CHEM Chapter 2&3 Vocab Terms
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Atomic Number
the # of protons in the nucleus of an atom (Z)
its value determines the identity of the atom
6= atomic number
atomic number (Z) indicates # of electrons too
Mass Number
the # of protons + the #neutrons
the mass number is not on the period table
Atomic Symbol
the element symbol from the periodic table
EX: C for carbon, Cl for Chlorine, etc.
Isotopes
atoms that have the same # of protons but different # of neutrons -
same atomic number but different mass number
versions of the same element
Cation
positively charged ion
loses an electron
Anion
negatively charged ion
gains an electron
Visible Light
Electromagnetic Radiation
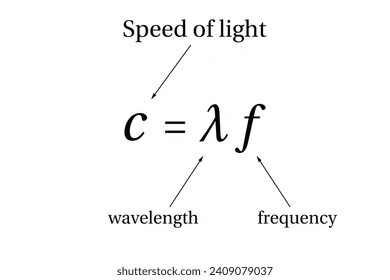
Frequency
“v”
Hertz= 1/s
Radiation w/ high frequency = short wavelength
Radiation w/ low frequency= long wavelength
Directly proportional to energy
inversely proportional to wavelength
Wavelength
upside down “v”
m=units
inversely proportional to radiation & energy
Speed of Light
3.00 × 10^8
m/s
constant (always this same equation)
Quantum Theory
developed by Max Planck (1900)
the energy of a small particle is quantized: it occurs in fixed quantities rather than being continuous
Each fixed quantity of energy (packet) is called a photon
E=hv
Energy
E= energy of photon
J (joules)
Directly proportional to Radiation
Inversely proportional to wavelength
Planck’s Constant
h
6.626 × 10^-34 J (x) s
The Bohr Model
Niels (1913)
addressed gaps of “early atomic model”
electrons occupy specific orbits around nucleus (each corresponds to a fixed energy level)
Electrons can jump between energy levels, BUT cannot exist between them
His wife contributed greatly to this theory, Margrethe
Quantum Staircase
lowest energy orbit (n=1) is the GROUND STATE
every other orbit is called EXCITED STATES (n=2 and so on)
Moves from LOW to HIGH orbit, electron absorbs a photon
Moves from HIGH to LOW orbit, electron emits a photon
Atomic Orbitals (wave-function)
a 3D standing wave that describes where an electron is most-likely to be found & its associated energy
3 specific quantum numbers
size
shape
orientation
Principal Quantum Number
n
describes the energy level & general size of the orbital
the number in orbital notation
Larger numbers= higher energy & farther from nucleus
Angular Quantum Number
l
describes the shape of the orbital region where electron is most-likely to be found
s= spherical
p=dumbell
d/f= more complex
written as the letter in orbital notation
Magnetic Quantum Number
m
describes the orientation of orbital in 3D space
each unique orientation is written as a unique subscript
written as z in orbital notation
Shells
n
energy value
Subshells
n + l
a specific shape & size
Orbital
n + l + m
specific shape, size, & orientation
Wavelength Ranking (shortest to longest)
gamma ray< x-ray< ultraviolet< Visible< infrared< Microwave< Radio Wave
Frequency Ranking (smallest to largest)
radio wave< microwave< Infrared< visible< ultraviolet< x-ray< gamma ray
Blackbody Radiation
when a solid object is heated to high temps it gives off electromagnetic radiation
incandescent lightbulb
Photoelectric Effect
when sufficient frequencies of light shines on a metal plate, a current flows
solar panels
Atomic Emission
when atoms are excited by energy they admit radiation w/discrete wavelengths not in a continuous spectrum
neon signs
Atomic Mass
the weighted average of all the masses of isotopes present in a natural sample
approximately equal to and individual isotope/element’s mass number
weighted average is reported on the periodic table
Molar mass
mass of 1 gram of substance per mol
g/mol
Molecular Mass
sum of the atomic masses of each element in a formula
amu