Pulp Morphology
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
tooth morphology involves what structures
enamel
cementum
dentin
pulp
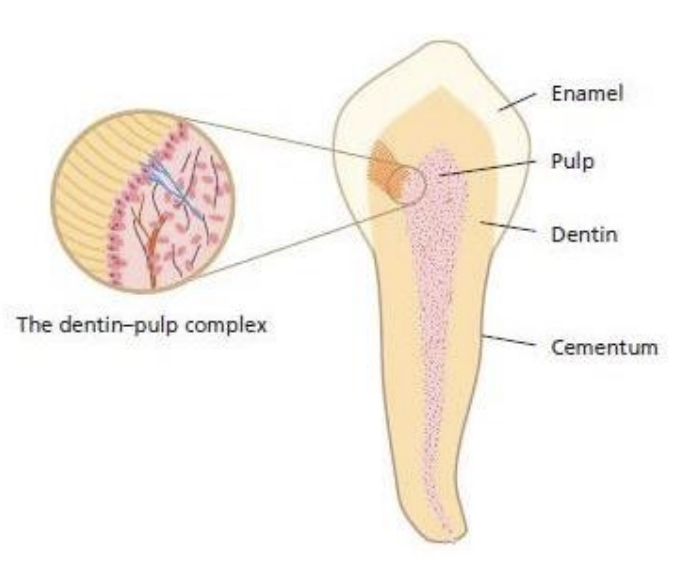
function of pulp includes:
formative
nutritive
sensory
protective
what is the formative function of pulp?
Mesenchymal cells form dentin
what is the nutritive function of pulp?
Nourishes the avascular dentin
what is the sensory function of pulp?
Free nerve endings: pain sensation
what is the protective function of pulp?
produces secondary or reparative dentin
where does the neurovascular bundle enter/exit the tooth?
apical foramen
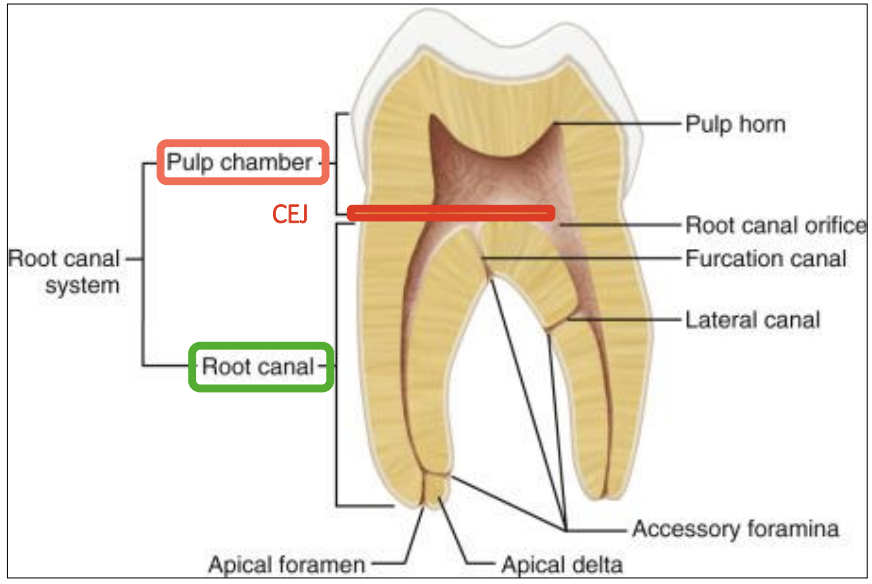
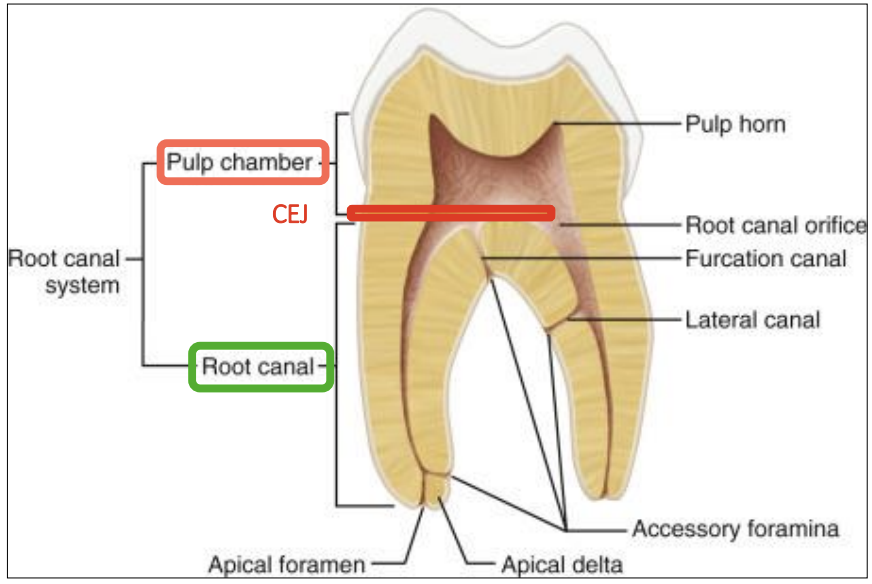
pulp chamber consists of
coronal portion
pulp horns
pulp orifice
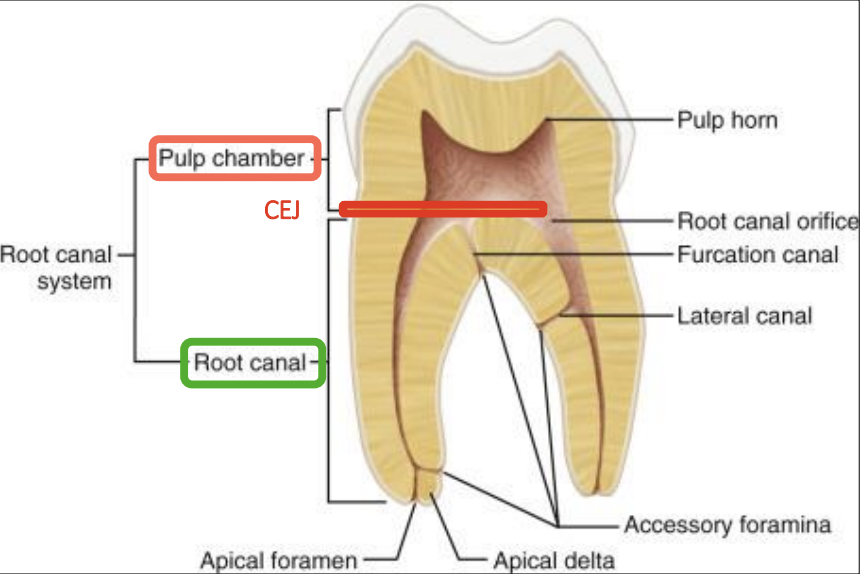
root canal consist of
apical portion
apical foramen/delta
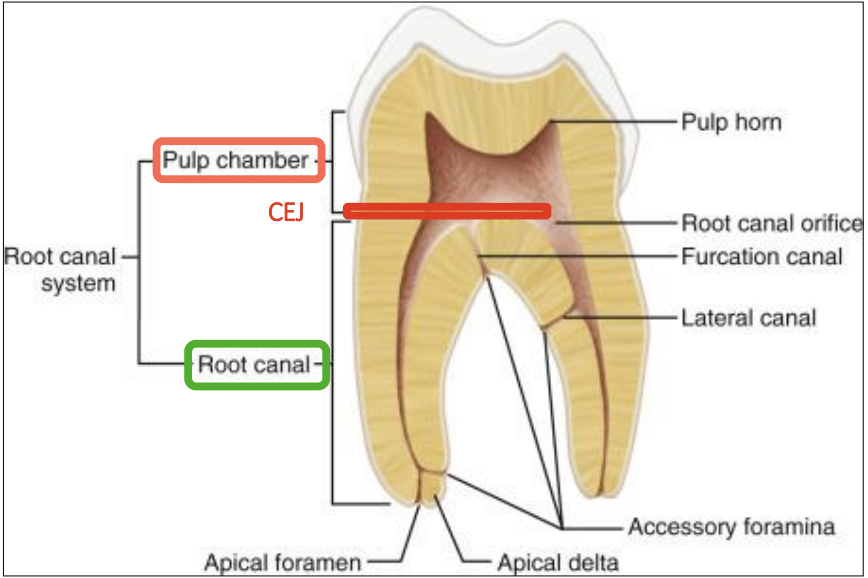
which part of the root canal communicates to periodontal tissues?
apical foramen/delta
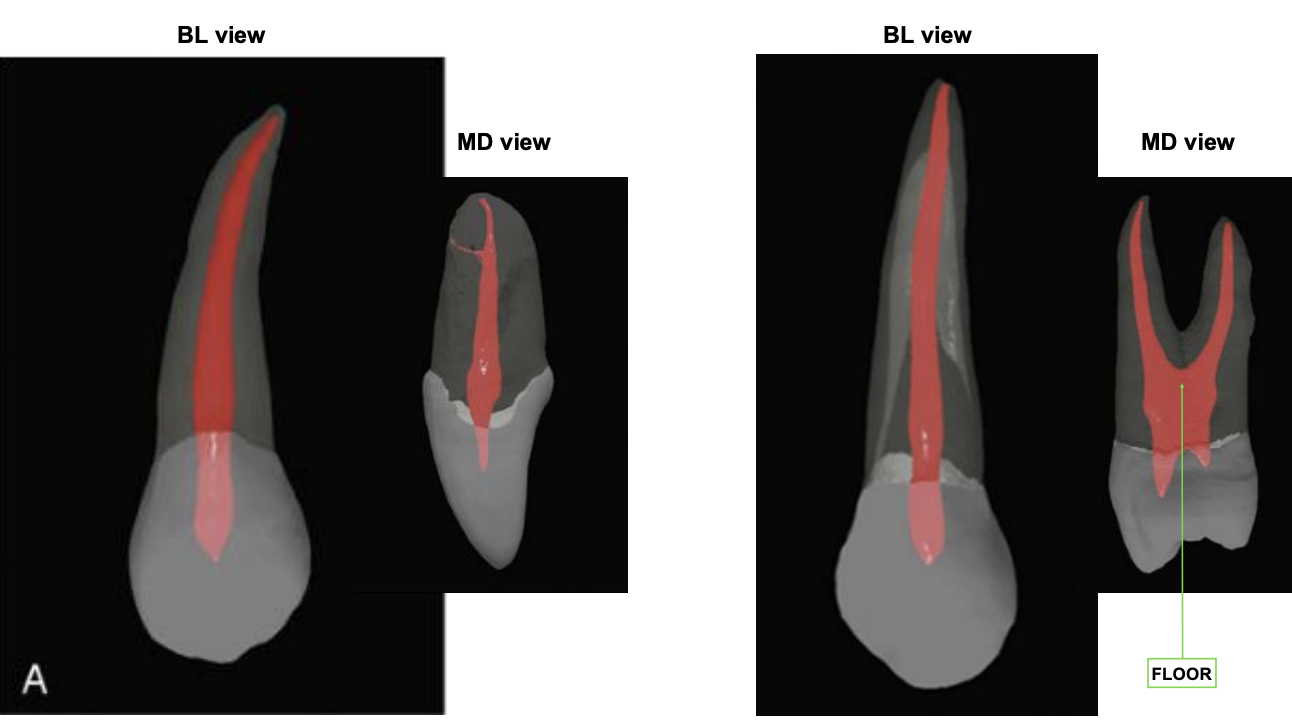
canines w single vs 2 canals
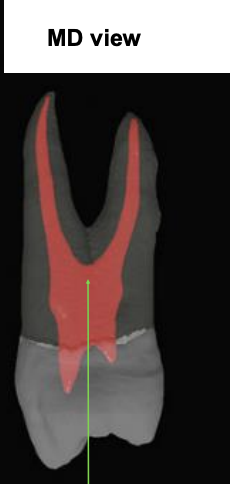
what is the arrow pointing at?
floor of pulp chamber (important landmark for endodontic therapies)
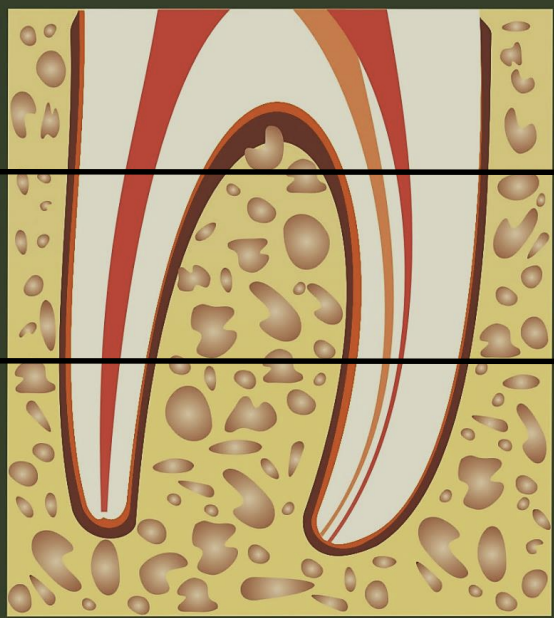
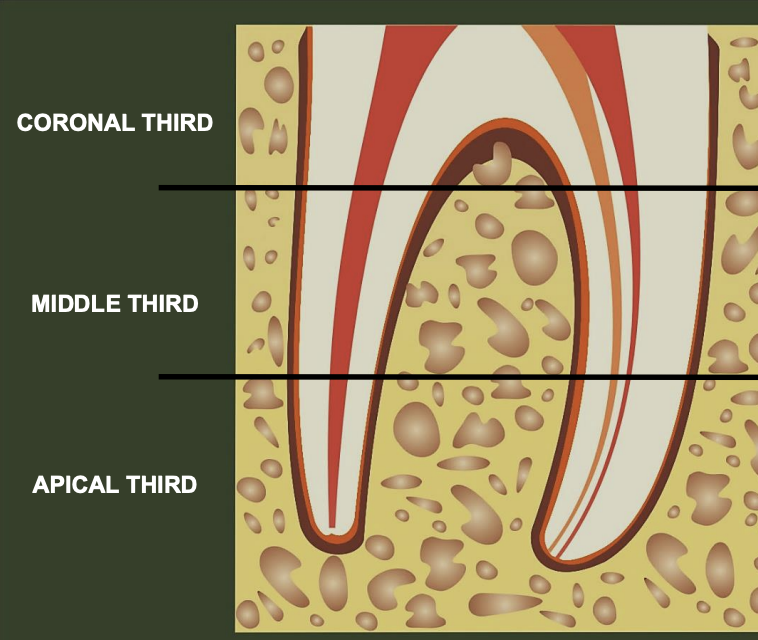
what are the thirds of root canals?
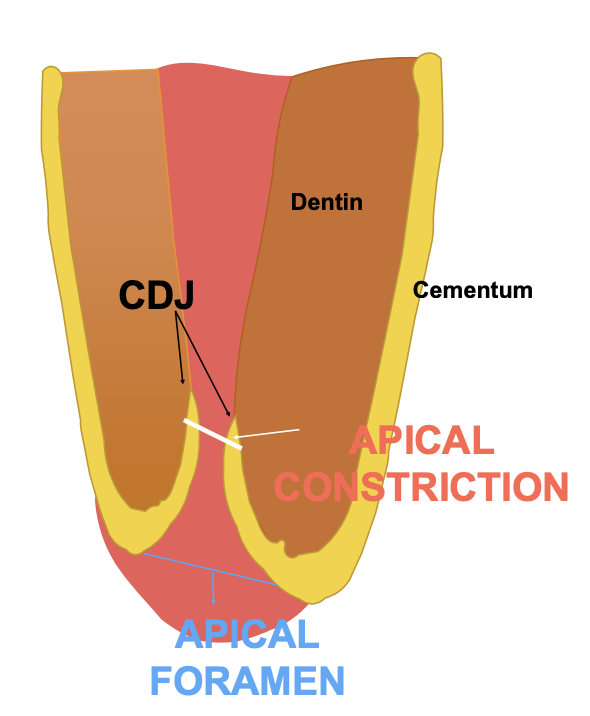
CDJ delineates what structure
apical constriction
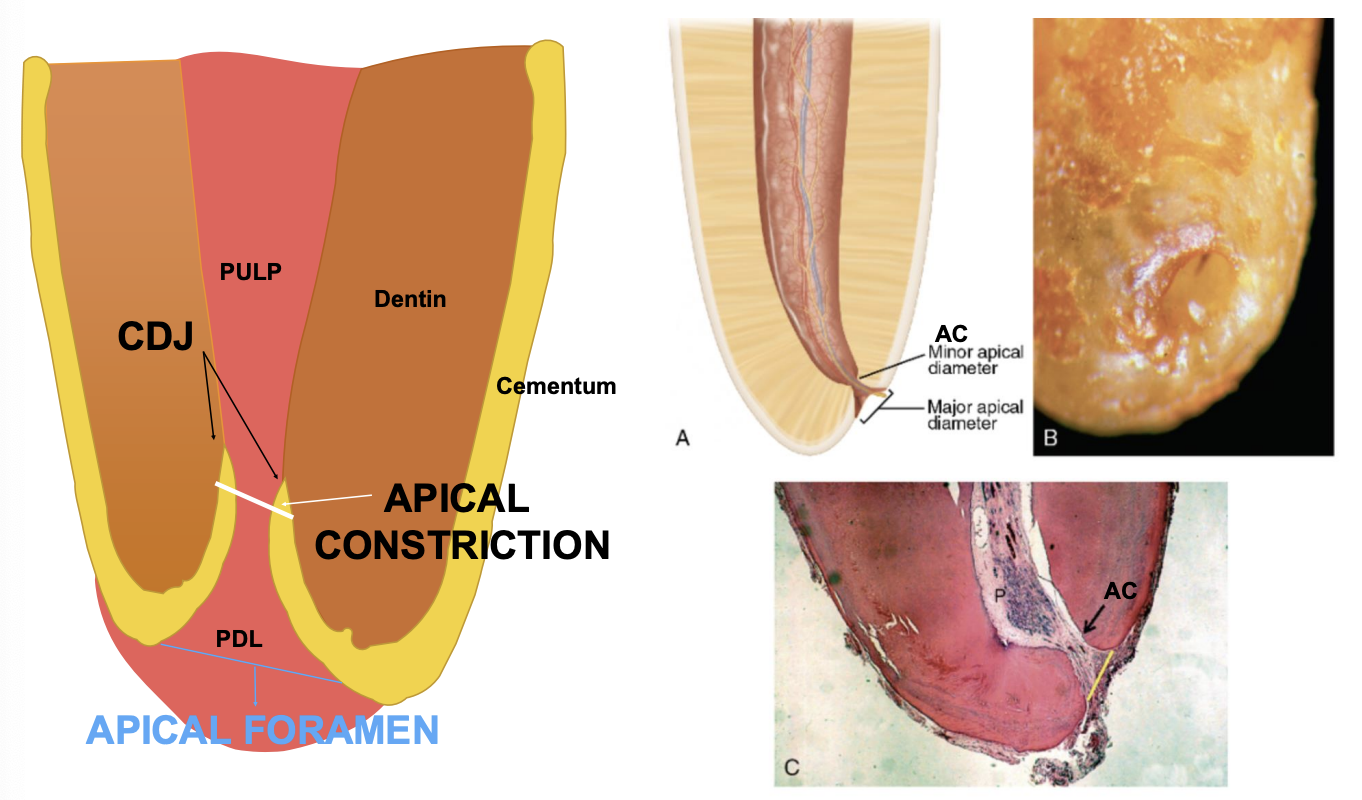
t/f: apical constriction and apical foramen may be different from radiographic terminus of tooth
true
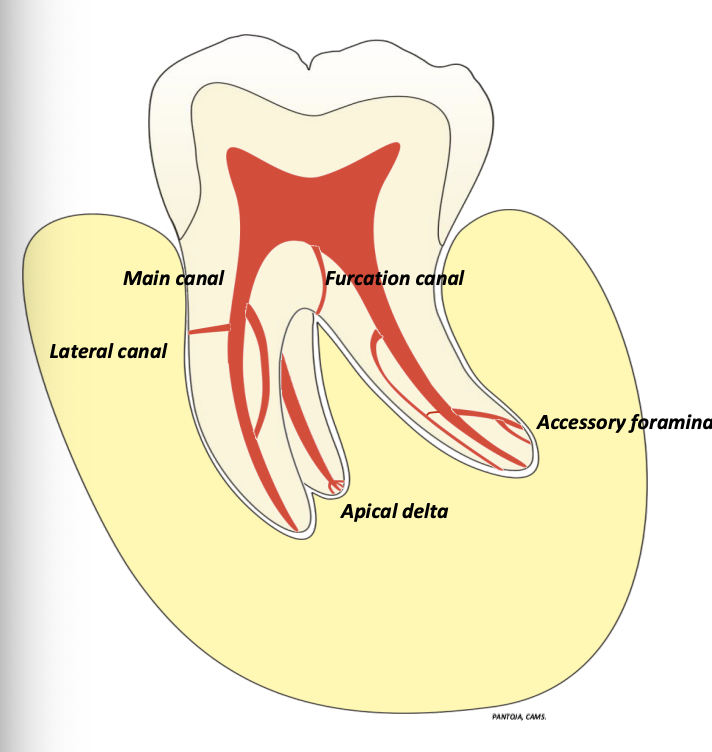
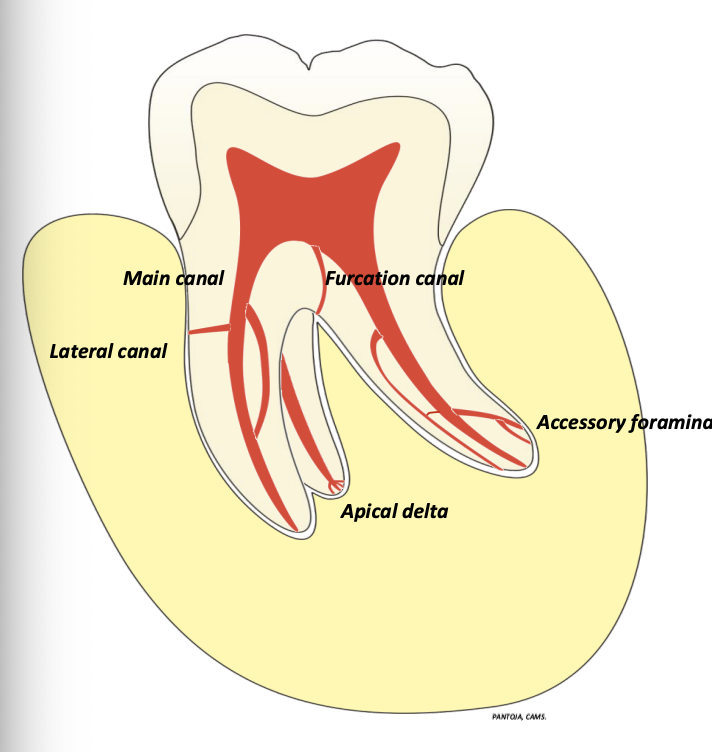
what are accessory canals?
minute canals that extend in a horizontal, vertical, or lateral direction from the pulp space to the periodontium
in what % of cases are accessory canals found in the apical 1/3 of root? middle 1/3? cervical 1/3?
apical → 74%
middle → 11%
cervical → 15%
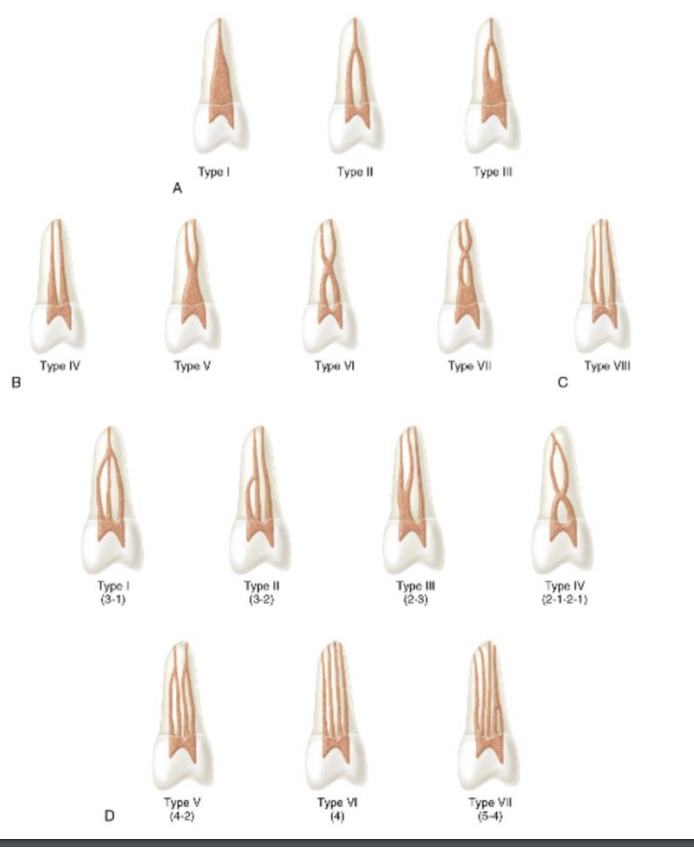
canal configurations
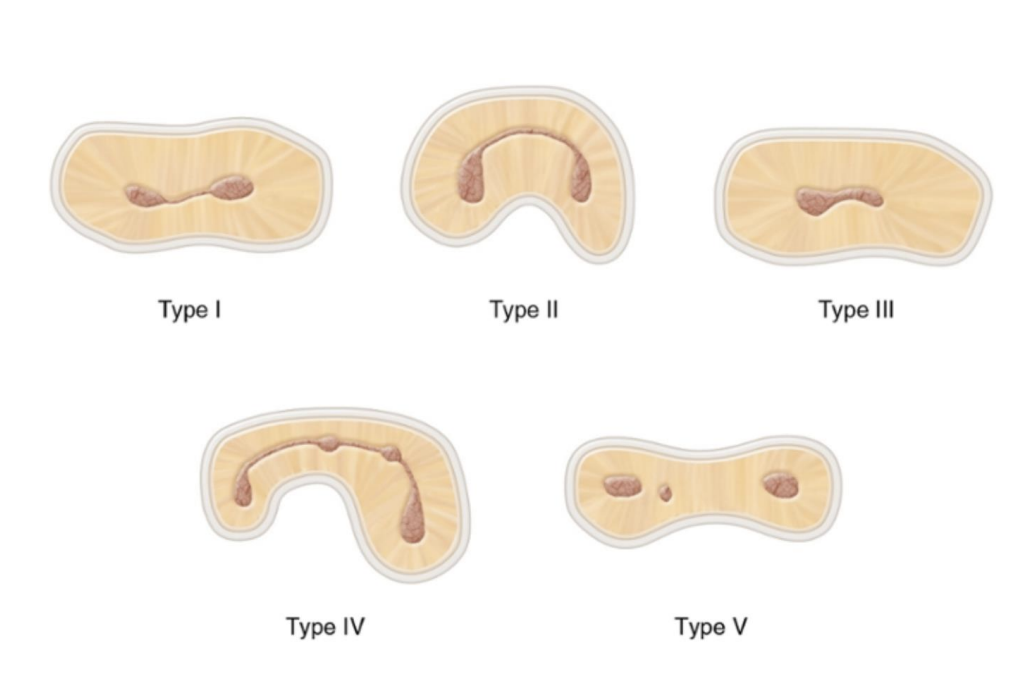
isthmus configurations (may make it harder to clean/treat)
what are some common sources of anatomical variation?
alteration w age
presence of carious lesions
presence of dental materials/procedures
trauma
calcifications
how does pulp chamber change with age?
reduces in size
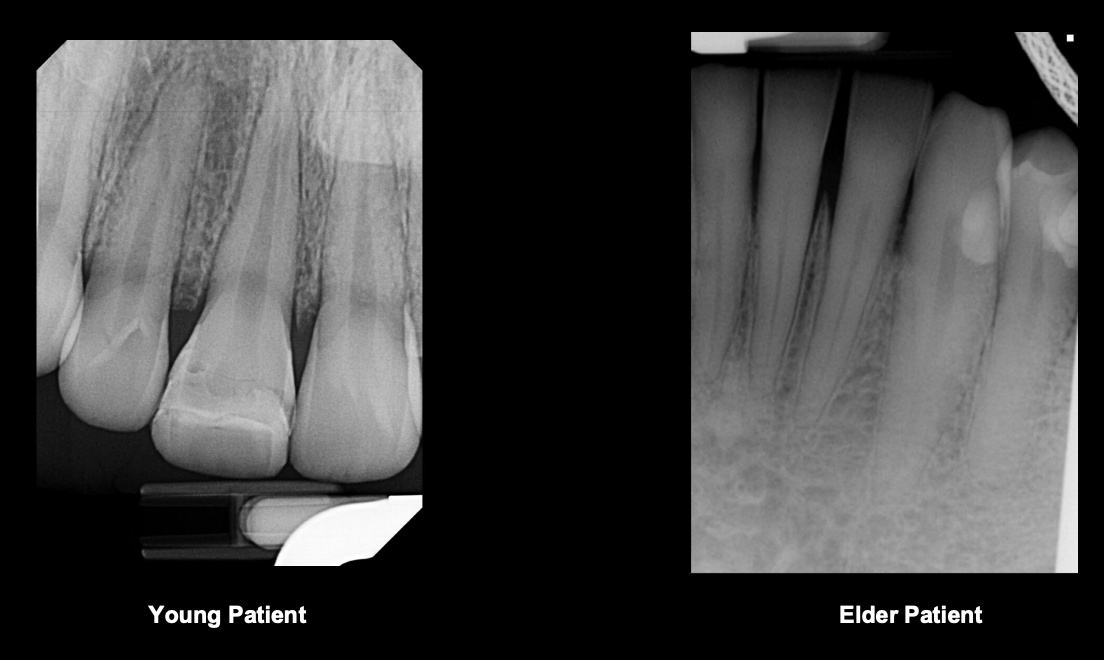
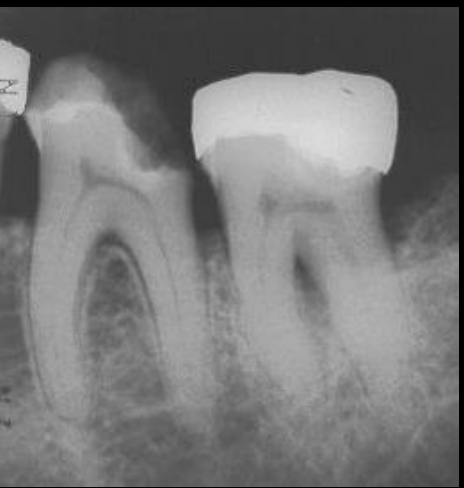
altered pulp due to reacting w carious lesion
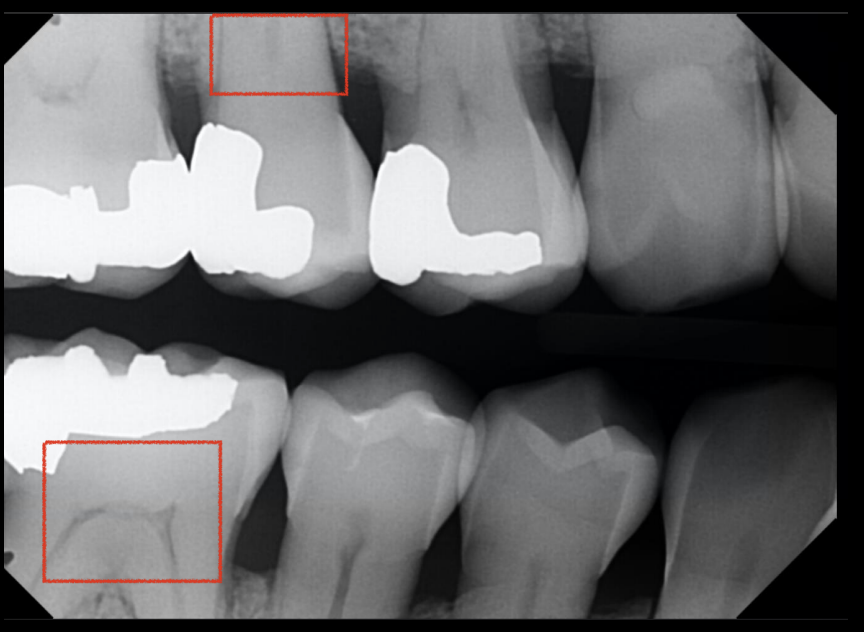
pulp chamber has receded due to restoration