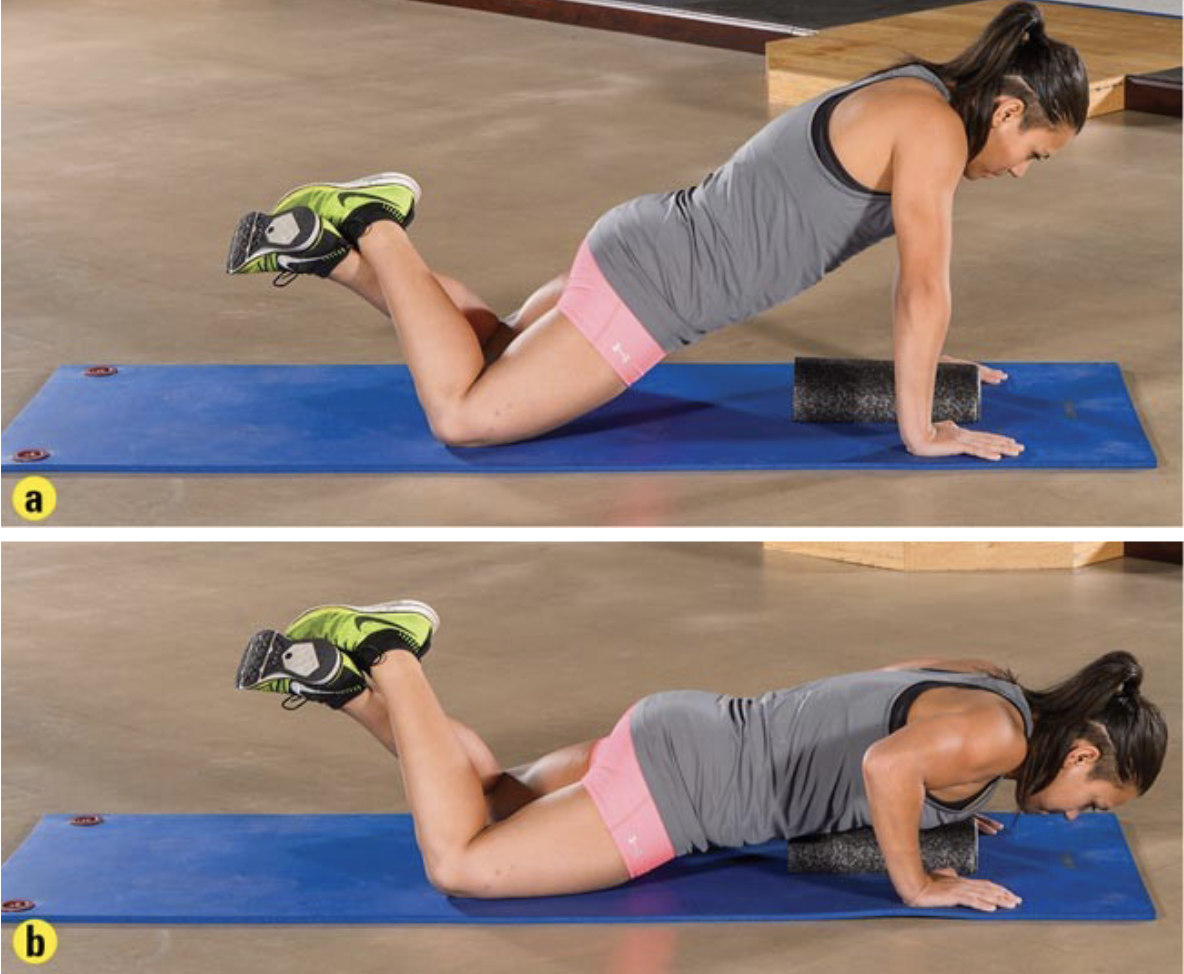

push up test according to ACSM for females is as many reps as possible until _____
failure
_____ test is when resistance is set at _____ pounds for males and _____ pounds for females, then a metronome is set at _____ beats per minute to establish a rate of 30 reps per minute (one beat up, one beat down); it’s performed until the athlete can no longer perform reps with metronome
YMCA bench press; 80; 35; 60
_____: athletes should perform this test as quickly as possible at a steady pace that they can barely maintain over the distance; each runner’s time should be recorded in mins and seconds
1.5 mile run
_____: should be performed on a 400m track or flat course with markers ever 100m; athletes should travel as far as possible in 12 minutes; the distance covered should be calculated and recorded (# of laps x 400m = total distance)
12 minute run
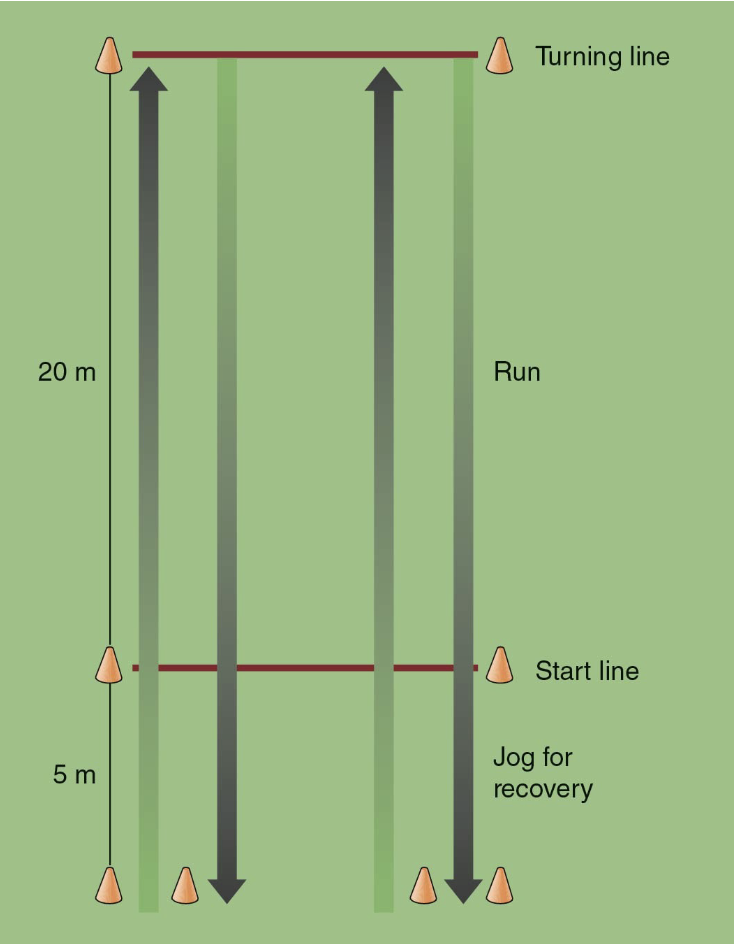
_____ test: a 20m test course with markers 2m apart at each end of the course and 5m distance behind the start line; at the signal, athletes run forward to turning line, then at second signal athletes arrive at turning line then run back to the starting line; athletes jog toward the 5m mark after the start line and return to start line to wait for the next sound; the test is terminated when the athlete cannot maintain their required pace for two trials
yo-yo intermittent recovery
_____ test: marker cones placed at 20m intervals around the running track; initial speed of test is set between 8 and 12 km/h depending on the fitness level of the athlete; speed is then increased by 1 km/h every 2 mins until athlete cannot maintain speed; the last speed maintained for at least 2 minutes is considered the speed associated with VO2max or MAS; test is terminated if athlete fails to reach the next cone on two consecutive occasions in the required time; the speed at last completed stage is increased by 0.5 km/h if athlete is able to run a half stage; VO2max of athletes can be calculated by multiplying 3.5 by MAS (speed in km/h)
maximal aerobic speed
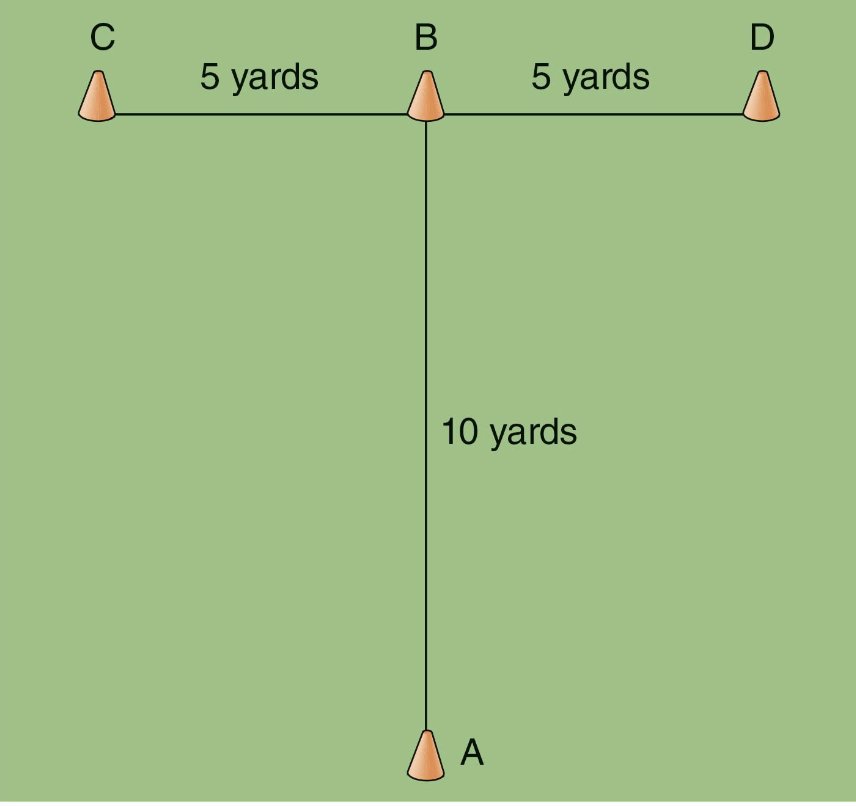
_____: begins at point A, sprints to point B touches base of cone with right hand, shuffles left and touches base of cone C with left hand, shuffles right and touches base of cone D with right hand, shuffles left and touches base of cone B with left hand, then runs back ward past point A
t-test
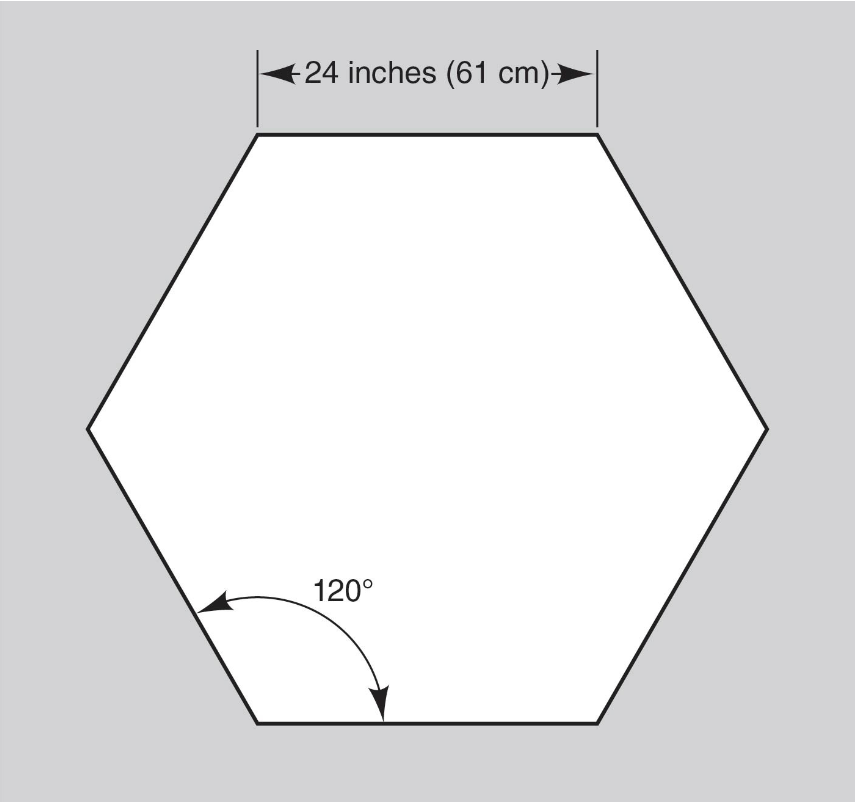
_____ test: athlete double leg hopes from center of hexagon over each side and back to center, starting with side directly in front of athlete; athlete continues clockwise until all 6 sides are covered 3 times (total of 18 jumps)
hexagon
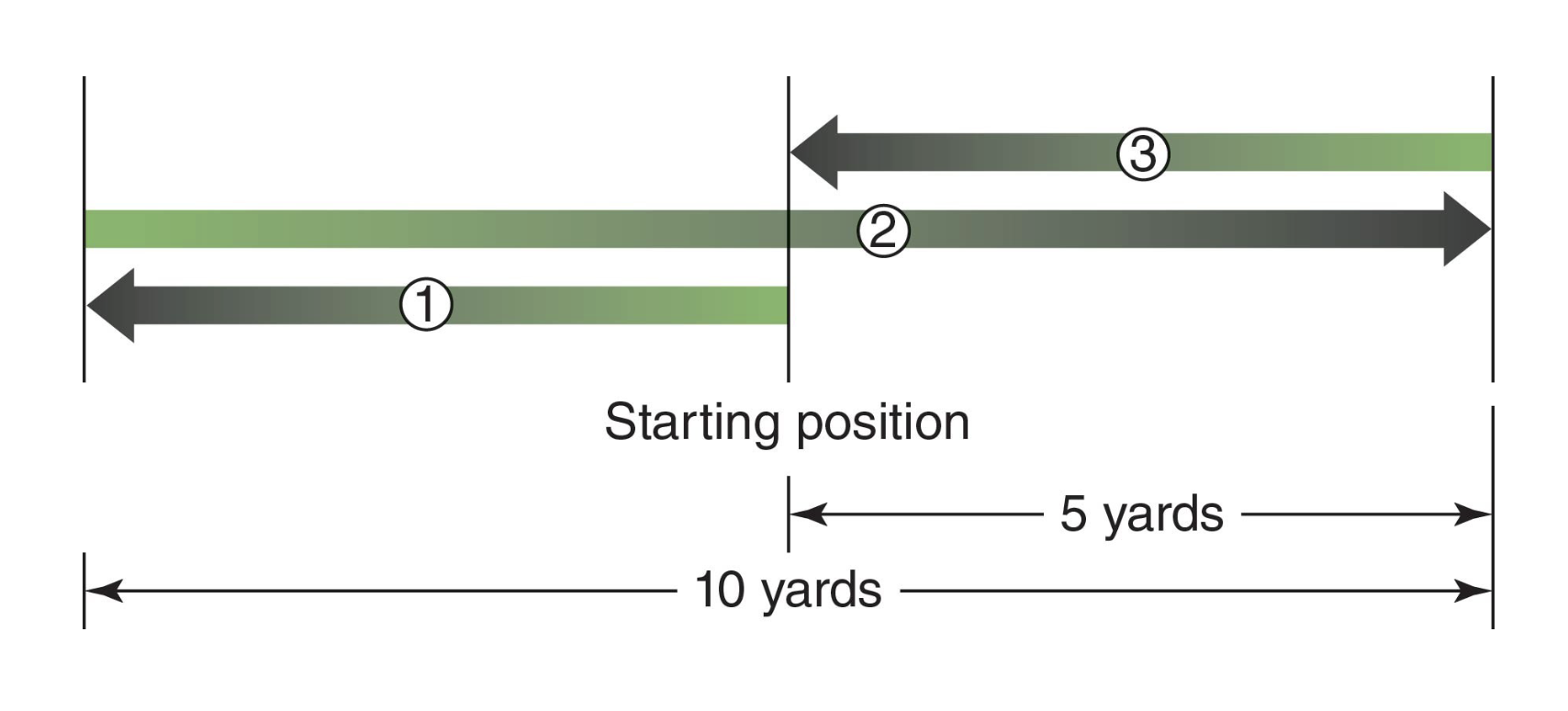
_____ test: athlete straddles centermost of three parallel lines using three point stance; on signal, athlete sprints 5 yards to the line on the left, then changes direction and sprints 10 yards to the line on the right, then again changes direction and sprints 5 yards to the center line; foot contact must be made with all indicated lines; the best time of two trials is recorded to the nearest 0.01 second
pro agility
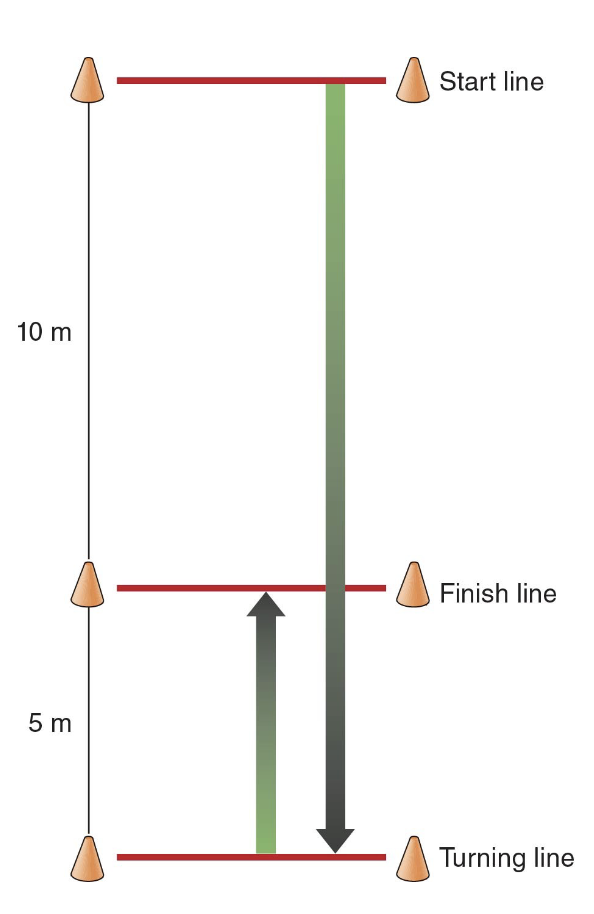
_____ test: athlete taking the test does the following:
sprint forward 10m to first set of timing lights
sprint additional 5m past timing lights to turning line (one foot on or going over line)
turn back toward first set of timing lights
spring 5m back to (and past) timing lights
*best time of two trials recorded to the nearest 0.1 second
505 agility
_____ test: have athlete warm-up and dynamically stretch for several minutes; allow at least two practice runs at submaximal speed; athlete assumes starting position using 3 or 4 point stance; on auditory signal, athlete sprints specified distance at maximal speed; the best split times of two trials are recorded to the nearest 0.1 second; allow at least _____ minutes of active recovery or rest between trials
straight line sprint; 2
_____ system includes three stance positions: double-leg stance with feet together, single leg stance on non-dominant foot with contralateral leg in approximately 90˚ of flexion, and tandem stance with dominant foot in front of non-dominant foot; test conducted on a firm surface and soft surface; each stance is held for 20 seconds with eyes closed for each condition and hands on hips; athletes are told to keep as steady as possible and if they lose balance, they attempt to regain their initial position as quickly as possible
balance error scoring (BESS)
errors of BESS test include the following:
_____ eyes
_____ hands from hips
_____ of nonstance foot
_____, _____, or other movement of stance foot/feet
lifting _____ or _____
moving hip into more than 30˚ of hip _____ or _____
remaining out of position for more than _____ seconds
opening; lifting; touchdown; step; hop; forefoot; heel; abduction; extension; 5
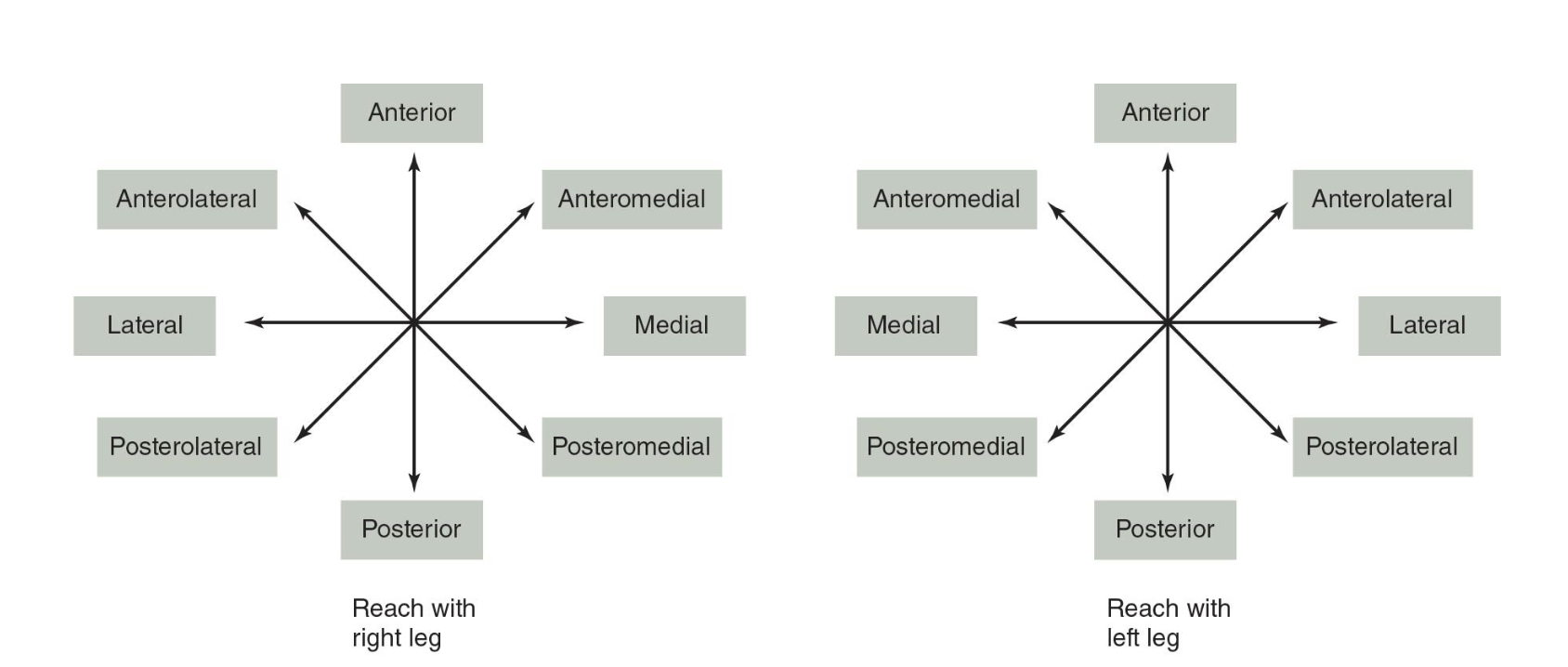
_____ balance test (SEBT): athlete stands in center of a grid with 8 lines extending out at 45˚ increments; athlete maintains single leg stance facing in one direction while reaching with contralateral leg as far as possible for each taped line, touching the farthest point possible, and then returning to bilateral position; within single trial, athlete remains facing in beginning direction and stand leg remains the same with other leg doing all the reaching, the distance from the center of the star to the touch position is measured; starting direction and support leg are chosen randomly; 3 trials are performed for each condition and averaged; 15 seconds of rest is allowed between each of the reaches; athletes should be given a minimum of _____ practice trials before being tested; it’s been suggested that testing the anteromedial, medial, and posteromedial positions is sufficient for most situations
star excursion; 4
trials are discarded during the SEBT if the athlete…
does not touch the _____
_____ stance foot from center grid
loses _____
does not maintain start and return positions for _____ full second
line; lifts; balance; 1
common sites for girth measurements include:
_____
_____ arm
_____
_____
_____
_____
_____
chest; upper; forearm; waist; hips; thigh; calf
_____ is the average of the scores
mean
_____ is the middlemost score when a set of scores is arranged in order of magnitude
median
_____ is the score that occurs with the greatest frequency
mode
_____ is the interval from the lowest to the highest score
range
_____ is a measure of the variability of a set of scores about the mean
standard deviation
_____ is the percentage of test takers scoring below an individual
percentage rank
normal _____ is “normally distributed” scores form _____ is most useful when scores are normally distributed
bell curve; standard deviation
_____ statistics allow one to draw general conclusions about a population from information collected in a population sample, which must be representative
inferential
_____ statistics allows for interpretation of the clinical significance of fitness testing
magnitude
_____ is the ability of a test to detect the smallest practically important change in performance
smallest worthwhile change
_____ is a statistic used for calculating group performance following a training program or comparing between groups of athletes
effect size
when developing an athletic profile, select tests that will measure the specific _____ most clearly related to the characteristics of the sport or sports in question
parameters
when developing an athletic profile, choose _____ and _____ tests to measure these parameters, and arrange the testing battery in an appropriate order with sufficient rest between tests to promote test reliability
valid; reliable
when developing an athletic profile, administer the test battery to _____ athletes as possible
as many
when developing an athletic profile, compare to _____ data where appropriate and develop own norms when standardized procedures are used
normative
when developing an athletic profile, conduct _____ testing (i.e., before and after the training program) and use the results to present a visual profile with figures
repeat
when developing an athletic profile, identify the _____ and _____ of the athletes and design the training program with these in mind
strengths; weaknesses
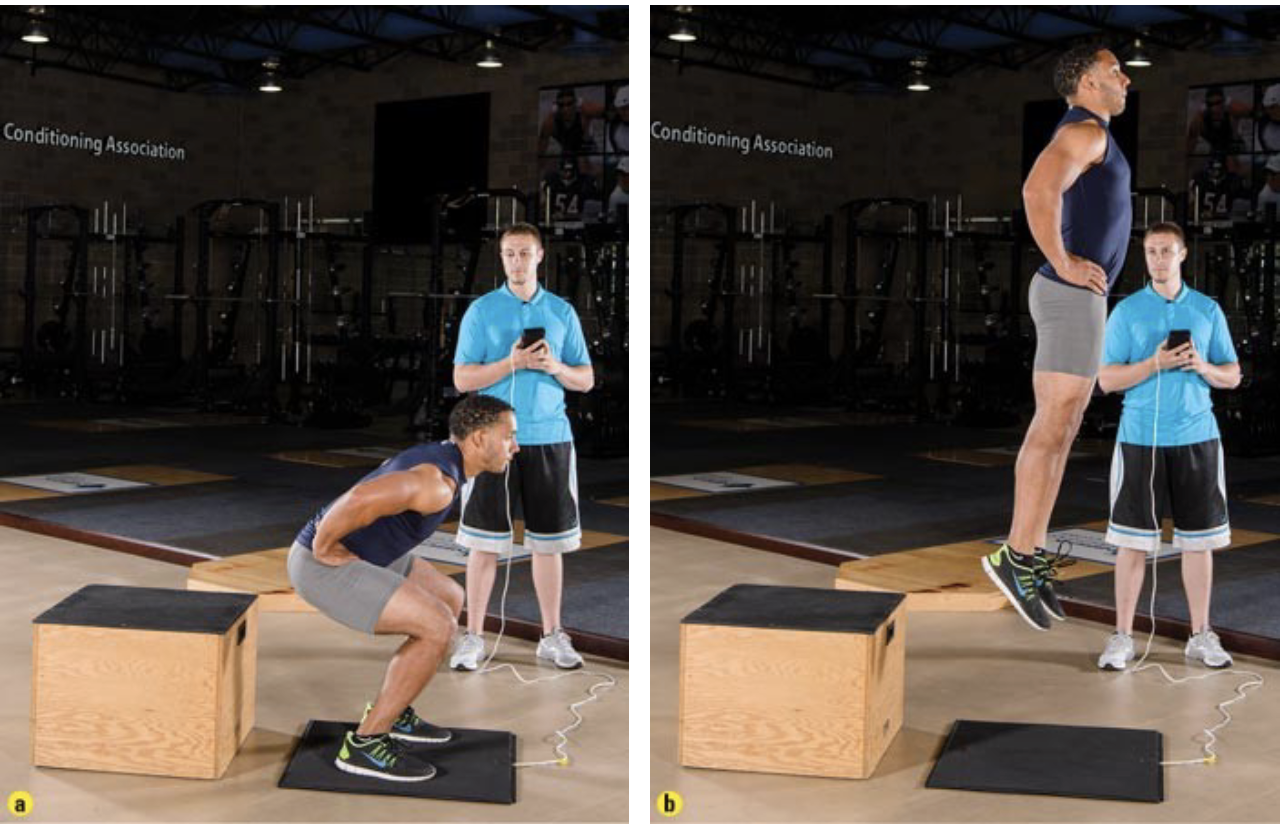

this is the _____ jump
static vertical
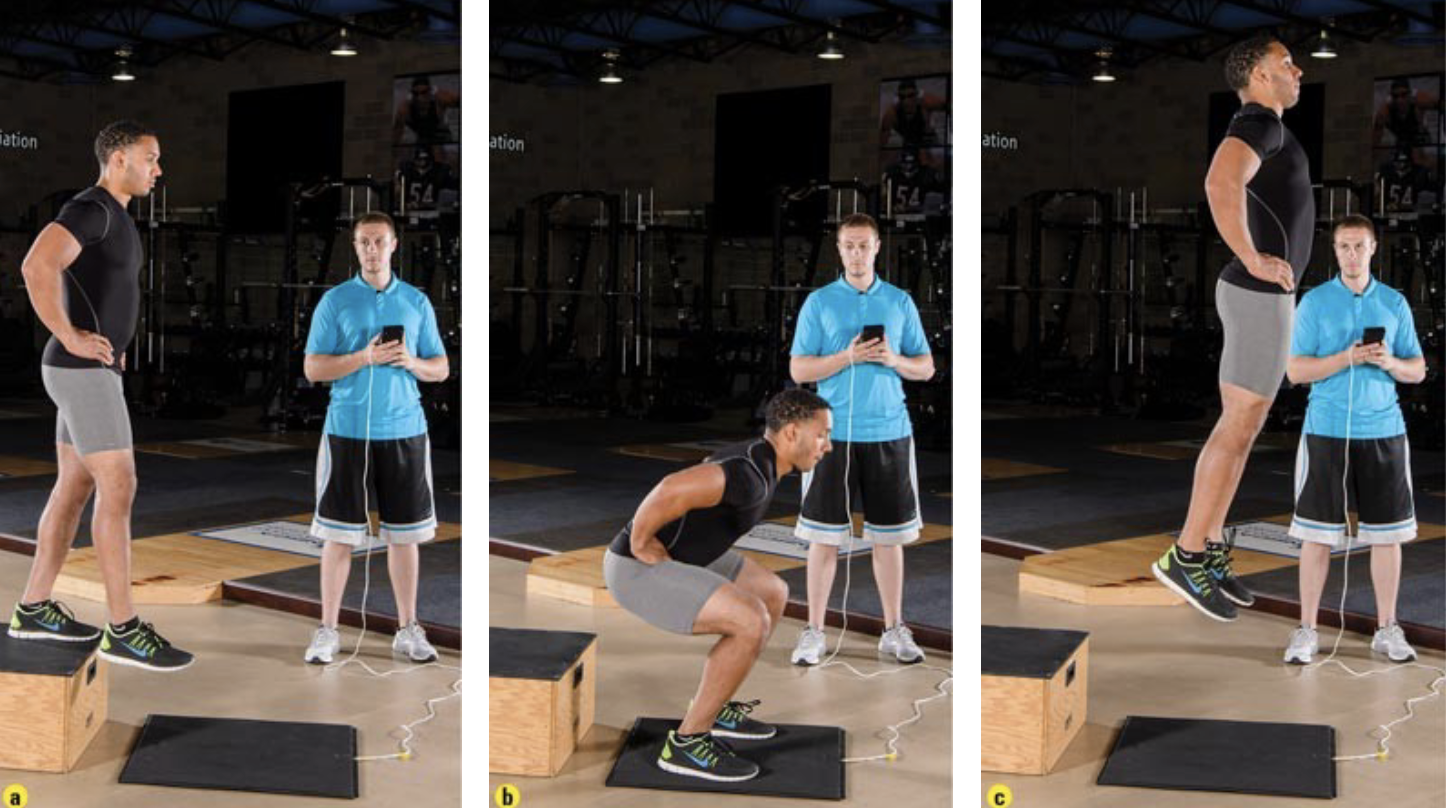

this is the _____
reactive strength index
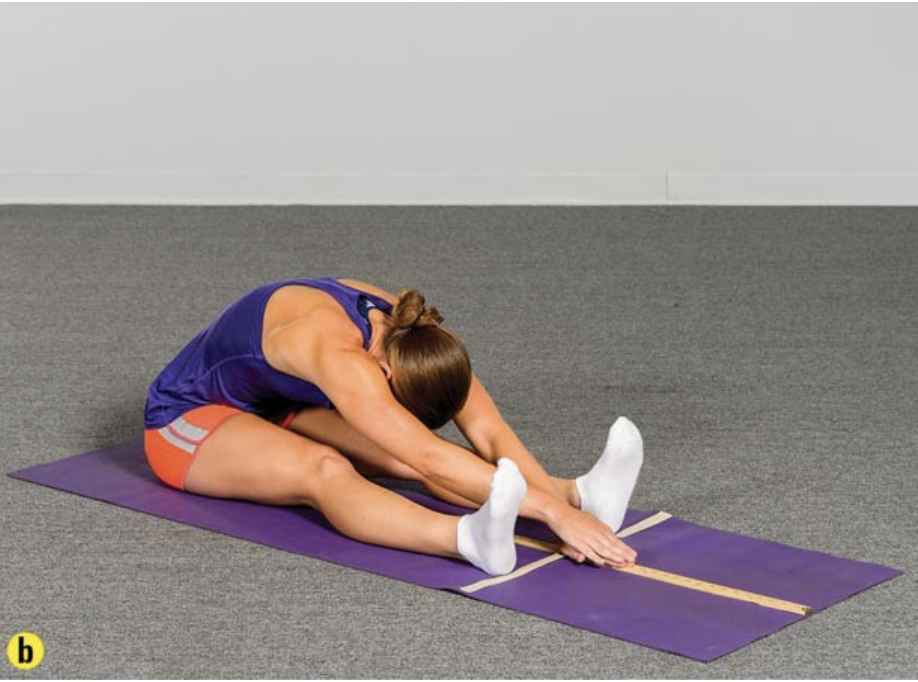

this is the _____ test
sit and reach
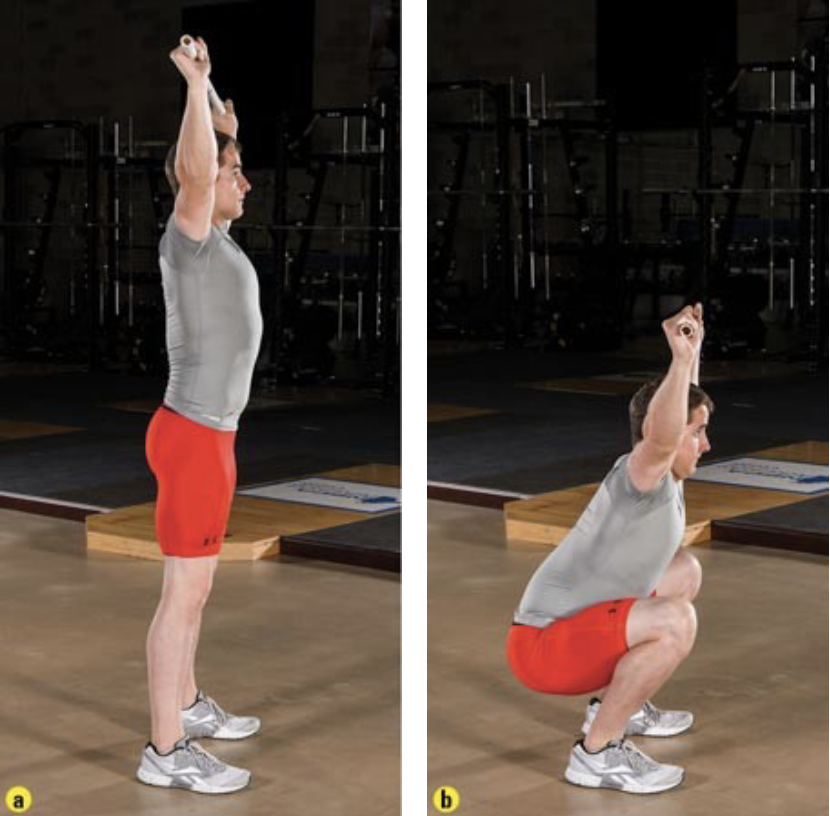

this is the _____
overhead squat