Pathology MICROSCOPIC - 2nd Semester Lab Exam
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is this?
HEART:
Fibrinous Pericarditis: deposits of Fibrin on surface of pericardium
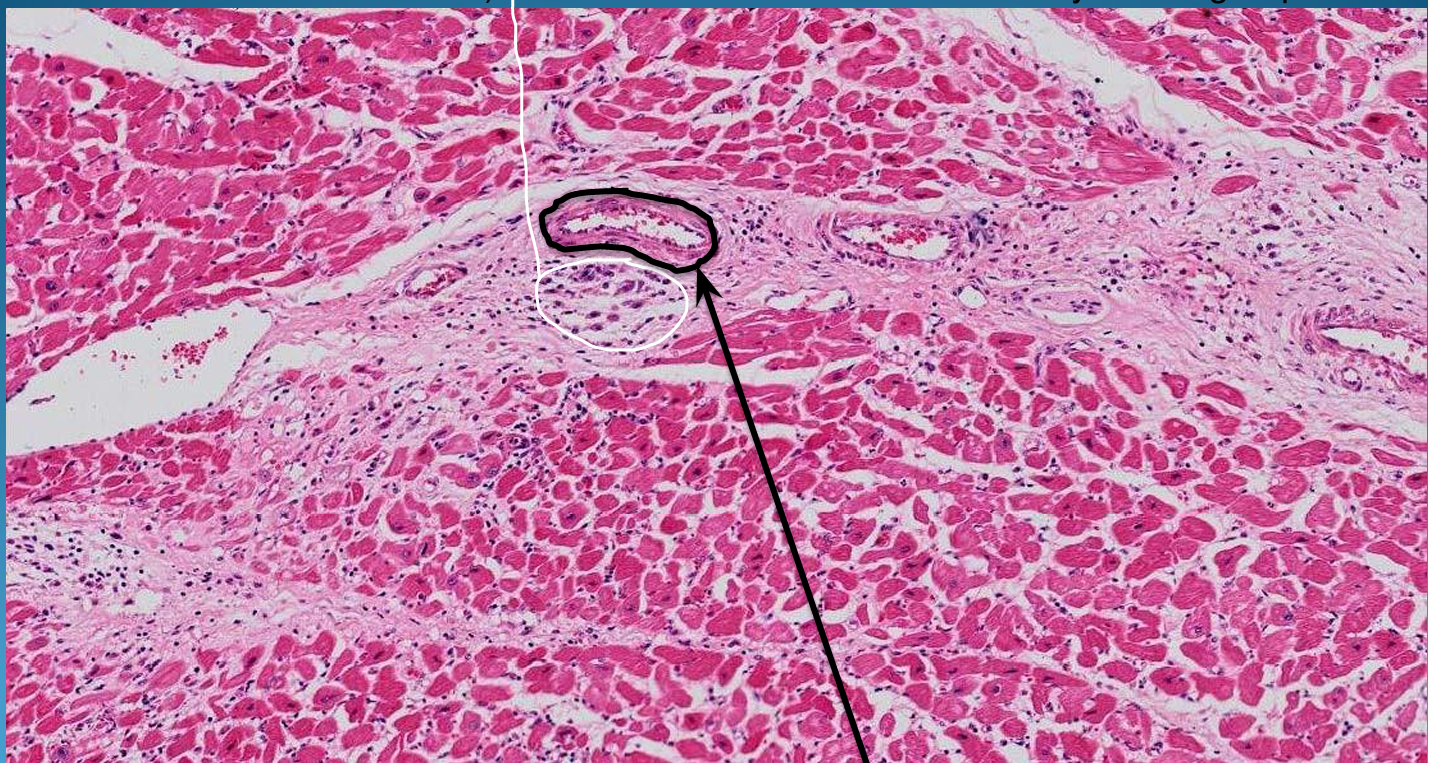
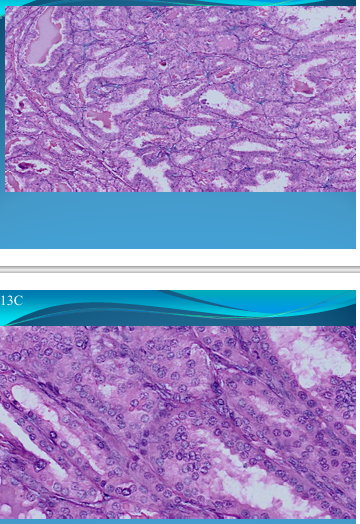
What is this?
HEART:
Rheumatic Myocarditis: Aschoff Nodules under vessel perivascular and Aschoff cells
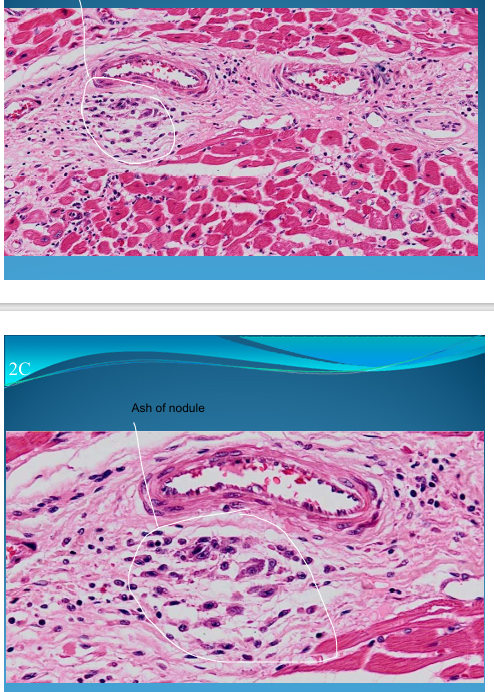
What is this?
HEART:
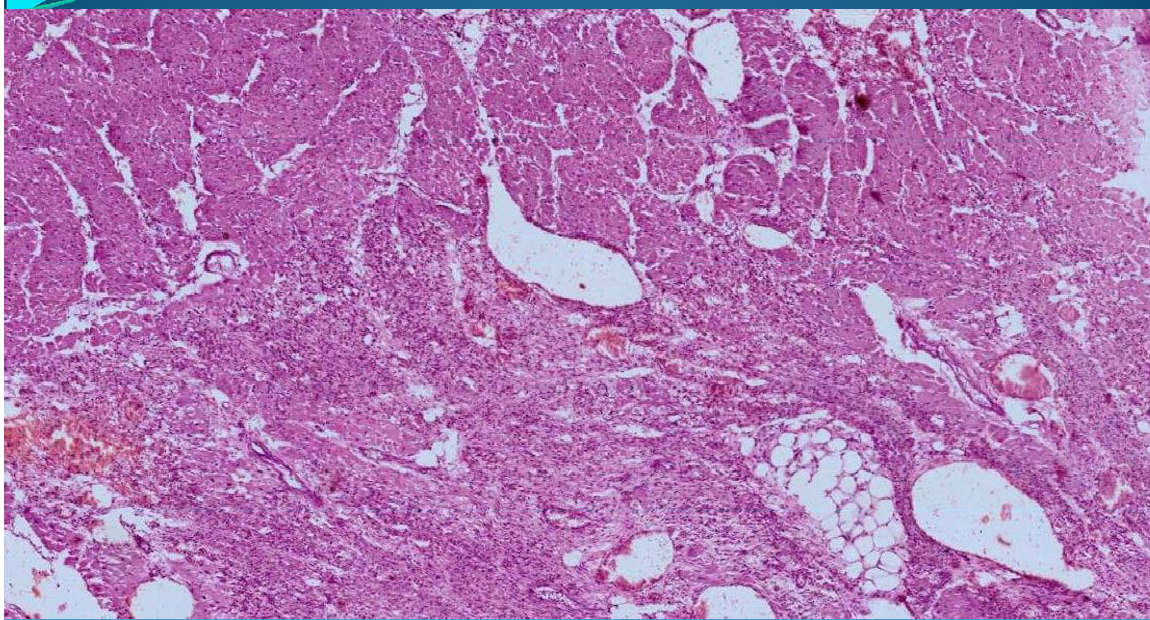
Acute myocardial infarction: granulation tissue and PMNs, well delimitated, neformation vessels; about to organize phase
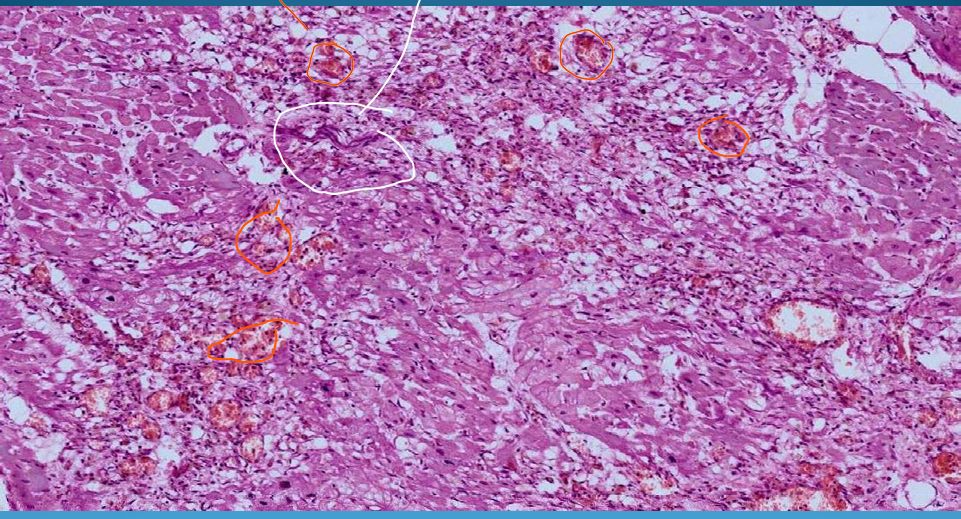
What is this?
HEART:
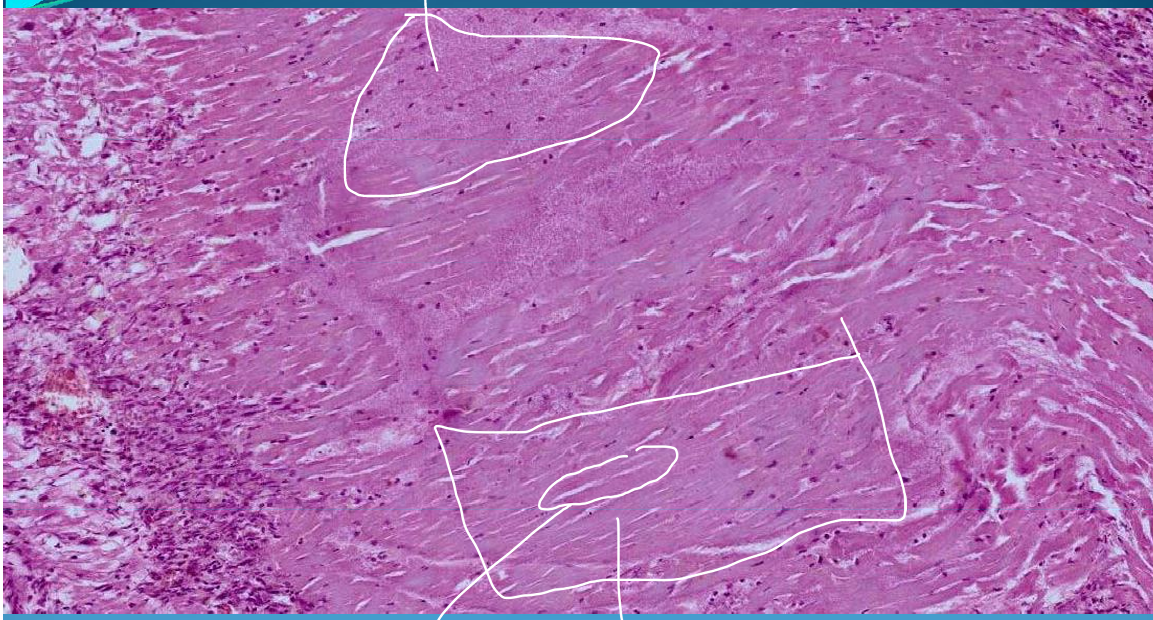
Acute Myocardial Infarction: structured & unsctructured necrosis (structured coagulation necrosis)
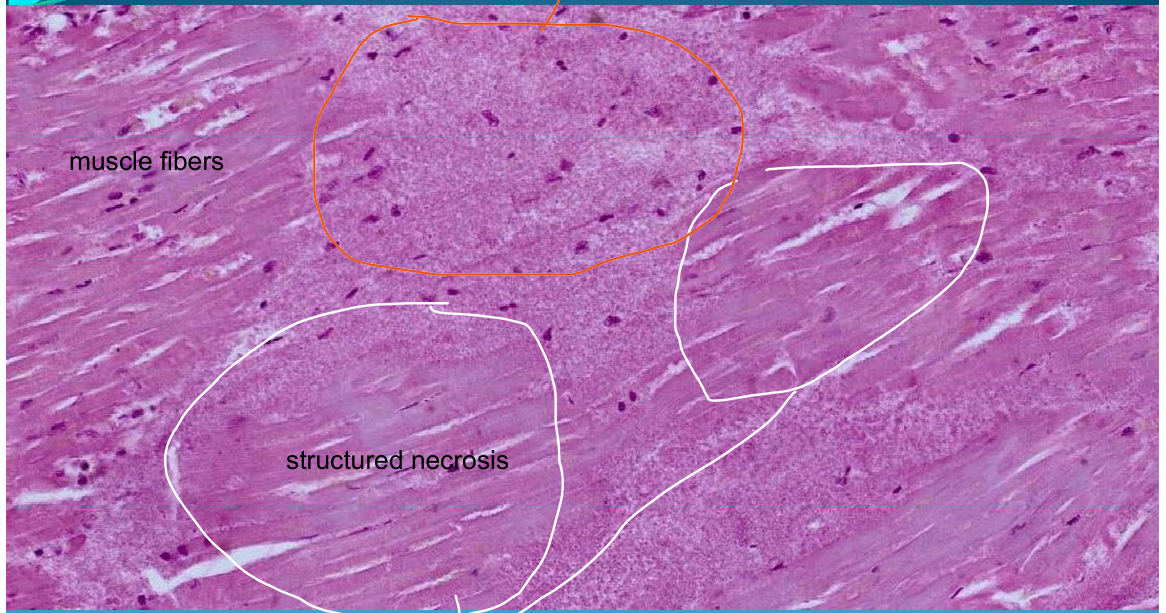
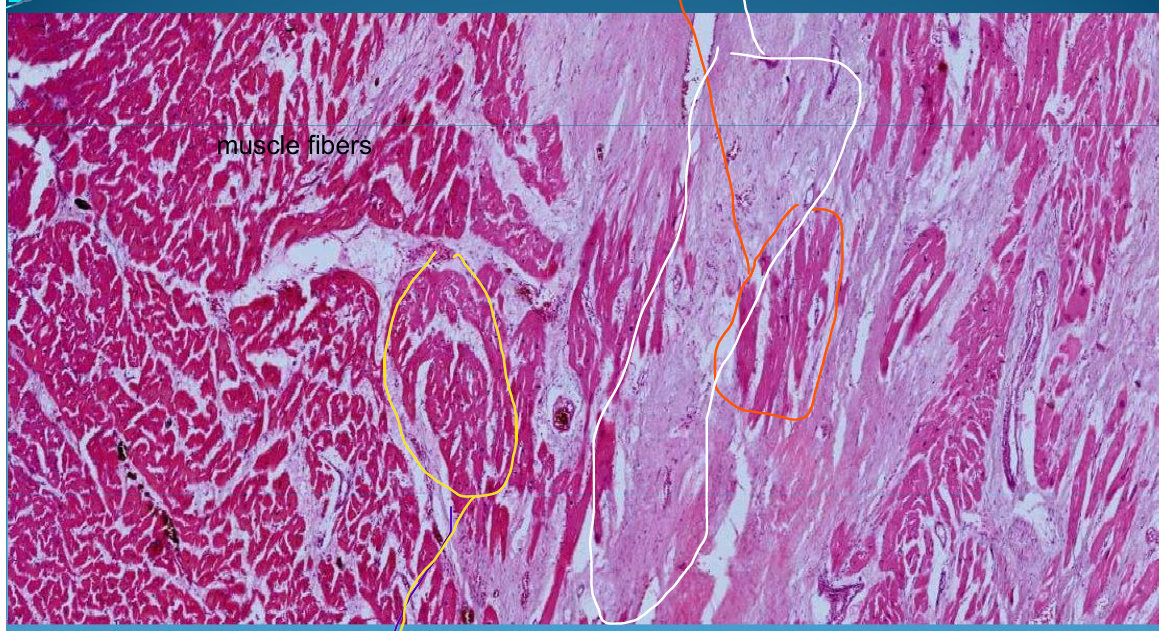
What is this?
HEART:
Sclerosis and Fibrosis: Old infarction/chronic
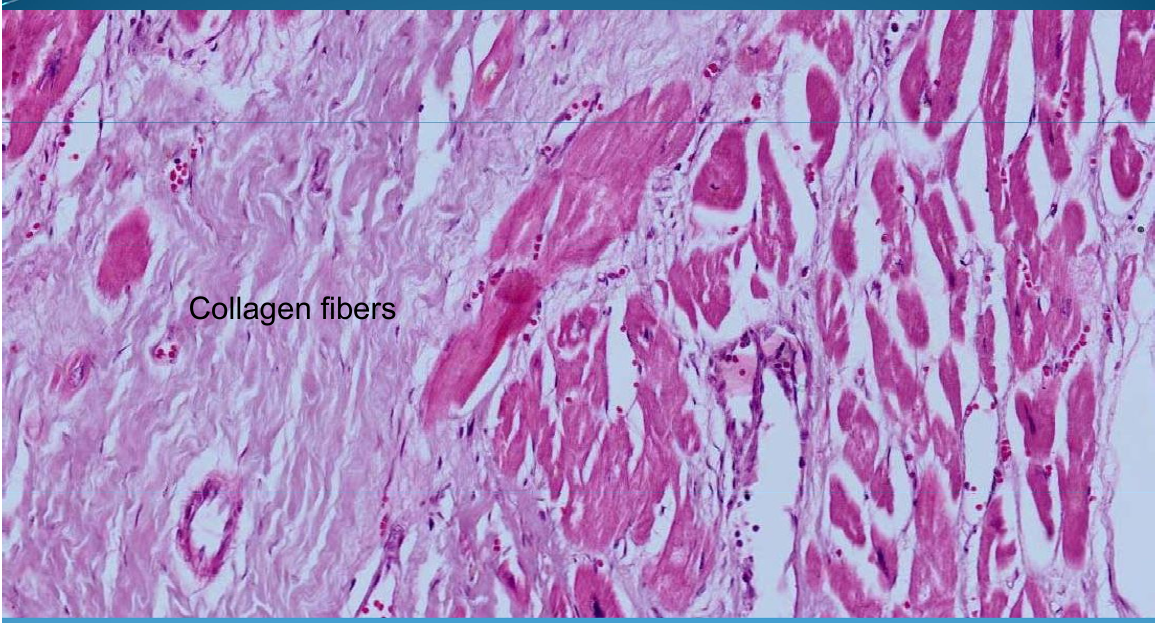
What is this?
ARTERY:
Atherosclerosis: cholesterol crystals and complicated by thrombosis
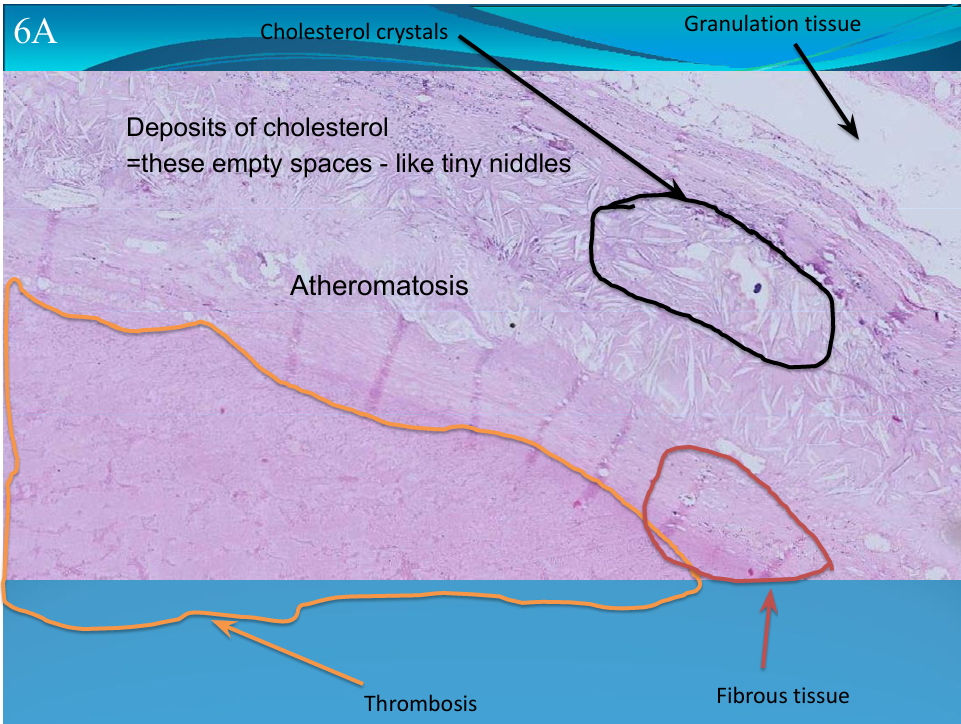
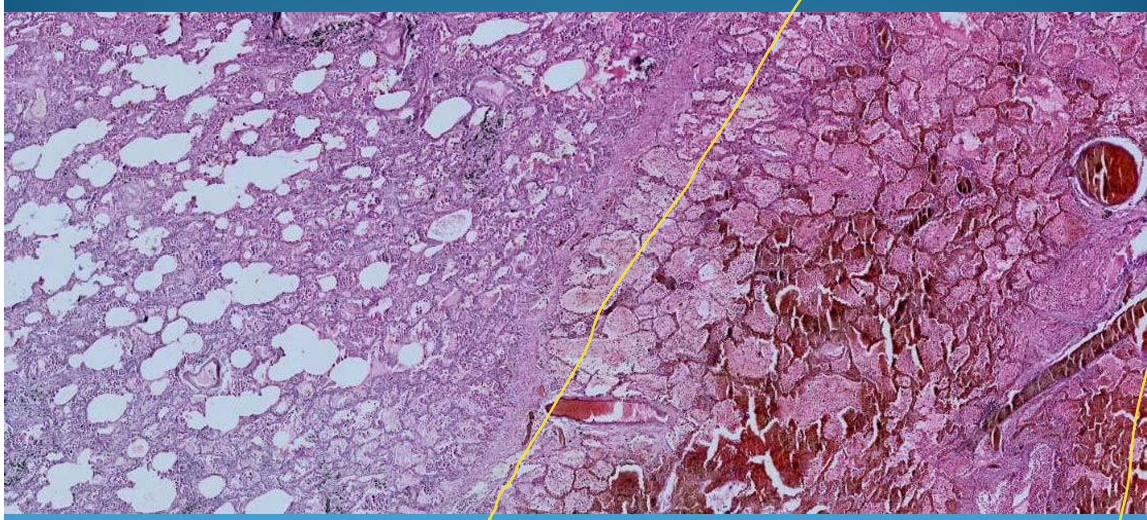
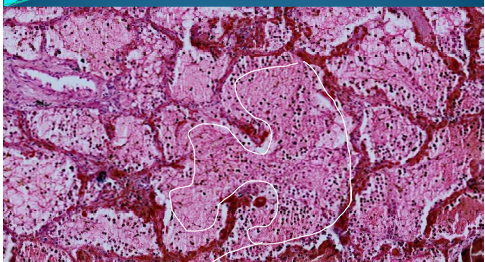
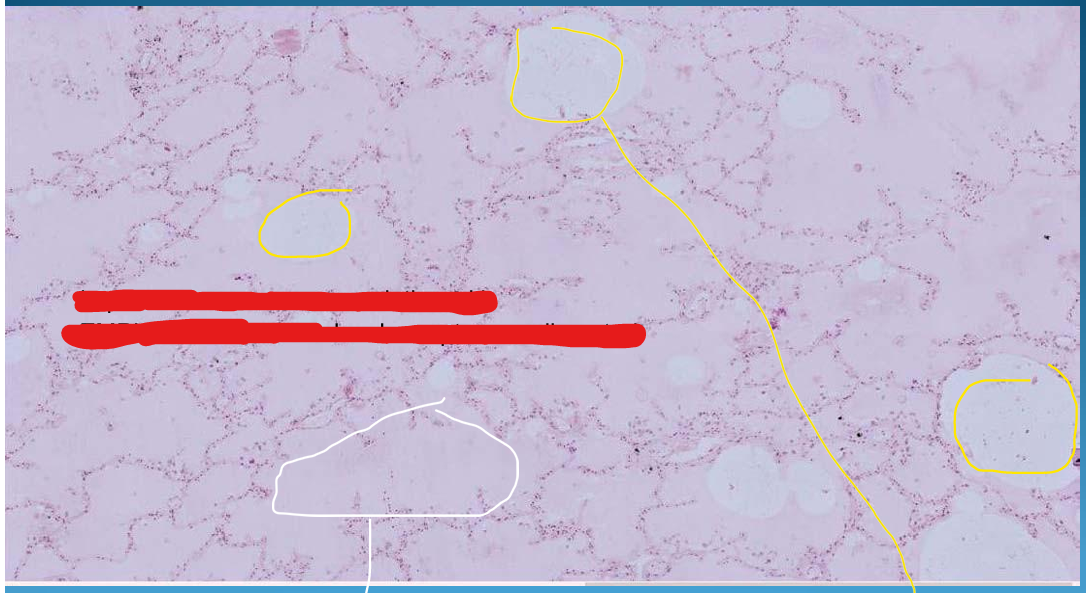
What is this?
LUNG:
Lung Infarction: Pulmonary hemorrhagic infarction with structured necrosis; reddish area = red infarction,
What is this?
LUNG:
Pulmonary Edema & Emphysema: liquid inside alveolar space; association with emphysema because interalveolar septa is disrupted
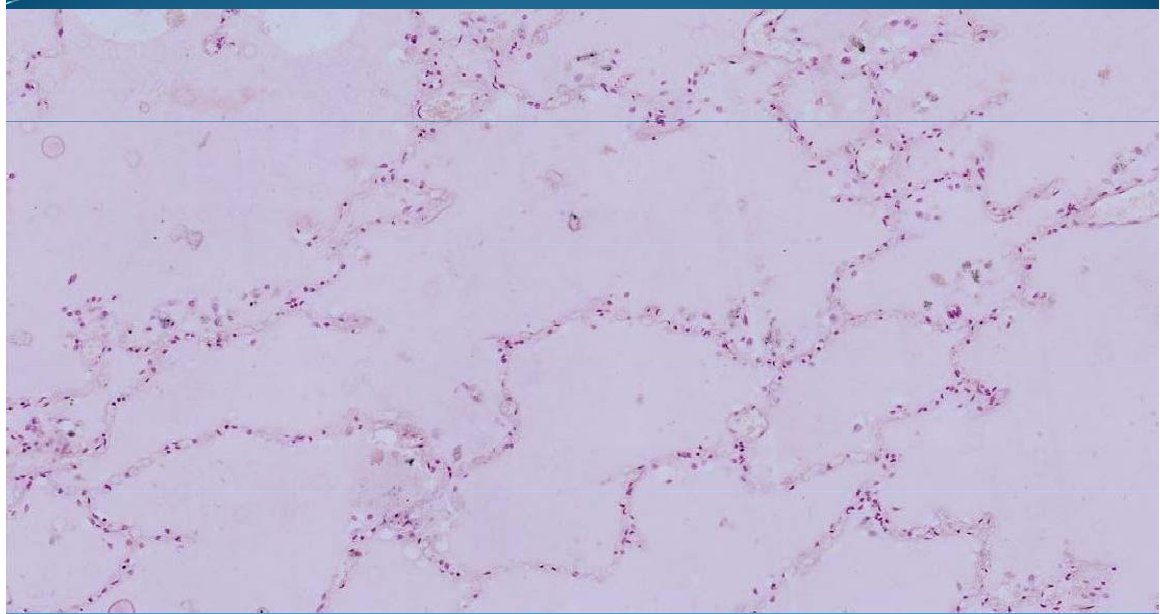
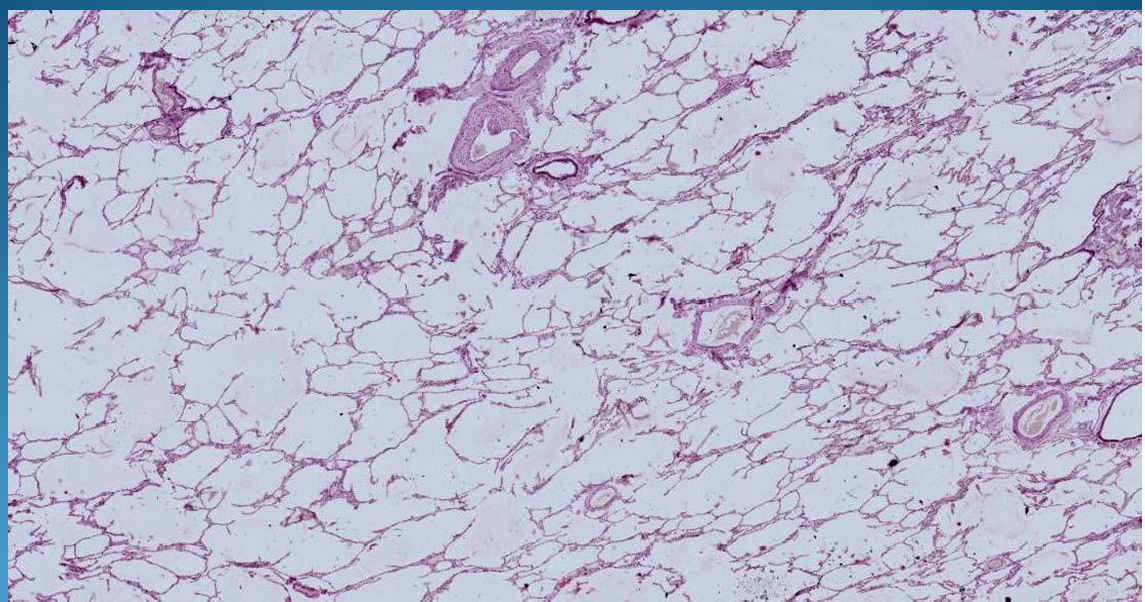
What is this?
LUNG:
Chronic emphysema and Atelectasis with disrupted and detached alveolar septa
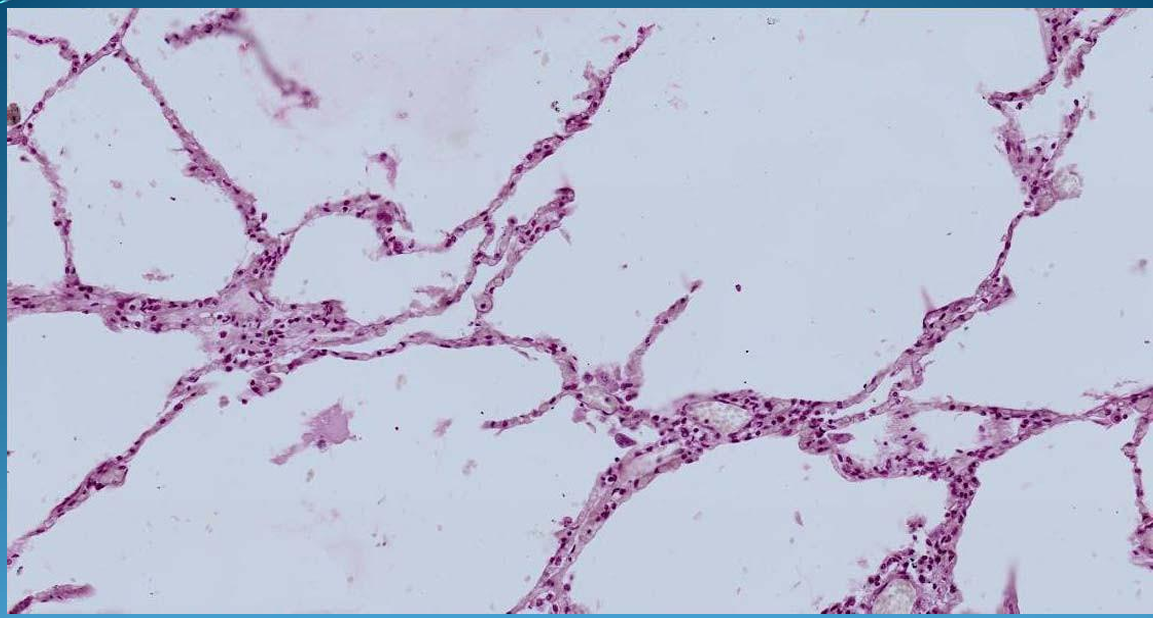
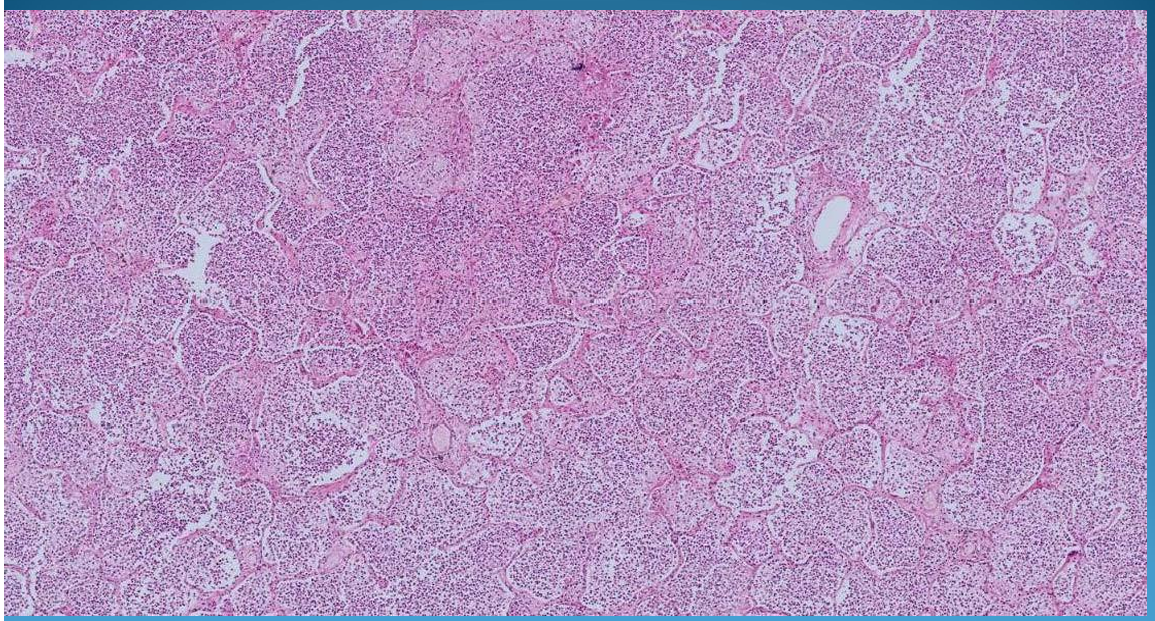
What is this?
LUNG:
Lobar pneumonia: monomorphic aspect of alveoli and gray hepatisation with PMNs, fibrin network
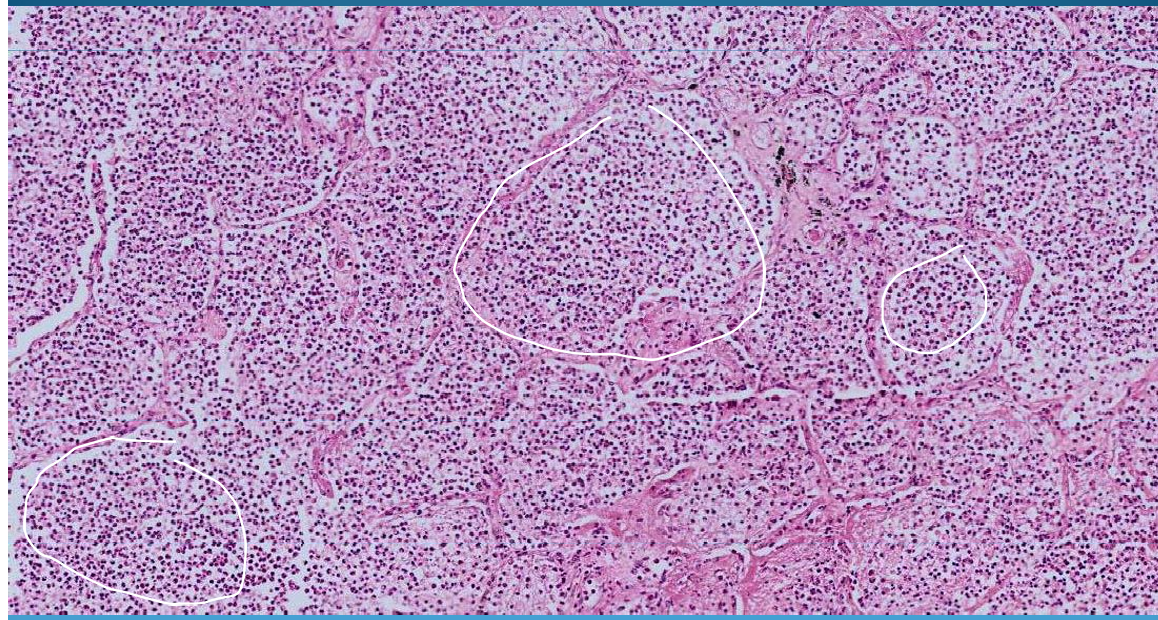
What is this?
BRONCHIA:
Bronchopneumonia with polymorphic aspect of alveoli, filled with pus
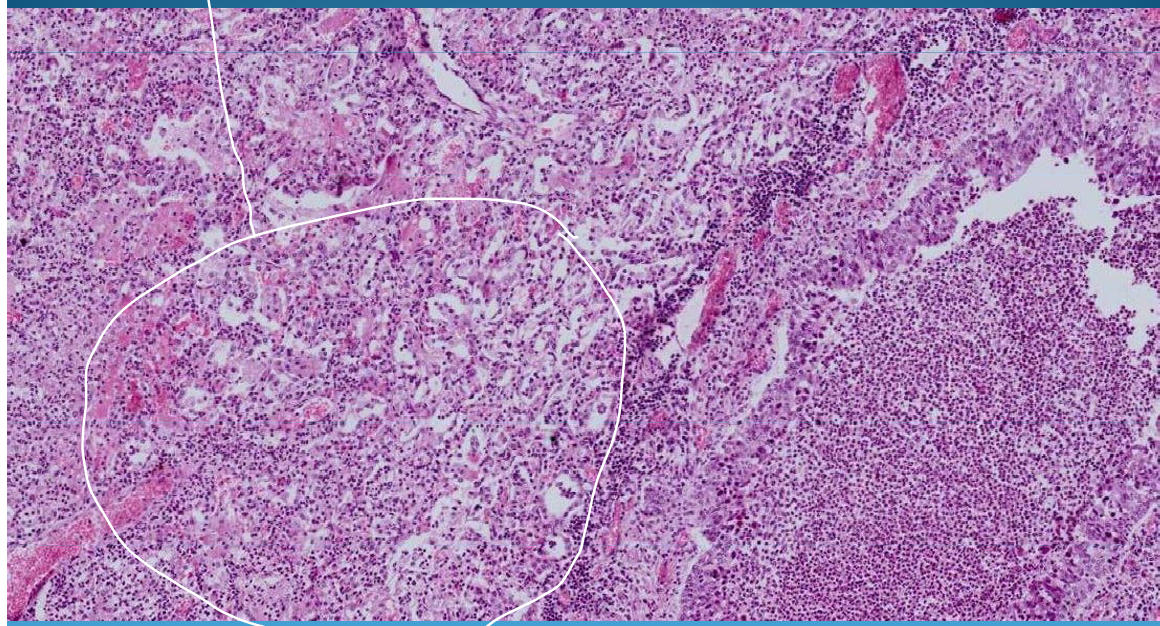
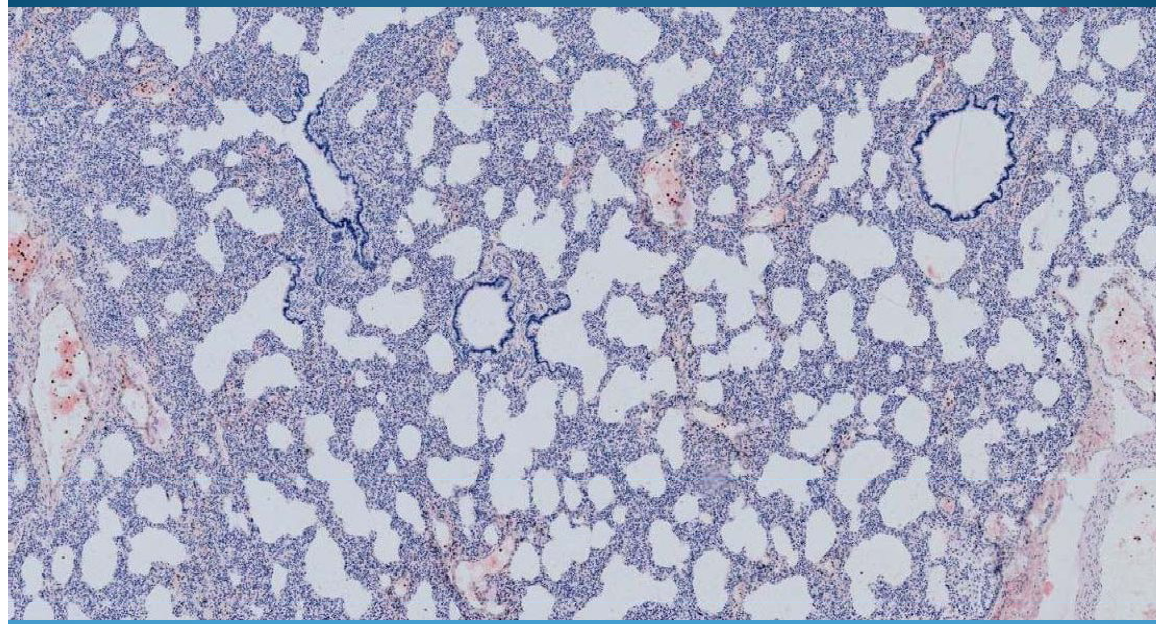
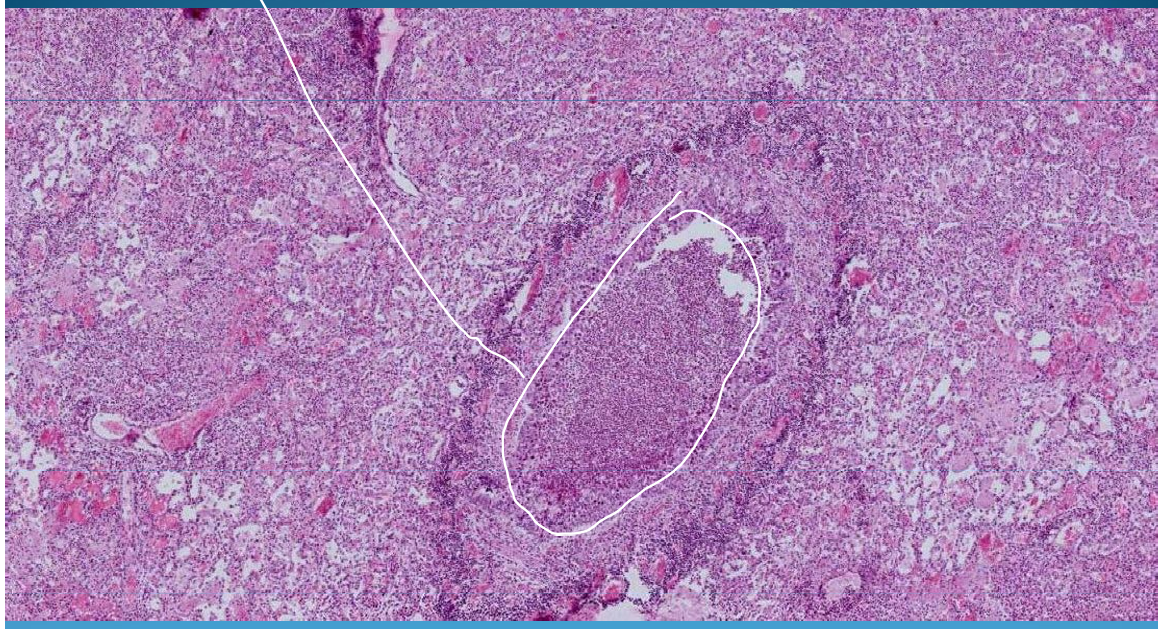
What is this?
LUNG:
Intersititial pneumonia - thick septum, lymphocyte and plasma cell infiltrate inside interalveolar septa, smooth alveoli
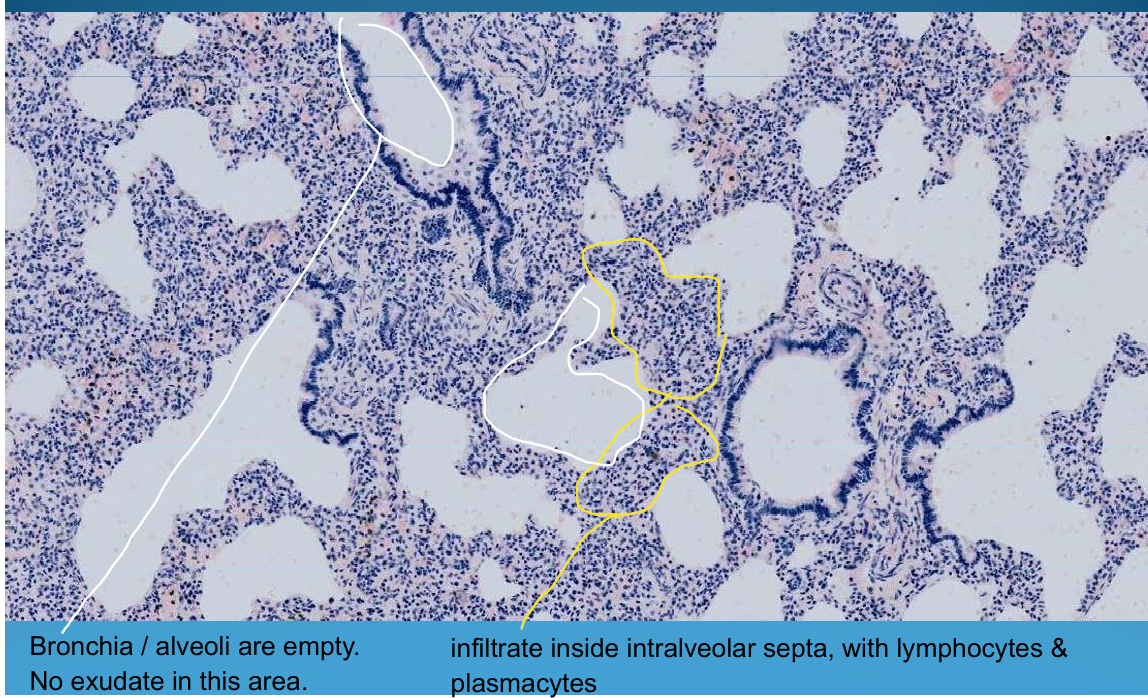
What is this?
LUNG:
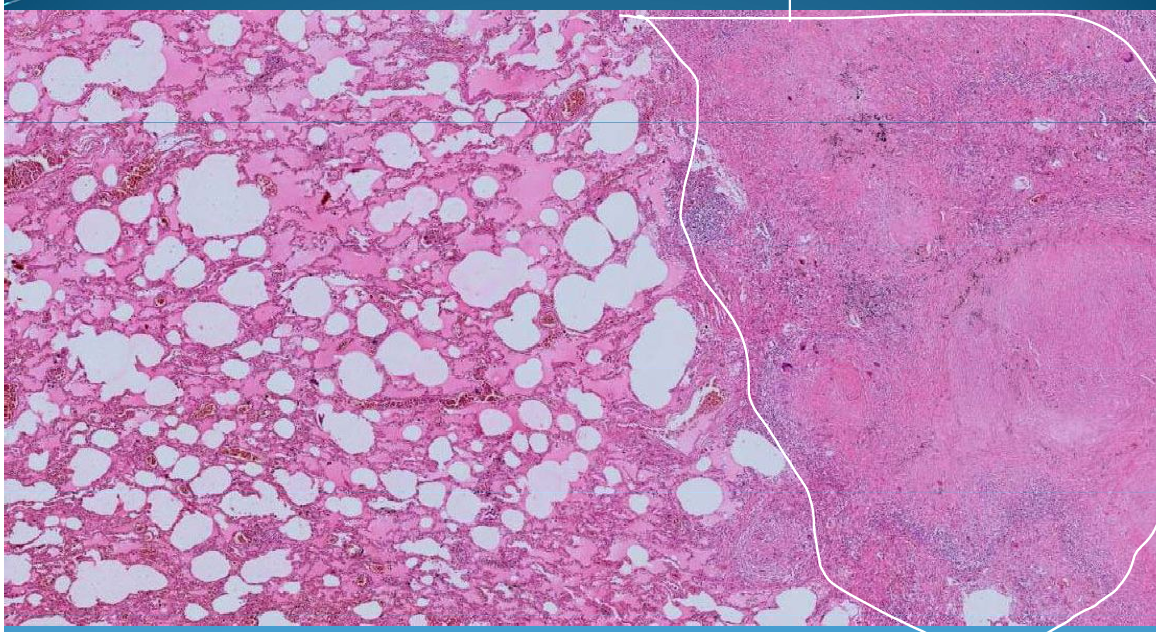
Pulmonary tuberculosis: Edema, tuberculous epitheioid granuloma with caseous necrosis and surrounded by lymphocytes; Langhans cells and epithelioid cells
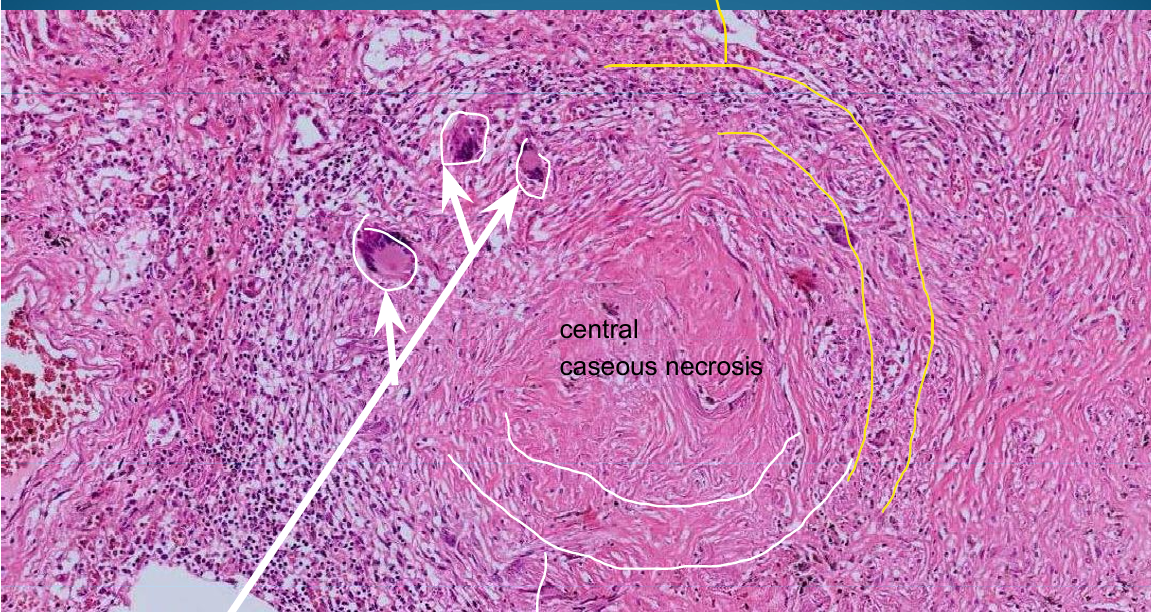
What is this?
LUNG:
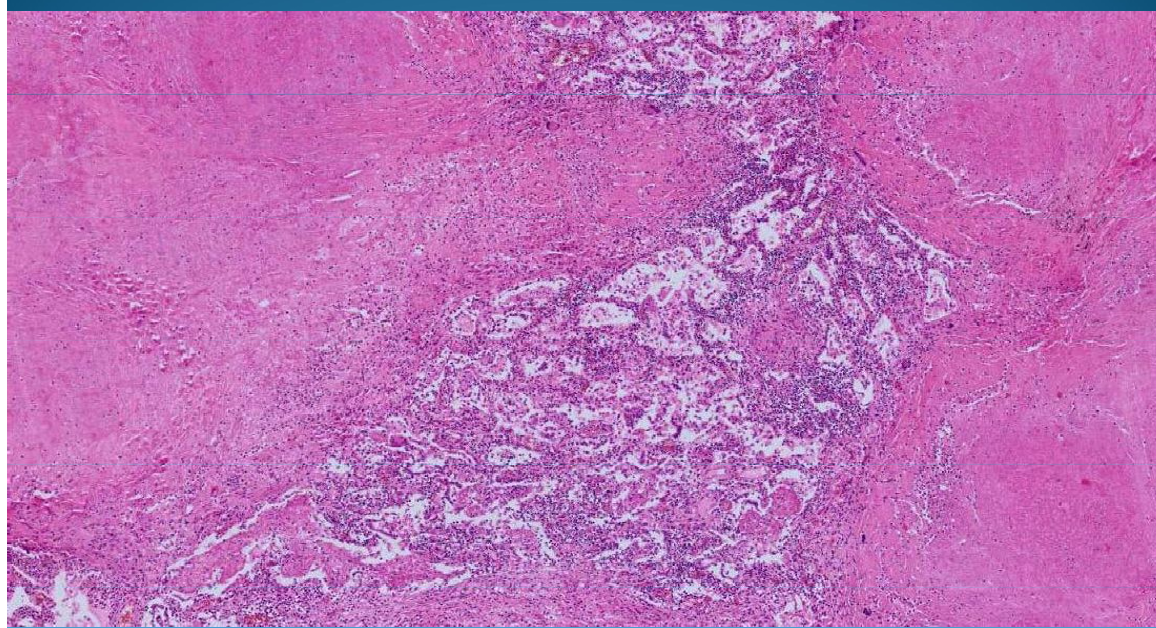
Pulmonary Tuberculosis + Bronchopneumonia: necrosis, inflammation and Langhans cells
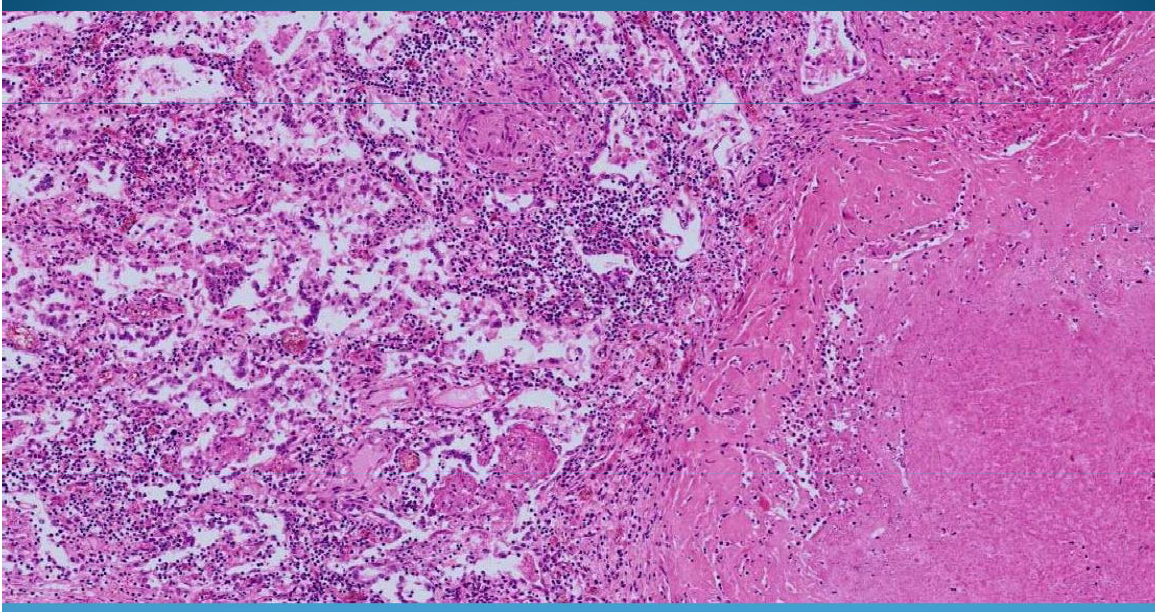
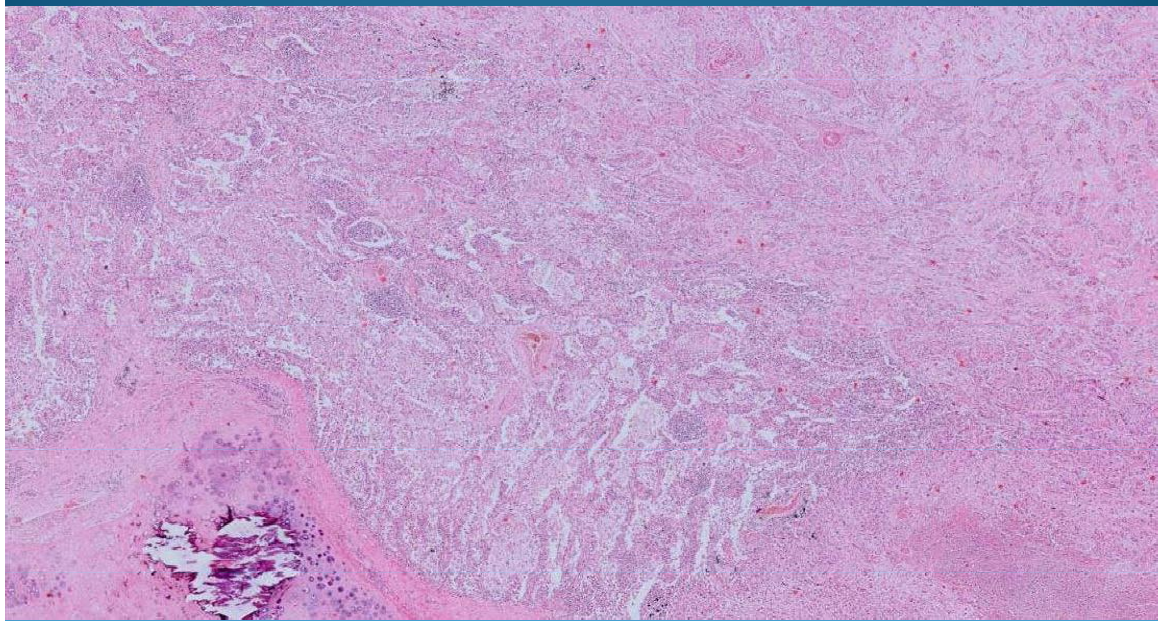
What is this?
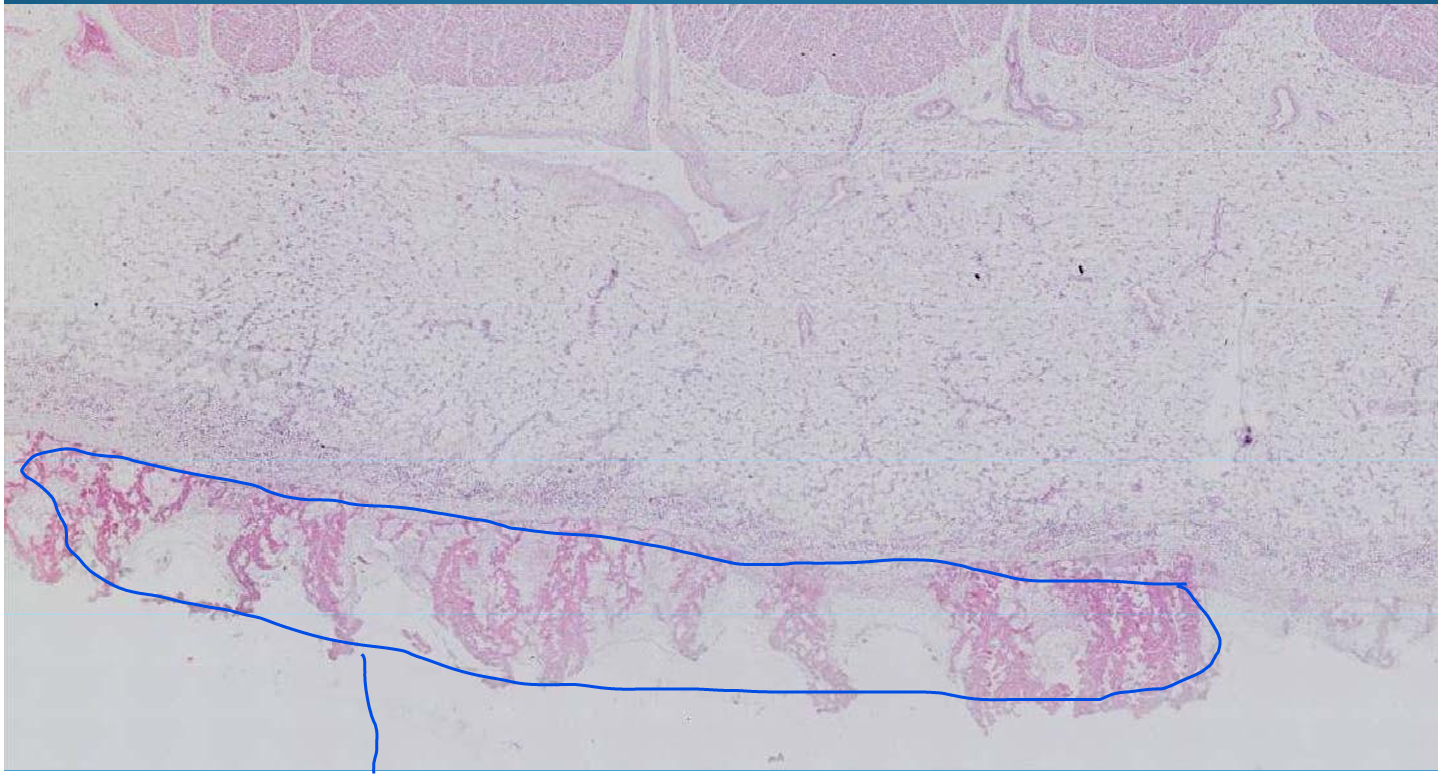
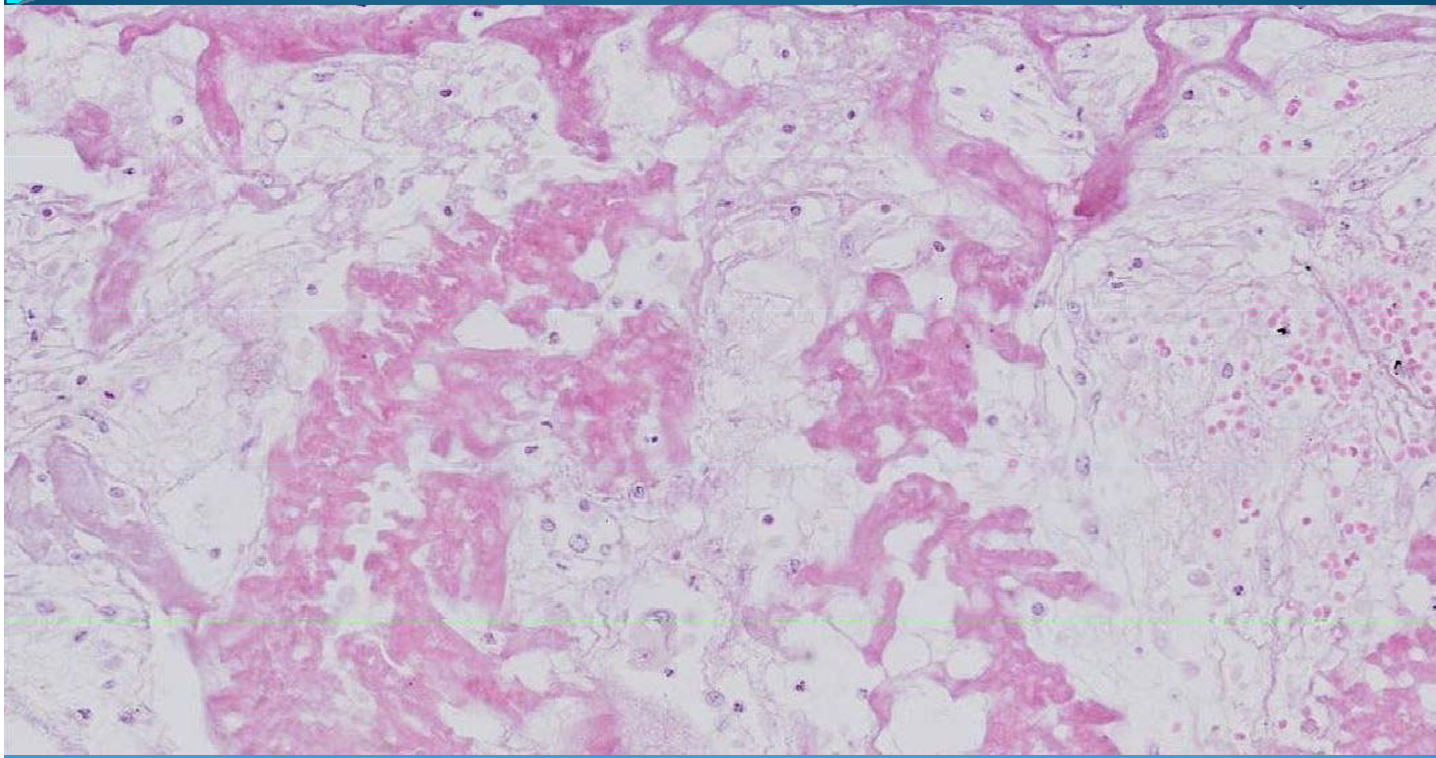
LUNG:
Pulmonary carcinoma: with well differentiated squamous cells and keratin pearls
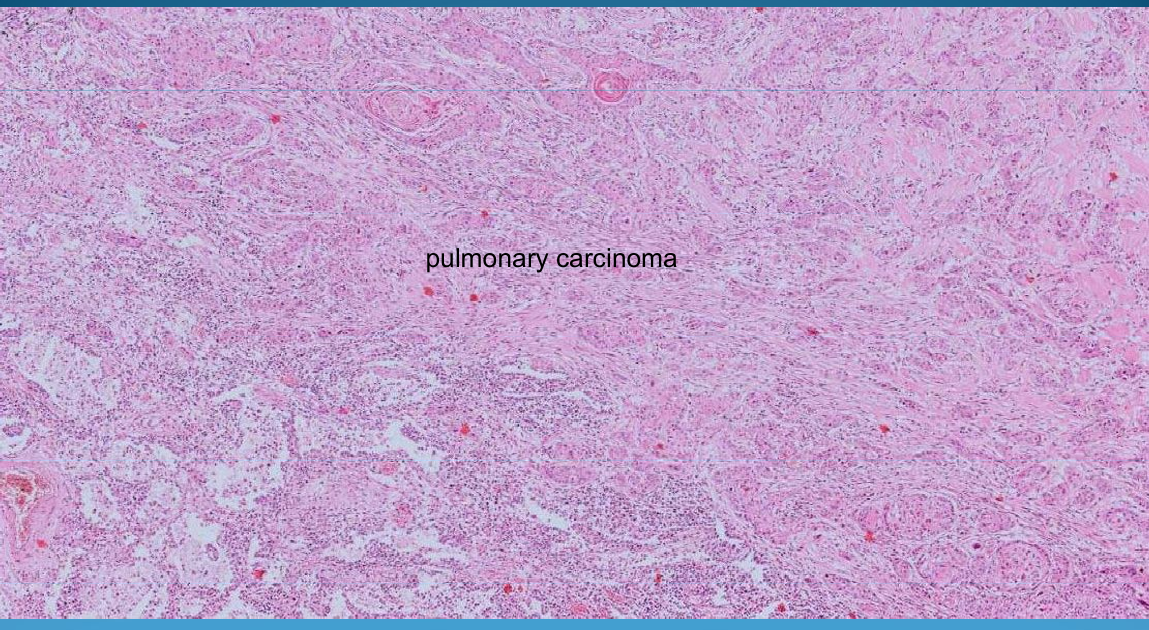
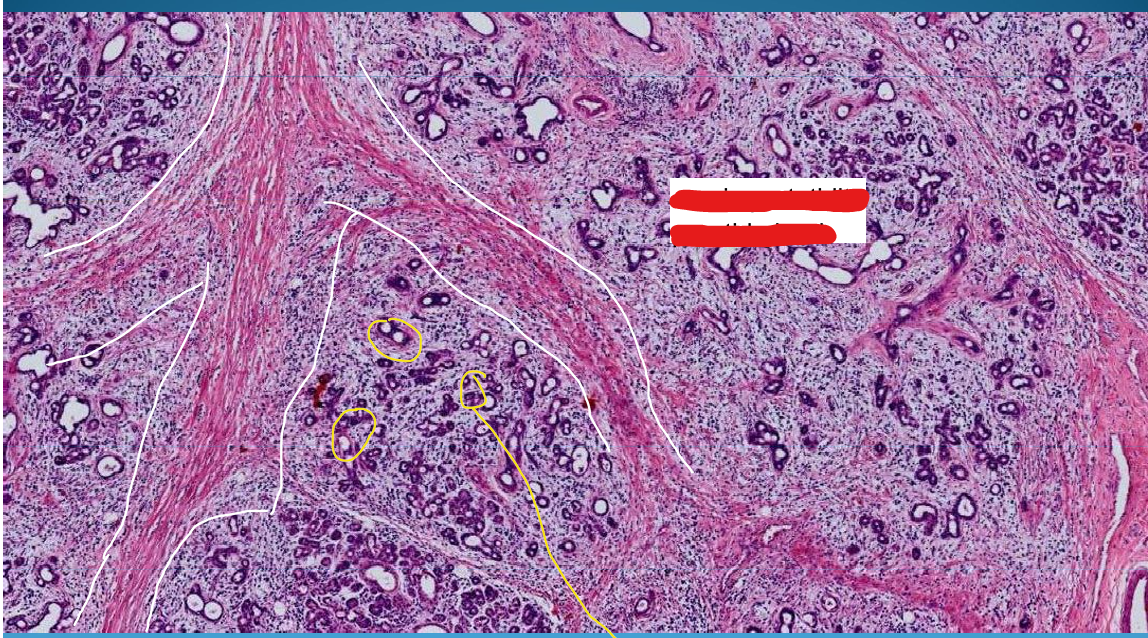
What is this?
Non-specific chronic parotiditis with atrophic parotid glands; gland disrupted by bands of fibrous tissue and lymphocyte/plasmocyte infiltrates
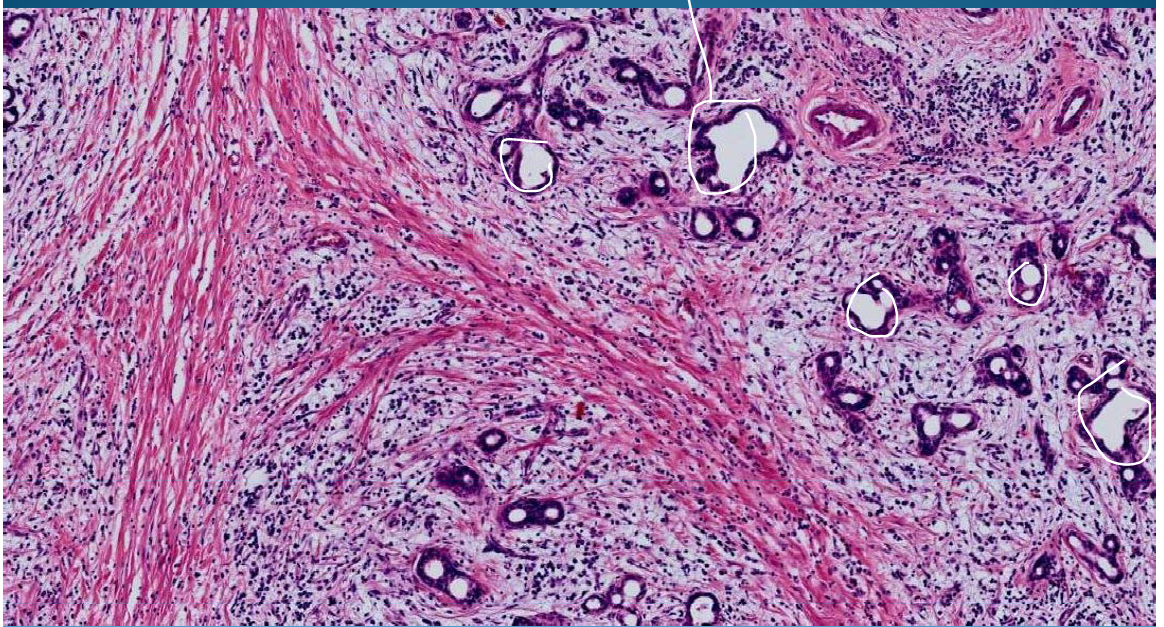
What is this?
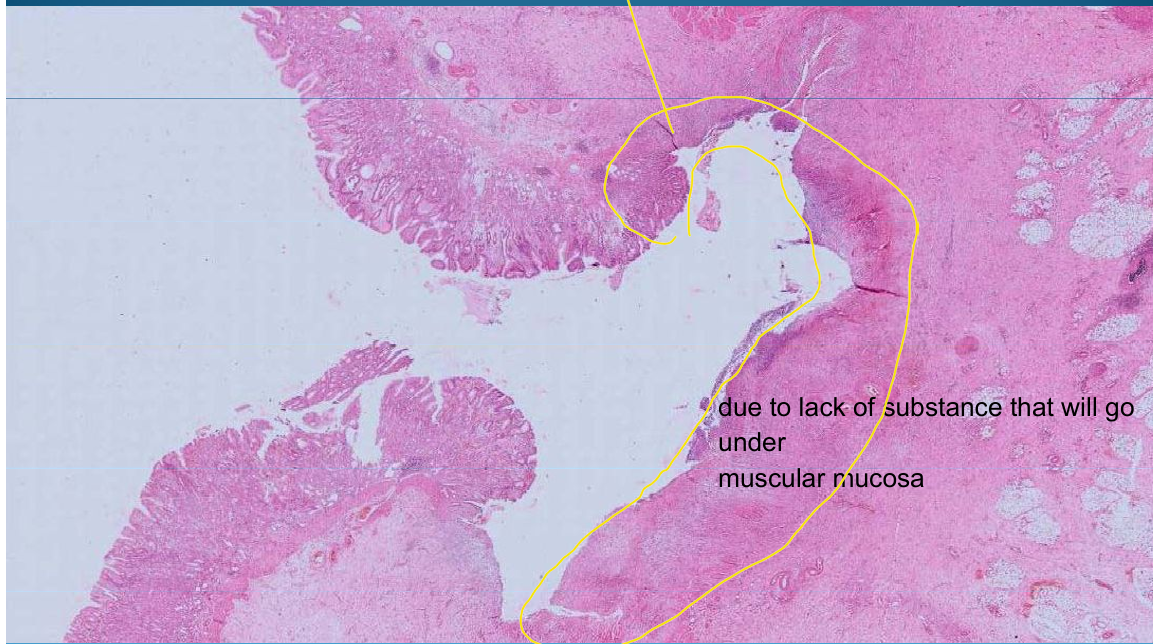
Chronic gastric ulcer: lack of substance that will go under muscularis mucosa
Layers of Ulcer:
1st layer - Fibrinoid necrosis
2nd layer - inflammatory cells
Granulomatous tissue layer between
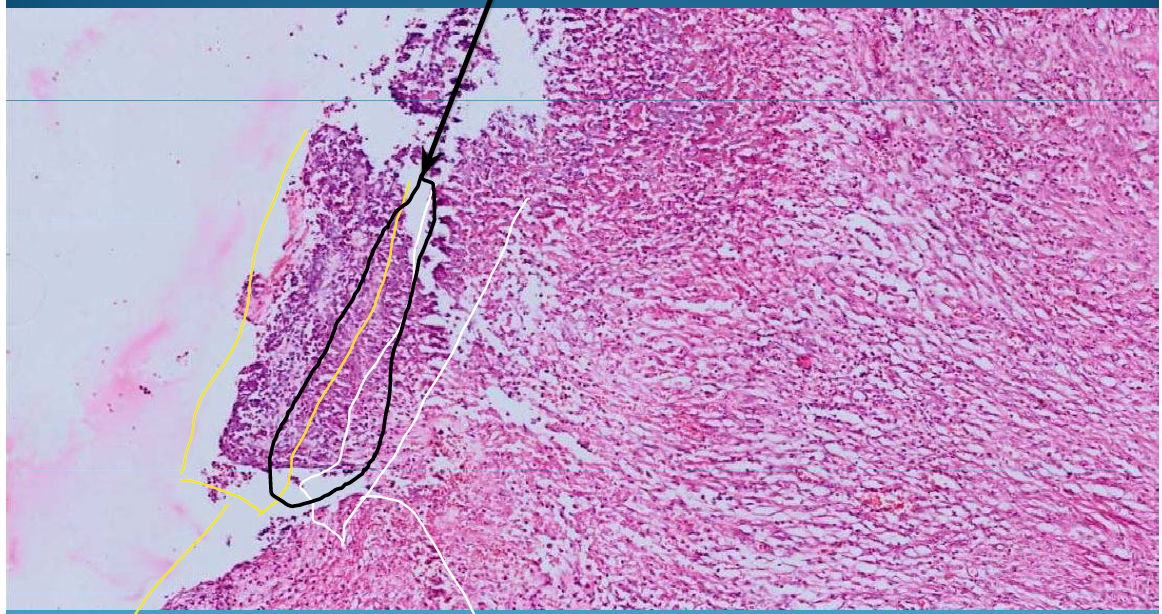
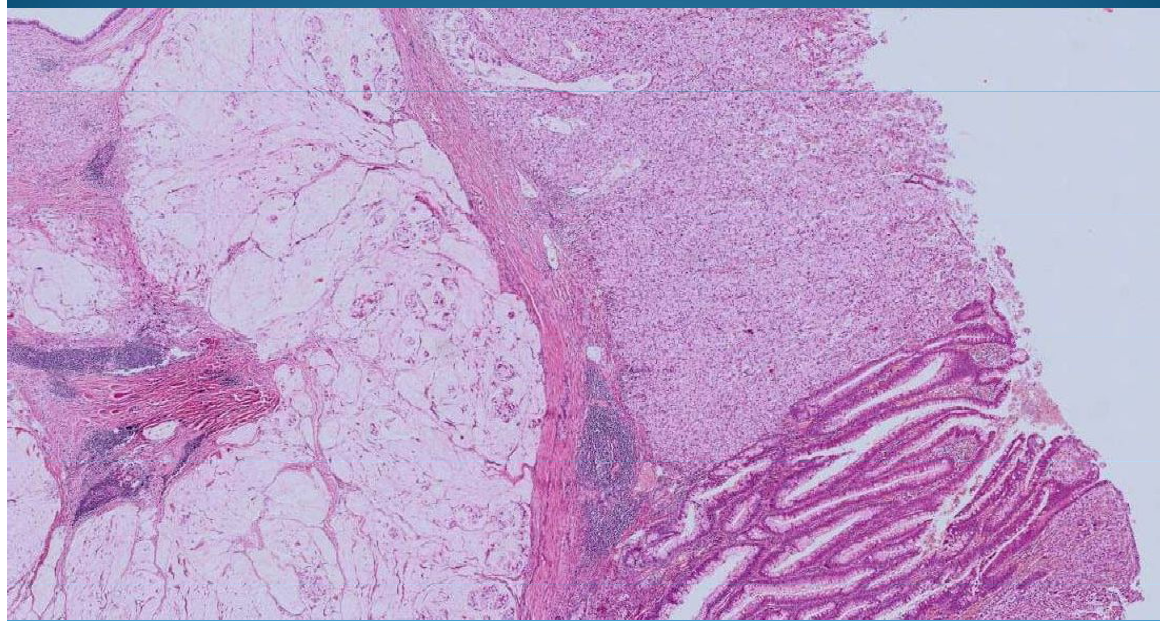
What is this?
STOMACH:
Diffused Gastric Cancer: Signet cell carcinoma (mucinous carcinoma)
What is this?
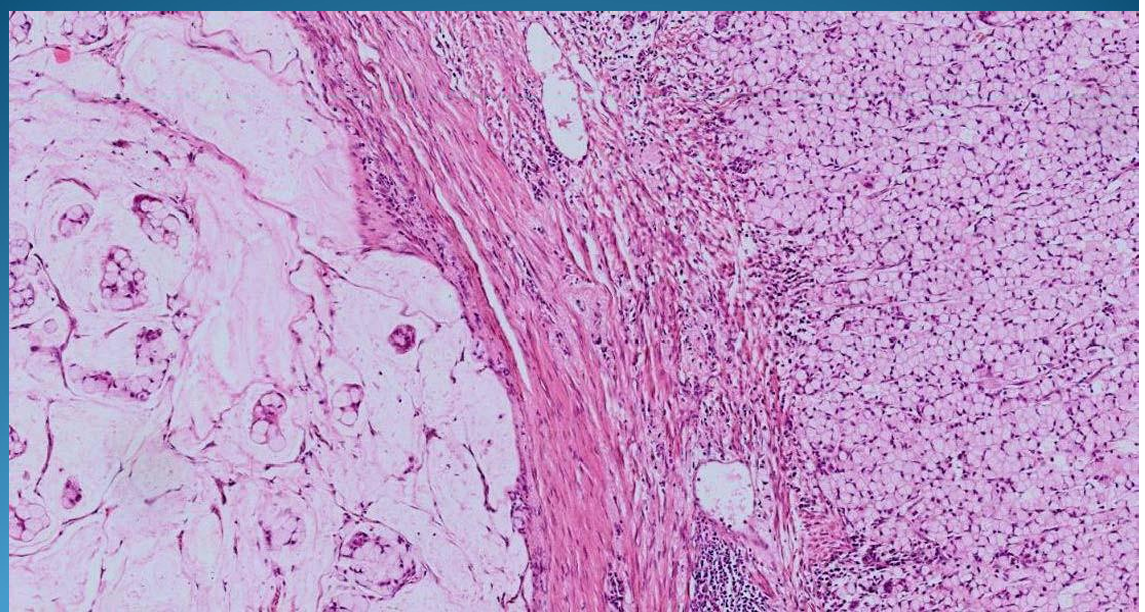
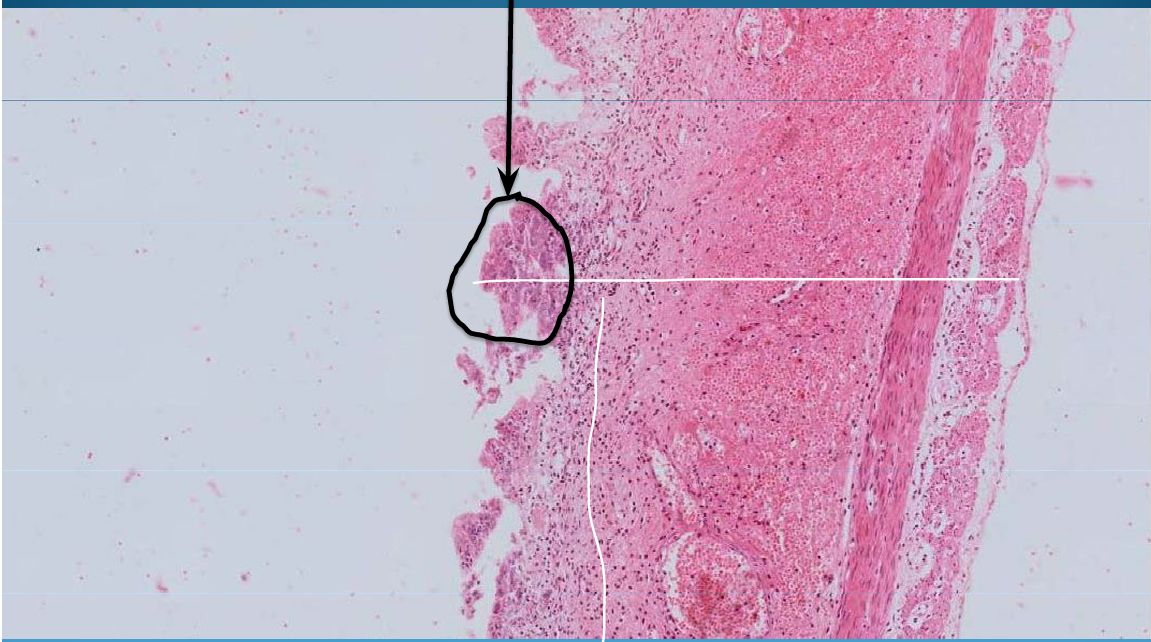
INTESTINE:
Enteritis: ulcerative and necrotic type with inflammation
What is this?
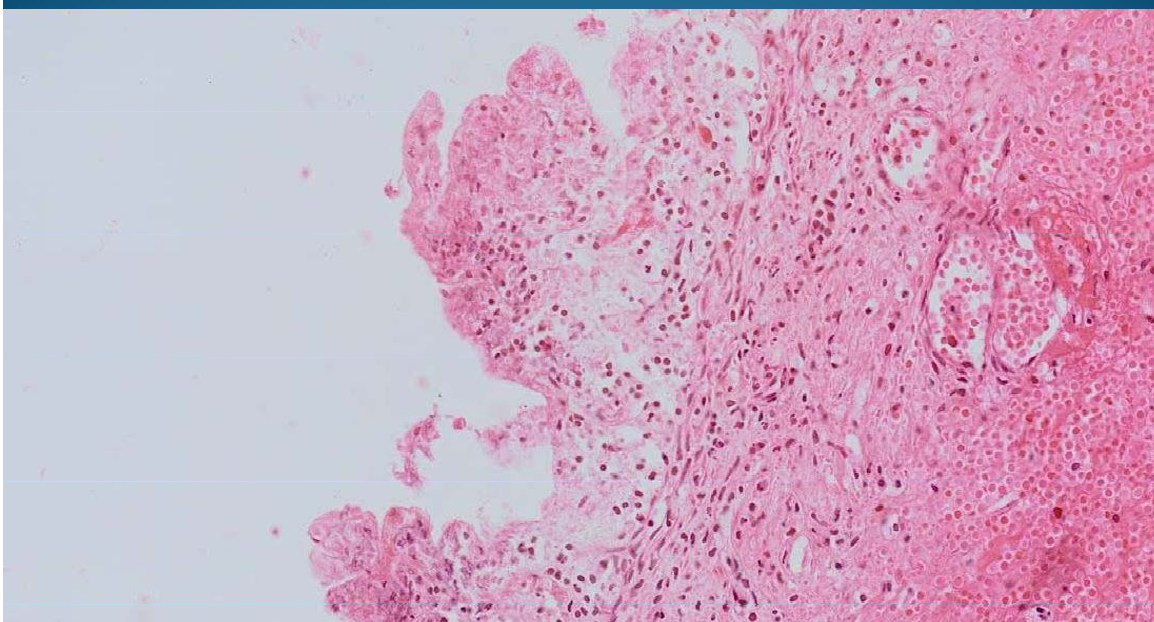
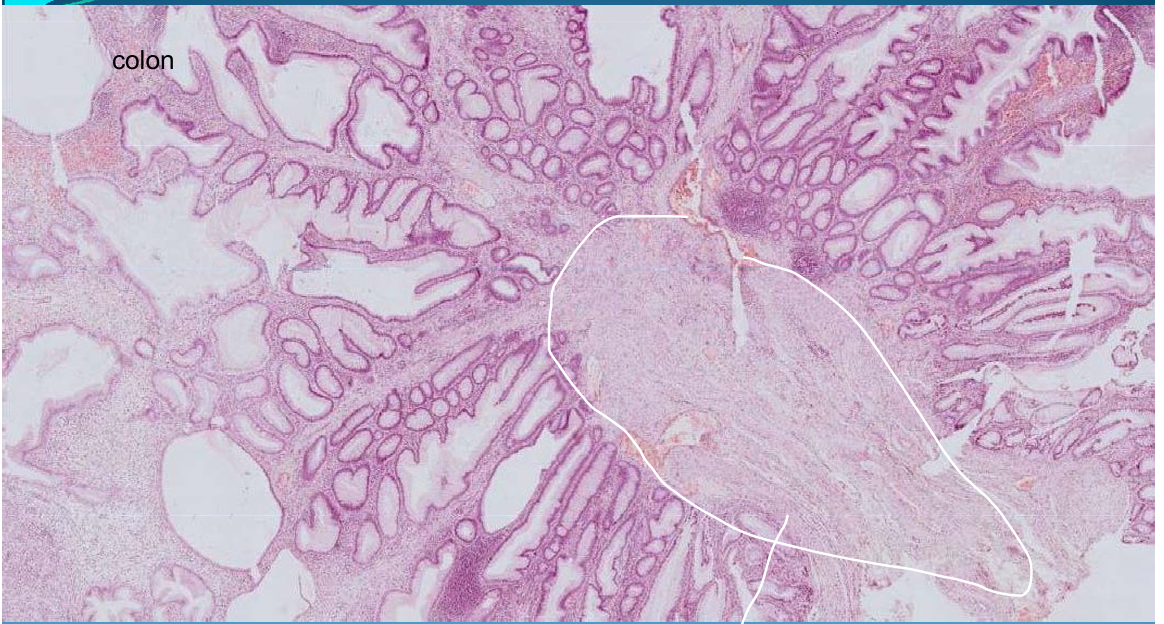
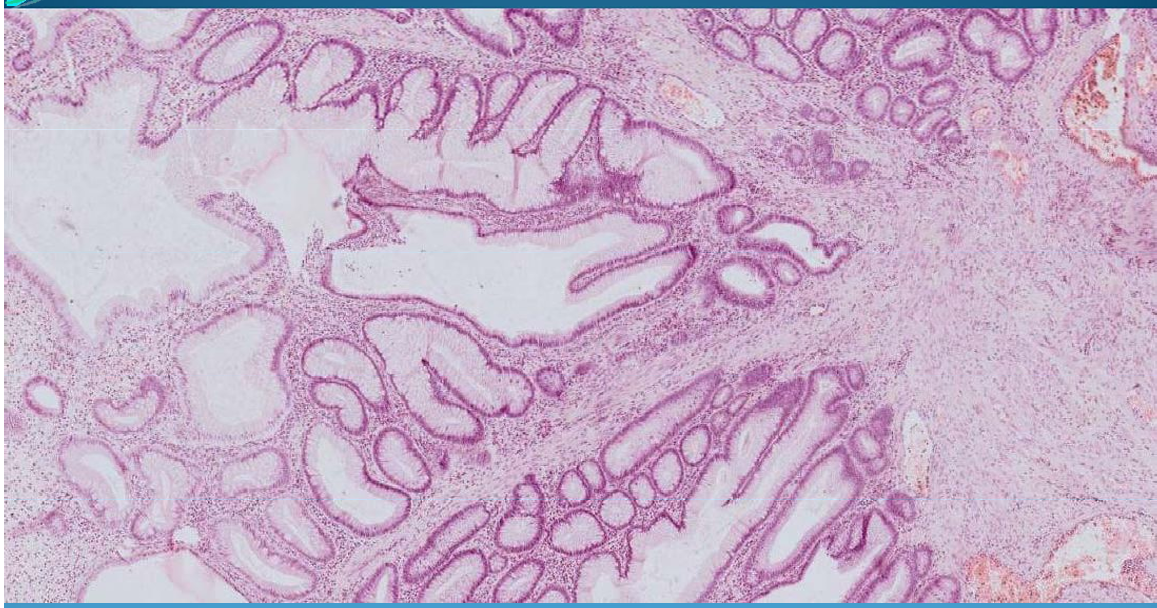
INTESTINE:
Colon adenomatous polyps - simple epithelial benign tumor
What is this?
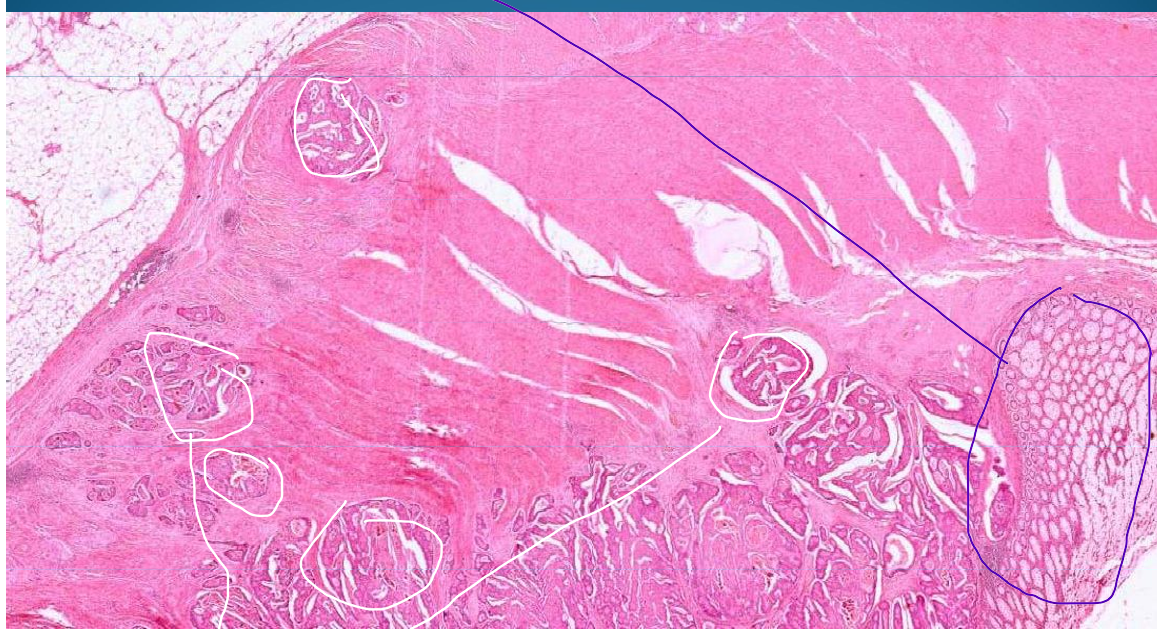
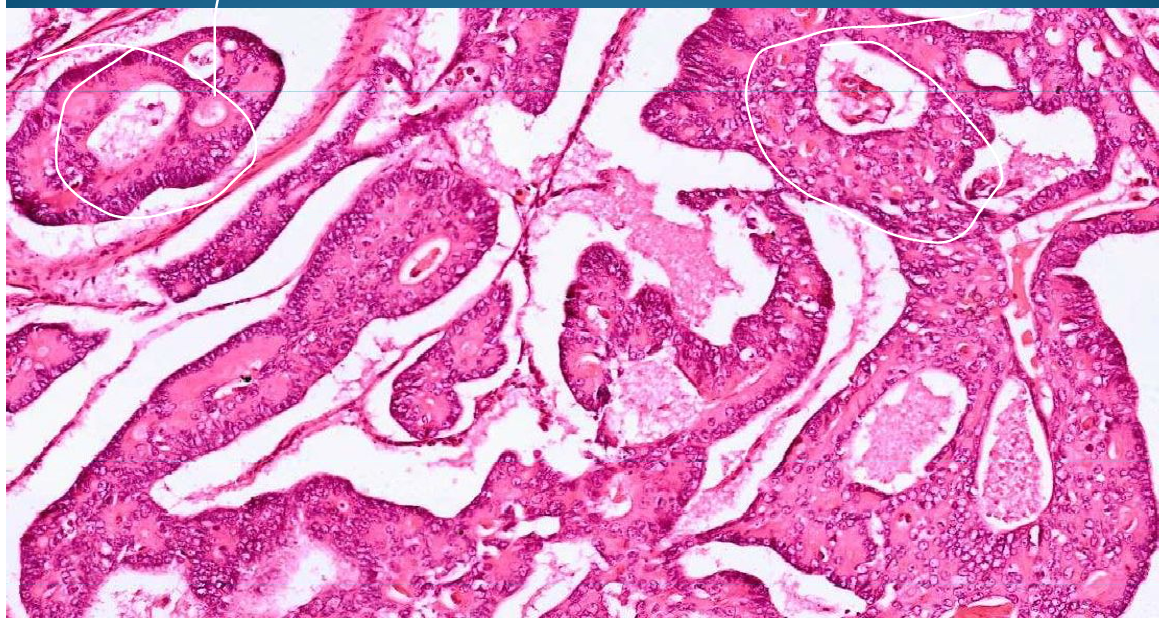
COLON:
Adenocarcinoma: Malignant epithelial tumor, moderately differentiated, crowded cells with small glands
What is this?
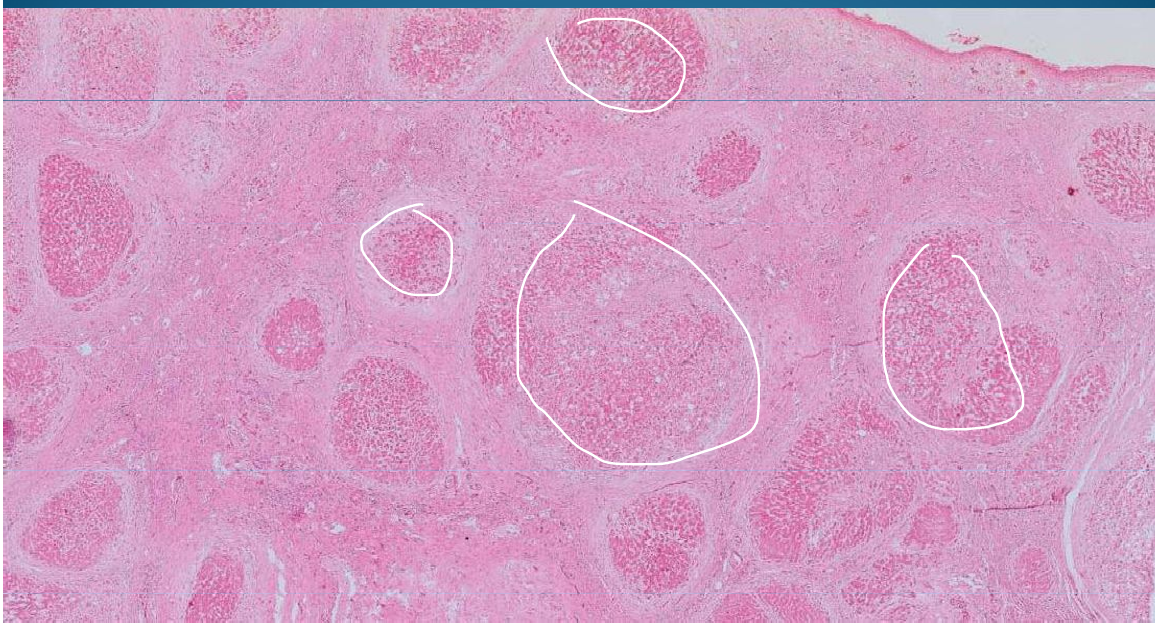
LIVER:
Liver cirrhosis: lots of fibrosis with regenerative nodules surrounded by sclerotic tissue and hyperplasia of biliary canaliculi; steatosis
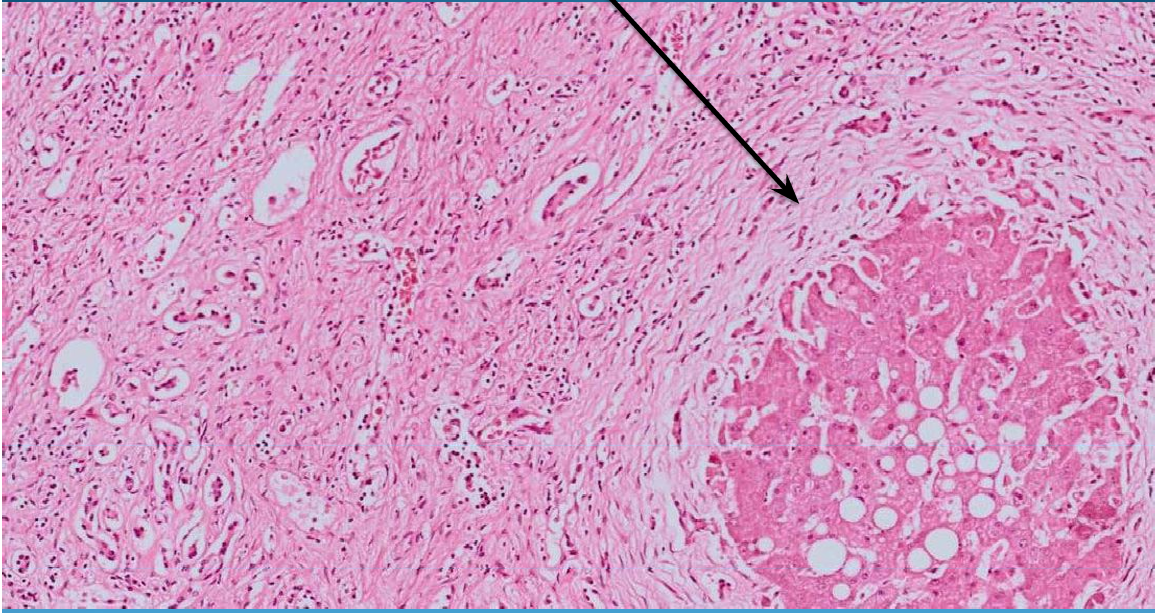
What is this?
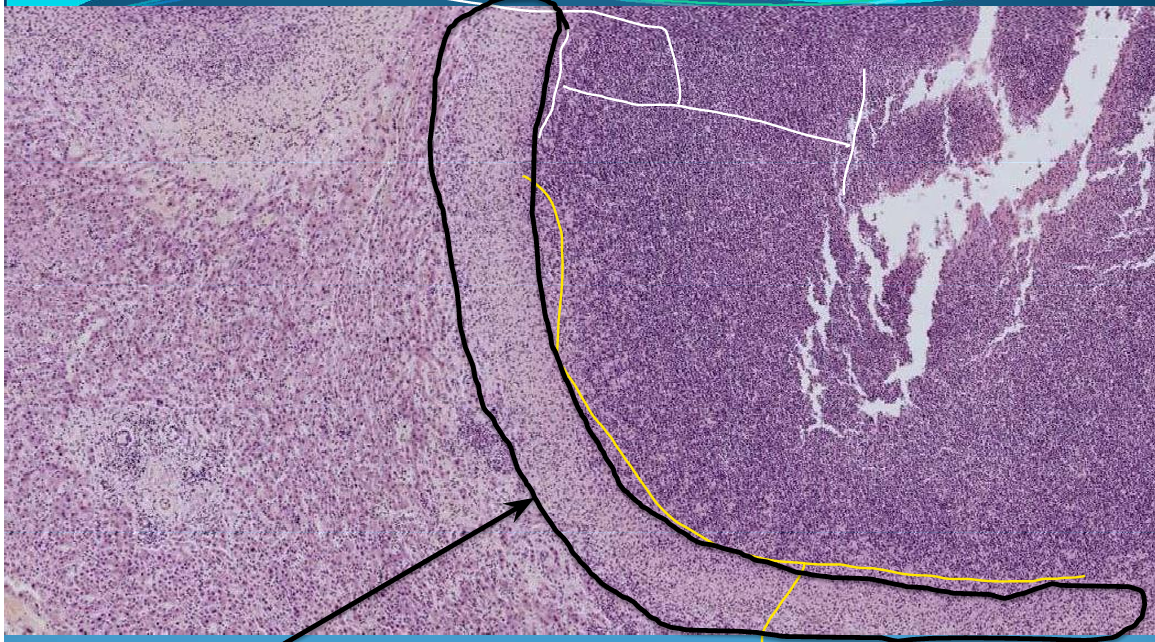
LIVER:
Hepatic abscess; well circumscribed area of liquefaction necrosis + PMNs; pyogenic capsule
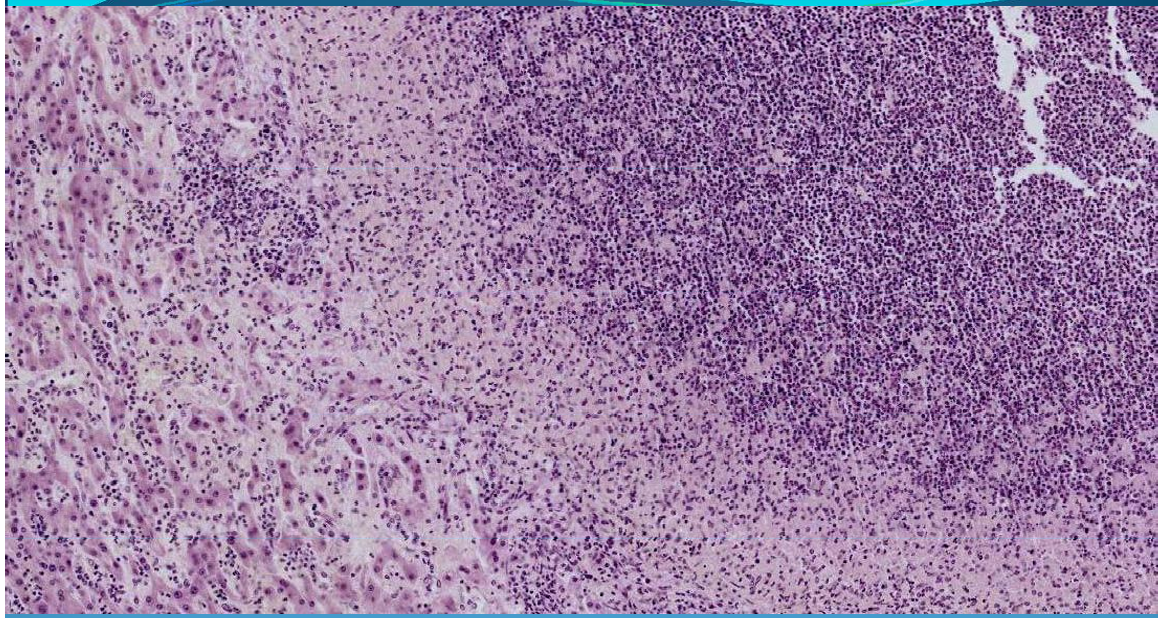
What is this?
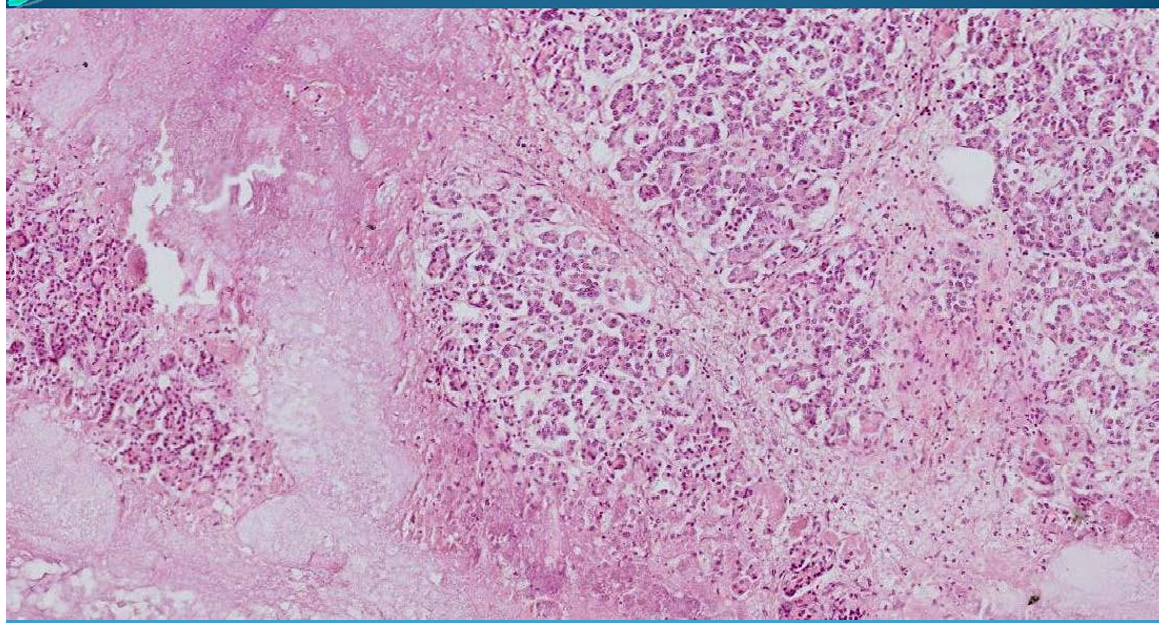
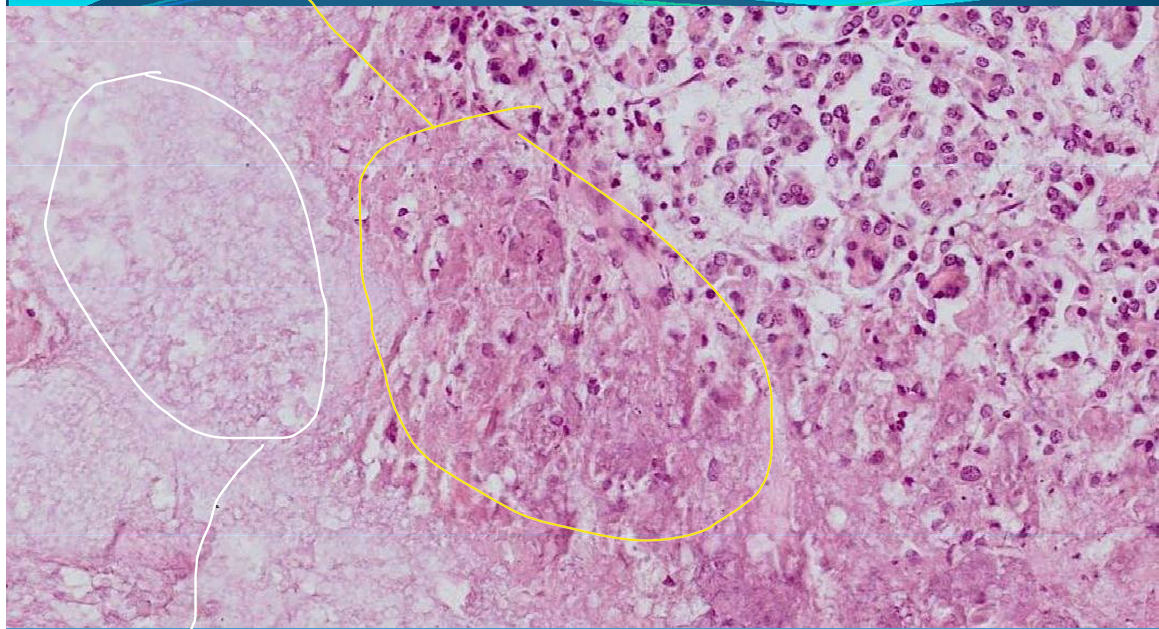
PANCREAS:
Cytosteatonecrosis: acute hemorrhagic pancreatitis, ulcero-necrotic pancreatitis; necrosis of pancreatic tissue, fatty tissue and acini
What is this?
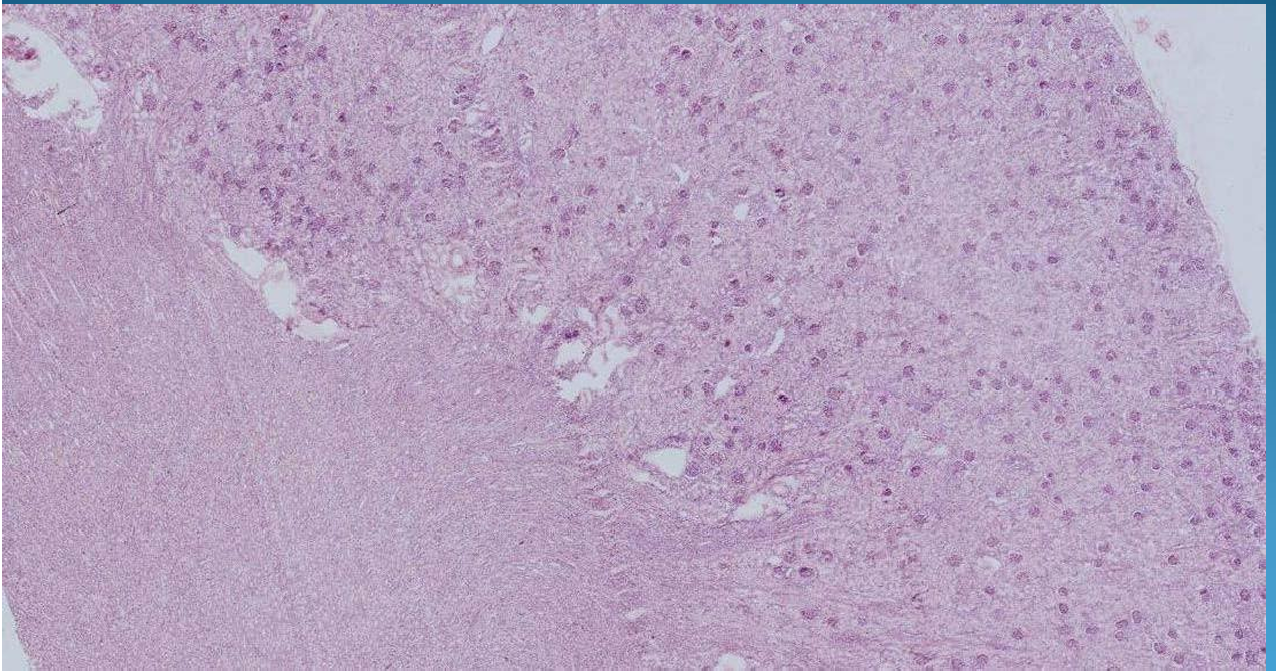
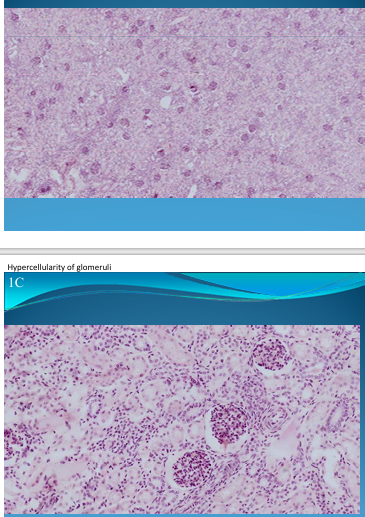
KIDNEY:
Acute diffused glomerulonephritis: Streptococcus infection, hypercellularity of glomeruli
What is this?
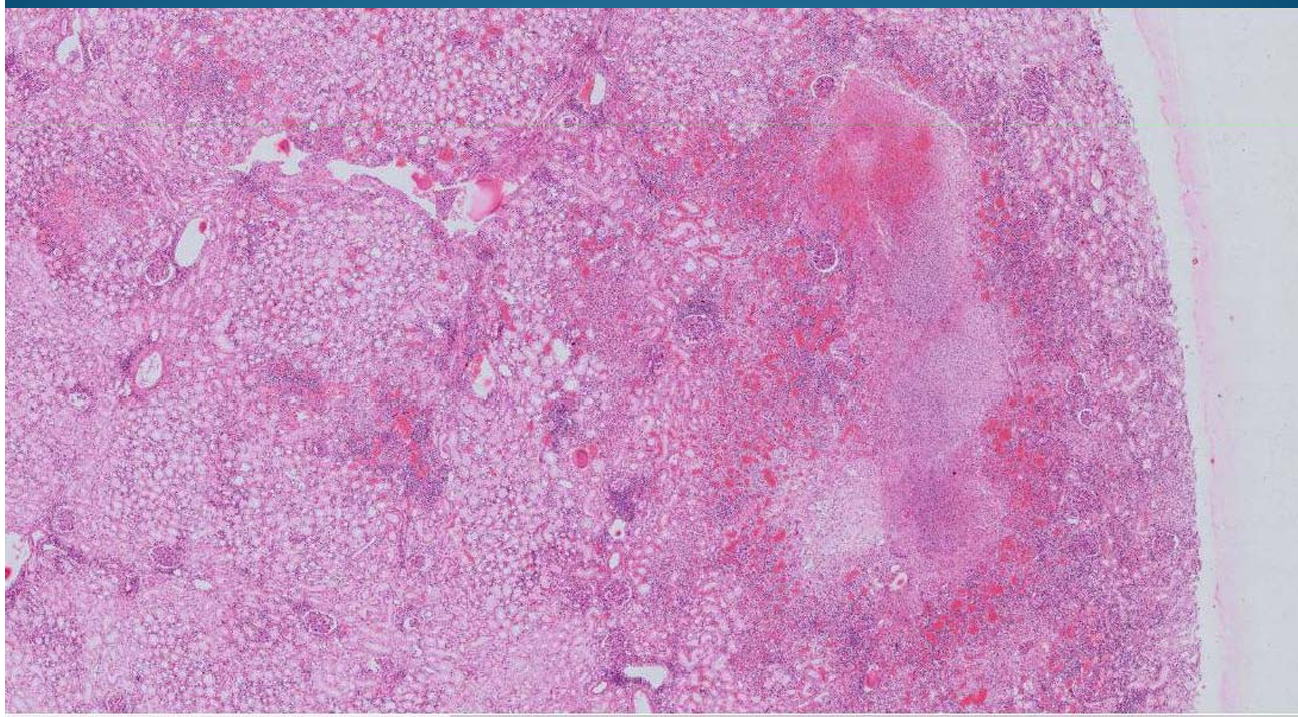
KIDNEY:
Pyelonephritis = Microabscess, similar to abscess in liver
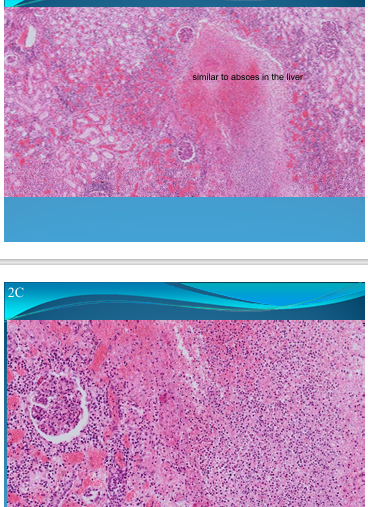
What is this?
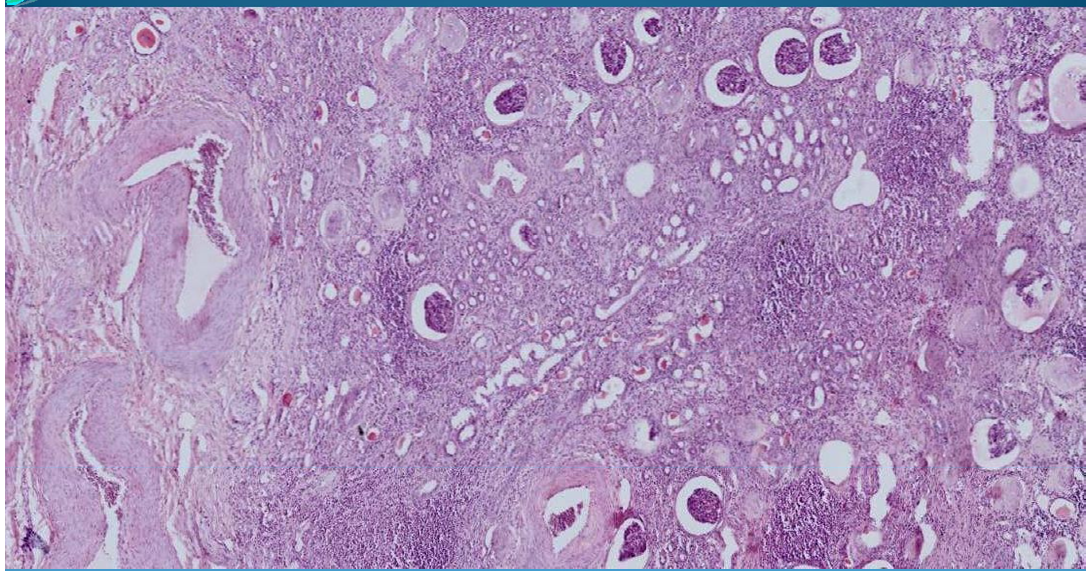
KIDNEY:
Chronic Pyelonephritis: Tubules are dilated → contain hyaline cylinders; glomeruli hyalinized due to scelrosis - centripetal type of sclerosis from periphery to center of glomeruli. Pseudothyroidization of aspect of renal parenchyma
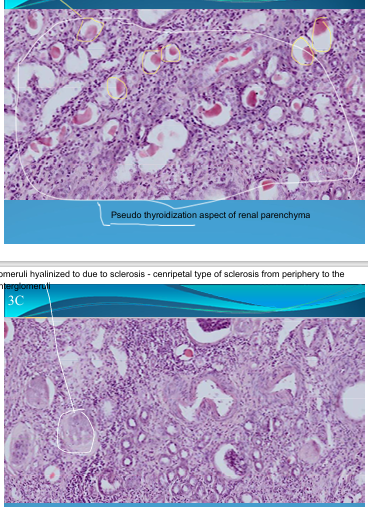
What is this?
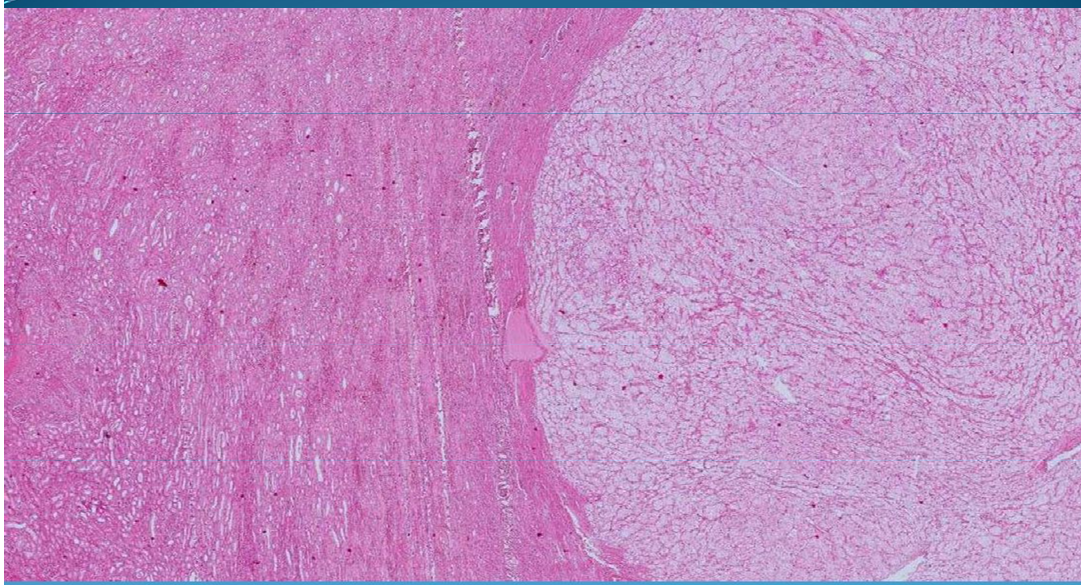
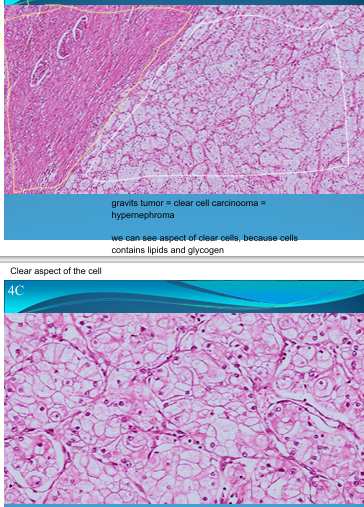
KIDNEY:
Grawitz tumor (renal cell carcinoma):
at periphery - atrophy of parenchyma due to compression of growing tumor
Grawitz tumor = Clear cell carcinoma = Hypernephroma
we can see aspect of clear cells because cells contain lipids and glycogen
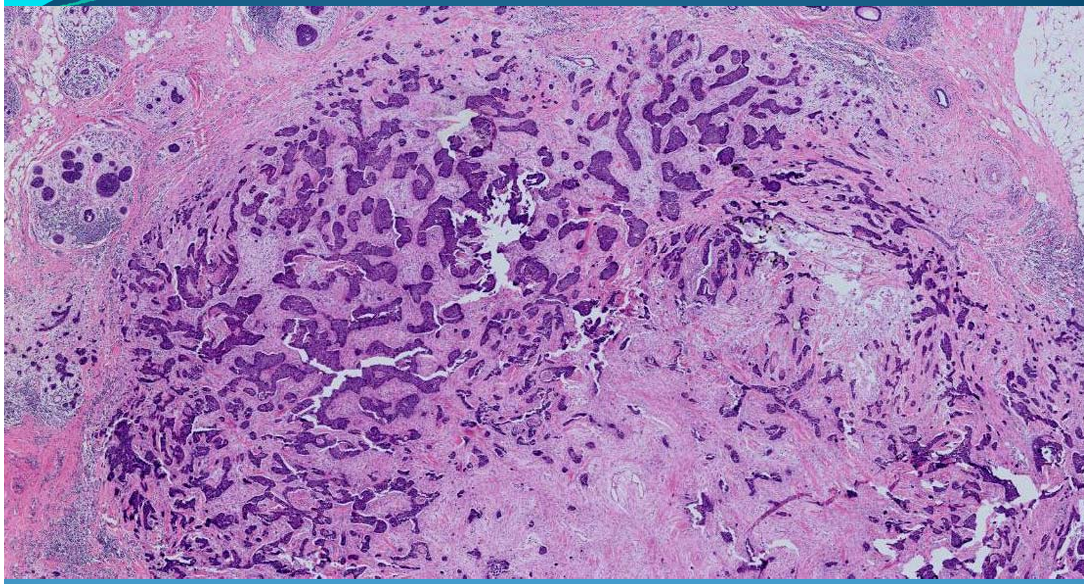
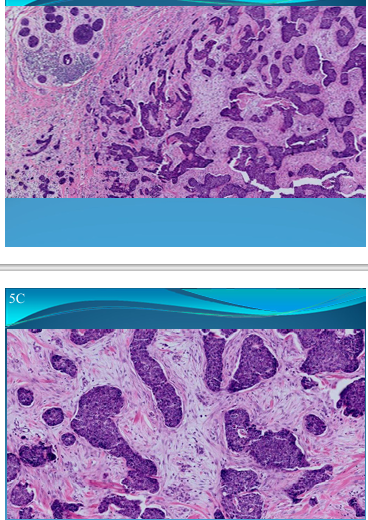
What is this?
BREAST(Mammary glands):
Mammary carcinoma: has invasive ductal carcinoma with fibrous stroma and trabecular and insular aspect
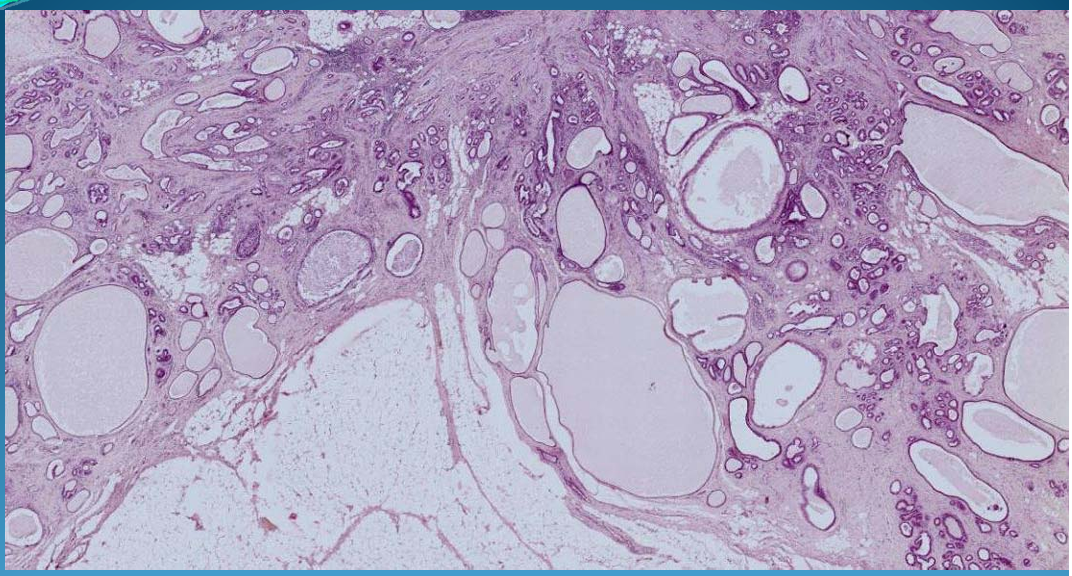
What is this?
BREAST (Mammary gland):
Fibrocystic mastosis
Dilated ducts
Glandular and mesenchymal hyperplasia
Apocrine metaplasia = ducts lined by follicular epithelium
Inflammatory cells
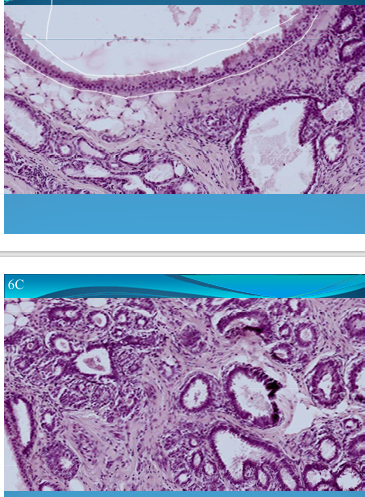
What is this?
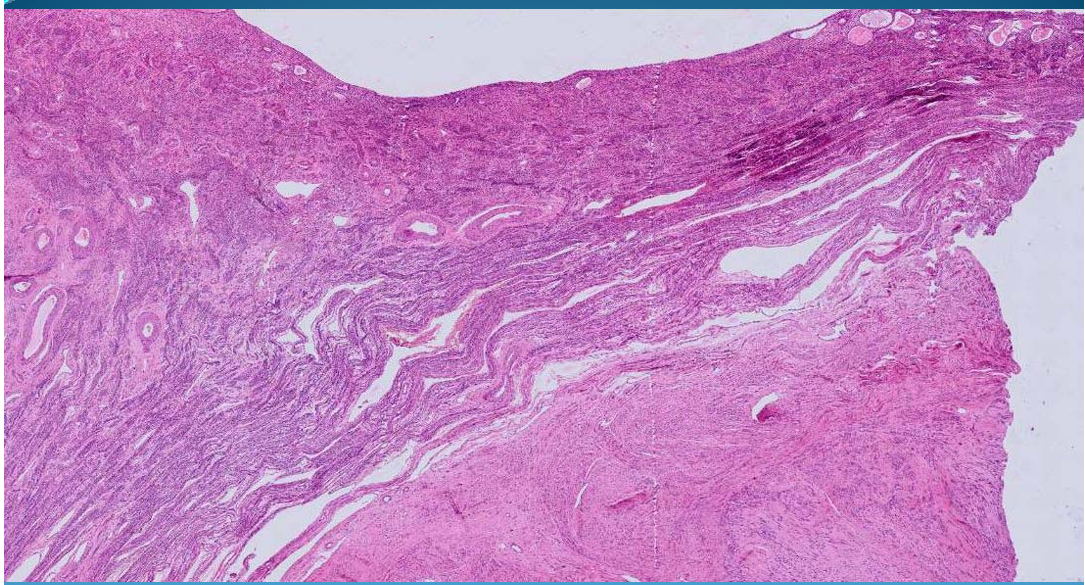
UTERUS:
Leiomyoma of endometrium = acute mesenchymal tumor, rising up from smooth muscle.
Pseudocapsule of tumoral growth due to compression
Styrofoam aspect of smooth muscle with nuclei which are elongated with rounded ends
Hyaline tissue
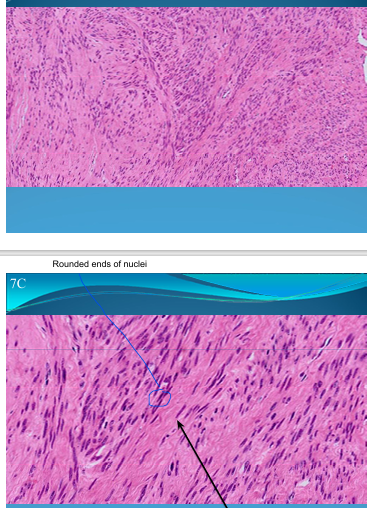
What is this?
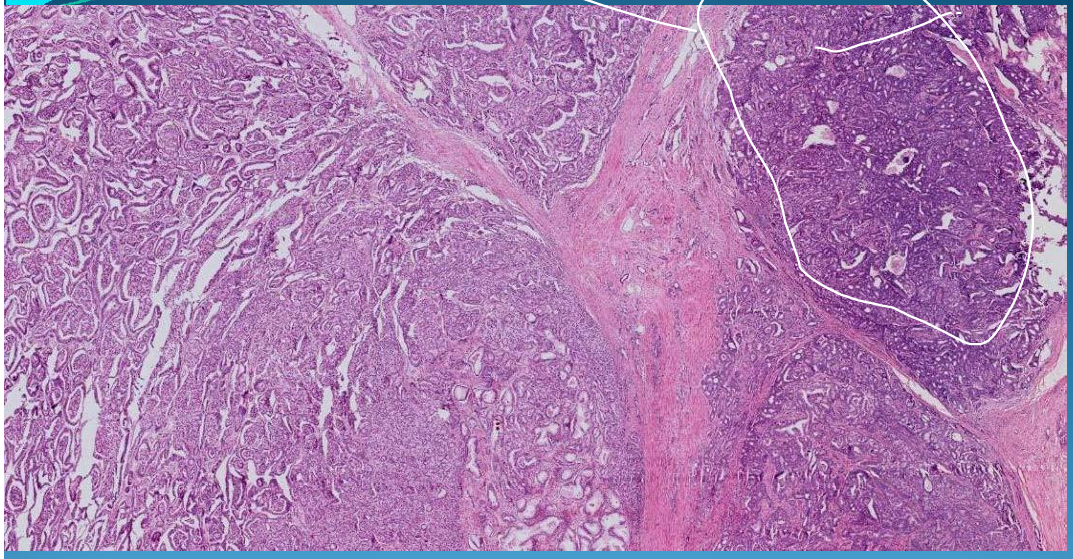
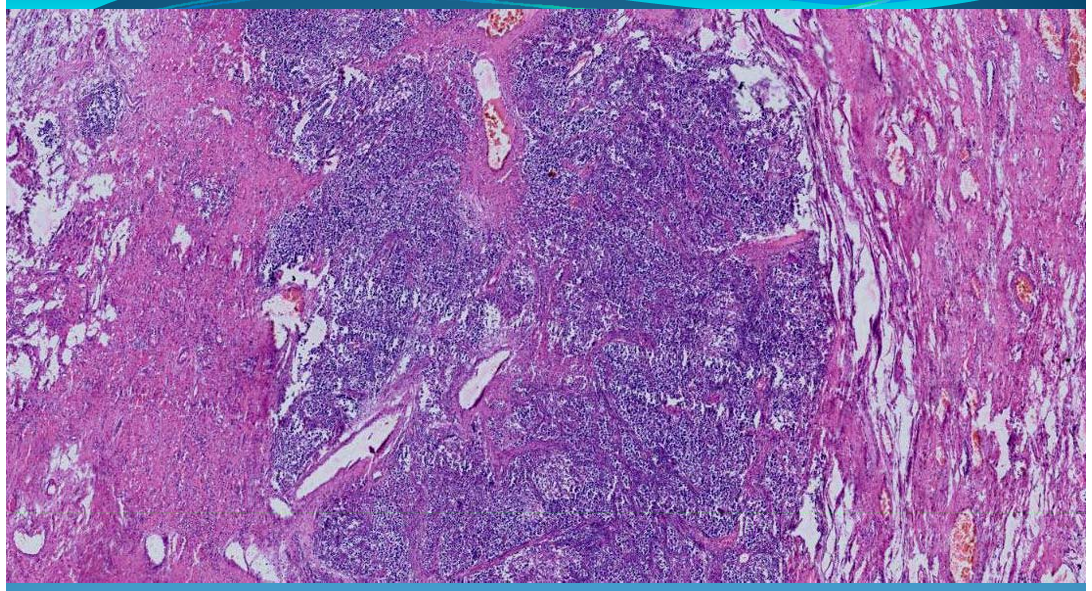
PROSTATE:
Prostatic adenocarcinoma: Grade 3/4, epithelial malignant tumor
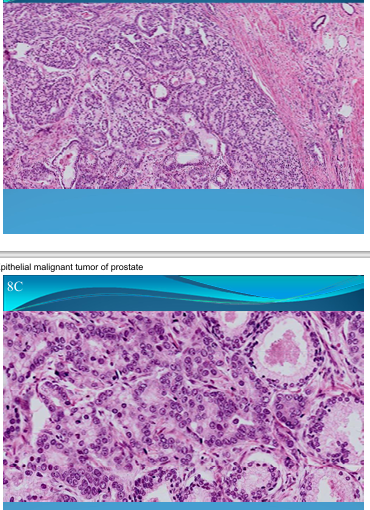
What is this?
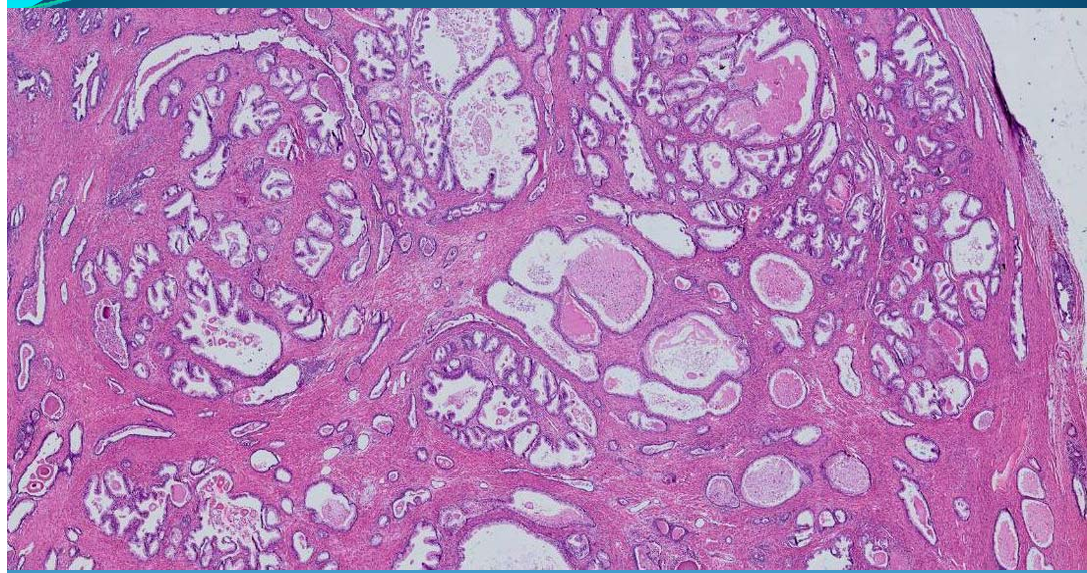
PROSTATE:
Benign Nodular Hyperplasia: fibrosis, muscular hyperplasia - dilated ducts with fern leaf aspect and some with sympexions
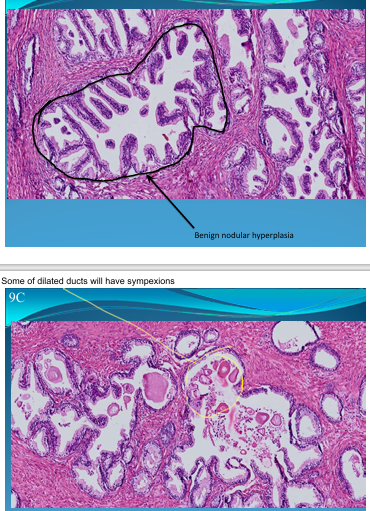
What is this?
TESTIS:
Seminoma = Malignant tumor of testicle rising from germ cells, clear cytoplasm + monomorphic, island of tubular cells separated by fibrostroma infiltrated with lymphocytes.
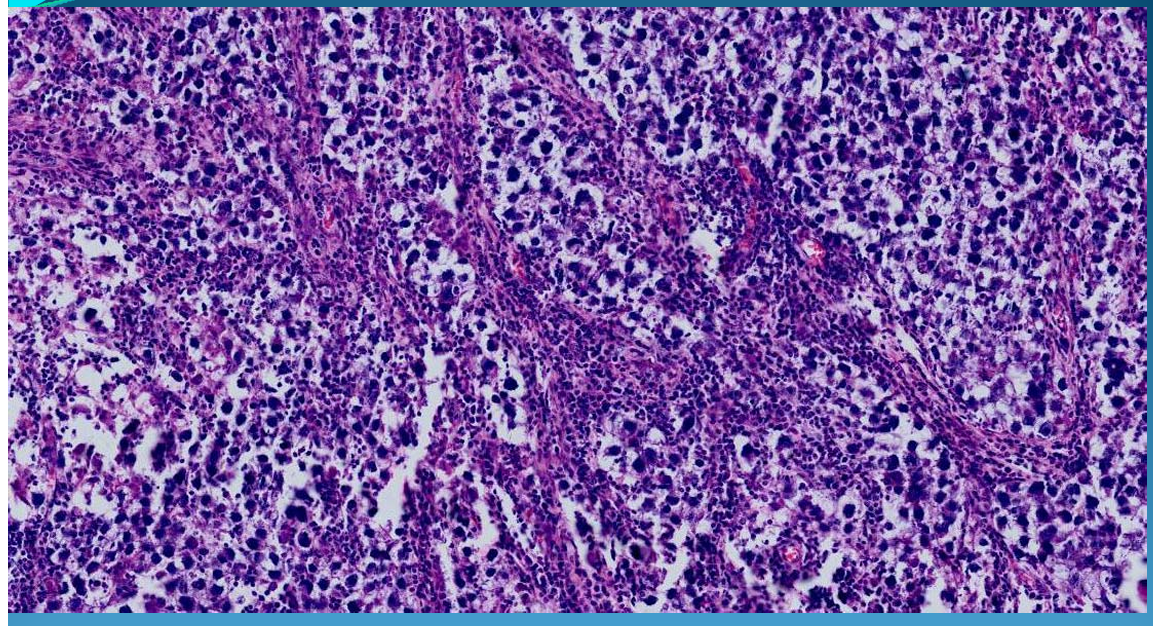
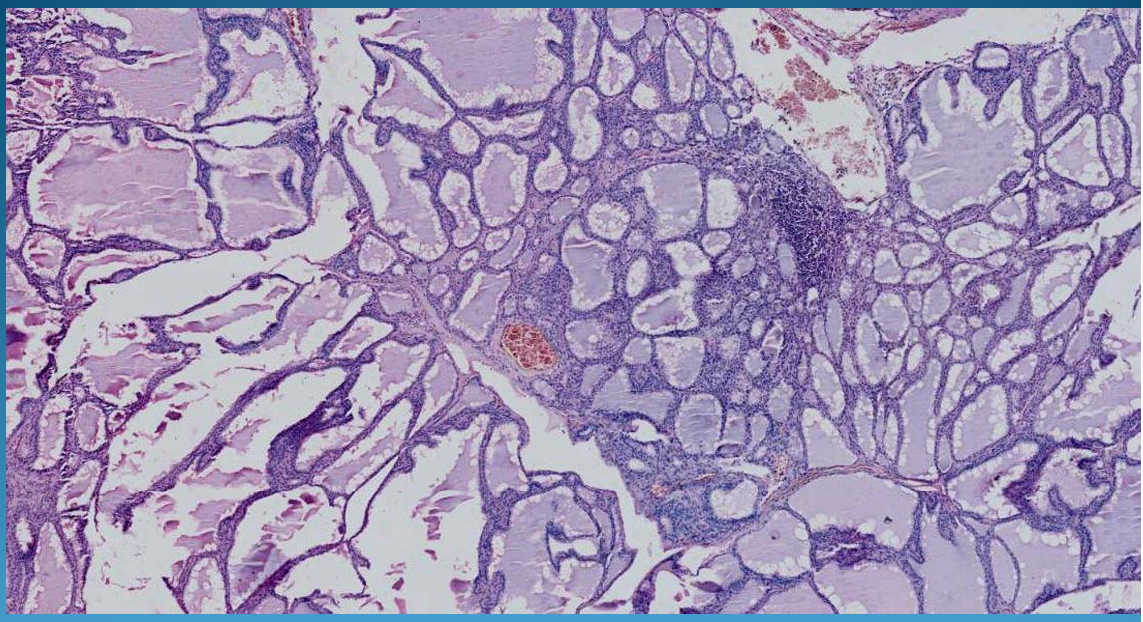
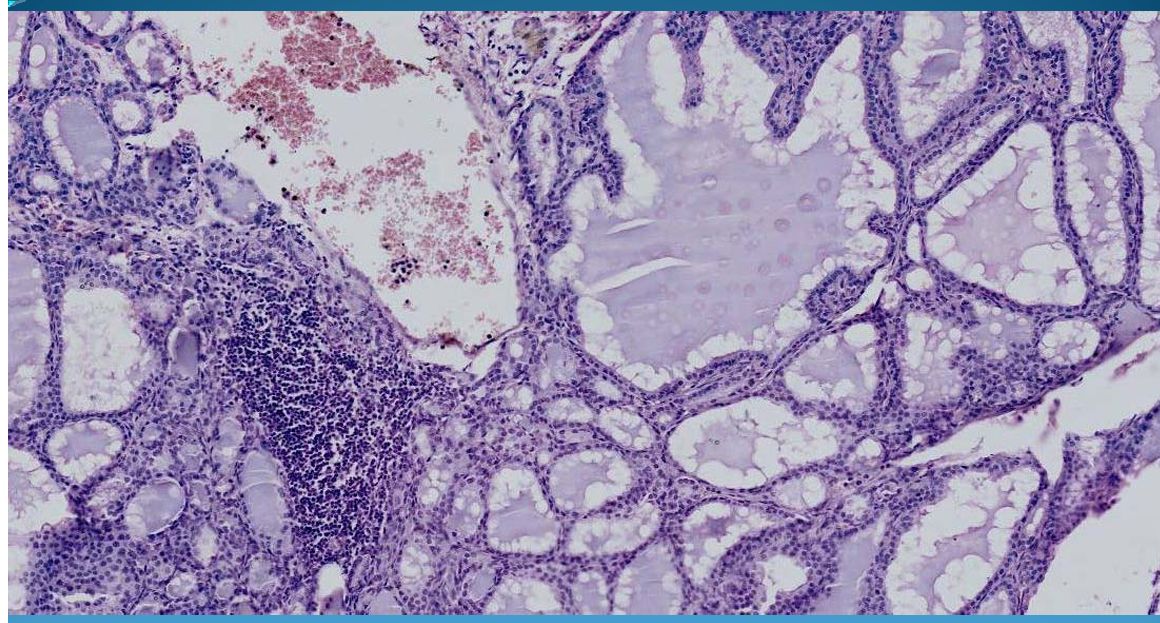
What is this?
THYROID:
Basedow-Graves: TOXIC goiters
follicles lined by columnar epithelium contain small amounts of colloid
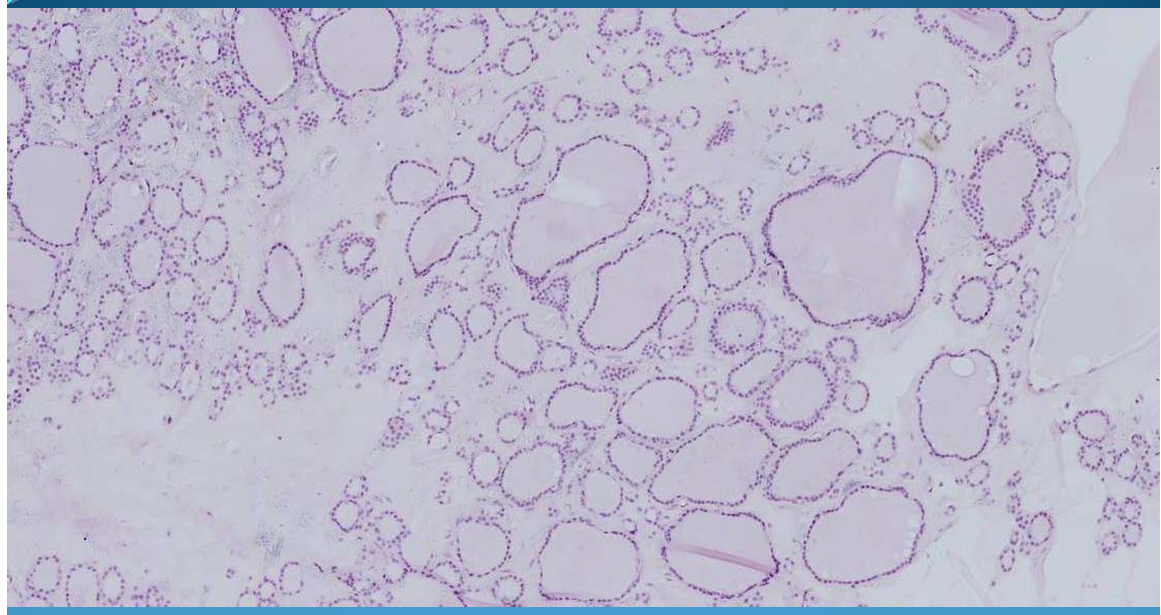
What is this?
THYROID:
Non-toxic goiter, diffused = anisophilicular type of gout; thyroid follicle dilated and full of colloid, lined up by cubic epithelium
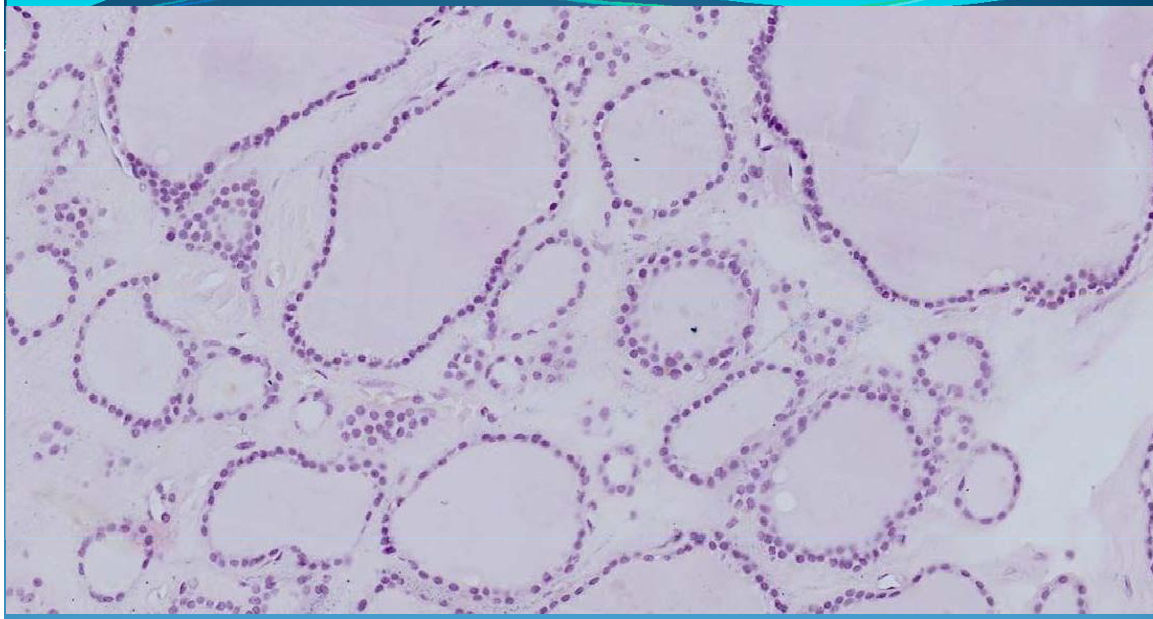
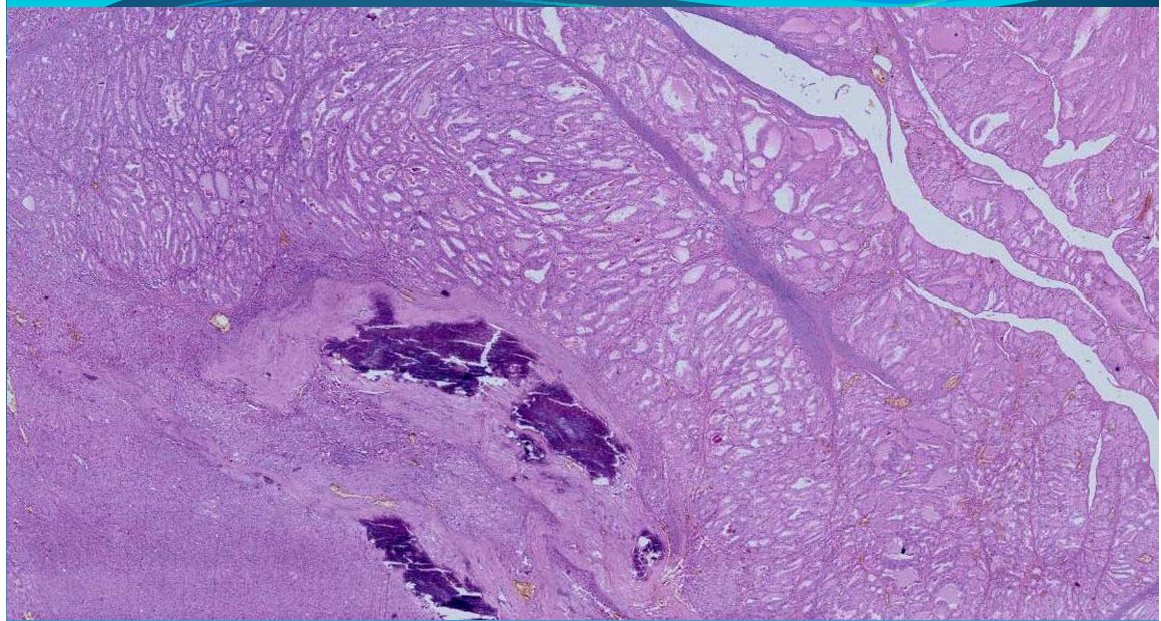
What is this?
THYROID:
Thyroid papillary carcinoma: epithelial malignant tumor; macrocalcification of thyroid = psammoma bodies, lethal Annie’s orphan eye nuclei - large and clear nuclei and intranuclear inclusions