WSU SLP 6480 week 1 brain anatomy
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
neurogenic communication disoder
a disturbance of communication arising from damage to the nervous system; including aphasias, dysarthrias, apraxia of speech, and the myriad of communication problems that may arise from RHDs, TBIs, and dementia; ‘neurodivergent conditions’
organic communication disorder
include disorders resulting from motor/neurological disorders (childhood apraxia, dysarthria), structural abnormalities (cleft lip/palate), and sensory/perceptual disorders (hearing impairment)
cognition
the ability to acquire and process knowledge about the world
arousal
the level of wakefulness and the ability to respond to stimuli
orienting
the ability to direct attention toward a stimulus
attention
the ability to hold focus on a stimulus when aroused enough to know that the stimulus is there and use orienting skills and direct attention to the stimulus
vigilance
the ability to stay alert to the occurrence of a possible stimulus
sustained attention
the ability to hold attention to a single stimulus
selective attention
the ability to hold attention on a stimulus while ignoring the present of competing stimuli
alternating attention
the ability to move or alternate attention back and forth from one stimulus to another
divided attention
the ability to attend to one stimulus while simultaneously attending to another stimulus
working memory
the ability to hold a finite amount of information in the mind for immediate processing and manipulating
short-term memory
the retention of information seconds and minutes, up to an hour
long-term memory
the ability to retain information successfully for months or years
procedural memory
the encoding, storing, and retrieving of sequences of individual actions used to achieve larger objectives
declarative memory
the ability to remember facts
episodic memory
the recall of specific, recently experienced events or episodes
orientation
the ability of individuals to know who they are, where they are, and when they are
problem solving
the ability to find an appropriate solution to a problem
inferencing
the ability to take previous knowledge and experience and apply it to the interpretation of the present situation; the ability to interpret details correctly to make a leap in judgment to a correct interpretation of the overall meaning
executive functions
high level cognitive abilities used to employ other lower-level cognitive functions appropriately to meet high-level goals
language
a set of symbols used to communicate meaning
speech
the sounds made by the vocal and articulatory structures of the body to create verbal language
evidence based practice
the notion that therapy and evaluation procedures must be determined to be effective based on clinical opinion or valid and reliable research
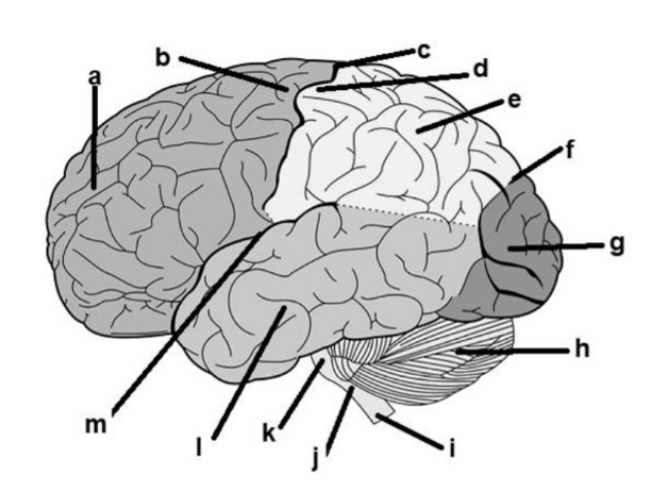
a. frontal lobe
b. pre-central gyrus
c. central sulcus
d. post-central gyrus
e. parietal lobe
f. parietal-occipital sulcus
g. occipital lobe
h. cerebellum
i. spinal cord
j. medulla oblangata
k. pons
l. temporal lobe
m. lateral sulcus
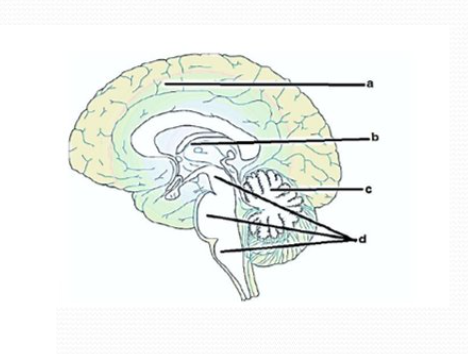
a. cerebral hemisphere (cerebrum)
b. diencephalon
c. cerebellum
d. brain stem