Chapter 15: Equilibria of other Reaction Classes
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Solubility Product Constant (Ksp)
Equilibrium constant for the dissolution of a slightly soluble ionic compound (saturated)
“Slightly” so it can be reversible for a K
Nothing is completely insoluble, just very little dissolves
At EQUILIBRIUM only
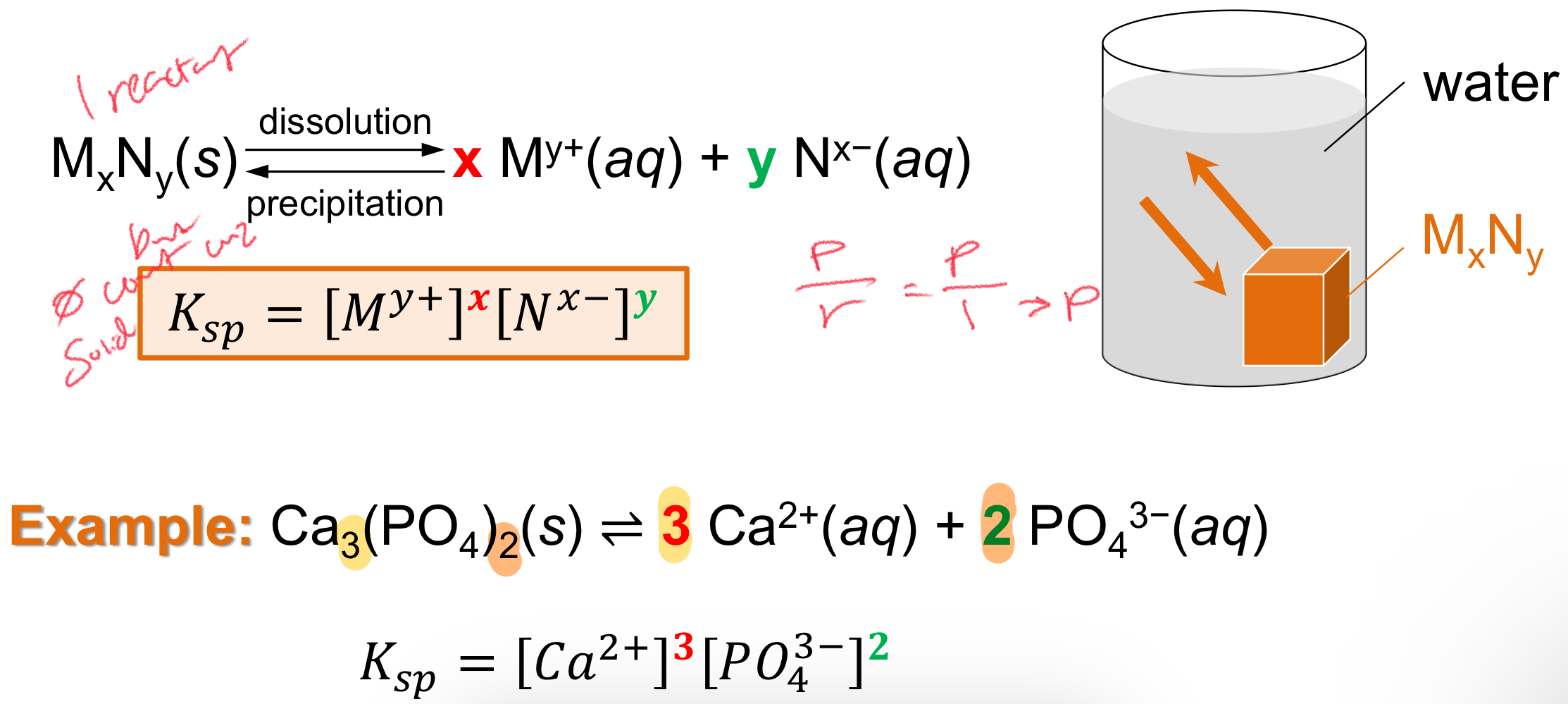
Solubility Product Constant (Ksp) Eqn
Ksp = [M^y+]^x [N^x-]^y
T/F: Change in temperature will change Ksp.
True; increasing temp will increase solubility which would give a higher Ksp.
Molar Solubility (S)
Solubility of a compound expressed in units of moles per liter (mol/L)
Related with Ksp
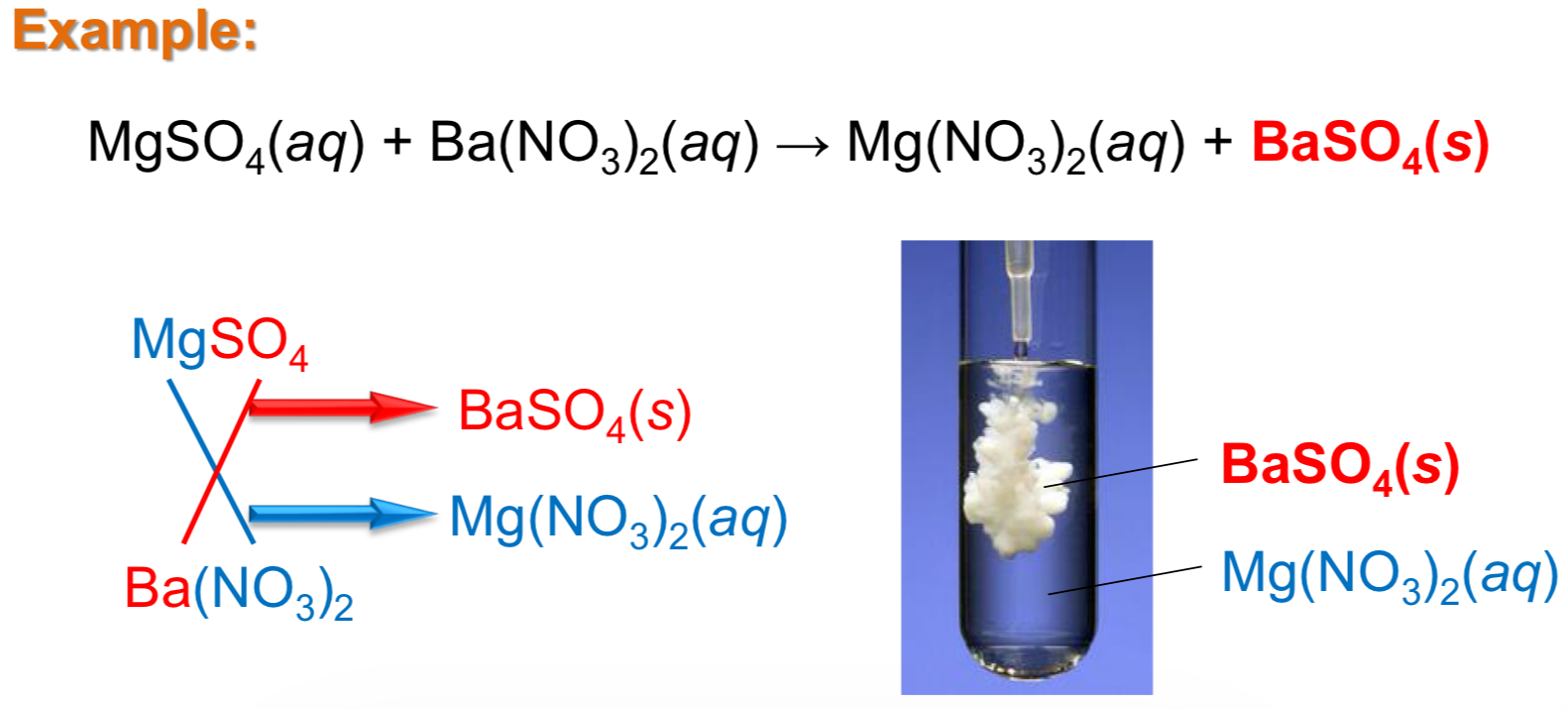
Precipitation rxns
Occur upon the mixing of 2 solutions when one of the cross products is insoluble
Reaction Quotient (Q)
For rxn by which an ionic compound dissolves is the product of the concs of the ionic components raised to their stoichiometric coefficients
Under ANY conditions

Reaction quotient Q < Ksp
Unsaturated
More solid dissolves
No precipitation

Q = Ksp
Saturated
Additional solid does not dissolve
Precipitate forms

Q > Ksp
Supersaturated
Excess solid precipitates out
Precipitate forms
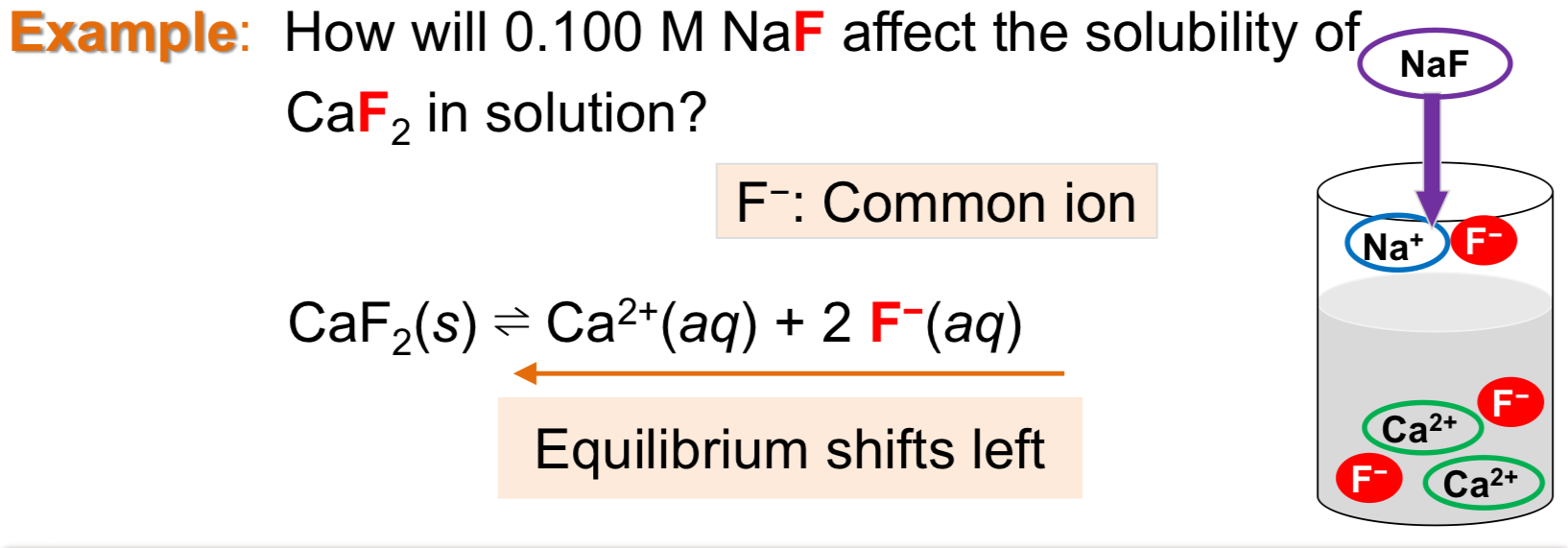
Common Ion Effect on Solubility
Effect on equilibrium when a substance w/ a common ion with the dissolved ionic species is ADDED to the solution, which decreases the solubility of an ionic species
Solubility of an ionic compound is (higher/lower) in a solution containing a common ion than that in pure water.
Lower
T/F: For an ionic compound with a basic anion, the lower the pH, the higher the solubility.
True
Common basic anions: OH-, S^2-, and F-
Solubility in basic solution
Equilibrium shifts LEFT ← due to common ion effect = lower solubility
Solubility in acidic solution
Equilibrium shifts RIGHT → due to neutralization of H3O+ and OH- = higher solubility
Selective precipitation
Process where ions are separated using diffs in solubility w/ given precipitating reagent
Ion reqs that the smallest amt of added ion precipitates first
T/F: The salt that forms at the lower ion precipitates first, so compare the 2.
True
Arrhenius Acid
Produces H+
Arrhenius Base
Produces OH-
Bronsted-Lowry Acid
Donates H+
Bronsted-Lowry Base
Accepts H+
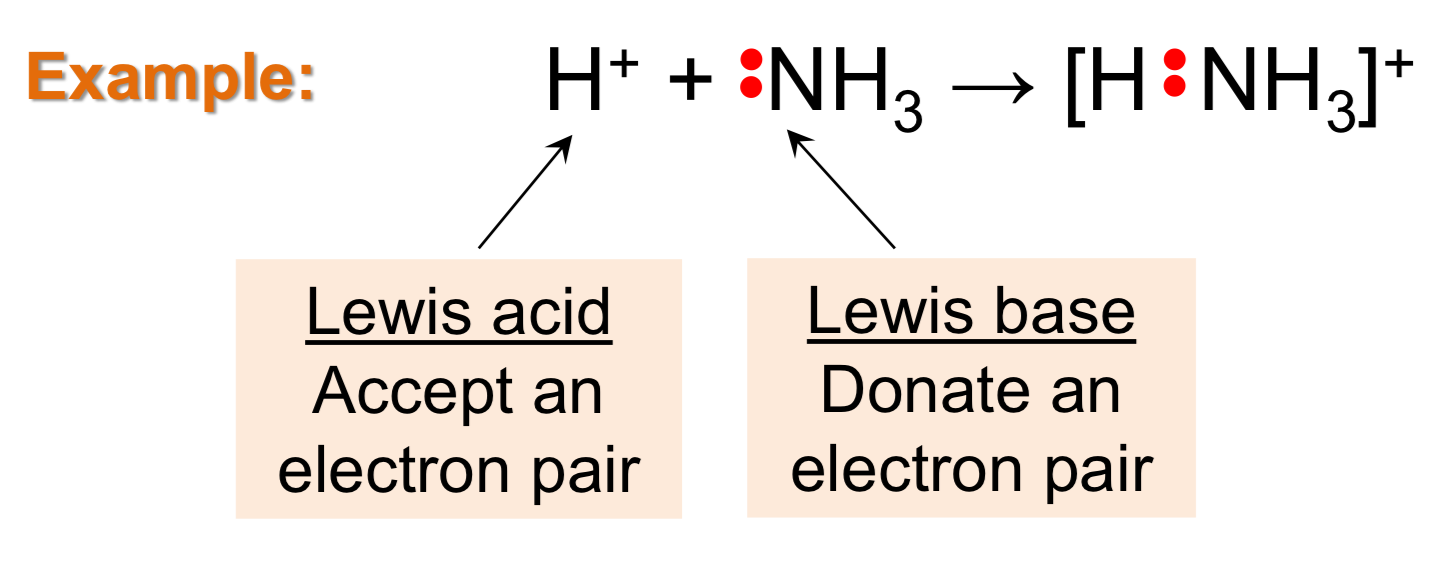
Lewis Acid
Accept pair of electrons (e-)
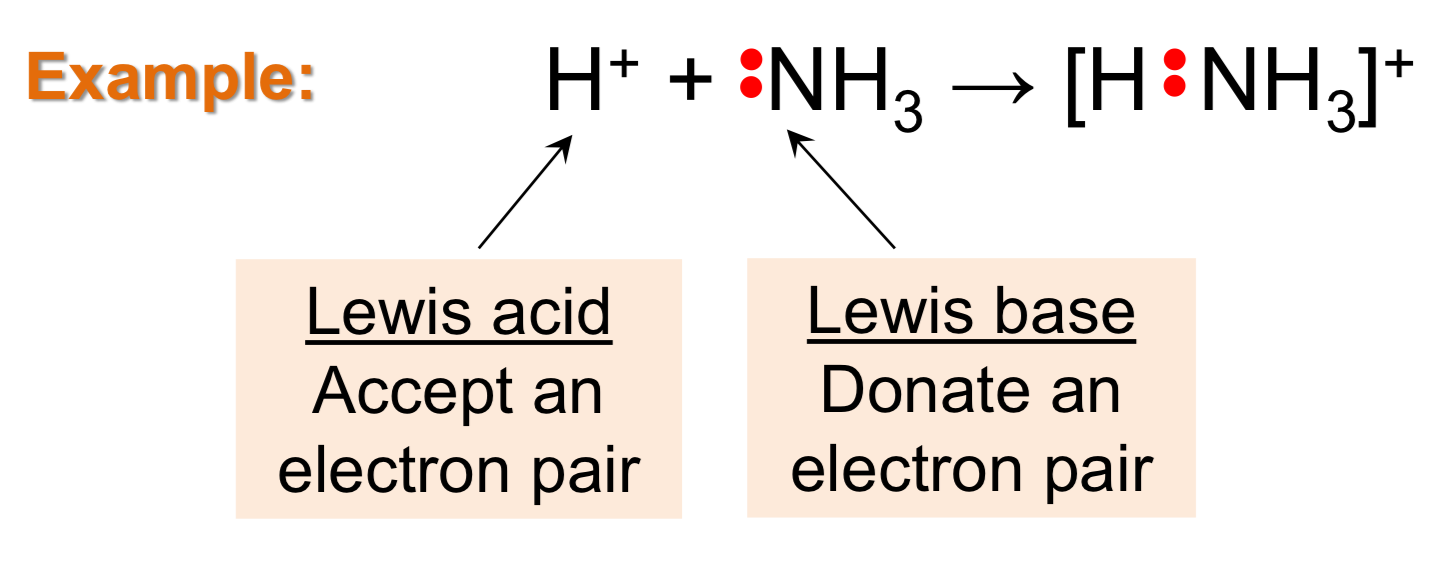
Lewis Base
Donate pair of electrons (e-)
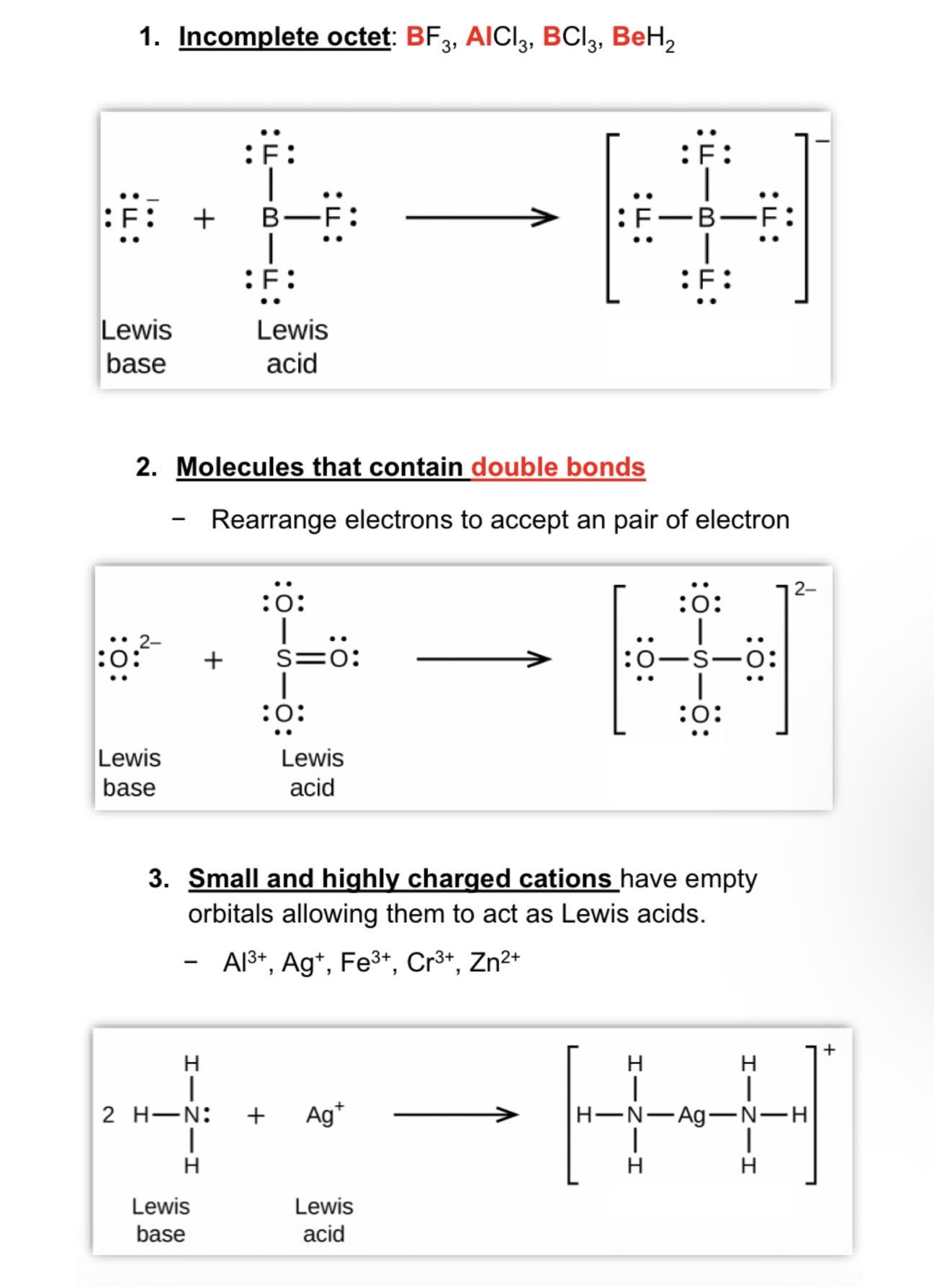
Lewis Acids and Empty Orbital Types
Lewis acids have an empty orbital that can accept an electron pair (cannot include H)
Incomplete octet = BF3, AlCl3, BCl3, and BeH2
Molecules that contain double bonds = rearrange electrons to accept a pair of electrons
Small and highly charged cations = Al^3-, Ag+, Fe^3+, Cr^3+, and Zn^2+