Physical Diagnosis Exam 1 Year 2 Small Animal
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
What is Alabama State Practice Act Rule 930-X-1-.31.01
Records must be:
1. maintained on every animal and be legibly documented in an accurate and timely manner
2. Readily accessible and permit prompt retrieval of information
3. Kept for a minimum of 3 years following the last office call or visit or discharge of the animal from the veterinary facility
4. Filed in an adequate filing system
6. Paperless record keeping should meet all the written plus proof of periodic back up
T/F Herd or flock animal records may be kept on a per-client basis rather than a per-pet basis
True
T/F The Alabama state practice act rule requires records be kept for a minimum of 5 years following the last call, visit, or discharge of the animal from the veterinary facility.
False, 3 years is the minimum
T/F Follow up email not only educate the client but can serve as a medical record
True
________ are a more formal problem oriented medical record. Emailing them to the owner directly serve as client education and medical record
Discharges
T/F It is okay to email the owner a more formal and less in depth discharge note as long as the SOAP is well detailed and recorded in the patients medical records
True (most owners may not understand the wording of a well detailed soap)
T/F Everyone writes SOAPs the same way to ensure everything regarding the patient is easy to follow and in the same order
False, everyone writes up soaps differently. It is important to Figure out a procedure that works best for you to ensure the maximum amount of detail regarding the patients status and history
Information in a soap that you CANNOT put a number or rigid descriptor on
Subjective
What should be included in the Subjective portion of a SOAP?
Signalment
Complain
History
Mentation
Information you cannot put a number or rigid descriptor on
Information that you CAN put a number or rigid descriptor on
Objective
What should be included in the objective portion of a SOAP?
"Measurables"
Most of your Physical exam findings
TPR
BCS
Pain score
Hyration status
T/F Subjective and Objective (S/O) portions of your soap are for data collection. They are often combined because there is so much overlap in a physical exam. The more date you collect the more accurate and better your assessment and plan will be.
True
Analysis of the subjective and objective data, problems, differential diagnosis
Assessment
SOAP stands for:
Subjective, Objective, Assessment, Plan
Why might the pneumonic DAMNIT be significant to the assessment portion of a SOAP?
D - Degenerative, Developmental
A - Allergic, anomalous, Auto-immune
M - Metabolic, mechanical, Mental
N - neoplasia, nutritional
I - Inflammation, infection, immune-mediated, Iatrogenic, Ischemic, Idiopatic
T - Trauma, Toxin
What might be included in the Planning portion of your SOAP?
What do you want to do?
What are you going to do?
Diagnostics?
Treatments for each problem/ differential?
Client communications?
Findings?
Possibilities?
Prognosis?
Recheck?
T/F It is required by law to do your job as a Vet to get the animal back to health regardless if you communicate with the Owner or not
False, It is vital that you communicate with the owners and that you report what the owner communicates to you in the Planning portion of your SOAP to not only get the animal healthy but to ensure the owner is aware of the situation, cost, and options
Why might it be important to record what the owner stated in a phone call when treating/ following up with the owner? Is a date and time necessary?
If something were to go wrong with the animal/ treatment, documentation can help save you from a lawsuit
A date and time provides proof when the communication occurred and what was said during the communication
T/F A pencil can be used to record a soap in clinics because young veterinarians may make mistakes
False, ALWAYS USE A PEN
T/F A SOAP is a legal record
True (Every detail is important)
Select the incorrect statement regarding SOAP:
- Always use a pencil or pen
- Helps to approach a case in a logical manner
- Works through problems systematically
- Establishes a legal recod
False: ALWAYS USE A PEN
Select the incorrect statement regarding discharges:
- Similar approach but more formal
- Client education and Medical record
- Sent directly to the owner
All statements are correct regarding discharges
Signalment, complaint, and history are contained in which portion of the SOAP?
S

Route of Drug administration include:
Oral, Sublingual, feeding tube, Rectal, Topical, Ophthalmic, intranasal, intratracheal, intradermal, subcutaneous, intramuscular, Intravenous, intraosseus, intraperitoneal, intracardiac, Enteral, Parenteral
Enteral vs Parenteral
Enteral - Given Via GI tract
Parenteral - NOT given via GI tract
Why might you advise the owner to give a treat via "Greenies pill pocket" as opposed to giving it with a piece of cheese?
Cheese is high in calories, fat, sodium
Greenies are low in calories, made to meet the dogs dietary needs
What is the 1,2,3 Rule?
Dogs are smart and can sniff out pills, they may not consume the pill as a result:
- 1/3 Slice of cheese rolled and empty
- 1/3 of a slice of cheese rolled and loaded with meds
- 1/3 of a slice of cheese rolled and empty
T/F Cheese is not needed for Carprofen (Rimadyl), Oclactinib (Apoquel Chewable), Compounded drugs.
True
T/F If a dog or cat is unwilling to consume a drug it is acceptable to force it down the back of their throat
True, some drugs may be live saving and can only be administered orally so we may have to force it down their throat
What is important when it is necessary to force a pill down a dog/ cats throat?
- Hold the dogs head in a safe manner
- Tilt the dogs head back to open the esophagus / mouth
- Place your hand on the roof of the dogs mouth
- Place pill in the back of the mouth, Get it over the hump at the caudal portion of their tongue and esophagus
- Administer water with a syringe to aid swallowing
- Lick their nose/ ensure they swallow
What might be used if you cannot get a dog/ cat to swallow a pill?
Pilling device / pill popper
Treats
4 ml Water, tuna juice, food, butter
T/F When giving liquid oral medications, administer drugs in the front of the mouth
False, it is best to insert the syringe in the side of the mouth, just behind the canine teeth
T/F Adult cats can only swallow 1/2 ml at a time
True
When might it be necessary to give intradermal injections?
Localized block
Allergy testing
What size needle should be used for intradermal injections
25-27 gauge
What are you looking for with intradermal injections?
SHOULD feel resistance
SHOULD get a "Bleb" (see image)
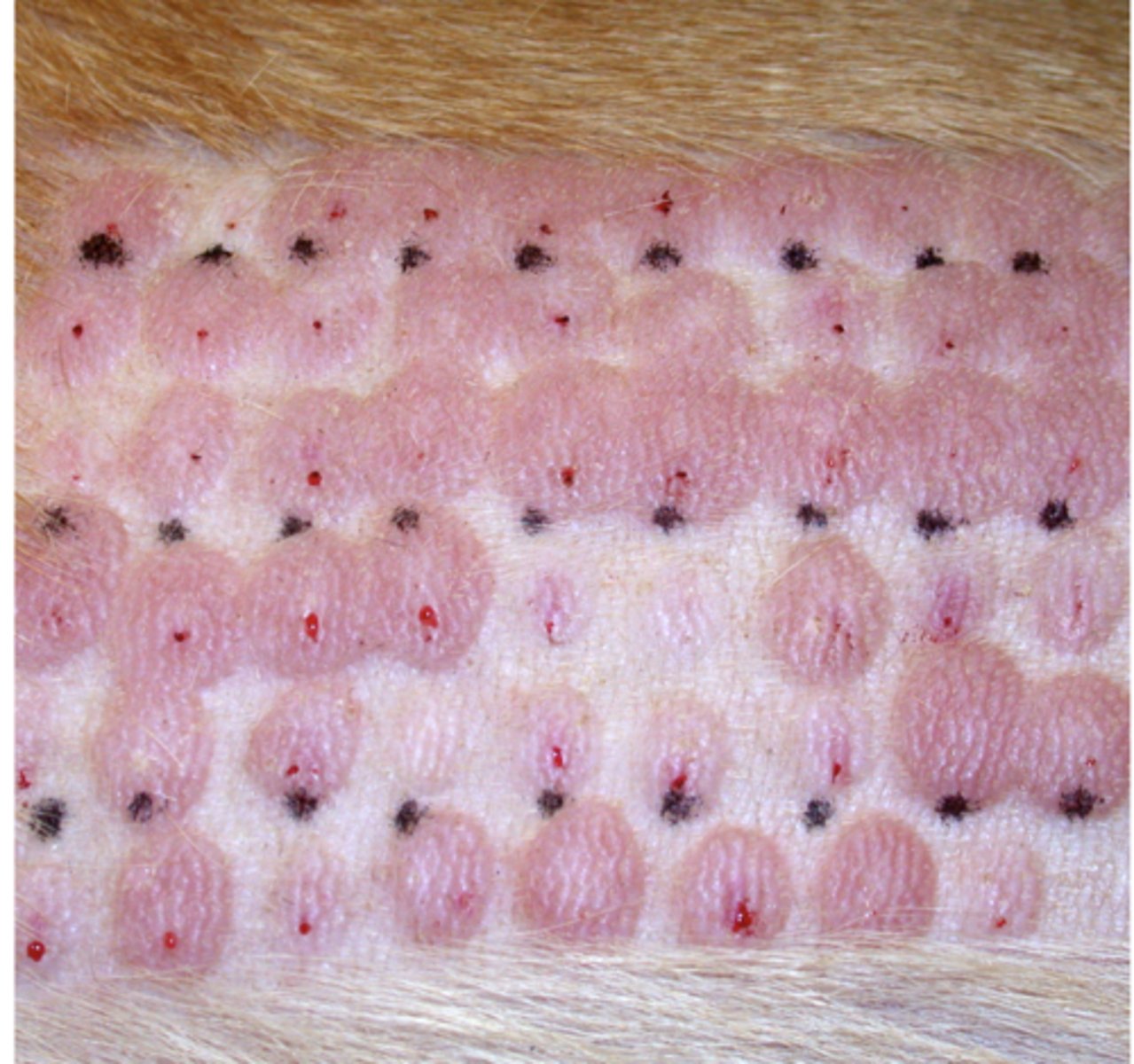
What is important for injections?
Good restraint / distraction
Bevel UP
Smaller the number of needle, the Bigger the lumen (Gauge)
Match gauge to patient and drug
Aseptic Technique
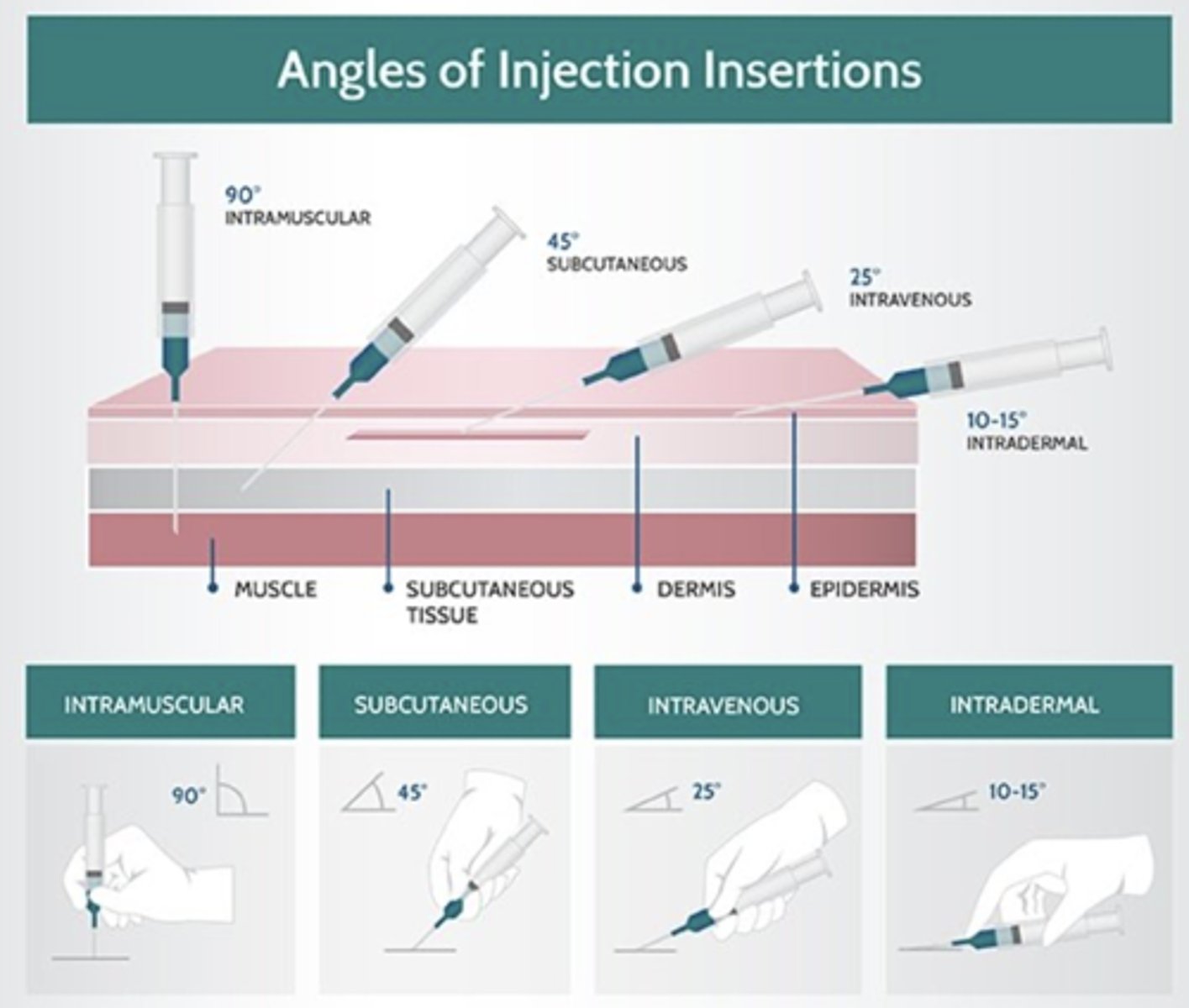
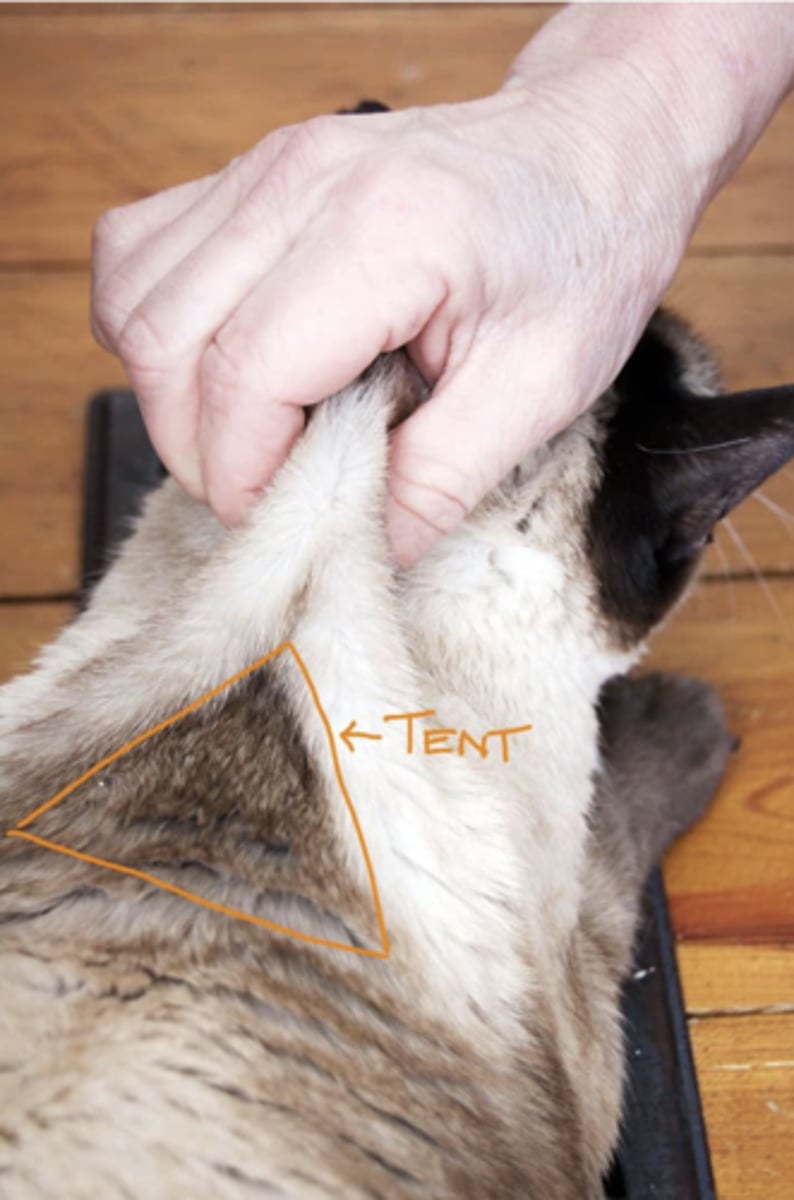
T/F Subcutaneous injections are more common for large volumes of fluids that require less restraint and are less painful for the animal
True
Select the incorrect statement regarding Subcutaneous injections:
- 18-25 gauge needle
- Pick up an area of loose skin typically over the shoulders, neck, or lateral thigh
- Insert needle at the Peak of the skin tent and aspirate
- Inject following no blood into syringe and negative pressure
False statement that is corrected: Insert the needle at the base of the skin tent and aspirate

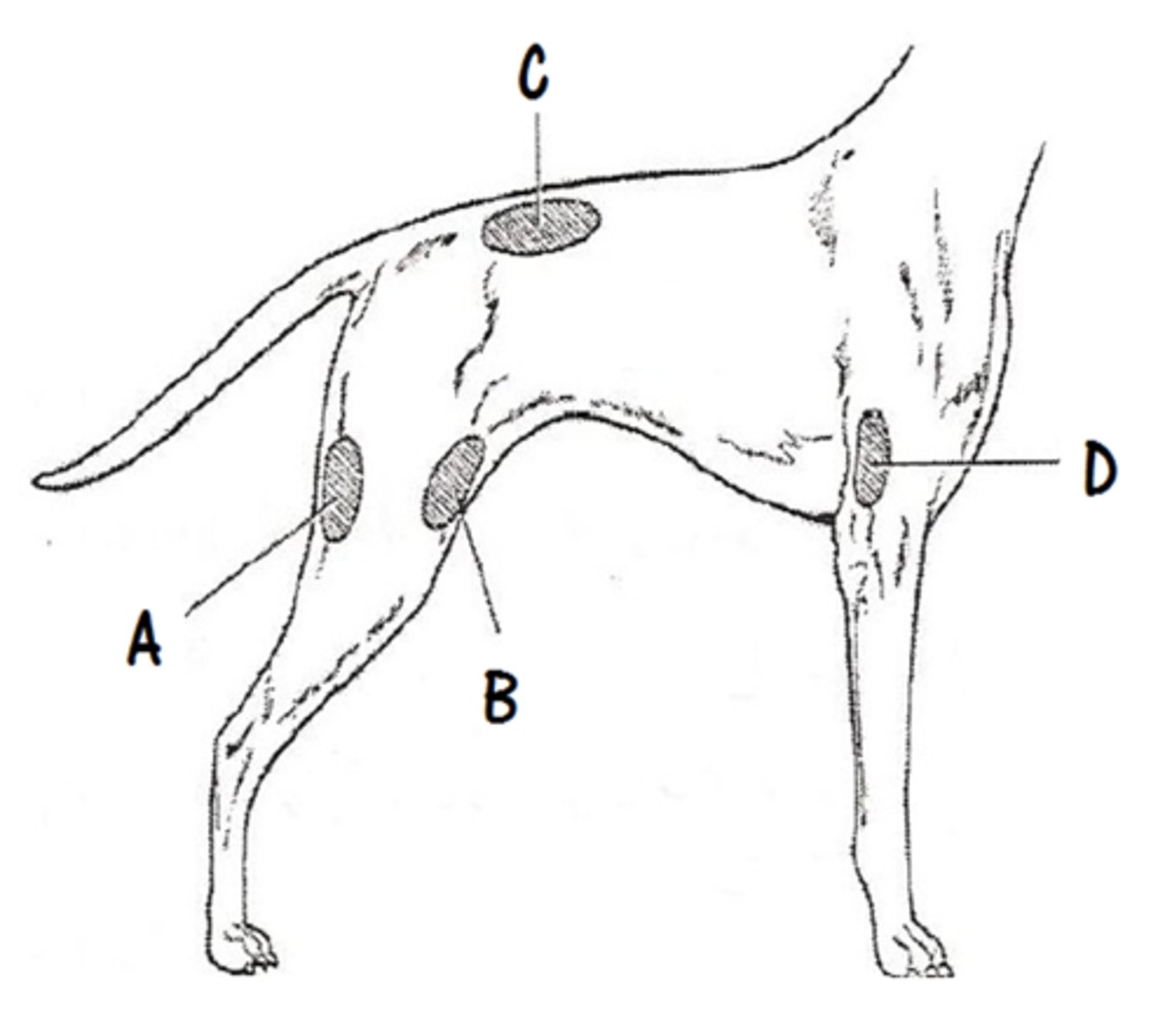
AAHA Recommendation for Vaccination sites in dogs:
Rabies: Right Pelvic limb, SubQ
DA2P: Right Thoracic Limb, SubQ
Lepto: Left thoracic limb, SubQ
Lyme/ influenza: Left thoracic or Pelvic Sub Q
AAHA Recommendation for Vaccination sites in Cats:
Rabies: Right pelvic, SubQ
FVRCP: Right thoracic, SubQ
FeLV: Left pelvic, SubQ
Distal to the elbow and stifle due to concern of fibrosarcoma
What type of injection is common for Sedation, pain meds, and melarsomine?
intramuscular injections
What do I need to know about IM injections:
- Commonly used for sedation, pain meds, and melarsomine
- Typically, 20-22 gauge
- Smaller volumes and more painful
- Most common sites: hamstring, epaxial, quadriceps, triceps
- Perpendicular to the muscle, aspirate, and inject
Common sites of Intramuscular injections?
Hamstring
Epaxial muscles
Quadriceps
Triceps
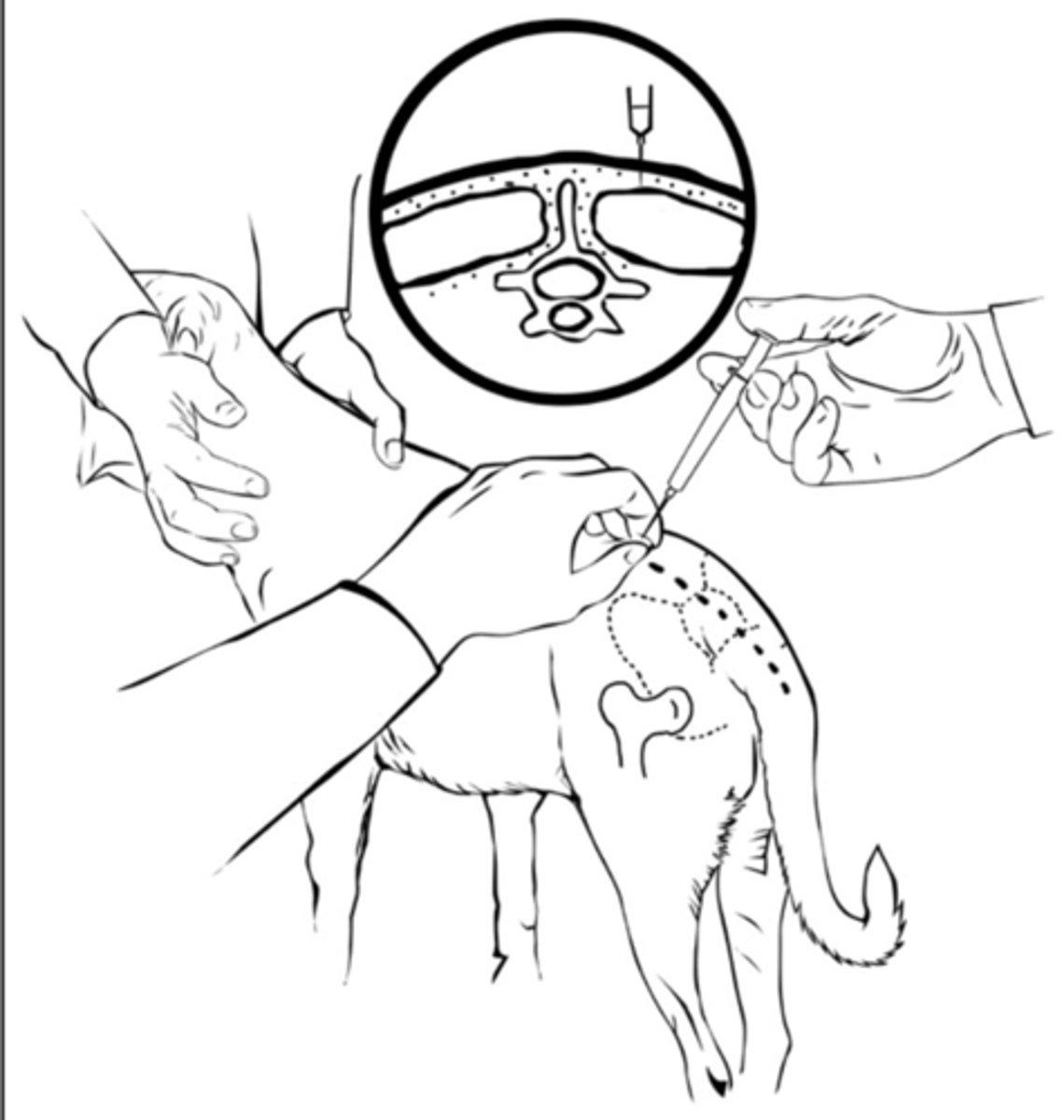
Steps to an Epaxial Muscle IM injection
1. Find the last rib
2. Count back 3-5 Dorsal sinuous processes
3. Come 1-3 cm off midline and palpate muscle
4. Insert needs PERPINDICULAR to skin, aspirate, inject
Pros and Cons of Epaxial Muscle injections
Pros:
- Easy to locate
- Can handle large volumes
- Less chances of complications
Cons:
- More painful
- Slower onset
Pros and Cons of Hamstring Injection site:
Pros:
- Safest for personel
- less painful than epaxial
- Faster onset than epaxial
Cons:
- Sciatic nerve damage
Rule of THUMB for hamstring injections:
Thumb in groove and/or angle caudally
Pros and Cons of Intravenous injections:
Pros:
- Most rapid onset
- Allows for prolonged administration via IV catheter
Cons:
- Takes the most skill
Where are the common sites of IV injections?
Cephalic (Accessory cephalic)
Lateral saphenous
Jugular
Steps to IV injections
Consider placing an IV catheter if multiple administrations are being performed
1. Occlude
2. 25-35 degree angle
3. Insert, aspirate, release, inject, withdraw, apply pressure
T/F It is important to match your needle to your patient and drug
True
What does it mean to Triage?
To sort issues based on scale of urgency
How can patients be sorted for Triage?
1. Likely to live no matter what
2. Likely to die no matter what
3. Likely to live if something is done
What are the goals of a triage regarding patients?
Based upon what patients are the most stable and who needs the most urgent care
- Emergent
- Urgent
- Delayed
How do we Triage Patients?
Very Brief history based on presenting complaint and duration of signs, previous diagnosis, should take less than a minute
-Don't get trapped, remind patients that they will be see in order of urgency
How do you preform a triage exam?
Perfusion parameters
- mentation
-Mucous membrane color
- Capillary refill time
- Pulse (Quality and rate)
- Distal extremity temperature
Respiratory
- Rate
- Effort
- Pattern
- Posture
If a patient is unstable what must be done?
- Immediately triage to treatment area
- CODE STATUS - (CODE RED)
Cardiovascular compromise
Respiratory distress
Active seizures or recently had a seizure
Lateral recumbency, non responsive
How might you triage a Patient that is Stable but Messy
Messy = Profound vomiting, diarrhea, bleeding wounds, or epistasis
- Get patient to an open exam room
- Ensure patient maintains stability
- Not incredibly urgent but can be treated in due time based upon severity of other patients
How might you triage a Patient that is Stable but Unusual appearance
Unusual appearance = Fractures with obvious displacement, anything on a gurney, altered mental status
- Get patient to an open exam room
- Ensure patient maintains stability
- Monitor pain
- Monitor triage based upon severity of other patients
How might you triage a Patient that is Stable but uncontrolled pain
Uncontrolled pain may be a code red
Stable but messy
Code Blue?
Stable, but Unusual Appearance
Code green - delayed
Stable but potentially infectious
Code purple - consider isolation unit / quarantine?
Why is it difficult to Triage Felines?
Non-cooperative due to stress
Escape to hide is their main goal
T/F ALL cats should be triaged in treatment area for the safety of the patient and staff
TRUE
What are the ABC's of triage?
A - Airway
B - Breathing
C - Circulation
D - Disability
E - Exposure
What else should be considered in your primary survey related to Triage?
ABC's
Respiratory, Cardiovascular, Neurological
Brief abdominal palpation or obvious external hemorrhage
Should only take 1-2 minutes
What do I need to consider when evaluating the A - Airway?
Is it patent?
Is the air moving?
Is supplemental oxygen necessary"
If the air is not moving when evaluating the Airway, What is the next step?
Remove the obstruction
Intubate the animal
Emergency Trachostomy
Provide supplemental oxygen
When evaluating the B - Breathing of the animal what are we looking at?
Breathing Rate
Breathing effort
Breathing pattern
Posture
Mucous membranes
Auscultations
Tachypnea / Bradypnea
You see a TACHYPNEA with increased effort while evaluating the patients breathing. What should we consider?
Evidence of thoracic trauma?
This may not be respiratory related.
- Pain / stress
- Hyperthermia
- TBI
- Shock
- Anemia
- Metabolic acidosis
How can we further classify our breathing evaluation?
Inspiratory dypnea
Expiratory dyspnea
Labored or prolonged and deep
Restrictive slow and shallow
Orthopneic posture
Why might mucous membranes be pink when a patient is cyanosis?
Delayed reaction of the mucous membranes
Decreased or dull sounds in the Dorsal aspect of the lungs is commonly associate with
Pneumothorax
Decreased or dull sounds in the Ventral aspect of the lungs is commonly associate with
Hemothorax
Decreased or dull sounds in the lungs is commonly associated with what 4 problems
Pneumothorax
Hemothorax
Diaphagmatic hernia
Severe pulmonary contusions
Increased sounds or crackles coming from the gut are commonly caused by:
pulmonary contusions
Gut sounds int he lung field are commonly associated with:
Diaphragmatic hernia
methods used to evaluate C - Circulation of patients
Mentation
Heart rate and rhythm
Pulse quality
Capillary refill time
Extremity pressure
Mucous membrane color