Seminar no. 5 Labor market
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
reservation wage
the wage that would make them indifferent between working or being unemployed.
The aggregate nominal wage W
depends on: – the expected price level Pe – the unemployment rate u – a catch-all variable z
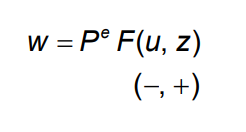
An increase in the unemployment rate
decreases wages. • Higher unemployment either weakens worker’ bargaining power or allows firms to pay lower wages and still keep workers willing to work.
z
all the factors that affect wages given the expected price level and the unemployment rate, for example:
– unemployment insurance as the payment of unemployment benefits to workers who lose their jobs
– employment protection makes it more expensive for firms to lay off workers
Real wage
The higher the unemployment rate, the lower the real wage chosen by wage setters.
The wage-setting relation is the relation between the real wage and the rate of unemployment
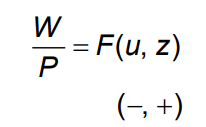
Natural rate of unemployment and function
The natural rate of unemployment is the unemployment rate such that the real wage chosen in wage setting is equal to the real wage implied by price setting.
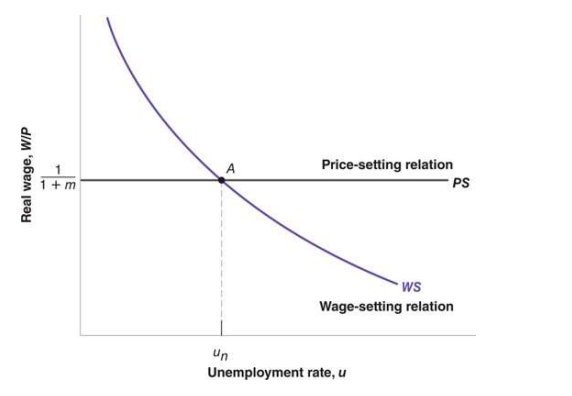
price-setting relation
Price-setting decisions determine the real wage paid by firms.
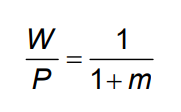
equilibrium unemployment rate un
• un depends on z and m.
• un is also called the natural rate of unemployment or thestructural rate of unemployment.
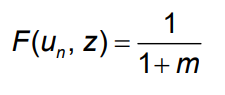
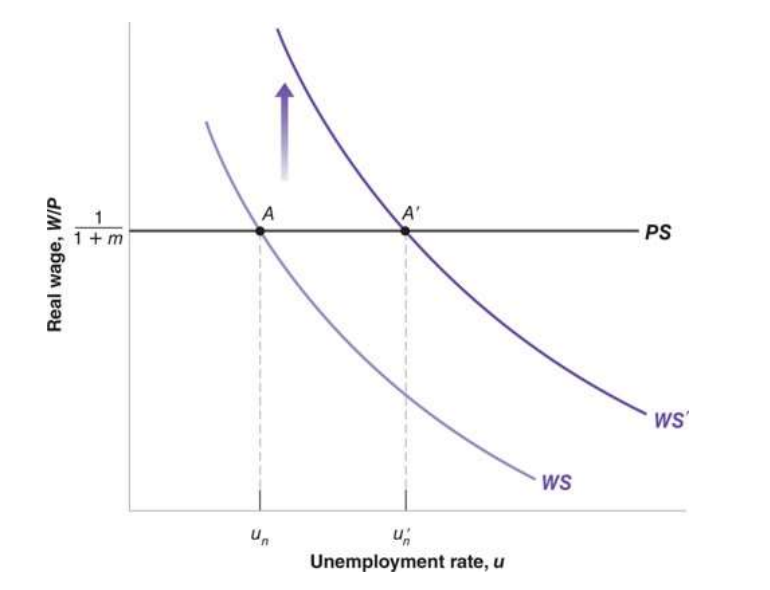
An increase in unemployment benefits
leads to an increase in the natural rate of unemployment
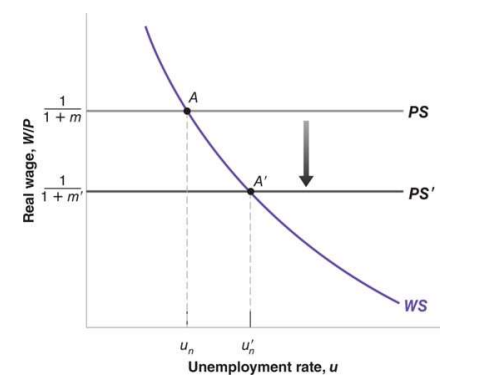
An increase in the markup leads to
an increase in the natural rate of unemployment.
The phillips curve
negative relation between inflation and unemployment.
When unemployment is low, more people have jobs and spend more → businesses raise prices (inflation).
When unemployment is high, people have less money to spend, so businesses keep prices stable or even lower them.
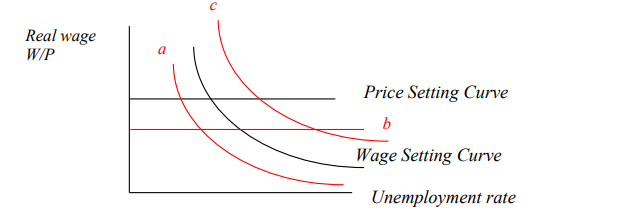
a
a - factor of unemployment, strength of wages, or sensitivity of unemployment
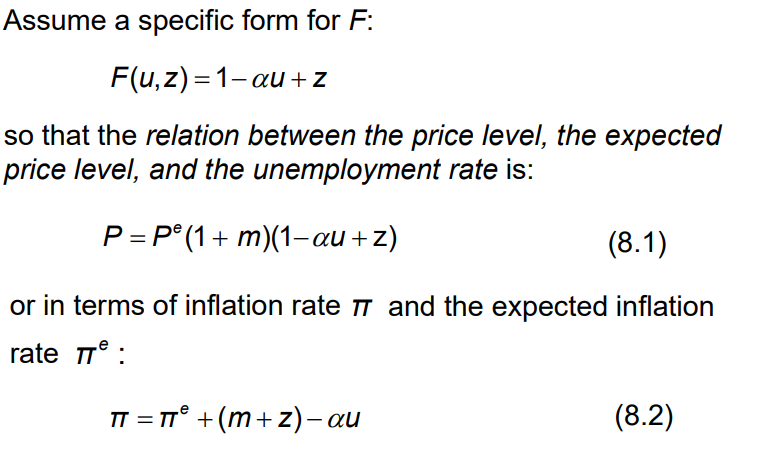
1. Using the wage equation, briefly explain how each of the following events will affect the nominal wage
a. Reduction in Pe
b. Reduction in the unemployment rate
c. A reduction in unemployment insurance
W = Pe F(u,z)
a. Reduction in Pe → W decreases
b. Reduction in the unemployment rate → Bargaining power increases → W increases
c. A reduction in unemployment insurance → Reservation wage decreases → W decreases
Using the price-setting equation, briefly explain how each of the following events will affect the price set by firms
a. Increased merger activity causes markets to become less competitive
b. Increased anti-trust legislation leads to increased competition
c. A reduction in the nominal wage
P = (1+m) W
a. Increased merger activity (markets are less competitive) → mark-up increases → P increases
b. Increased anti-trust legislation (higher competition competition) → mark-up decreases → P decreases
c. A reduction in the nominal wage → P decreases
This question focuses on the wage-setting (WS) relation
a. Briefly explain what effect a reduction in the unemployment rate will have on the real wage
b. What effect will a reduction in unemployment benefit have on the WS curve?
c. What effect will an increase in the price level have on the WS relation?
WS relation W/P = F(u,z)
a. A reduction in the unemployment rate → Bargaining power increases → nominal wage and real wage increase (Move along the curve) b. A reduction in unemployment benefit → More distressing to be unemployed → accept lower wages → given P, real wage decreases. WS curve shifts down. c. The increase in price→ Proportional increase in W. The curve does not shift as W/P remains the same.
5. Use the WS and PS relations to examine the effects of the following events on the natural rate of unemployment and on the real wage:
a. Reduction in unemployment insurance
b. Less stringent antitrust legislation
c. Increase in the minimum wage
a. Reduction in unemployment insurance → WS curve shifts down → un decreases. No change in real wage.
b. Less stringent antitrust legislation → mark-up increases → PS curve shifts down → real wage decreases and un increases.
c. Increase in the minimum wage → WS shifts up → un increases. No change in real wage.