PHYLOGENETIC TREES
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What does LUCA stand for
last universal common ancestor
When do we use LUCA
if there is an unknown common ancestor
What are phylogenetic trees also called
evolutionary trees
What do branching trees infer
evolutionary relationships
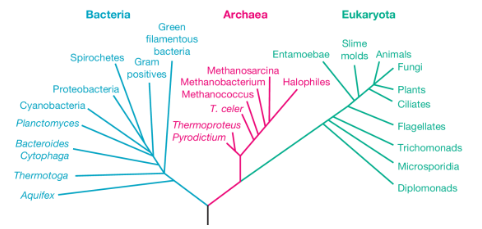
The phylogenetic tree of life
Is a product of what theory?
What does it illustrate?
Darwin’s evolutionary theory
Illustrates the interconnectedness of all life forms through evolution
Phylogenetic trees can be created by using
Genetic Data Molecular homology sequences
Genetic Data Molecular homology sequences include
Amino acids
RNA
DNA
DNA sequences could be
nuclear or mitochondrial
coding or non-coding
What do the tips/terminals of a tree represent
the descendant groups (taxa)
What do nodes in a phylogenetic tree denote
An ancestor of two (or more) descendants, referred to as the recent common ancestor
What do branches in a phylogenetic tree indicate
A speciation event
The relationship between an ancestor and a descendant of that ancestor
What is the root of a phylogenetic tree
The common ancestor of all taxa shown in the tree
What are sister taxa
Two groups, such as two species, with a common ancestor that is not shared with other taxa
What does branch length convey in a phylogenetic tree
Time scale (longer branches denote longer time periods)
OR
Molecular scale (amount of molecular sequence change, i.e., difference in DNA or amino acids)
What lines can be used to draw phylogenetic trees
Diagonal, horizontal, or vertical lines
What is the first step to construct a phylogenetic tree
Calculate the number of differences between the different species or groups provided
What is the second step in constructing a phylogenetic tree
Identify the sequences with the fewest differences
What is the third step in constructing a phylogenetic tree
Connect these groups with the fewest differences as sister taxa, joined via a node
What is the fourth step in constructing a phylogenetic tree
Determine the next group with the fewest differences to the sister taxa and add to the tree as a branch
What is the fifth step in constructing a phylogenetic tree
Continue this until all groups are added to the phylogenetic tree
What is the sixth step in constructing a phylogenetic tree
Determine the outgroup, if necessary, as the most distantly related group
Sample problem
maybe?
What taxonomic group is included with humans in a phylogenetic tree of vertebrates
Humans are included with the other placentals
How can phylogenetic trees be examined
To infer various relationships
Such as humans being more closely related to marsupials than monotremes among mammals that branched off 350 million years ago
What can phylogenetic analysis identify within natural populations
Genetic variation within a species and its subspecies
How does phylogenetic analysis assist in understanding species
By reconstructing the evolutionary history of a species or a genus
How is phylogenetic analysis valuable for understanding human prehistory
It assists in understanding
including early migrations of modern humans and clarifying the relationship between modern humans, Homo sapiens, and the extinct Homo species
How does phylogenetic analysis help with zoonotic diseases
By identifying the origin of human viral diseases that have jumped from other species