Exam 1 Kin 312
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
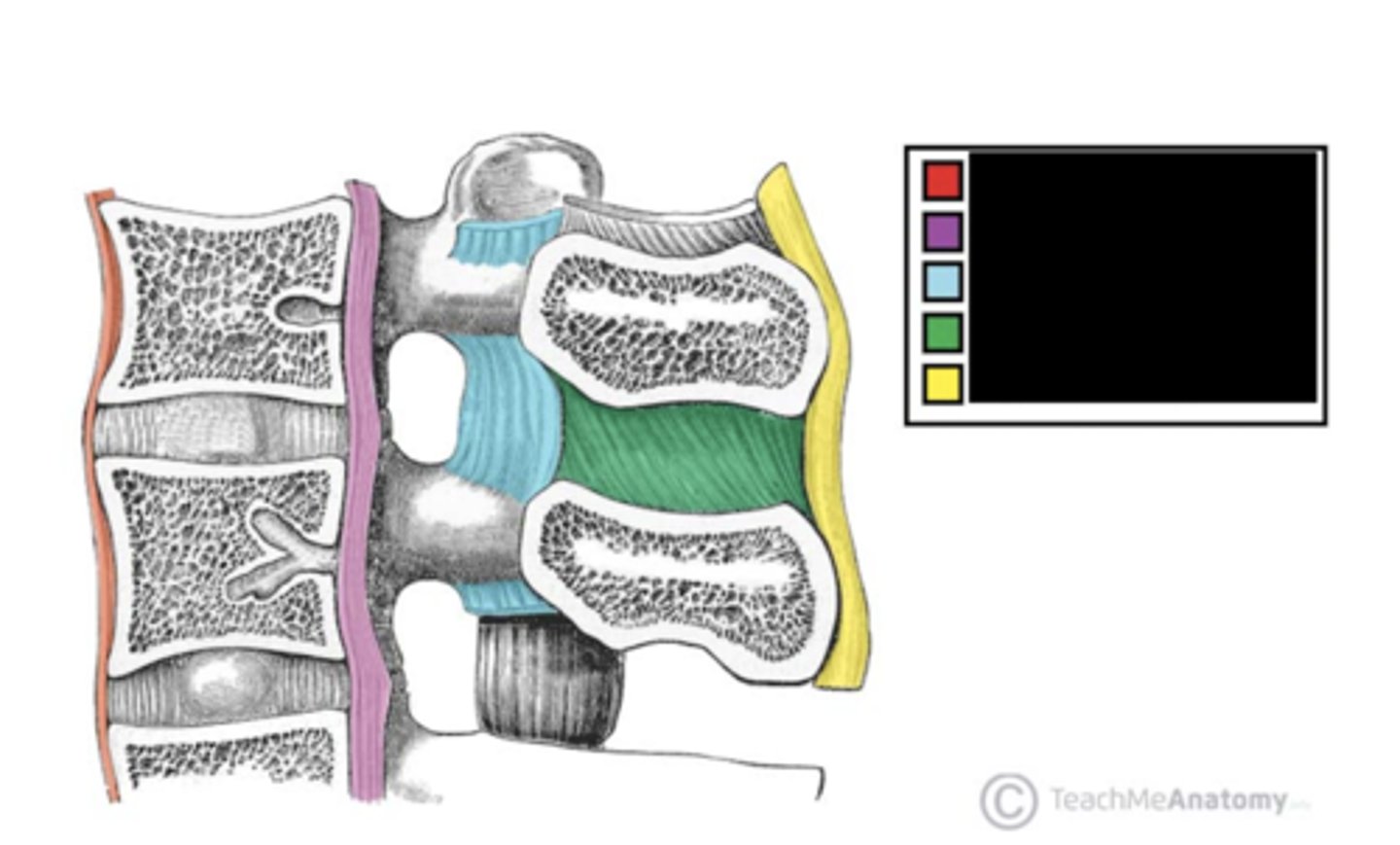
anterior longitudinal ligament
What is the part labeled red?
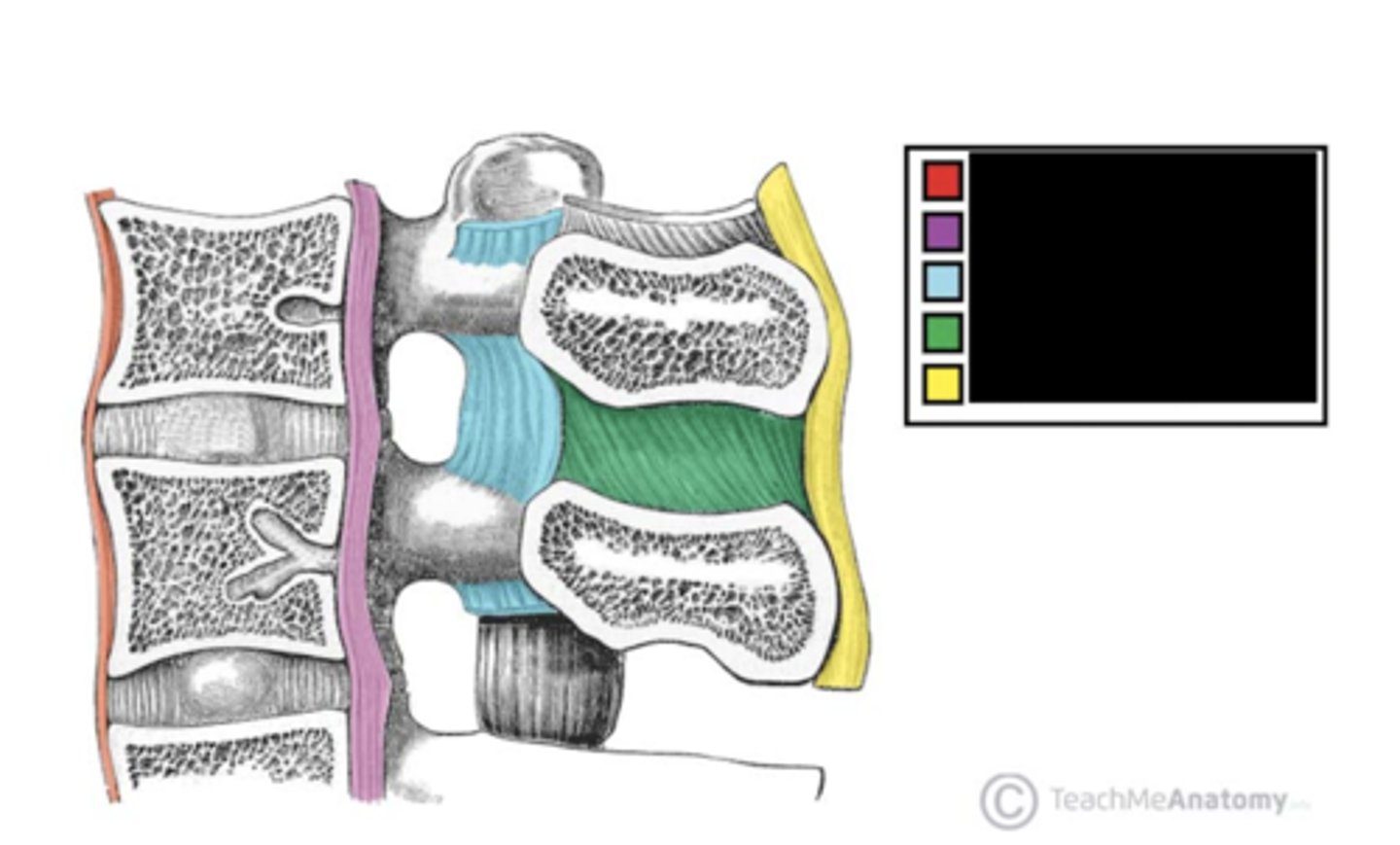
posterior longitudinal ligament
What is the part labeled purple?
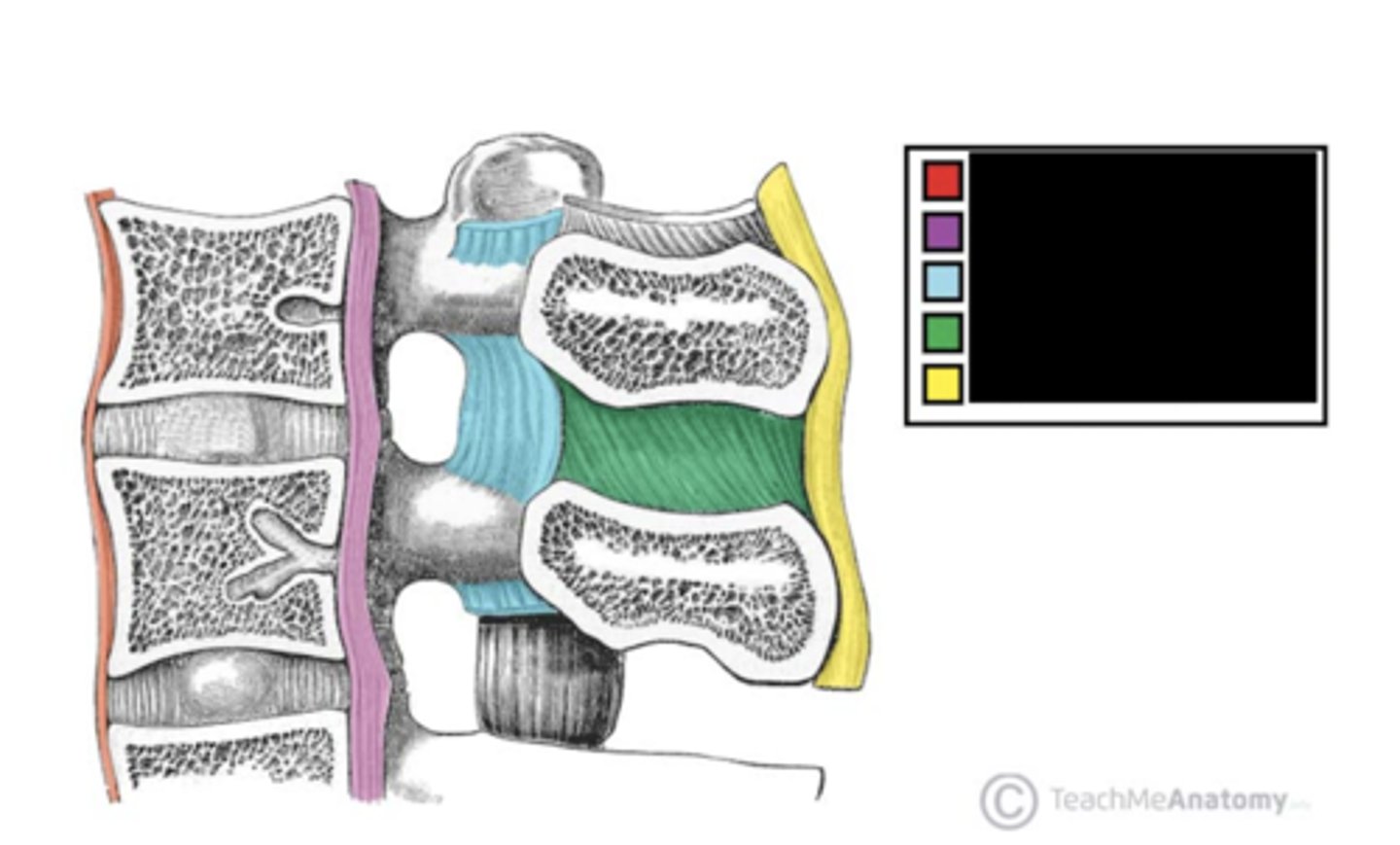
ligamenta flava ligament
What is the part labeled blue?
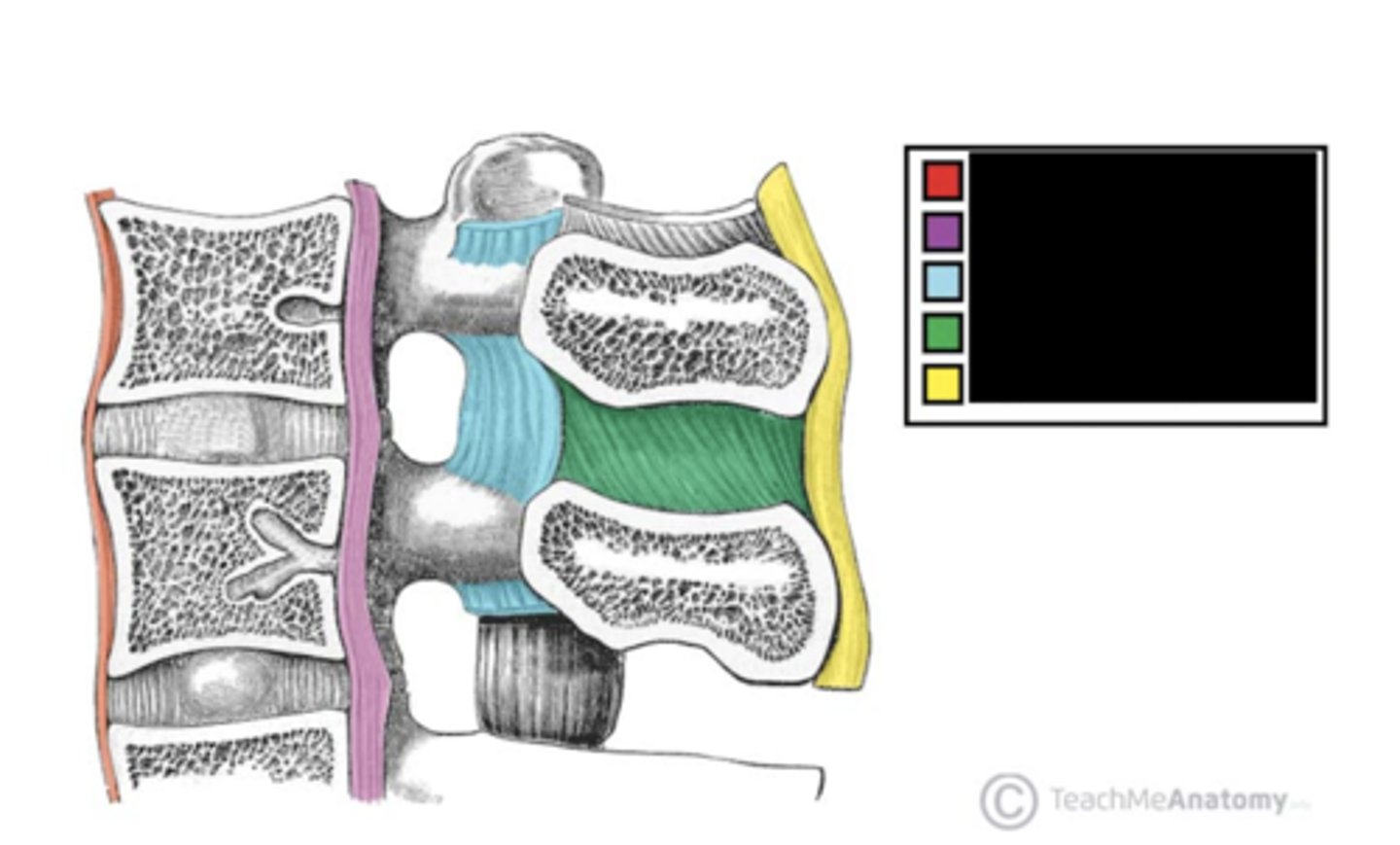
interspinous ligament
What is the part labeled green?
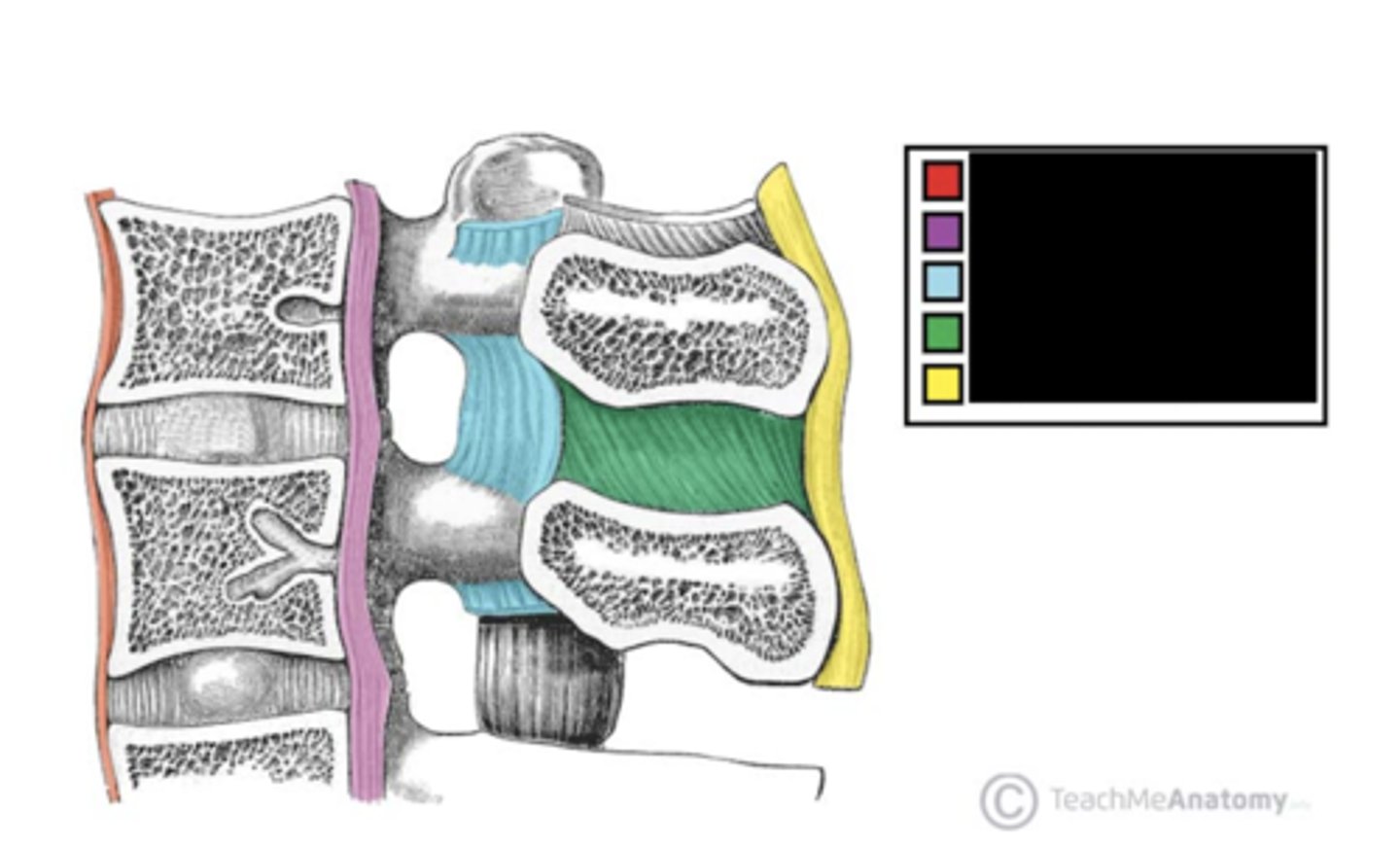
supraspinous ligament
What is the part labeled yellow?
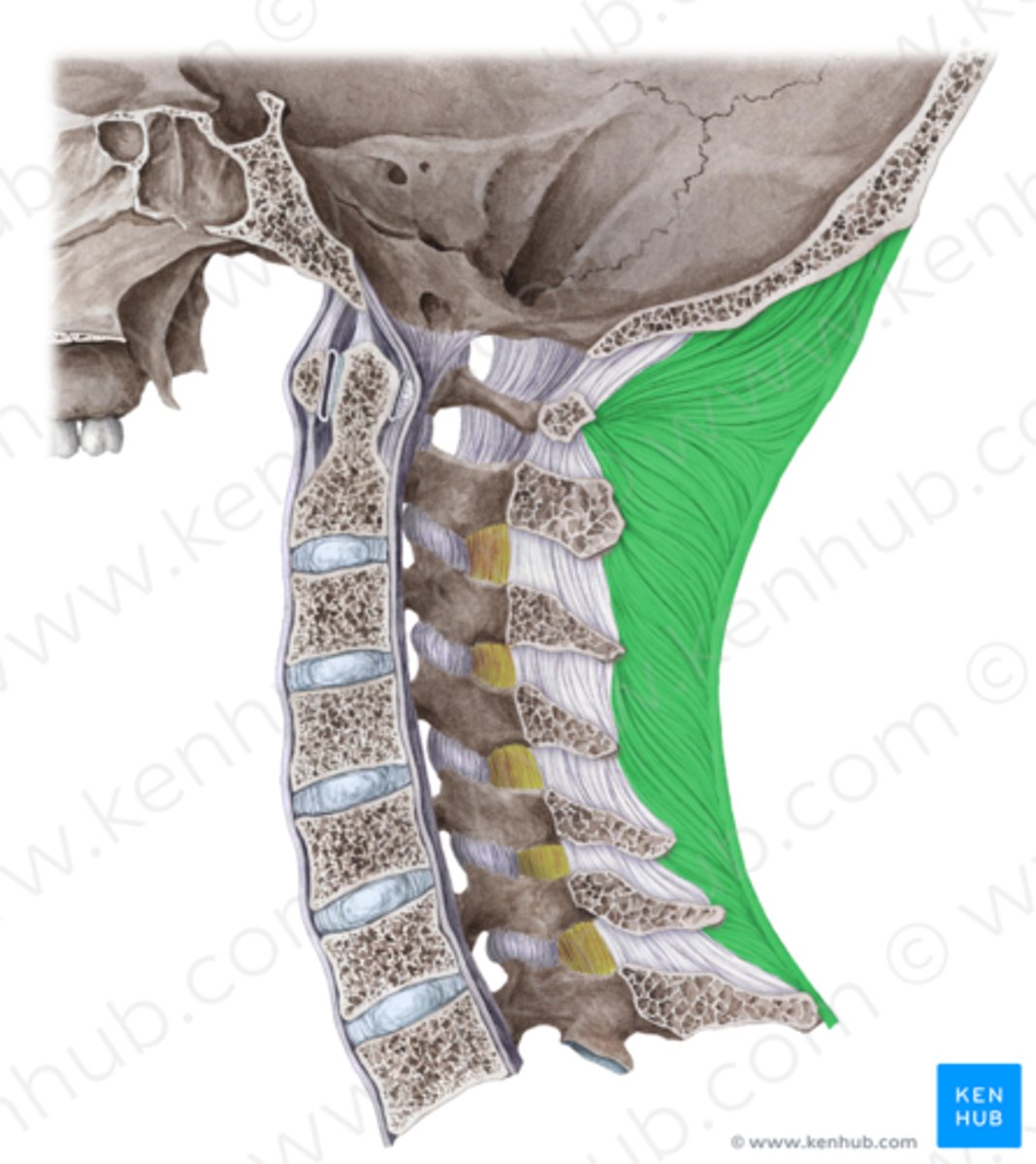
nuchal ligament
Helps to stabilize head and allows shoulders and head to be more independent. Allows improved balance during running
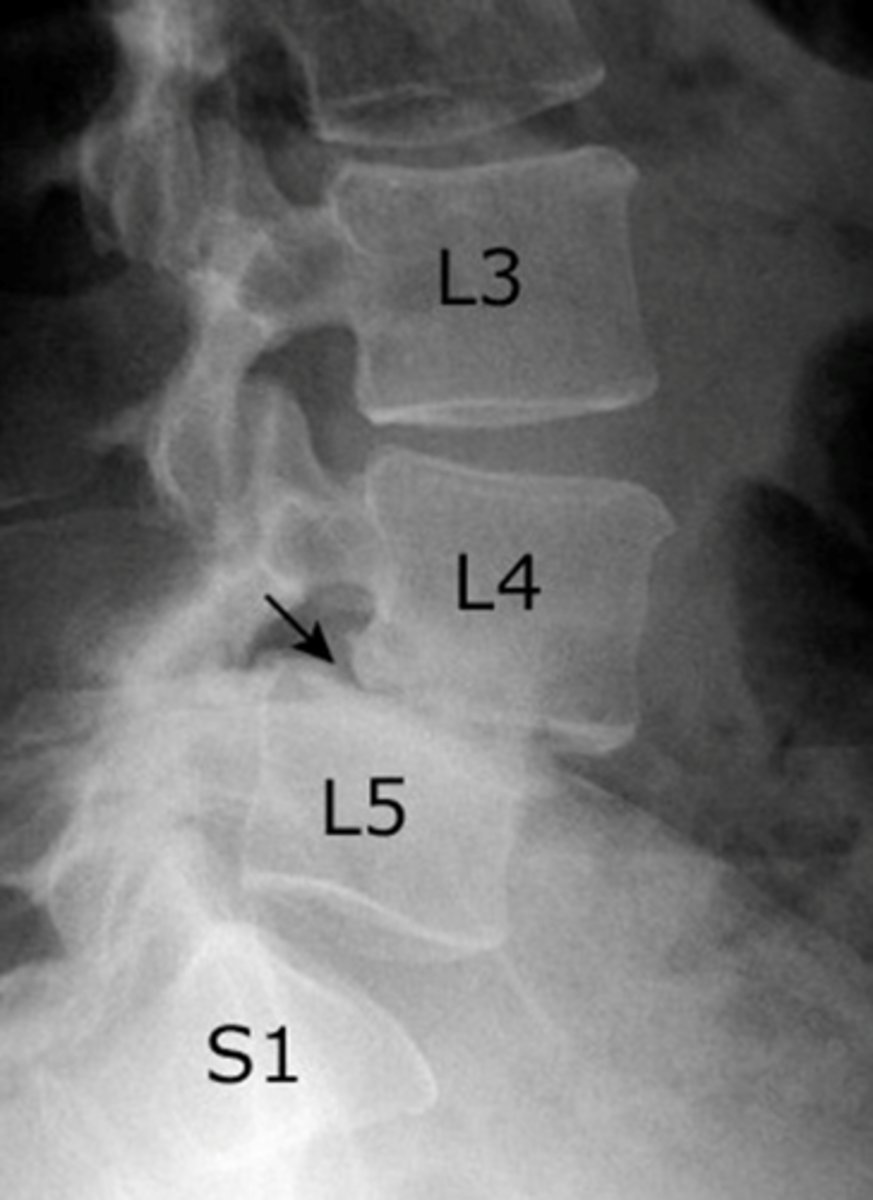
Spondylolysis
All degenerative conditions affecting the: Disks, Vertebral bodies, Associated joints of the lumbar spine
spondylolisthesis
forward slipping of one vertebra over another ( L4 & L5 or L5 & S1)
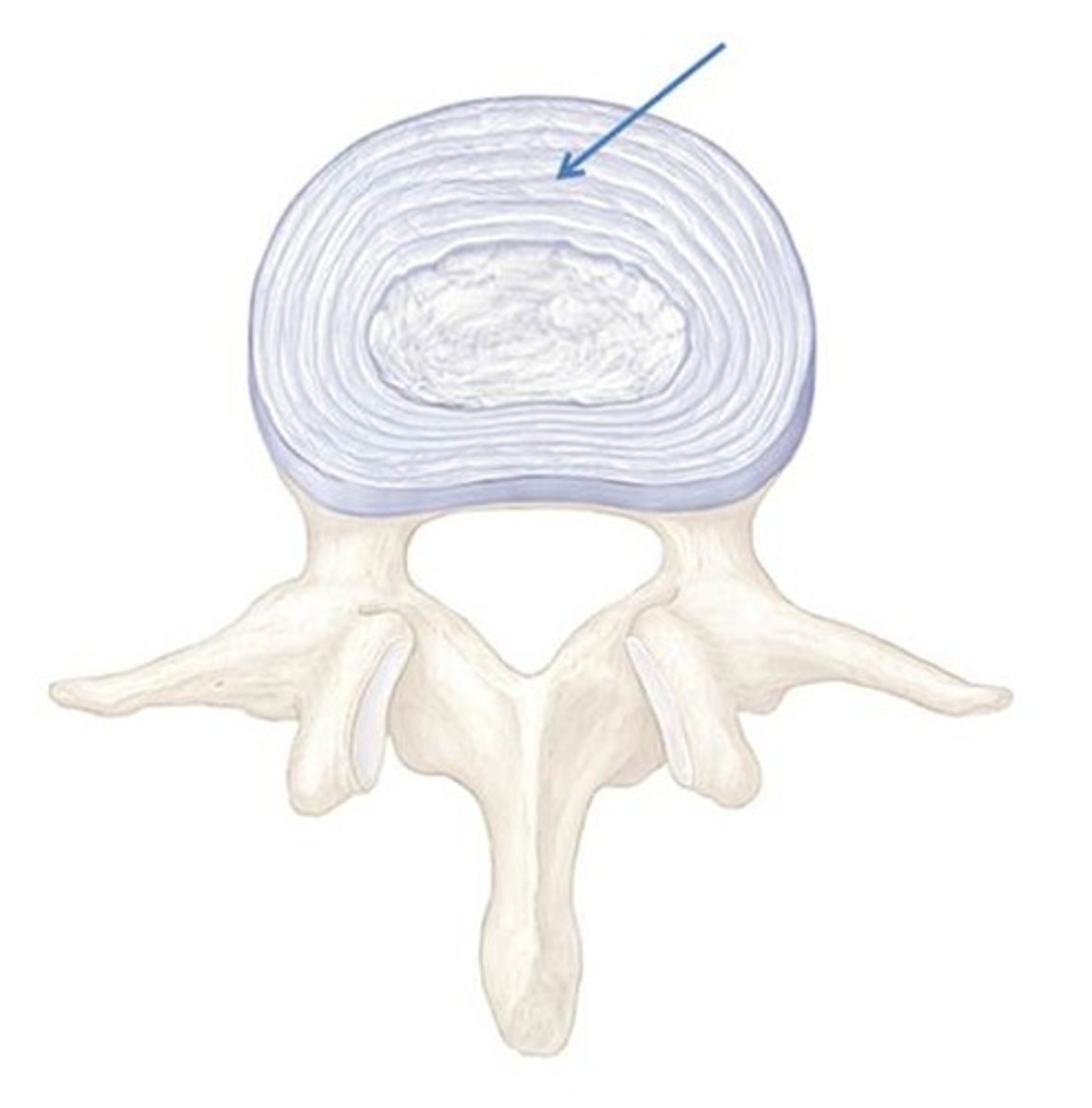
nucleus pulposus
the soft, fibrocartilaginous, central portion of intervertebral disk
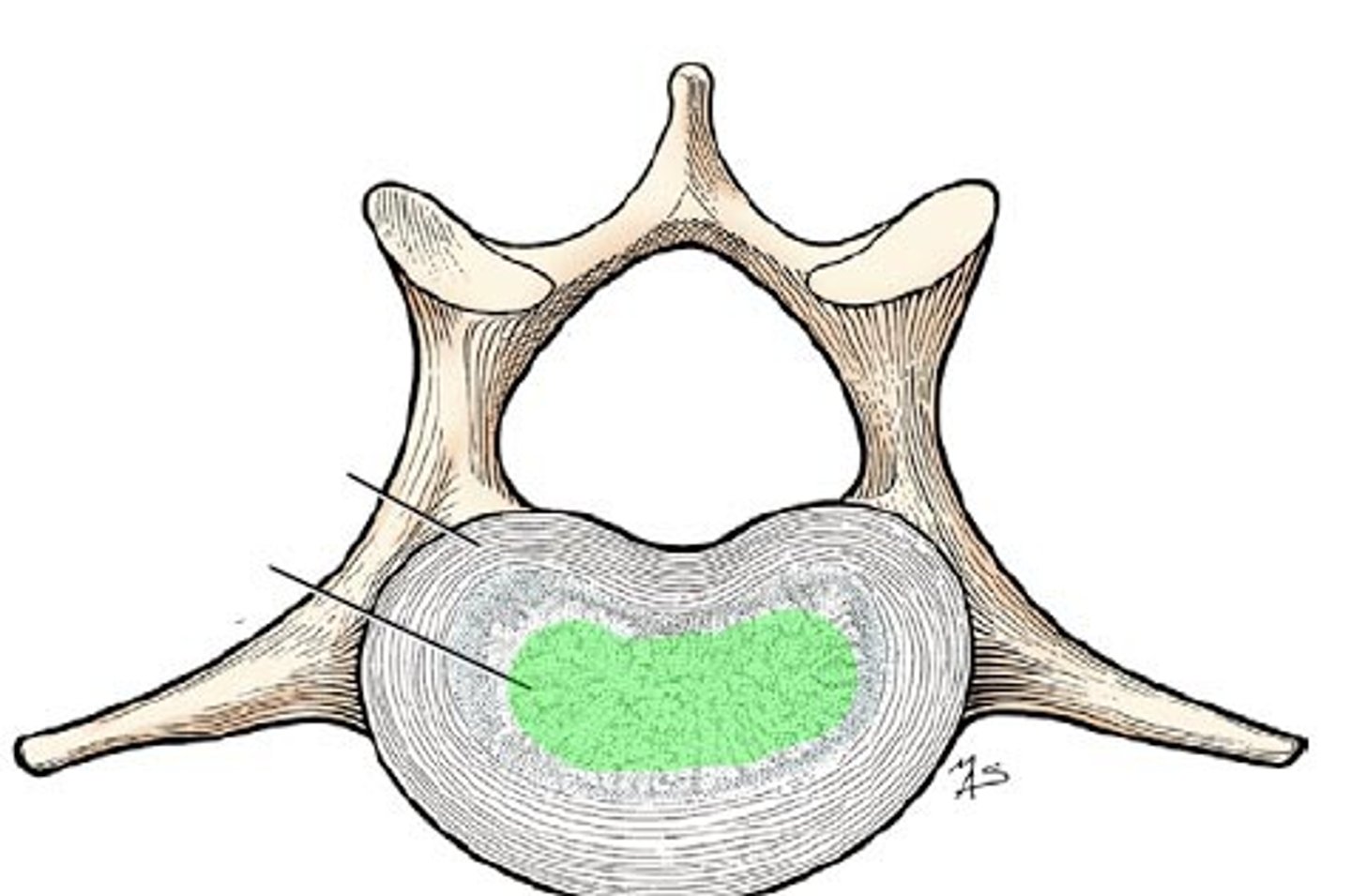
anulus fibrosus
outer collar composed of collagen and fibrocartilage
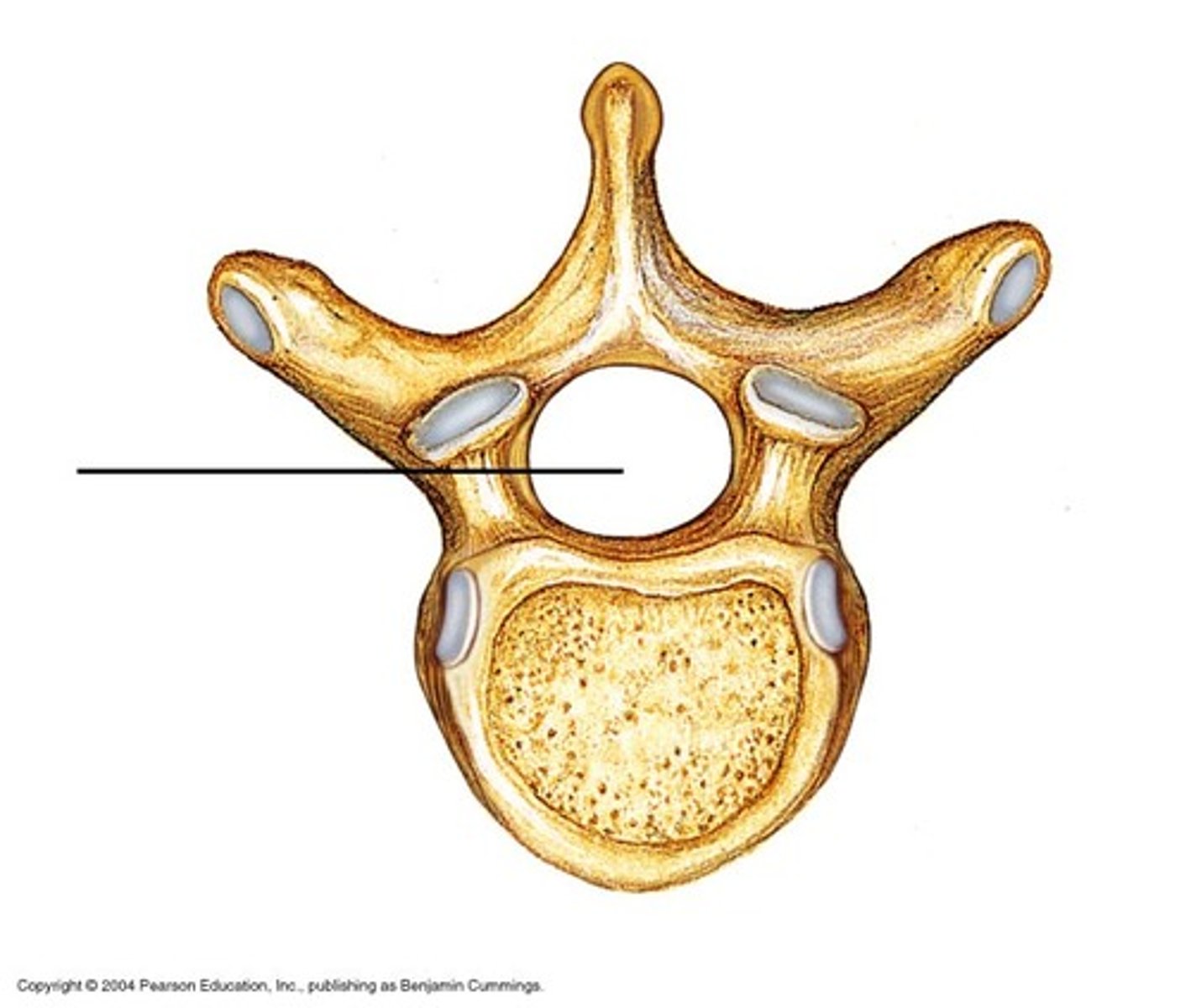
vertebral foramen
canal through which spinal cord passes
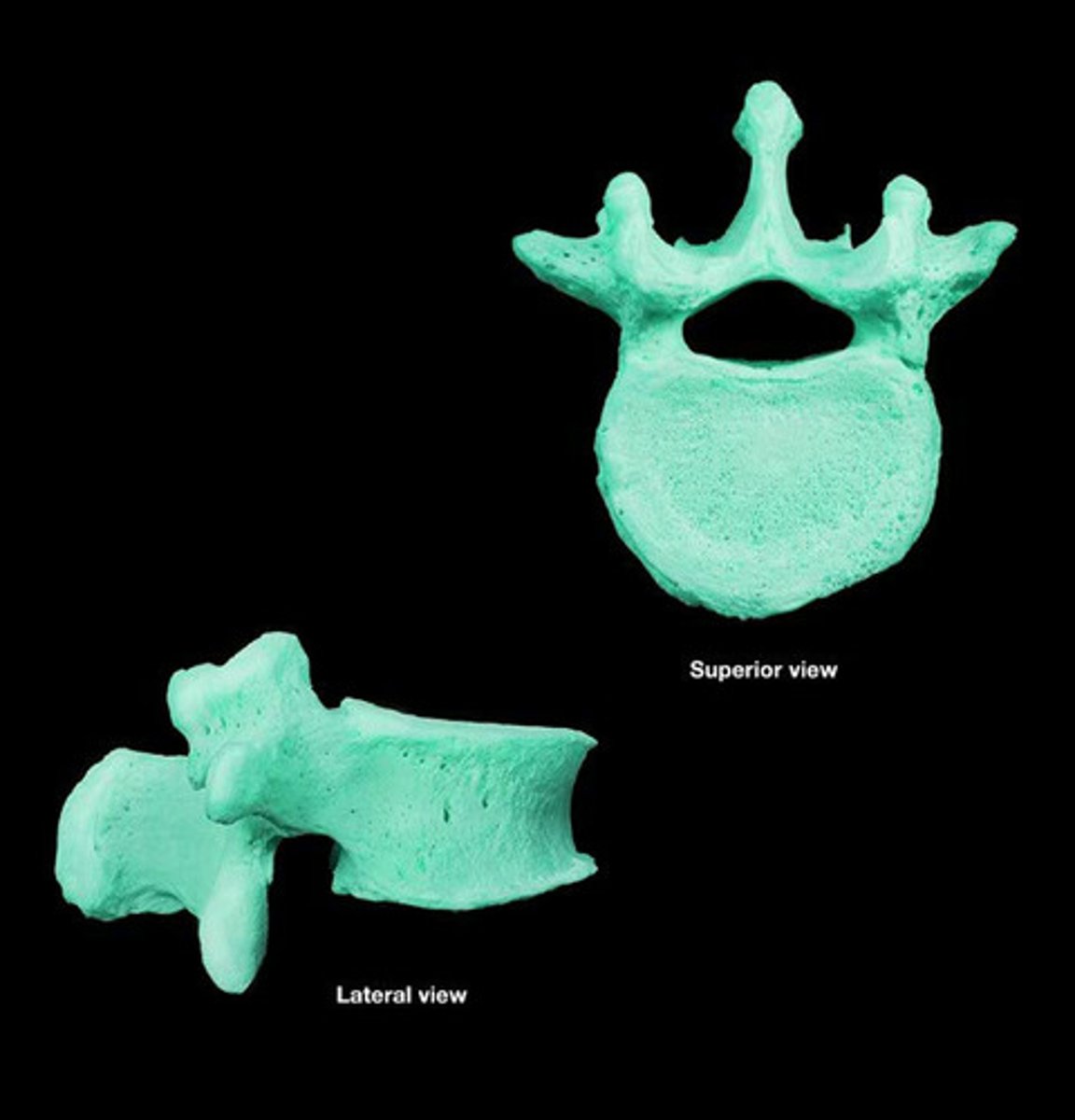
lumbar vertebrae
thoracic vertebrae
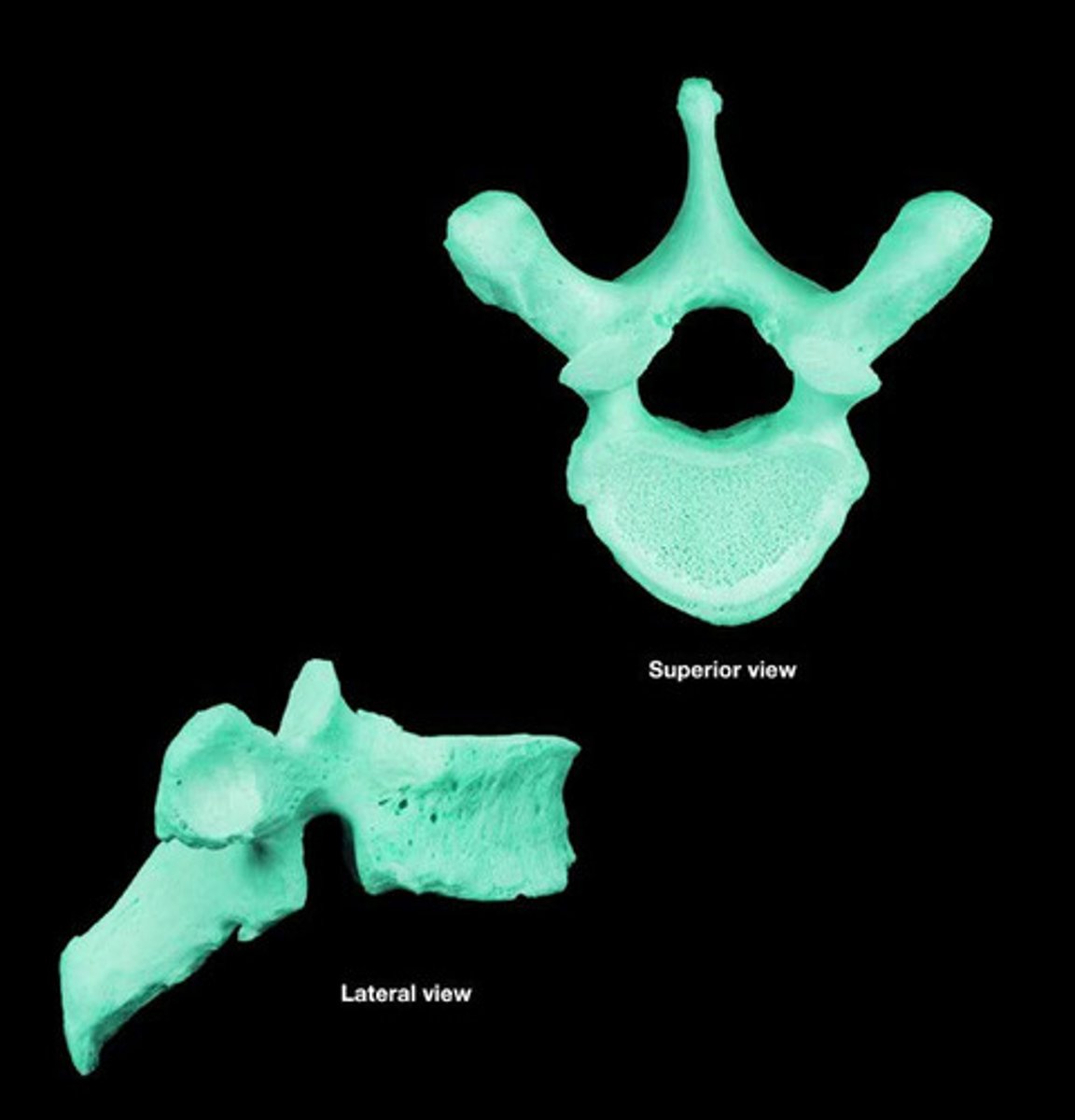
cervical vertebrae
True ribs (1-7)
have a direct attachment to the sternum via cartilage
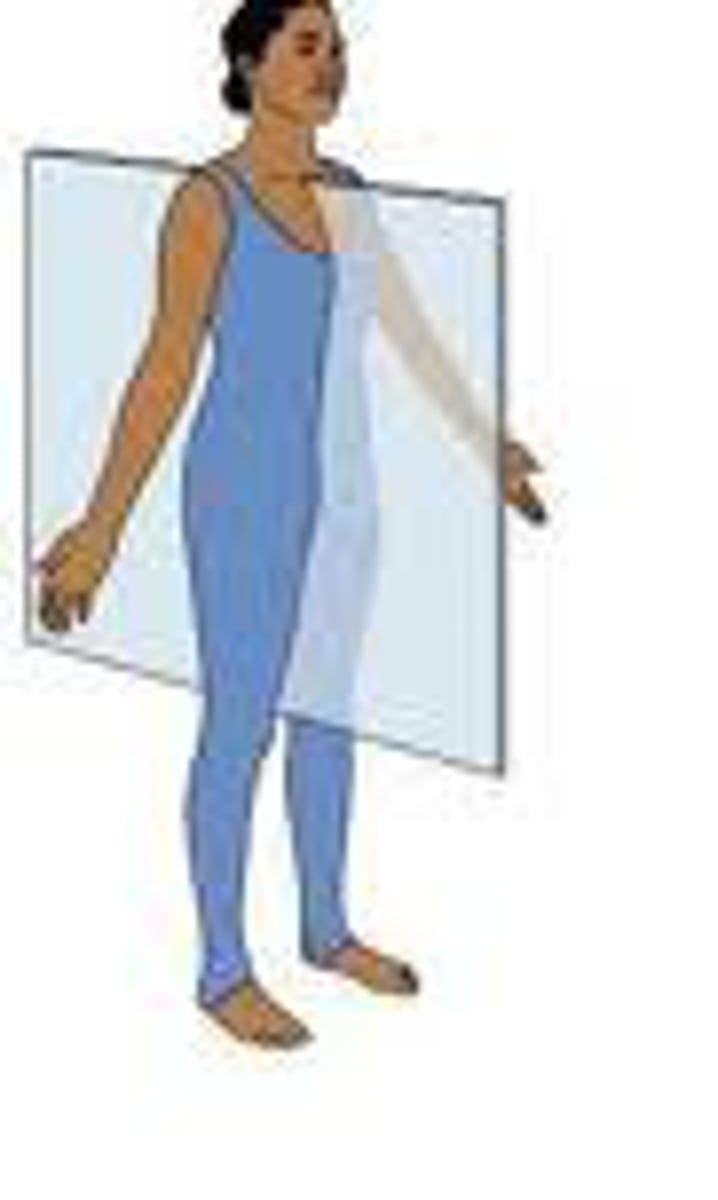
Ipsilateral
on the same side of the body
Contralateral
on the opposite side of the body
Saggital
divides body into left and right
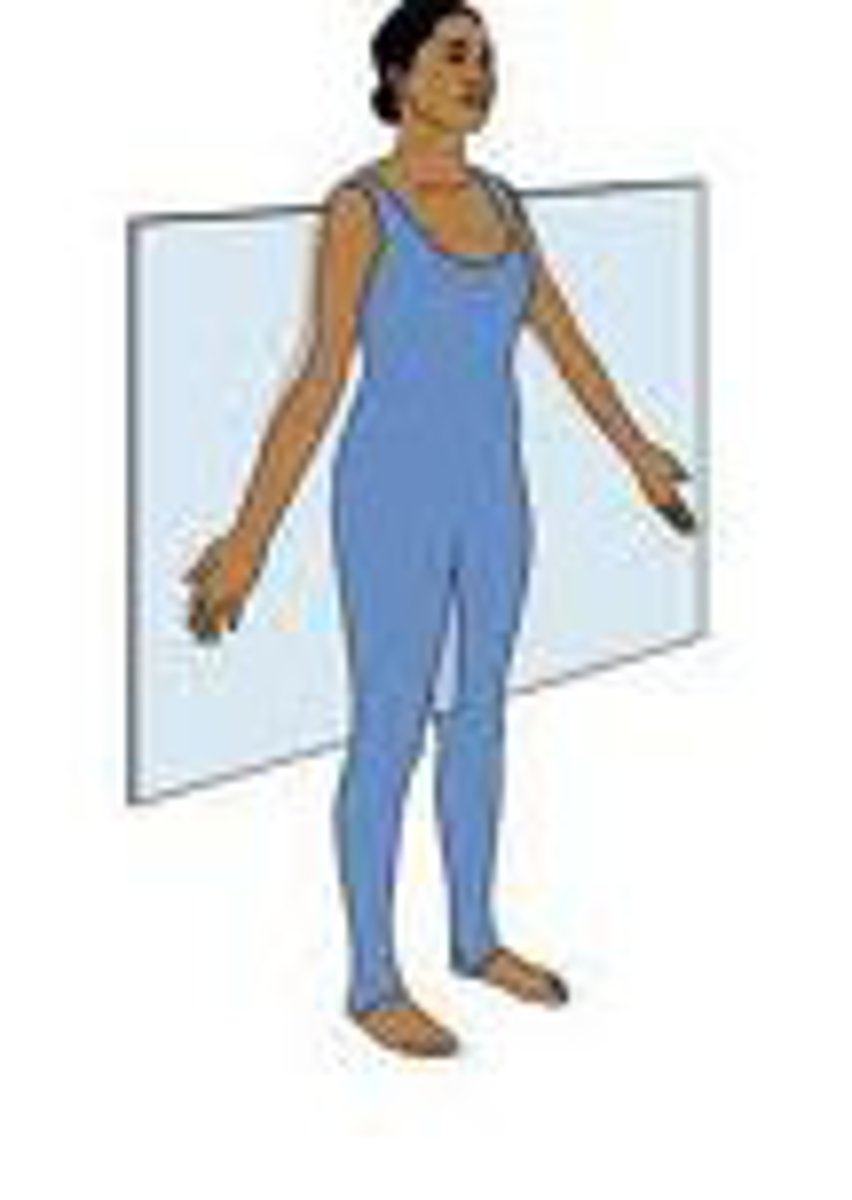
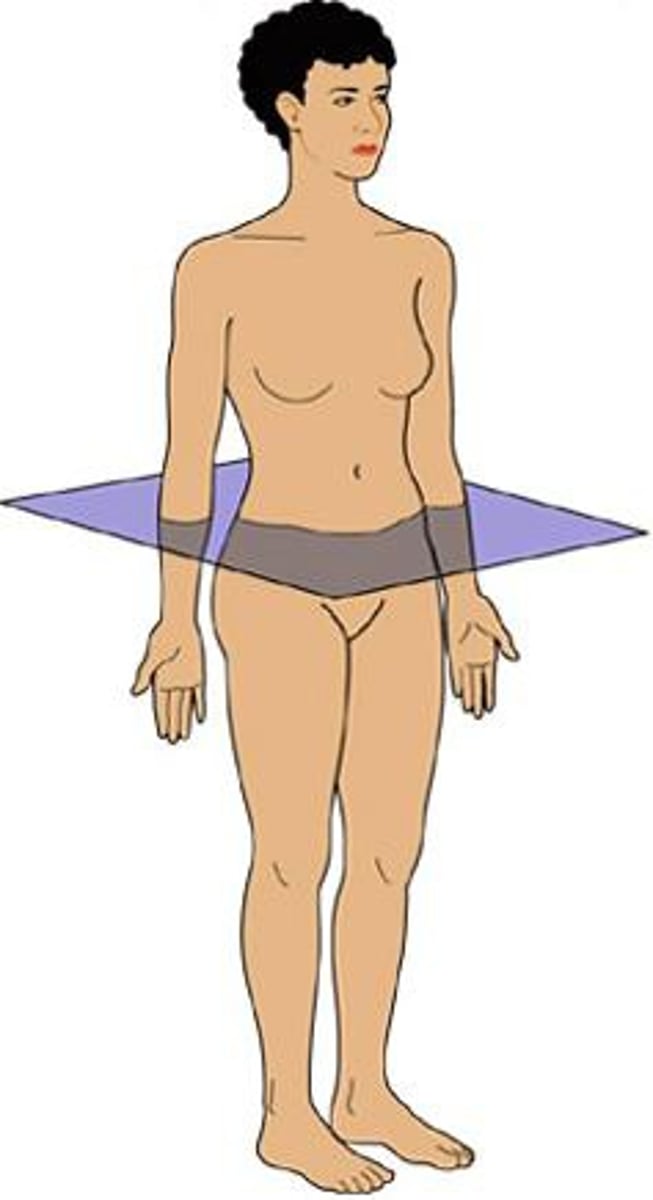
Frontal

transverse plane
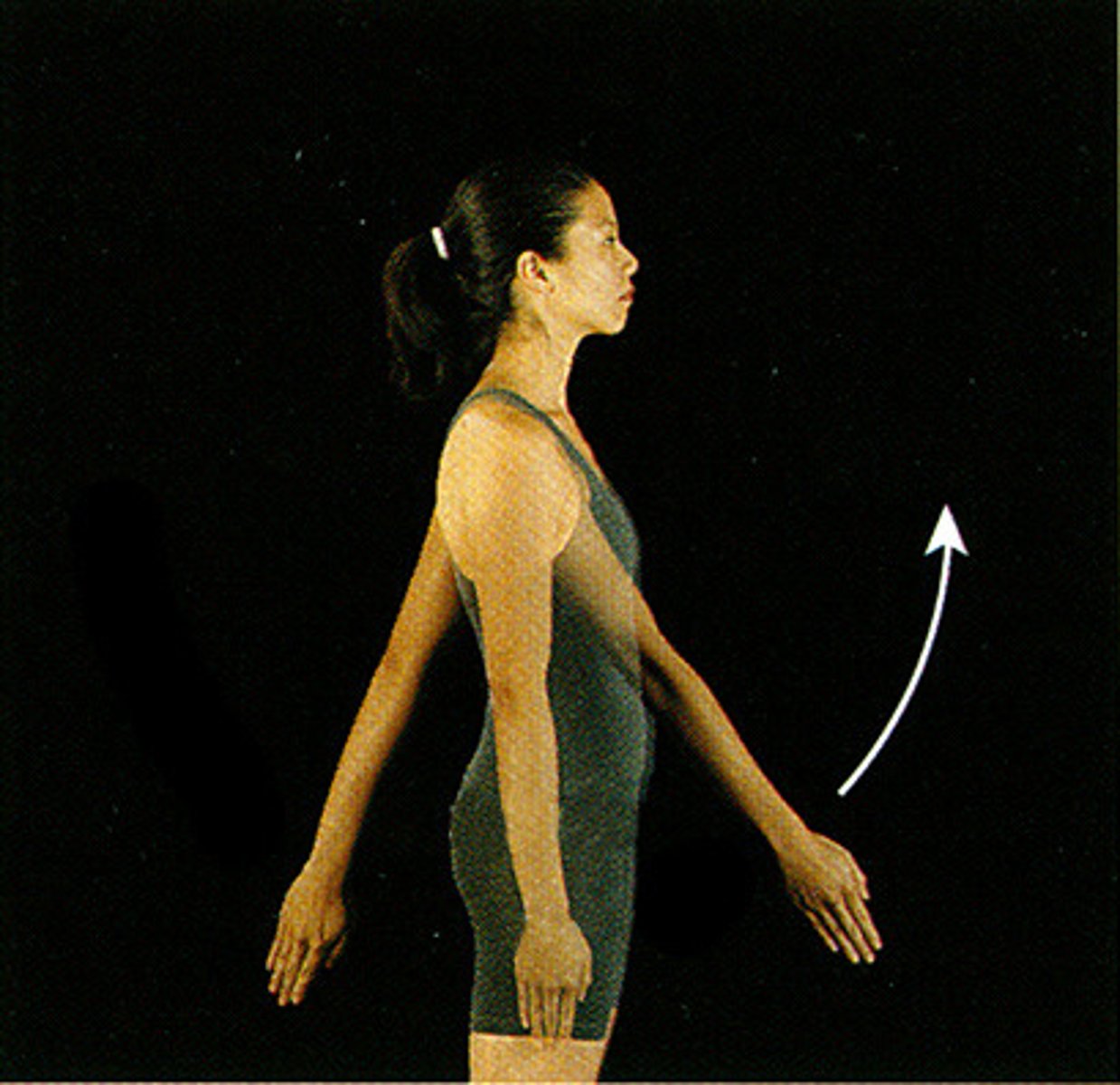
flexion of arm
what is this motion
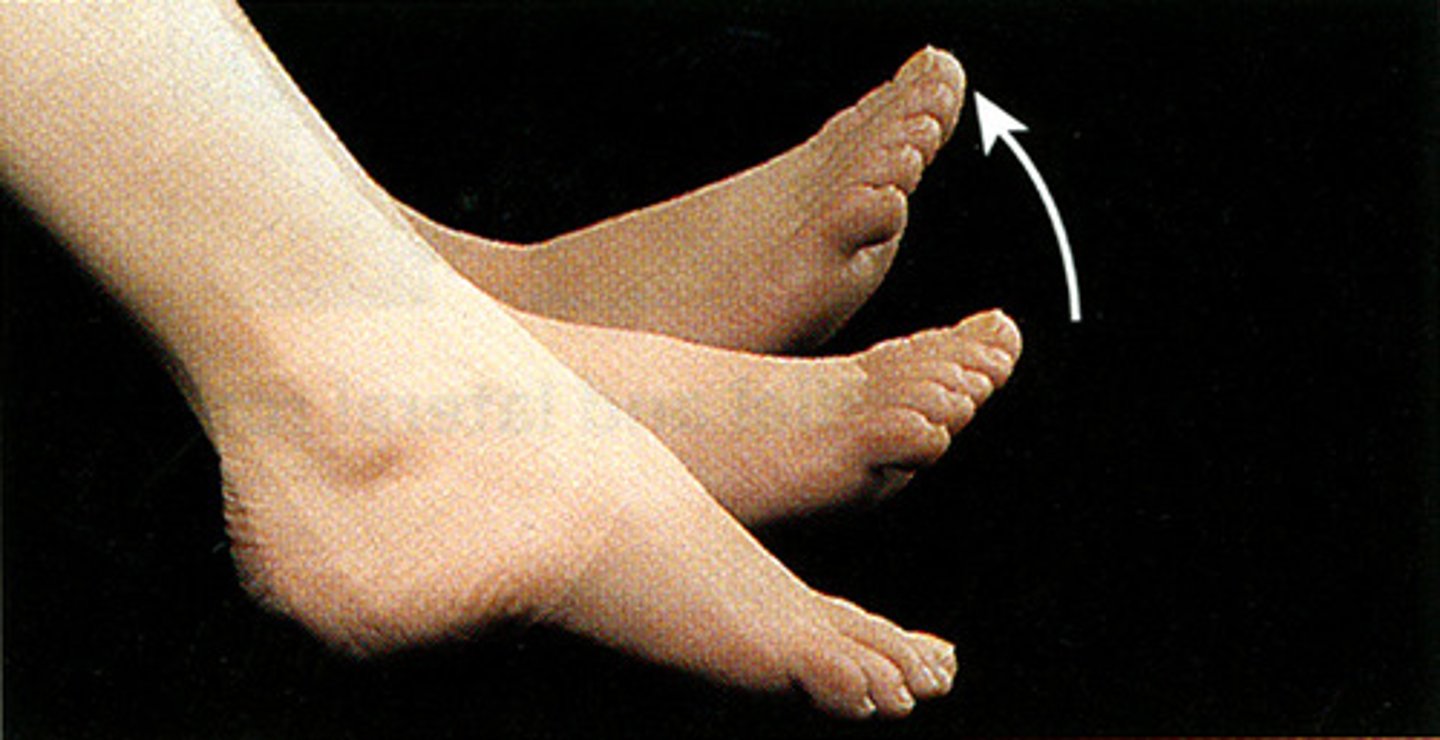
Dorsiflexion
bending of the foot or the toes upward
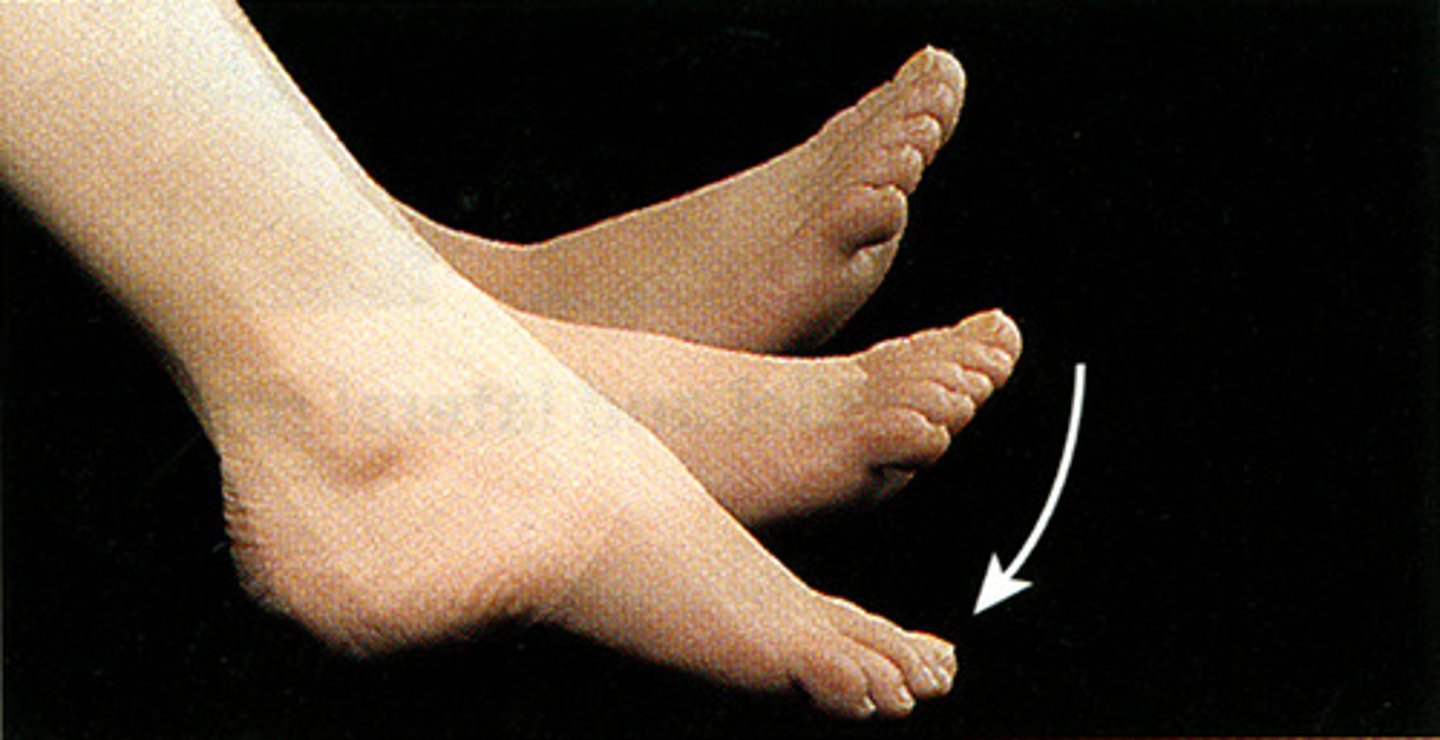
plantar flexion
bending of the sole of the foot by curling the toes toward the ground
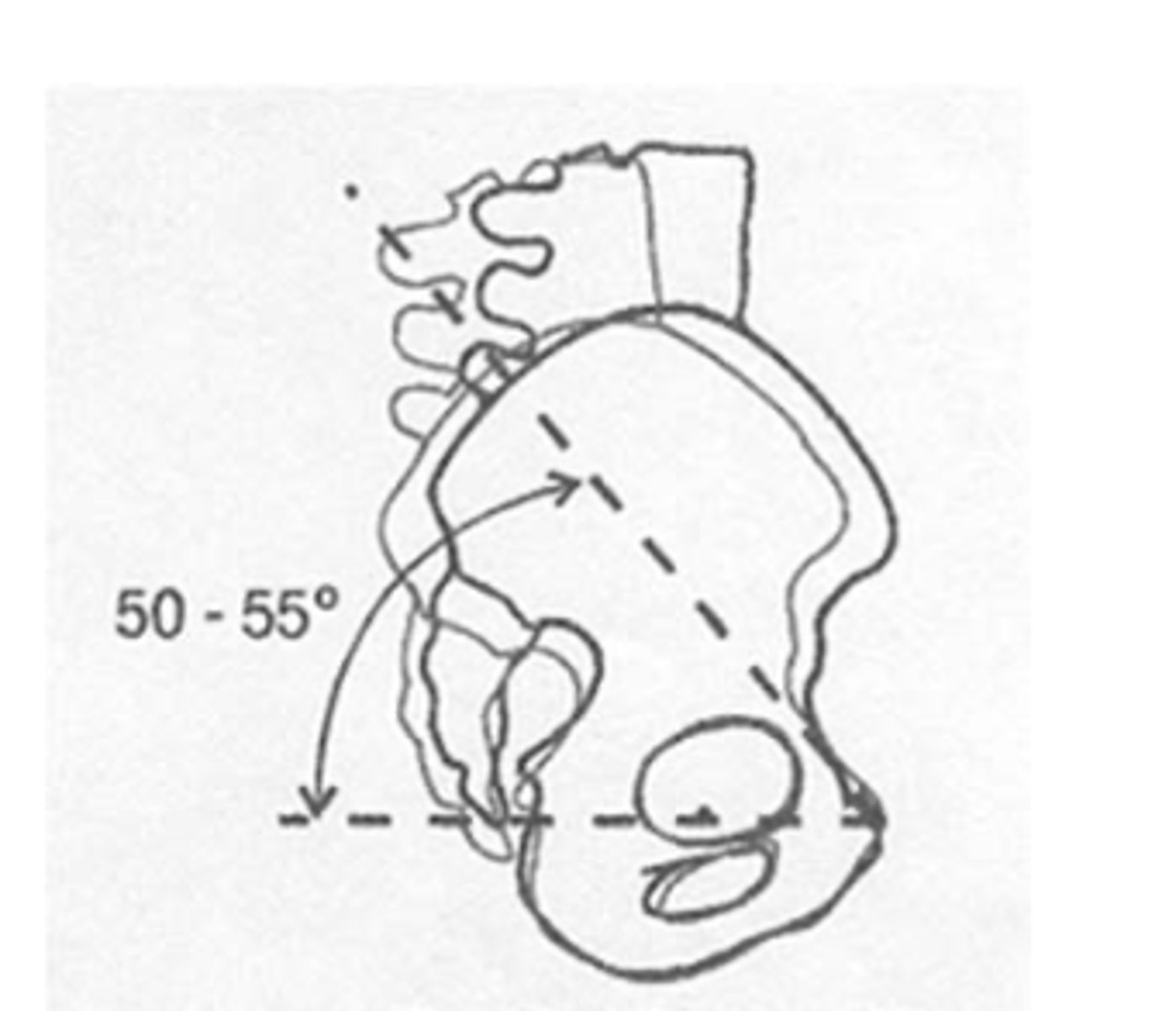
anterior tilt of pelvis
What is this?
posterior tilt of pelvis
What is this?
Abduction
Movement away from the midline of the body
Adduction
Movement toward the midline of the body
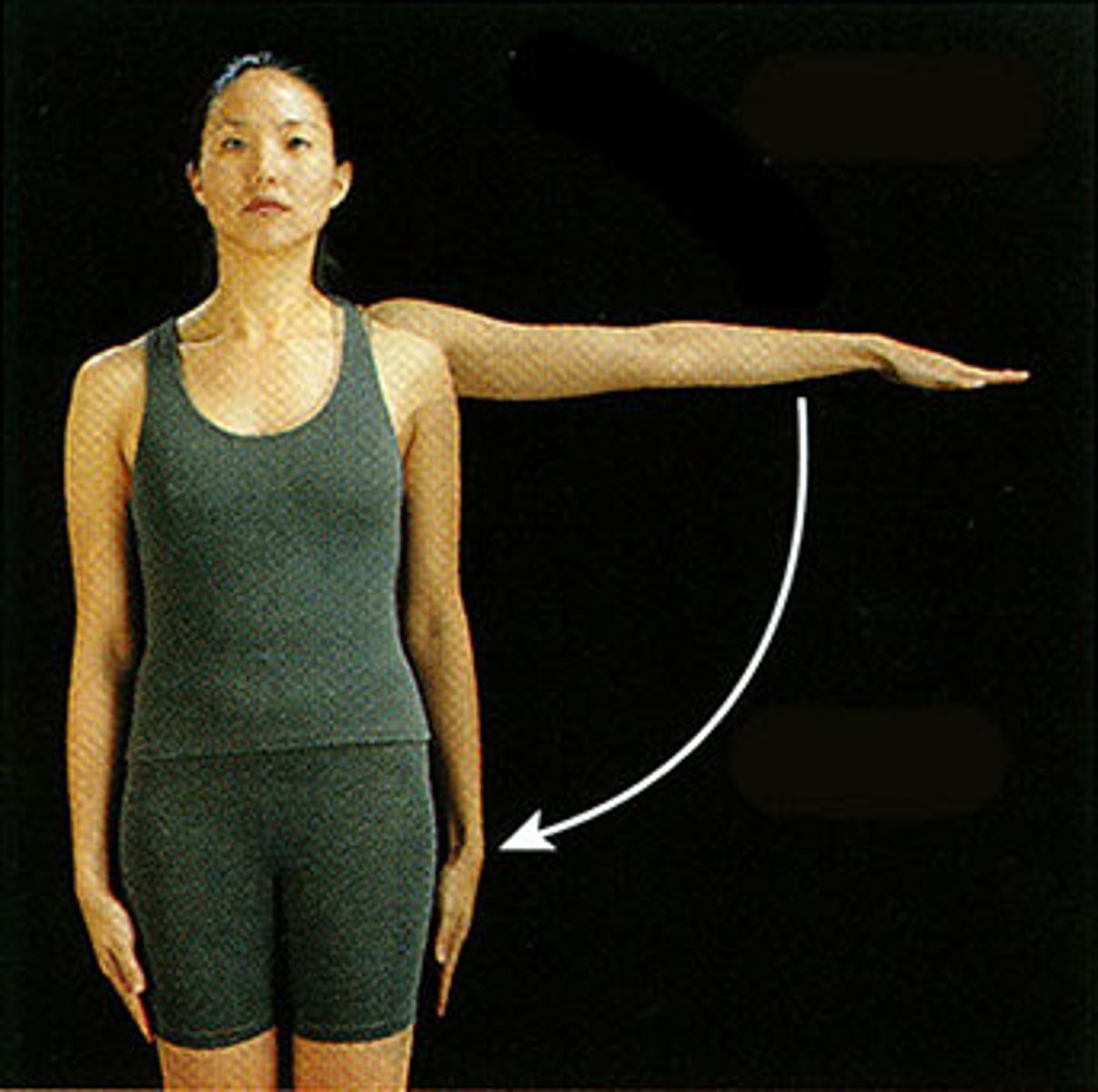

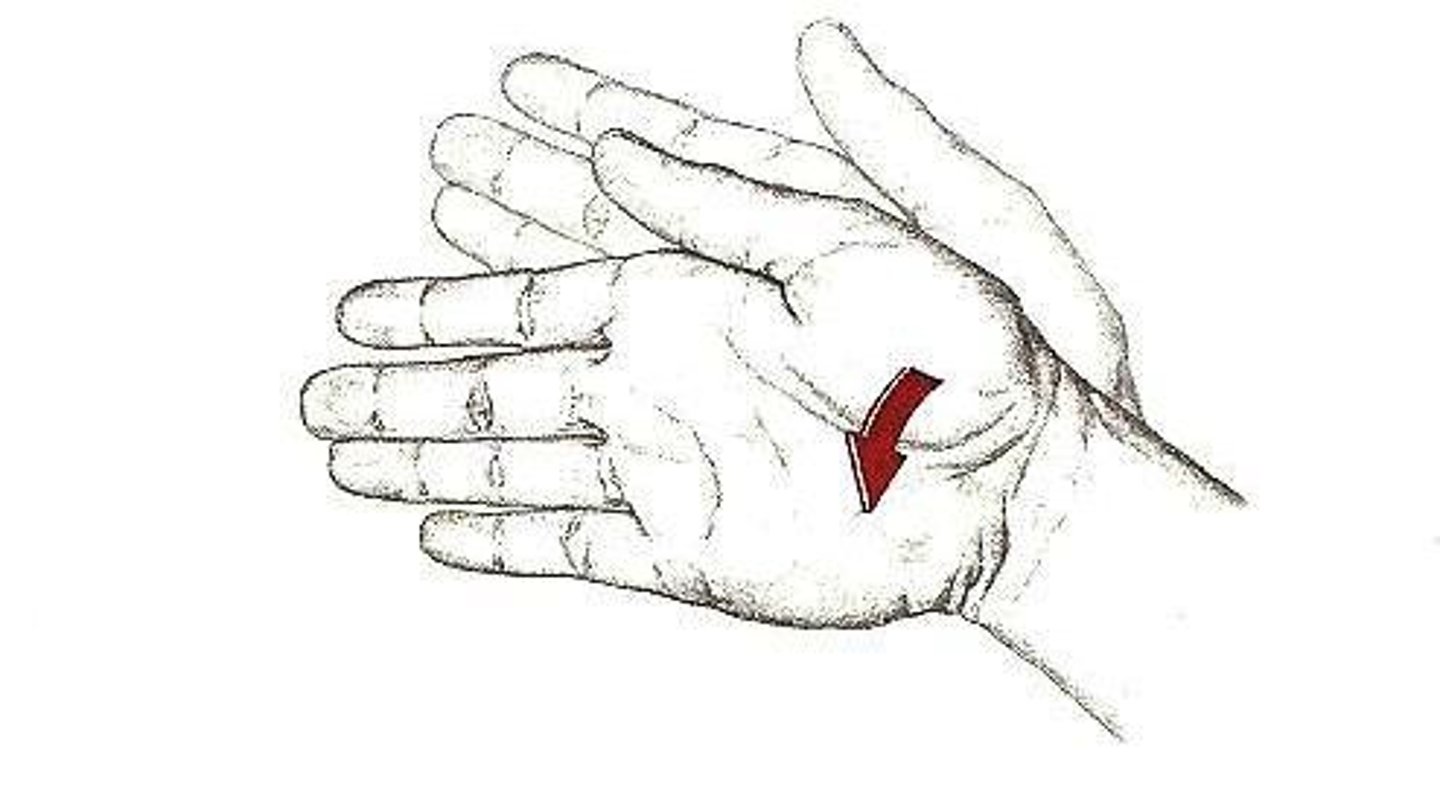
Ulnar flexion (ulnar deviation)
adduction movement at wrist of little finger side of hand toward forearm
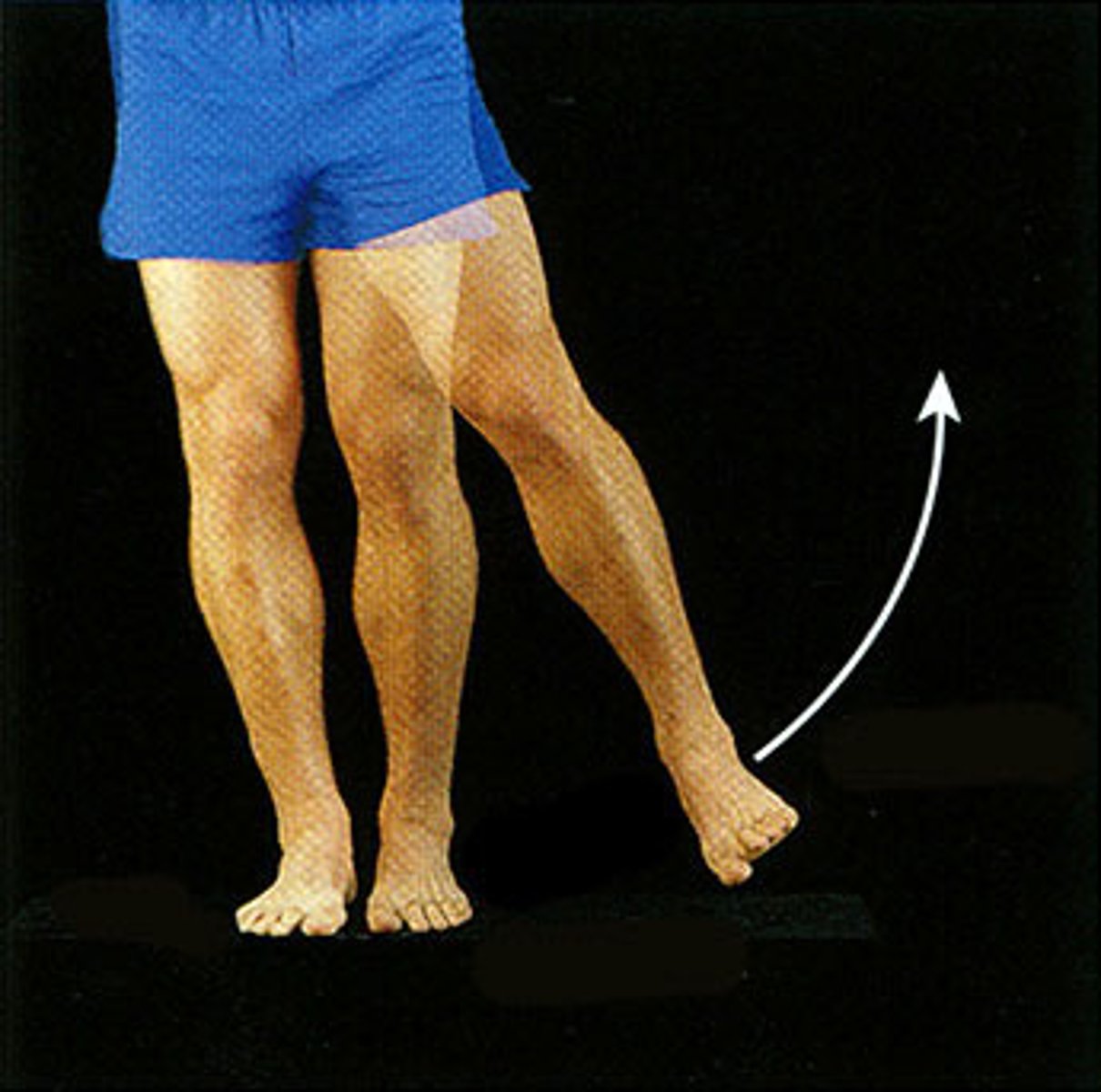
Radial flexion (radial deviation)
abduction movement at the wrist of thumb side of hand toward the forearm
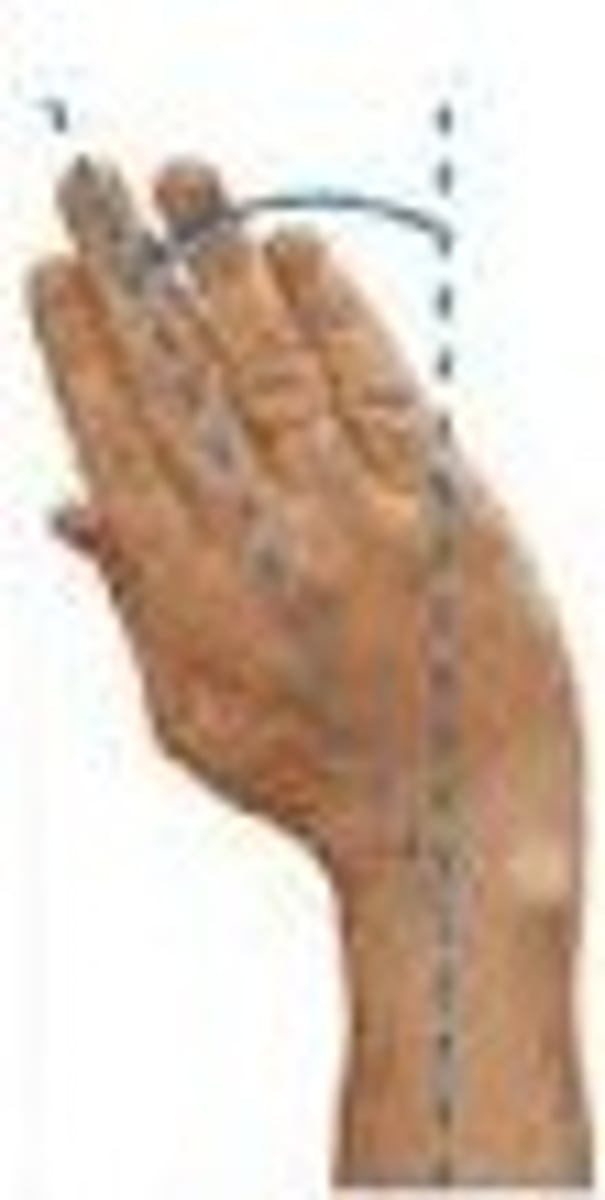

finger adduction
What is this?
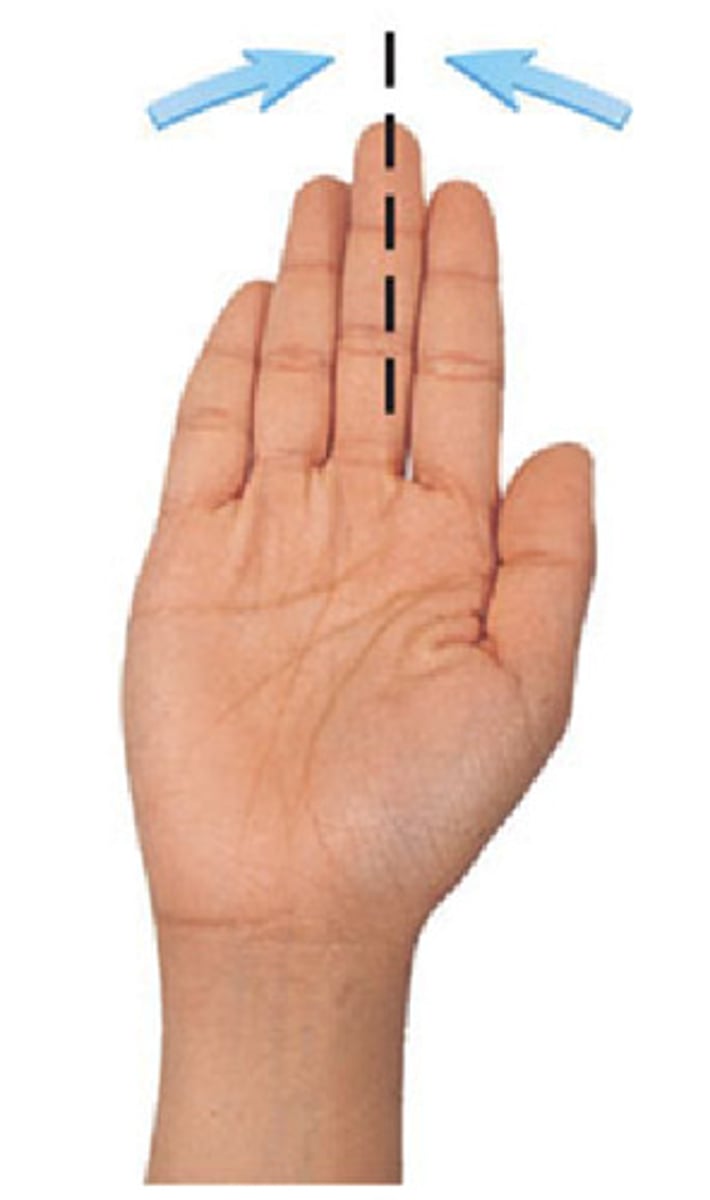

Foot Inversion
What is this?
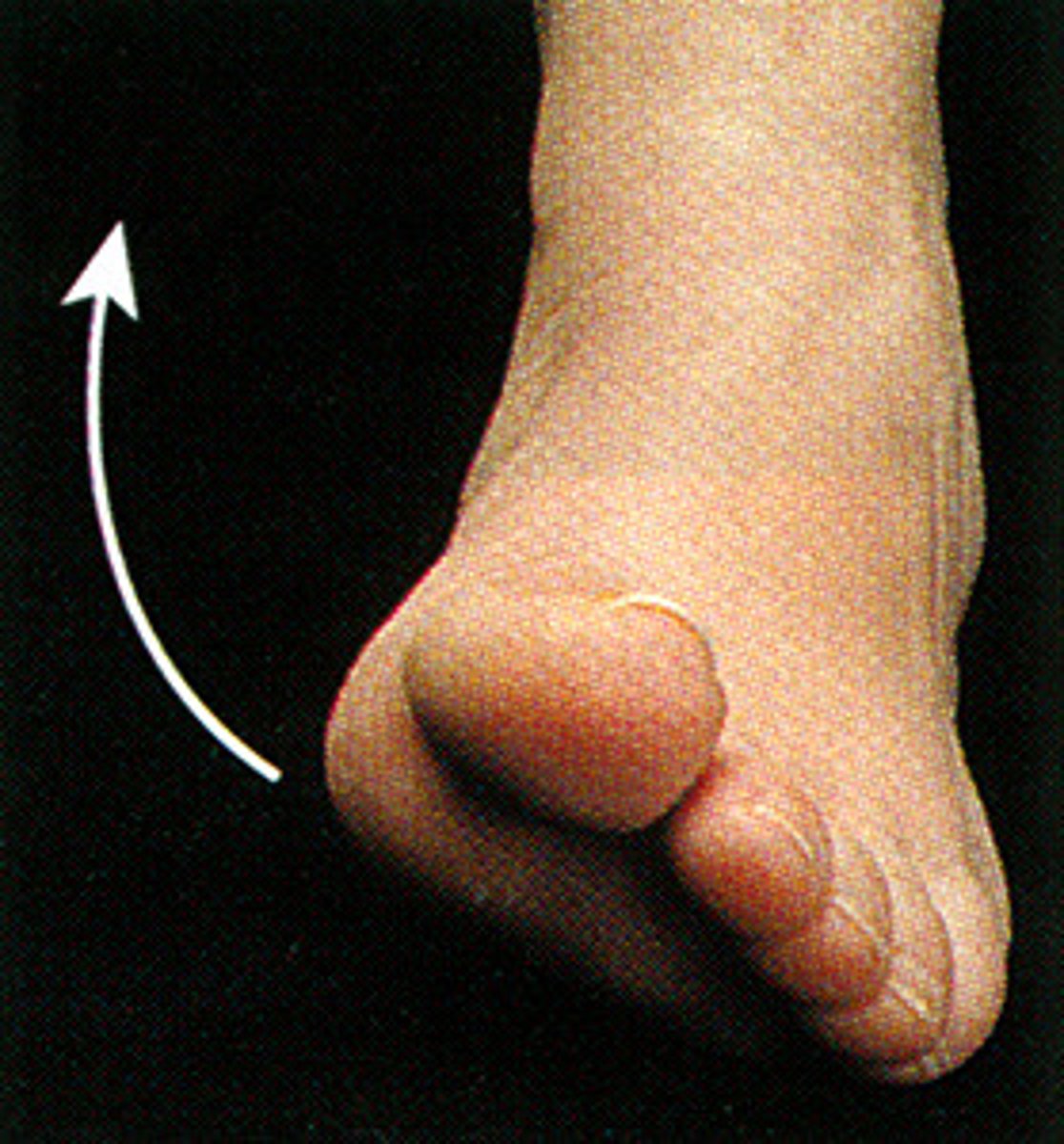
foot eversion
What is this?
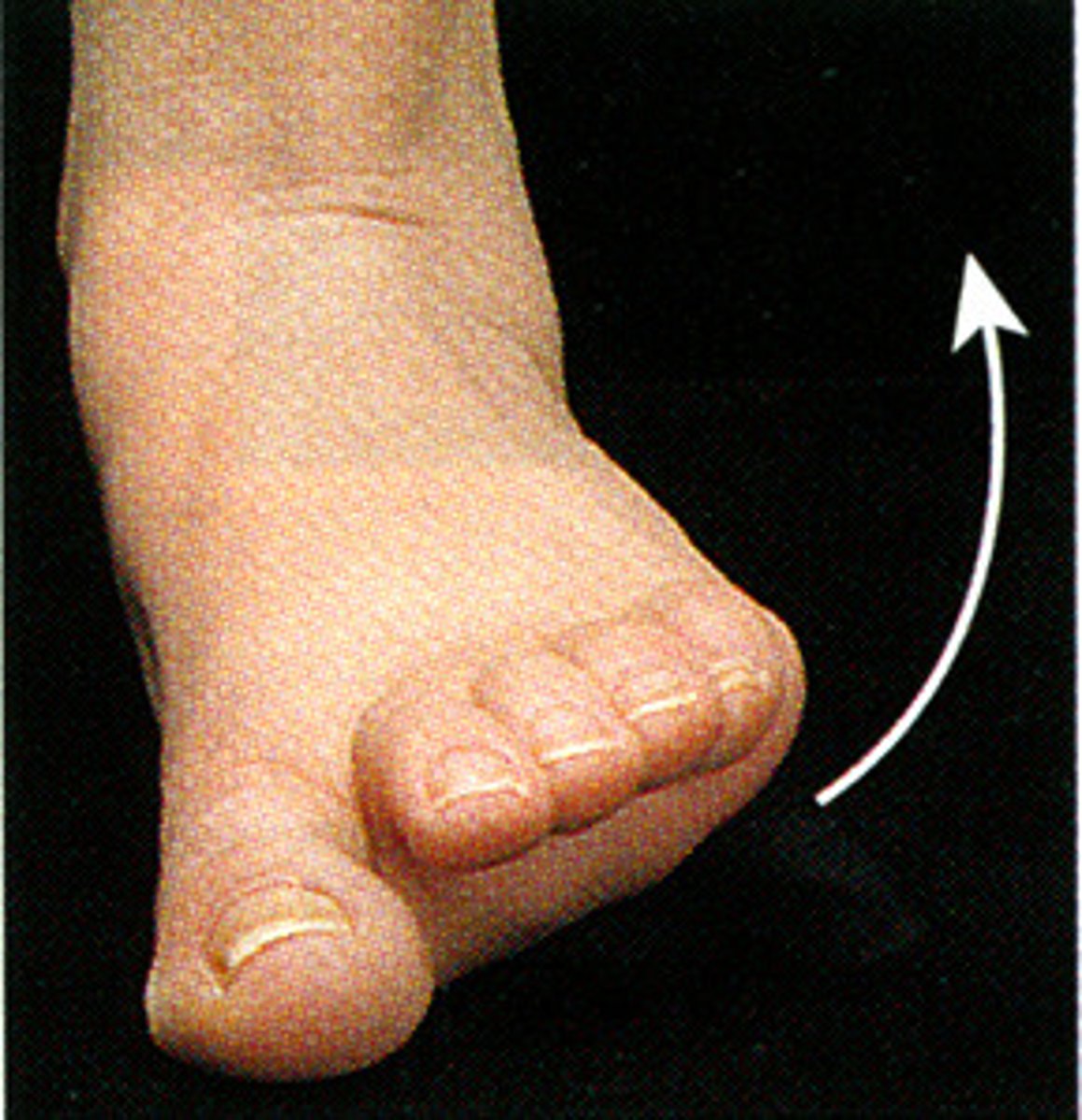
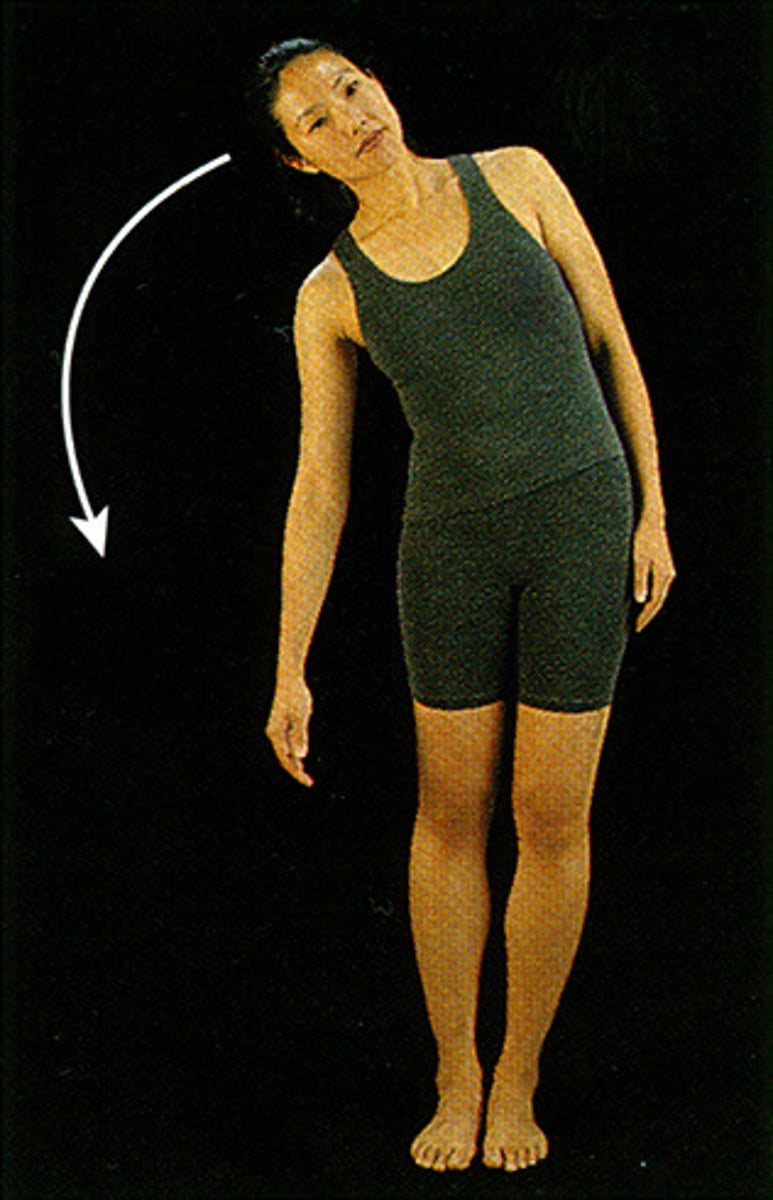
lateral flexion of trunk
What is this?
scapular plane
In line with the normal resting position of the scapula as it lies on the posterior rib cage; movements in the scapular plane are in line with the scapular, which is at an angle of 30 to 45 degrees from the frontal plane
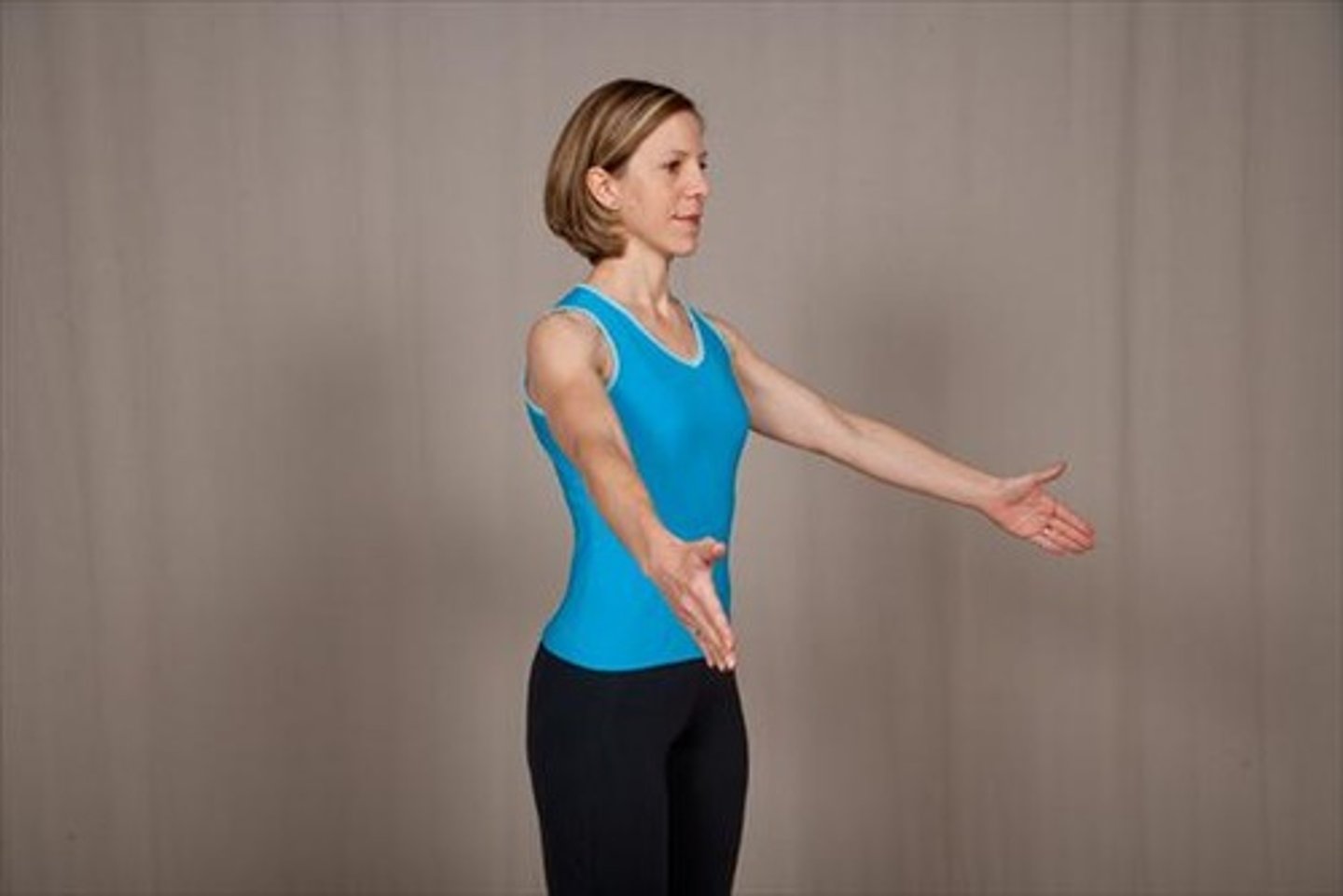

Pronation of the foot
A combination of dorsiflexion, eversion, and abduction
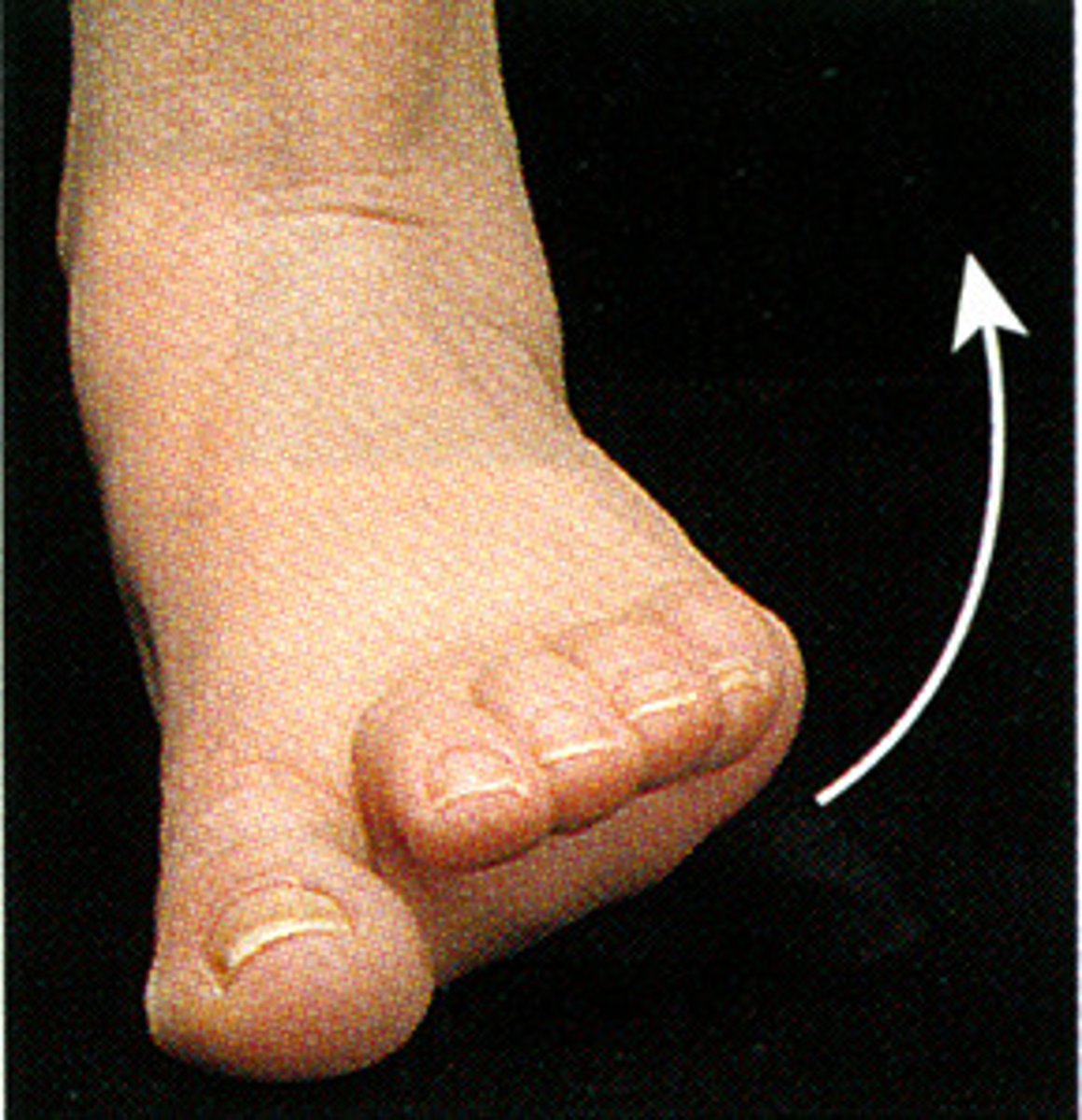
Supination of the foot
A combination of plantar flexion, inversion, and adduction
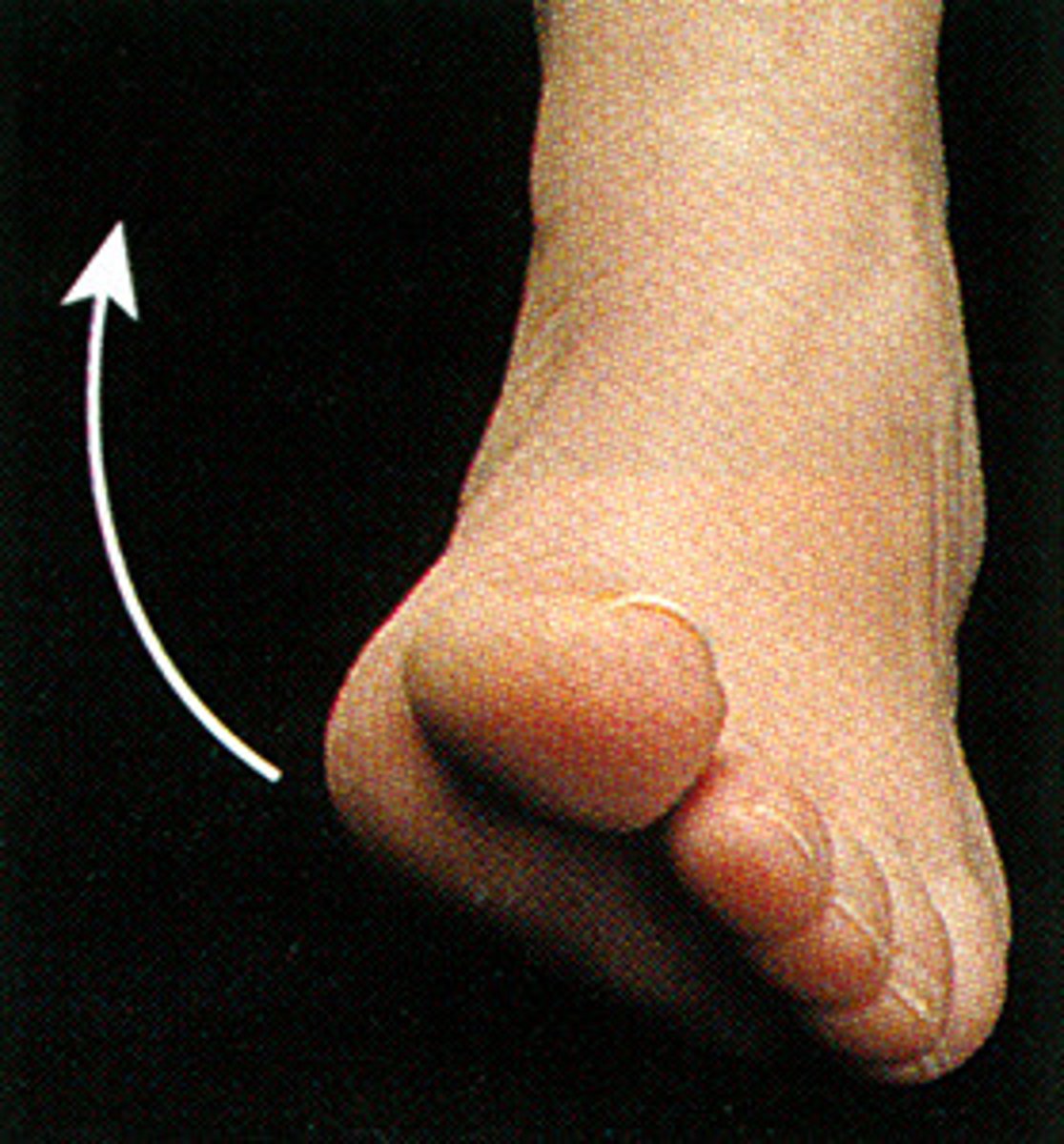
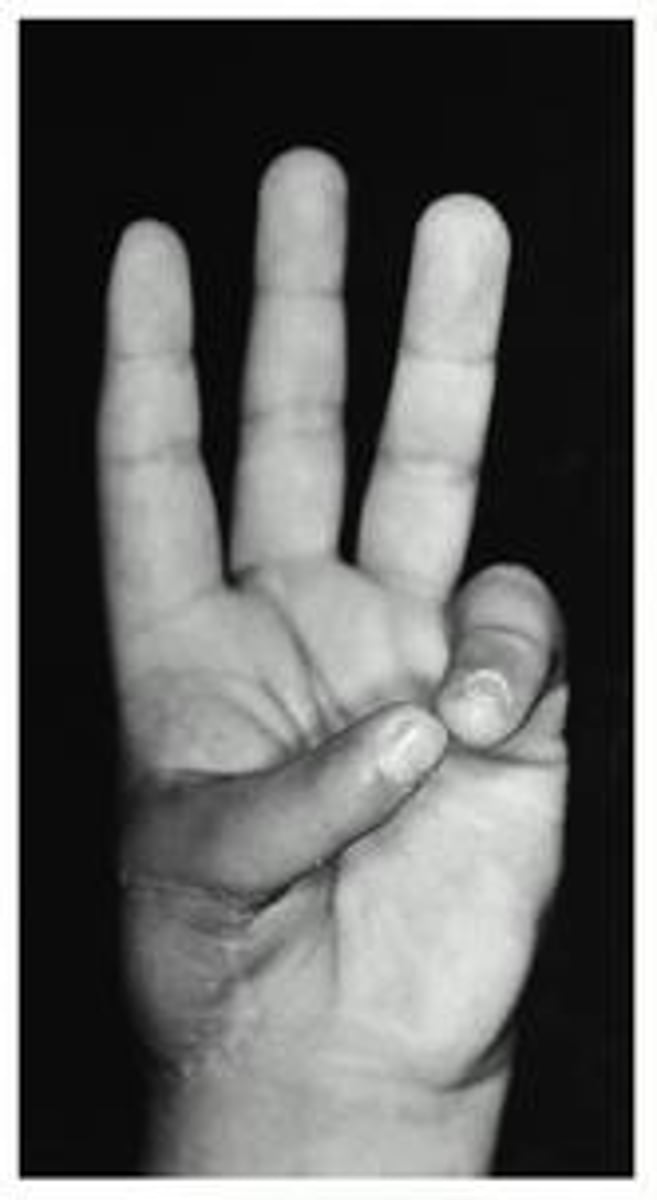
thumb opposition
What is this?
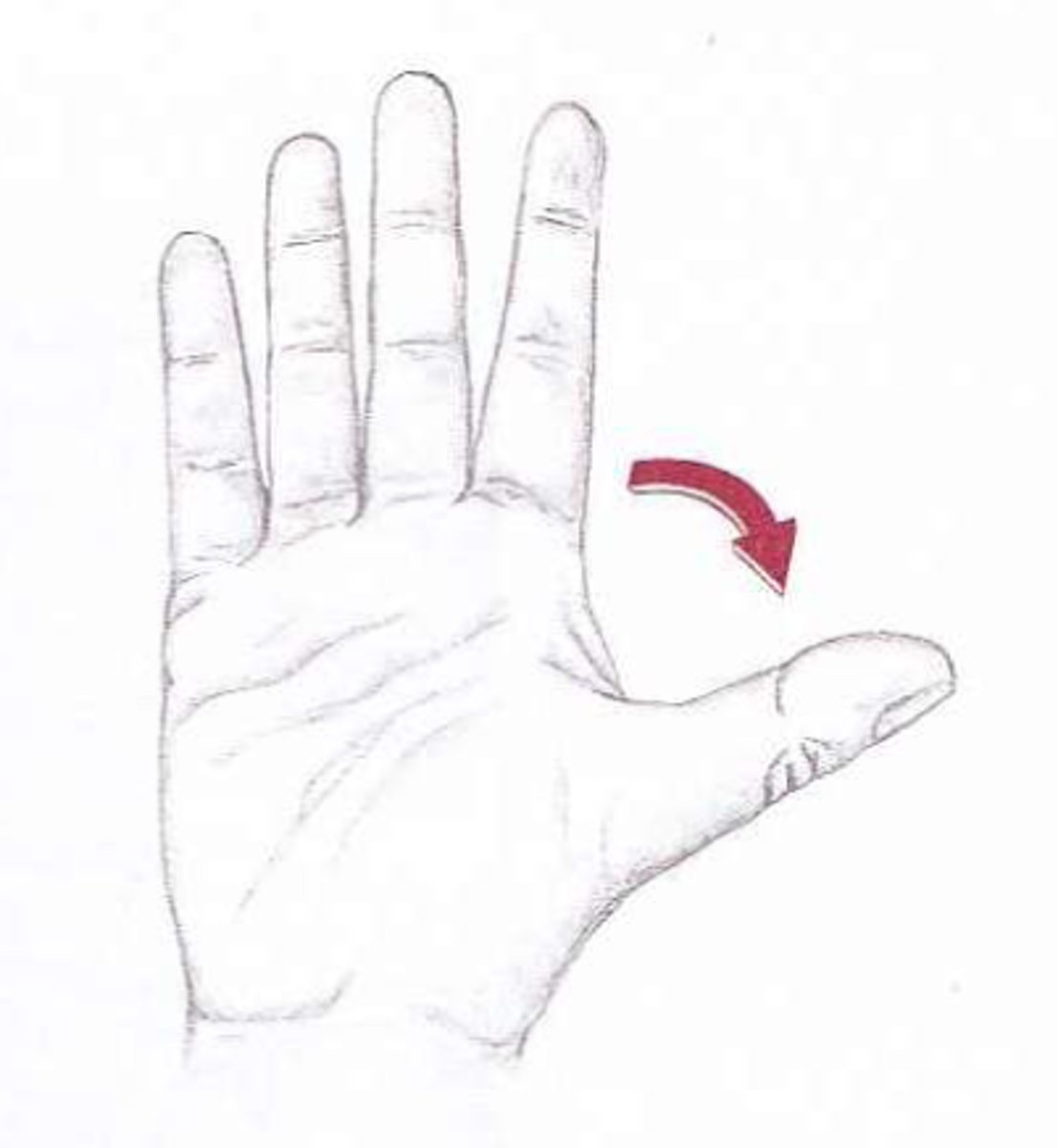
thumb extension
What is this?
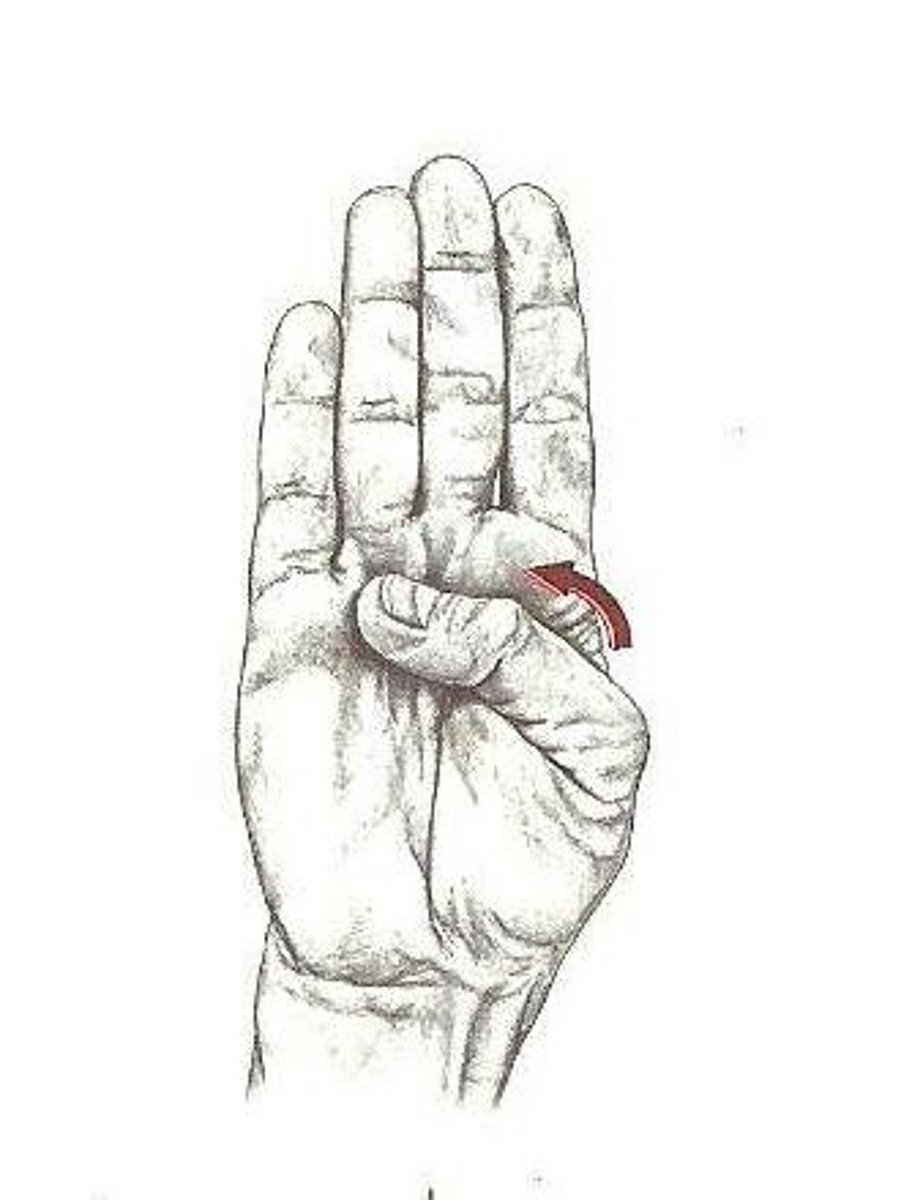
thumb flexion
What is this?
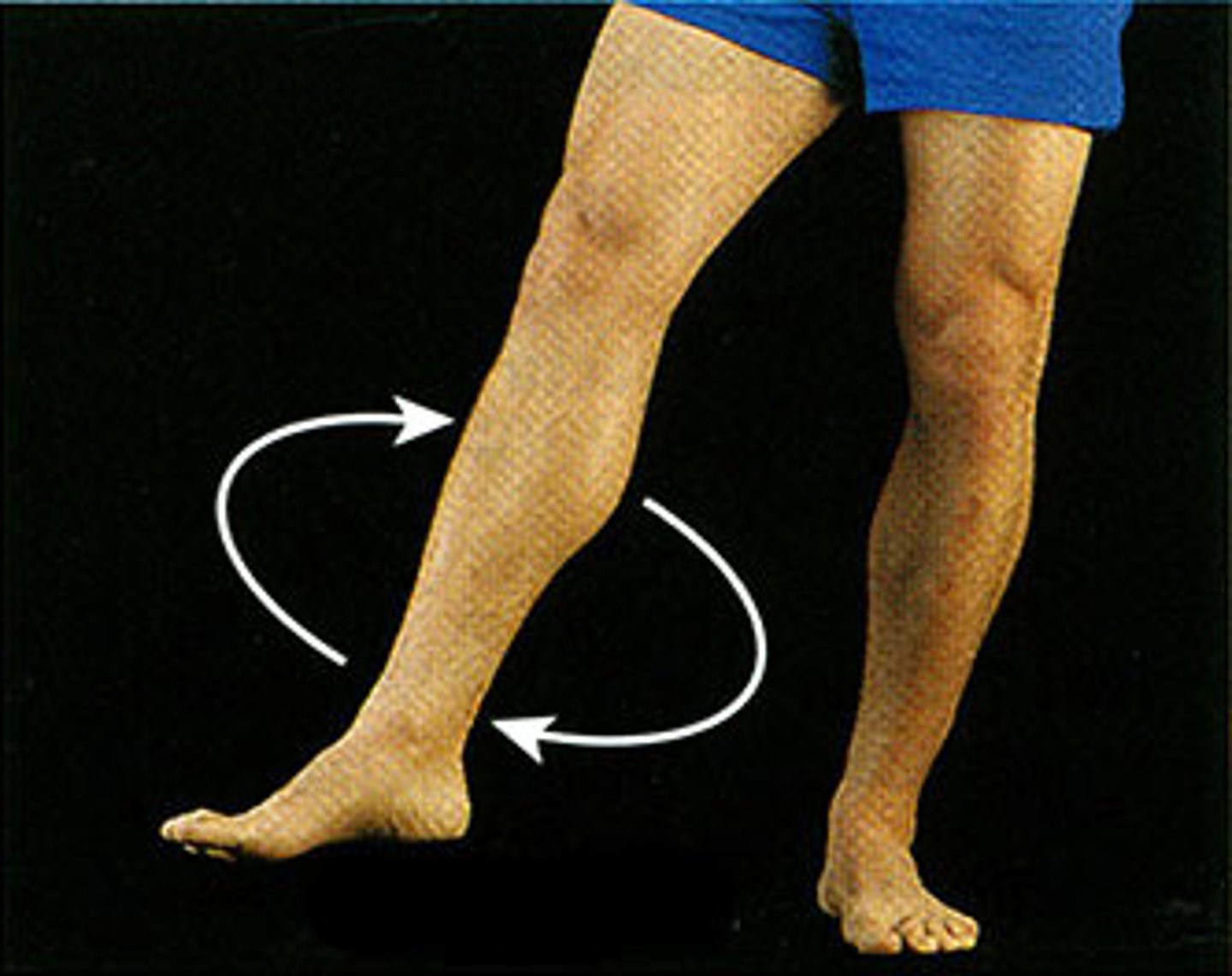
Circumduction
What is this?
movement, posture, glycogen storage, generate body heat, controls entry and exits
Skeletal muscle functions
Insertion
what do you call the moving part of the muscle
Orgin
attachment to immovable bone
Tendons
Connect muscle to bone
Ligaments
Connect bone to bone
musculotendinous unit
The group formed by a muscle and its tendons
motor neuron and the muscle fibers it innervates
Define a motor unit
history, observation, palpation, special tests
H. O. P. S. ??
Active ROM
Is movement initiated and completed by the athlete without assistance.
Passive ROM
Range of Motion in which the resident is unable to assist with movement
Resisted ROM
evaluator applies resistance to the motion
Weak or painful active ROM
Muscle that is contracting concentrically is injured
weak contraction
Nerve innervating a muscle, which produces the movement, is injured. This would be observed as a ?
long bones
bones of the arms and legs
sesmoid bones
special types of short bones formed in tendons, ex: patellas
Epiphysis
End of a long bone
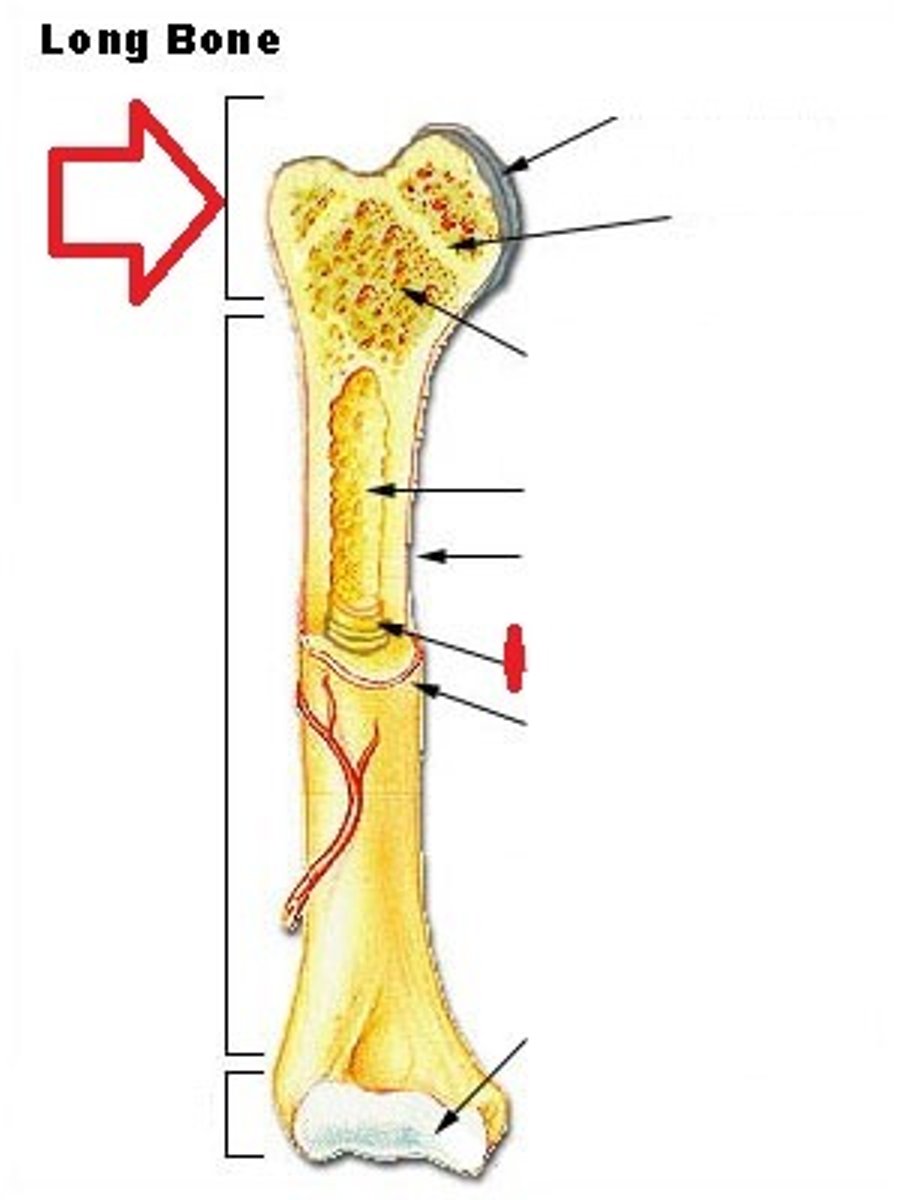
Diaphysis
shaft of a long bone
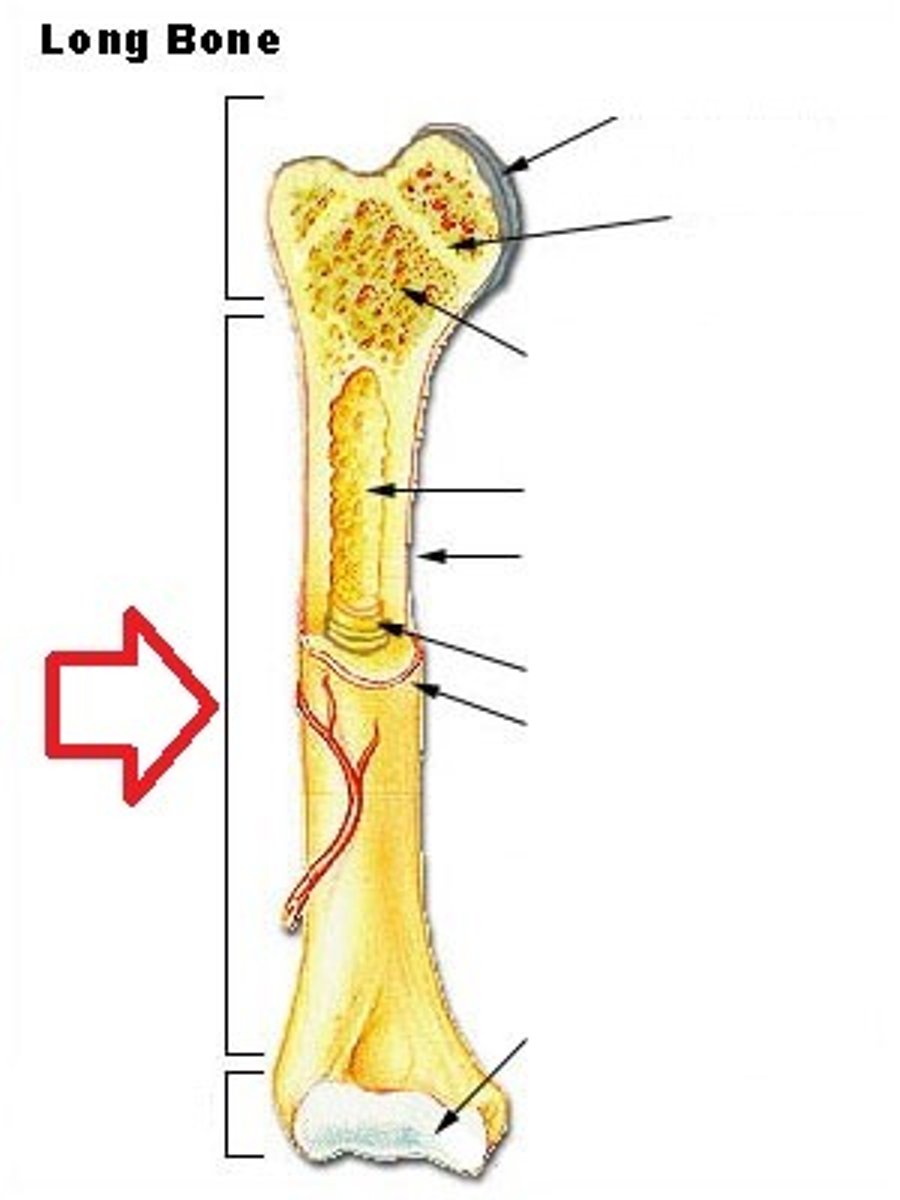
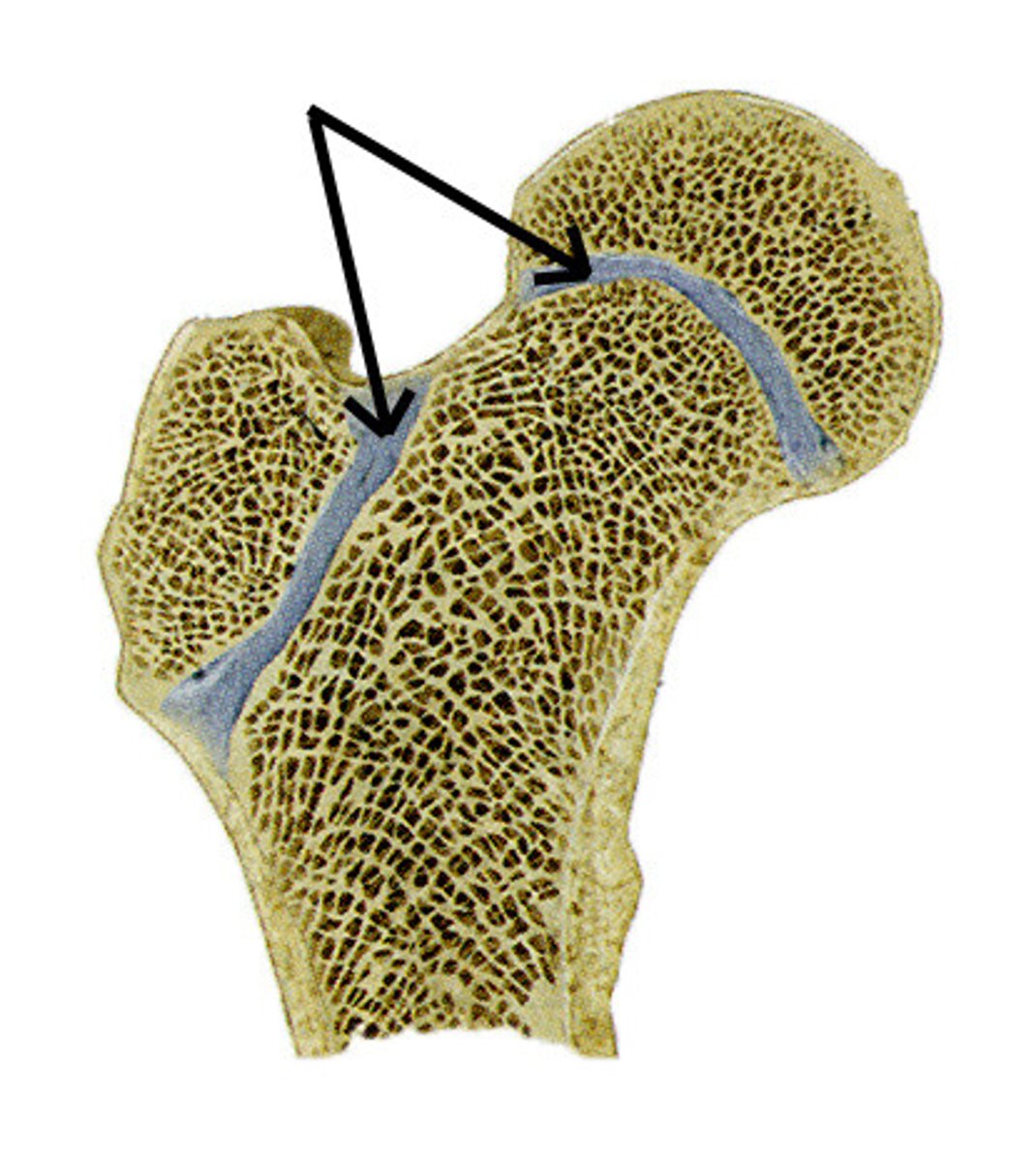
trabeculae
supporting bundles of bony fibers in cancellous (spongy) bone
ephiphyseal plate
forms between two ossification centers
band of hyaline cartilage
fuse together and growth stops when adult
osteogenic cells
stem cells that differentiate into osteoblasts
Osteoblasts
bone forming cells
Osteoclasts
bone resorption cells
Osteocytes
mature bone cells
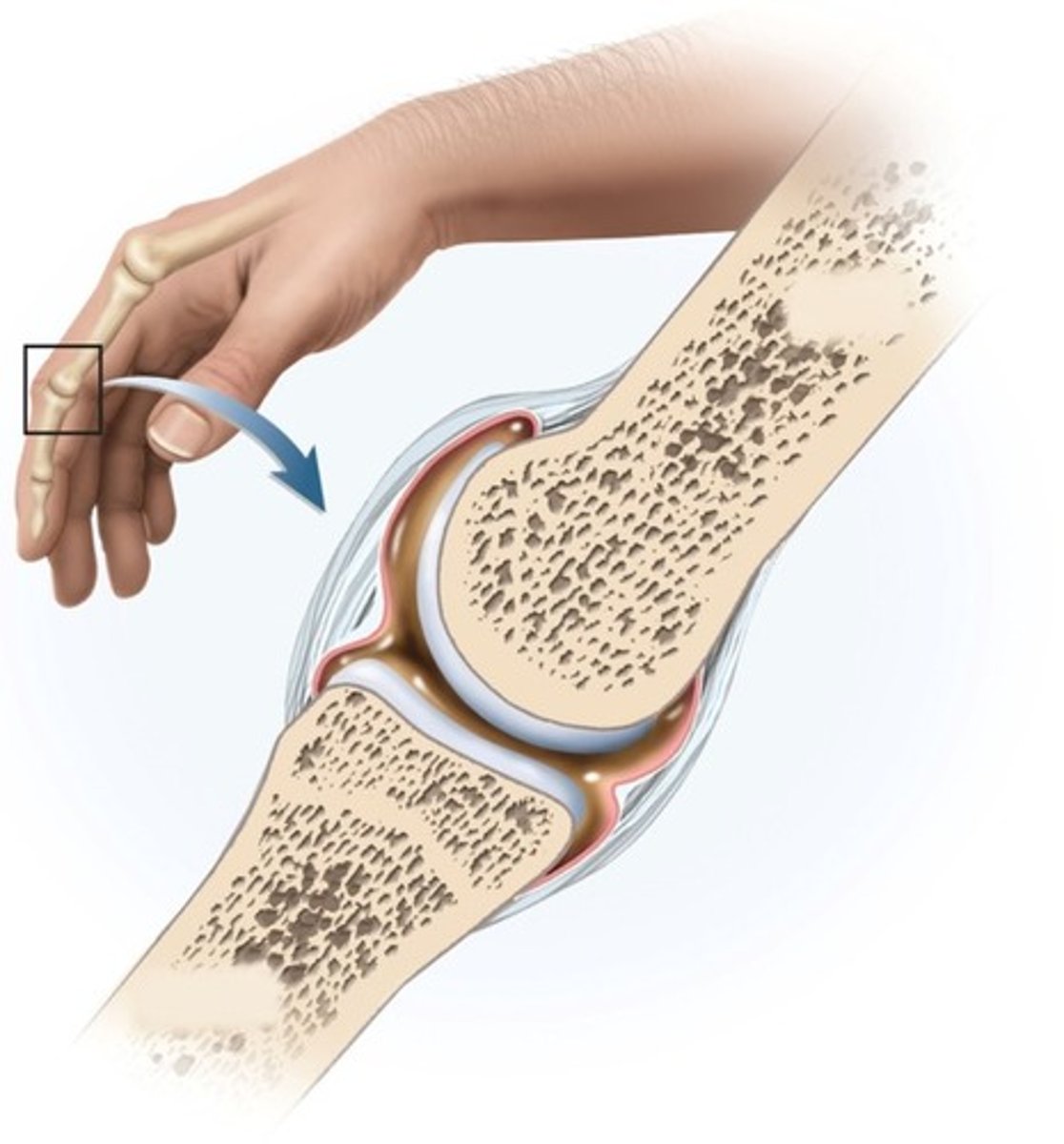
Osteoprorosis
the inability of the human body to absorb calcium, bone density decreases
Fibrocartilage
cartilage that contains fibrous bundles of collagen, such as that of the intervertebral disks in the spinal cord.
collagen, elastin , and reticulin
What are ligaments made of
Diarthrodial (synovial) joints
freely movable joint
Amphiarthrodial (cartilaginous) joints
slightly mobile, cartilage forms union between two joints

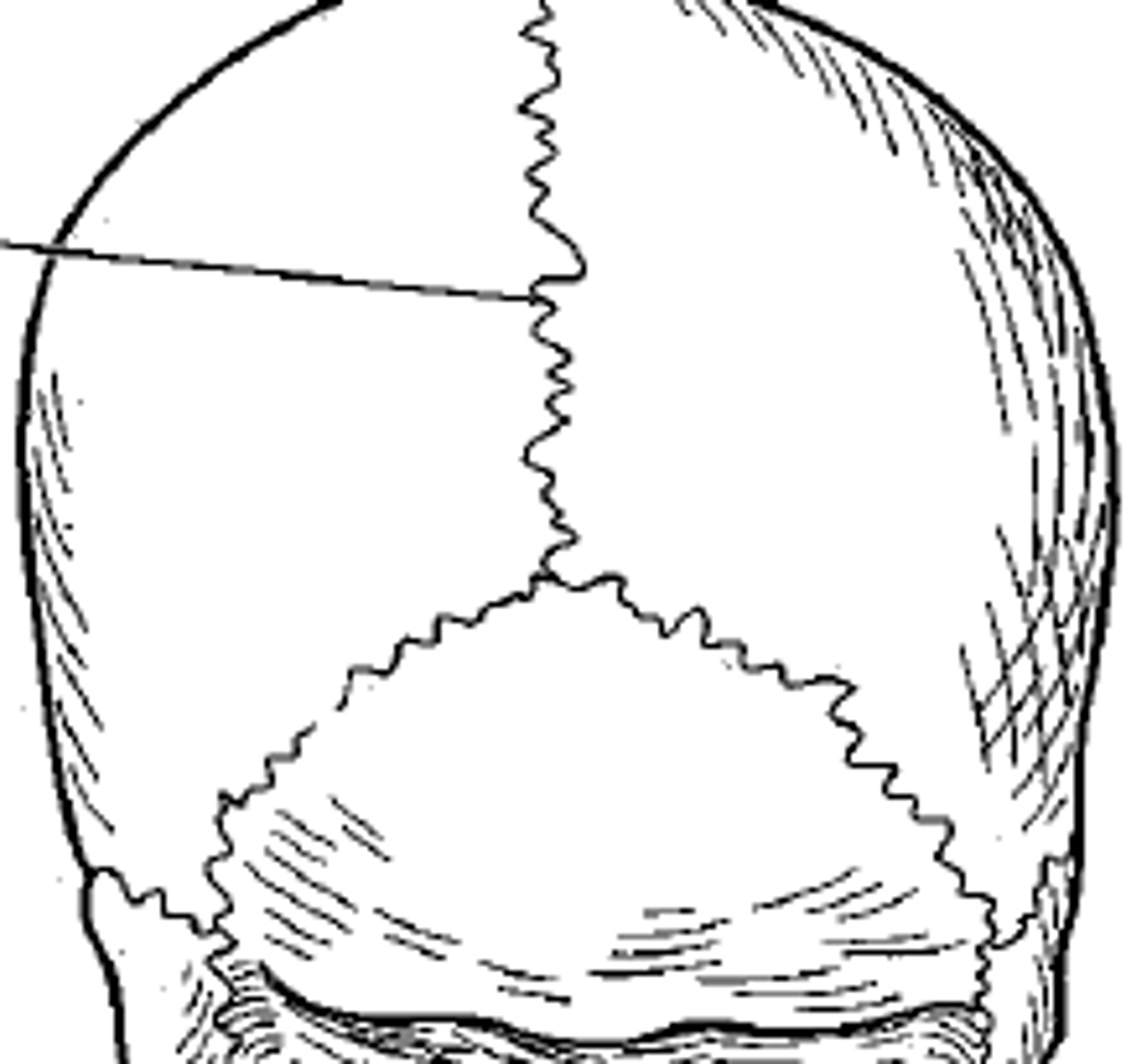
synarthrodial (fibrous) joints
-immobile
-bound by fibrous ligaments
-sutures, located between bones of the skull joints
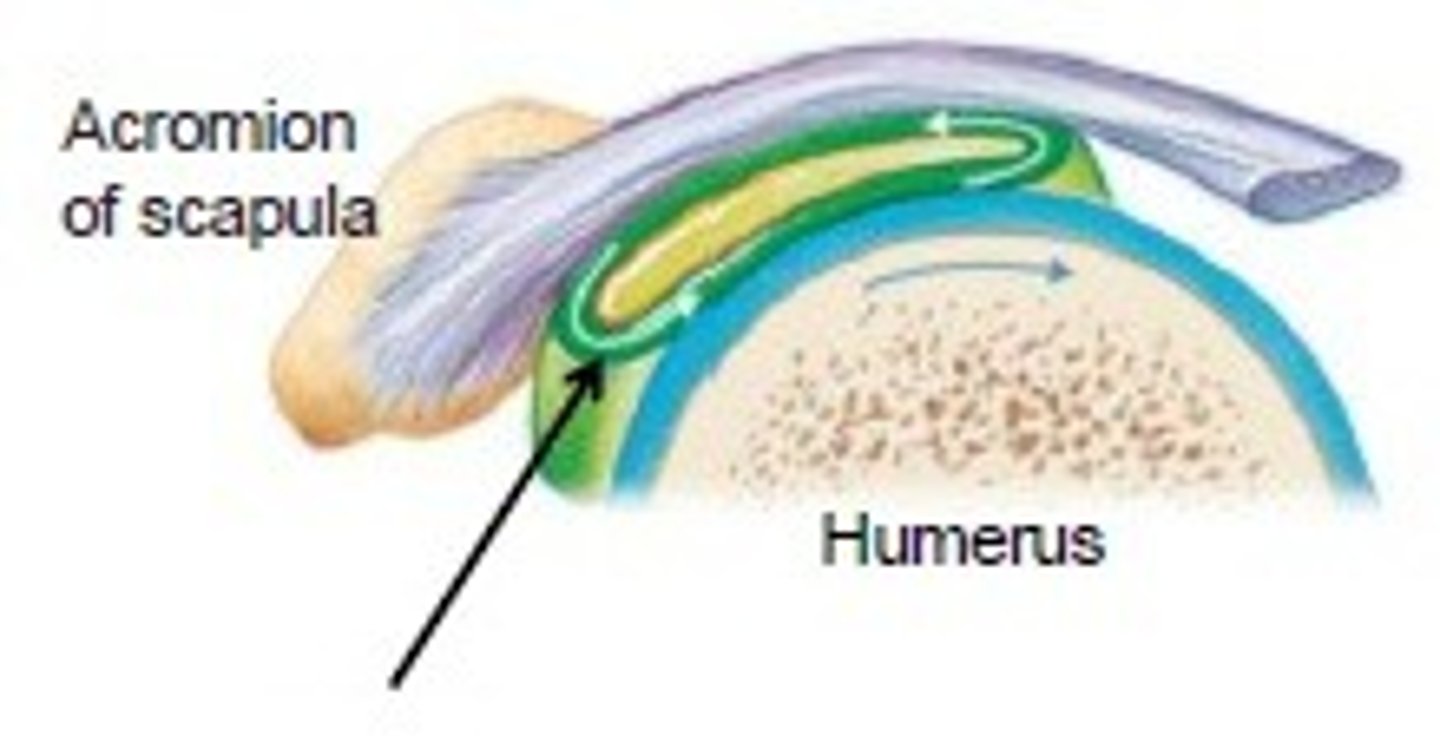
Bursae
flattened fibrous sacs lined with synovial membrane and containing a thin film of synovial fluid
hinge joint
Joint between bones (as at the elbow or knee) that permits motion in only one plane

pivot joint
rotating bone turns around an axis; i.e. connection between radius/ulna and humerus
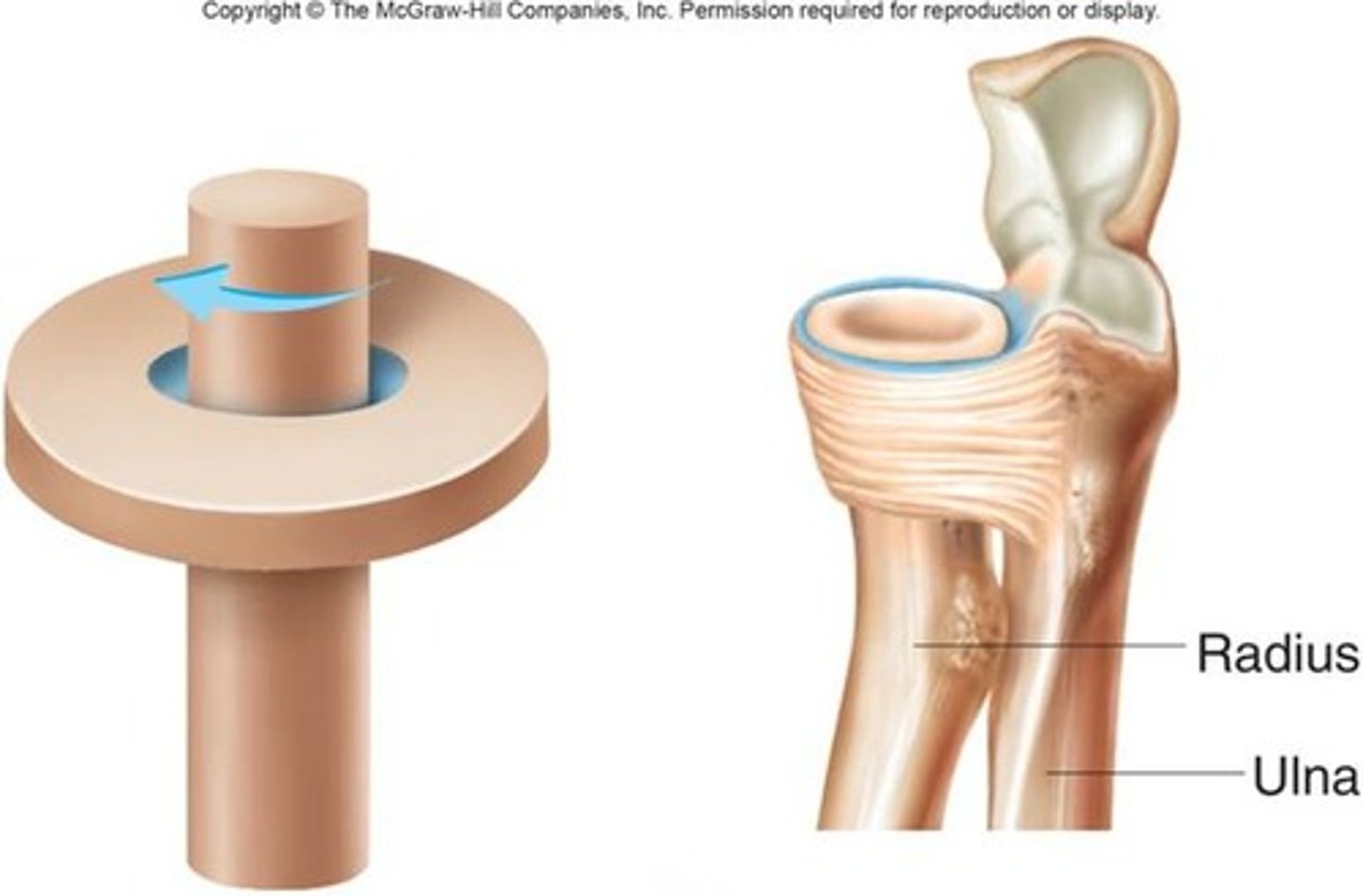
congyloid joint
Joint with two degrees of freedom (femur tibia)