Types of Operations Management
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Operations Management
Designs, operates, and improves productive systems — systems for getting work done (Taylor, 2011)
Supports the product
Evaluation of Suppliers
The process of choosing the best supplier for the business.
The business, in order to minimize or avoid defects and damages, must conduct a critical evaluation of their potential suppliers.
Materials and Requisition
Every when should the business replenish their supply.
Storage and Inventory System
Describes how the business stores the finished goods and protects its inventory against possible theft and losses.
It is also referred to as “stock control”
FIFO (First-In, First-Out)
This method is most used by food related businesses.
LIFO (Last-In, First-out)
Most used in businesses wherein their products can only be sold in a limited time frame (Trends, Fads, and Seasonal).
JIT (Just in Time Method)
also known as the JIT Production System, storage and warehousing are eliminated because only actual orders are produced at the exact required time.
Operations Functions
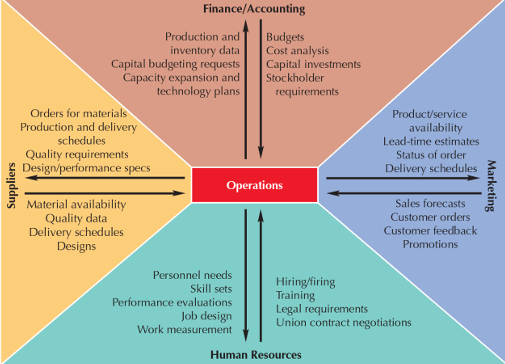
Business Models
Company's plan for how it will generate revenues and make a profit.
Direct Sales and Business Model
Under a direct sales business model, sales of products or services generate revenue through a network of salespeople who sell directly to customers.
Typically, no fixed retail location exists under a direct sales business model.
Arrangement where one party (the franchiser) grants another party (the franchisee) the right to use its trademark or trade-name as well as certain business systems and processes, to produce and market a good or service according to certain specifications.
Advertising Based Business Model
Strategic use of an advertising medium, with the goal of reaching a specific target audience.
Having a medium or platform for businesses to advertise on.
(Ex. Magazine Ads, Website Ads, etc. )
Brick and Mortar
It is a traditional streetside business that deals with its customers face-to-face in an office or store that the business owns or rents.
App Base → Utilizes software application that is installed in devices such as phones or PCs to offer the goods or services of the business.
Web Base → Can be visited through the world wide web via a web browser and purchase the product via online transaction.
A business can have multiple models and is encourages to.
(ex. FB is both an App base and Web based application).
Entrepise Delivery System (EDS)
It is defined by customers’ quality, delivery, and price expectations.
It starts from the (resources mobilized), proceeds to the (or the transformation process where input is converted into output) and produces the (the product).
The output is then marketed to the customers (in the case of goods) or experienced by the customers (in the case of services).
5 EDS Framework
Input
Throughout
Output
Final Delivery to Customers
Outcomes
Input
Resources Mobilized
Compose of 6Ms : Money, Men, Machines, Materials, Methods, Managements
Throughout
Transform Process
Conversion of Input to Output
Output
Product
Goods made or Service Rendered
Final Delivery to Customers
Marketing and Customer Servicing
Marketing Programs
Service Level Experienced
Outcomes
Customer Expectations: Quality, Delivery, Price
Market Expectations: Revenue/Sales, Market Share, Market Reach
Finance Expectations: Profits, Return on Investment