Variations in Psychological Attributes
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
What are individual differences?
It refers to the distinctiveness and variations among people’s characteristics and behavior pattern
What is one of the main concerns of modern psychology?
Study of individual difference
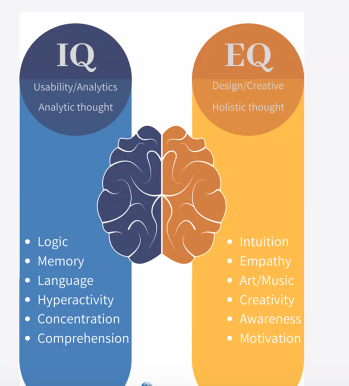
What are the characteristics of Emotionally Intelligent Persons?
Perceive and be sensitive to your feelings and emotions.
Perceive and be sensitive to various types of emotions in others by noting their body language, voice and tone, and facial expressions.
Relate your emotions to your thoughts so that you take them into account while solving problems and taking decisions.
Understand the powerful influence of the nature and intensity of your emotions.
Control and regulate your emotions and their expressions while dealing with self and others to achieve harmony and peace.
How did Salovey and Mayer define emotional intelligence?
“the ability to monitor one’s own and other’s emotions, to discriminate among them, and to use the information to guide one’s thinking and actions
What is situationism?
Situations and circumstances affect a person’s behavior
Human behavior is more a result of external factors
Ex. An aggressive person maybe submissive to their boss
How is Intelligence evaluated in India?
On Holistic grounds, attention if given to both cognitive and non-cognitive processes asn their integration as well
What is the first stop in understanding a psychological attribute?
Assessment
How does The American Association on Mental Deficiency define intellectual disablity?
views intellectual disability as “significantly sub-average general intellectual functioning existing concurrently with deficits in adaptive behavior and manifested during the developmental period
What is Assessment?
Measurment of psychological attributes of individual and their evaluation, using multiple methods
You can’t say an attribute exists without using scientific procedures.
Useful for predicting how person will behave in the future.
Uses systematic testing procedures to evaluate abilities, behaviors, and personal qualities of individuals
Formal and Informal
What is psychological assessment?
Uses systetematic testing procedures to evaluate abilities, behaviors and personal qualities of individuals
Difference between formal and informal assessment?
Formal assessment is objective, standardized, and organized (Psychologists are trained in formal assessment). Consistent. Only psychologists are trained
Informal assessment varies from case to case from one assessor to another, so it is open to subjective interpretation. Not standardized so inconsistent
What are the psychlogical attributes?
Multi-dimensional not linear or unidimensional. Described like a box
5 - Intelligence, Aptitude, Interest, Values, Personality
Intelligence - Is the overall global capacity to understand the world, think rationally and use available resources effectively when faced with situation/challenges. General cognitive competence/ability (Lower intelligence = lower test scores, tests tell if you can benefit from schooling). Global measure of a person’s general cognitive competence
Aptitude - refers to an individual’s underlying potential for acquiring skills (Used to see what you’re good at if given resources and environment)
Interest - a person’s preference for engaging in one or more specific activities. Person is more willing (Used to see what you want to do)
Personality - Relatively enduring characteristics that make a person distinct. (Used to see unique characteristics like if you’re outgoing. Helps predicts future behavior).
Values - Enduring beliefs about an ideal mode of behavior. A set of standard rules through which a people live their life (Guides life and judges others through it. Helps see how a person would act in a specific situation)
What are some methods or psychological assessment?
5 - Psychological Test, Interview, Case Study, Observation, Self-Report
Psychological Test - Objective and standardized measure of and individual mental and/or behavioral characteristics. Used for diagnosis, guidance, training and placement. 16PF, MMPI, MBTI
Interview - Involves seeking information from a person on a one-by-one basis
Case Study - In-depth study of the individual in terms of their psychological attributes, psychological history in the context of their psychosocial and physical environment, Used by Clinical psychologists. Based on data generated from other methods (Interview, observation, questionnaire, psychological test). Case study of great people can be illuminating
Observation - employing systematic, organized, and objective procedures to record behavioral phenomena occurring naturally in real time. Observer has little control over the situation. Reports suffer from subjective interpretations. Participant (Researcher engages in the activity) and Non-Participant (Researcher doesn’t engage).
Self-Report - a method in which a person provides factual information about themselves or opinions, beliefs that they may hold. Obtained by interview, questionnaire or a test or personal diary
Definitions of intelligence
Oxford - The power of perceiving, learning, understanding and knowing
Alfred Binet - Ability to judge well, understand well, and reason well
Wechsler - the global and aggregate capacity of an individual to think rationally, act purposefully, and to deal effectively with her/his environment. His tests are most widely used
Gardner and Sternberg - Intelligent individuals not only adapt to the environment but also actively modifies and shapes it
Sternberg - ability to adapt, to shape and select environment to accomplish one’s goals and those of one’s society and culture
Approaches to intelligence
Psychometric approach - intelligence is an aggregate of abilities, expresses performance in single index of cognitive abilities (Quantified)
Information-processing approach - describes the processes people use in intellectual reasoning and problem solving. Focuses on how an intelligent person acts instead of the underlying structure, cognitive function underlying intelligent behavior.
Theories of Psychometric Approach
Structure of Intellect model(J.P.Guilford)
Arthur Jensen (Level 1 and 2)
Charles Spearman two-factor theory
Uni Factor theory
Louis Thurstone
Theories of Information-Processing Approach
Howard Gardener’s Theory of Multiple Intelligences
PASS
Sternberg's Triarchic Theory Of Intelligence
What are the two types of aptitude tests?
Independant (Specialized) like Typing Aptitude test, numerical aptitude test,
Multiple (Generalized) include different aptitude tests battery, general aptitude test battery which measures intelligence in separate yet homogenous areas
Differential Aptitude Tests (DAT), the General Aptitude Tests Battery (GATB), and the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (
What is the Uni/One factor theory of intelligence?
Alfred Binet
One set of similar abilities that can be used to solve any problem. Disputes when psychologist began analyzing data (Mental Ability)
Psychometric Approach
Arose from his interest in differentiating more intelligent from less intelligent individuals.
What is the two-factor theory of intelligence?
Charles Spearman
Employed statistical method called factor analysis
Intelligence consists of general factor (g-factor) and specific factors (s-factors)
G-factor includes mental operations that are primary and common to all performances.
S-factor are the special abilities like a singer being good at singing
Psychometric Approach
General and Specific Factors
What is the Louis Thurstone’s Theory of intelligence?
Theory of primary mental abilities
Relatively independent of others
Comprehensive not independently judged
Seven primary abilities -
Verbal Comprehension (meaning of words),
Numerical Abilities (speed and accuracy of numerical skills),
Spatial Relations (visualizing patterns and forms)
Perceptual Speed (Speed in perceiving details)
Word Fluency (Using words fluently and flexibly)
Memory
Inductive Reasoning (Deriving general rules from presented facts)
What is Arthur Jensen’s hierarchical model of intelligence?
Consists of abilities operating at two levels
Level 1 - Associative learning output is similar to input (memory or rote learning)
Level 2 - Cognitive competence, higher order skills to transform input into effective output. Manipulating Level 1 to get a products
Psychometric Approach
What is J.P Guilford’s model if intelligence? Structure of Intellect model?
Classifies intellectual traits into Operation, Contents, and Products.
Operations is what the respondent does like cognition, memory, recording, memory retention
Contents are the nature of materials or information of which operations are performed (Visual, auditory, symbolic, semantic, and behavioral.
Products are the form in which the information is processed. Classified into units, classes, relations, systems, transformation, and implication
180 cells. Each cell has one factor or ability. may have more
Each factor is described of all three dimensions
Psychometric Approach
What is the Theory of Multiple Intelligences?
Howard Gardner
Intelligence is not a single entity. There are distinct intelligences that exist which are independent of each other.
Do work together sometimes
He studied talented people
Only Howard Gardner had a theory Multiple Intelligence not Louis Thurstone
First person to give a theory of Multiple Intelligences
Information-Processing Approach
What are the eight types of Intelligence in Gardner’s model?
Linguistic (Ability to produce and use language), known as word smart. Understand different word meanings and create linguistic images in their minds. Poets/Writers
Logical-Mathematical (An ability to think logically and critically and solve problems). Engage in abstract reasoning and can manipulate symbols to solve mathematical problems. Nobel Prize winners
Visual-Spatial (An Ability to form visual images and patterns). Represents spatial world in their mind. Pilots, sailors, sculptors.
Musical (An ability to produce and manipulate musical rhythms and patterns). Sensitive to sounds and vibrations, and create new patters of sound
Bodily-Kinesthetic (An ability to use whole or portions of the body flexibly and creatively). Athletes, dancers, actors, surgeon.
Interpersonal (An ability to understand to subtle aspects of others behavior). Psychologists, counsellors, politicians, social workers and religious leaders
Intrapersonal (An ability to understand of one’s own feelings, motives, and desires) Know their identity, human existence and the meaning of life. Philosophers and Spiritual leaders
Naturalistic (an ability to identify the features of the natural world). Hunters, farmers, tourists
What is Trarchic Theory of Intelligence?
Robert Sternberg (1985)
ability to adapt, to shape and select environment to accomplish one’s goals and those of one’s society and culture
Componential, Experiential and Contextual
Information-Processing Approach
Triarchic Theory of Intelligence. Robert Sternberg
Componential Intelligence is analysis of information to solve problems. Able to succeed in School
Knowledge Acquisition is responsible for learning and acquisition of doing things. Encode, combine and compare information
Higher / Meta Order Component is planning what to do and how to do it. Control, evaluate, monitor, plan
Performance Component is actually doing the thing
Experiential/Creative intelligence is using past experiences to creatively solve novel problems. Ability to filter out crucial information for a given situation. Novelty and Automation
Contextual Intelligence involves the ability to adapt to environmental demands. Street smart, Business sense
Has EQ (Contextual Intelligence)
Samarqand
Planning, Attention-arousal, and Simultaneous-successive (PASS)Model
information processing approach to intelligence
Neurological theory of Intelligence
Functional Units of Brain
by J.P. Das (Indian), Jack Naglieri, and Kirby (1994).
Interdependent functioning of three neurological systems called Functional Units of Brain
Responsible for Planning, Attention-arousal, and Simultaneous-successive
Arousal/Attention: Focuses attention on stimuli. Teacher tells you test is coming
Simultaneous-successive Processing: Simultaneous is Perceive relations among various concepts and integrate them into a meaningful pattern (RPM test). Meaning and relationship between abstract figures
Successive processing is when one memory retrieves another memory sequentially. like learning digits, alphabets.
Simultaneous needs both because you need a relationship to solve problem
Planning: Allows to think of possible courses of action. Higher cognitive concept used in last one. Helps review the gaps and device alternate plans. If plan does not work it is modified
Information-Processing Approach
What is Raven’s Progressive Matrices (RPM) Test about?
A design is given to you of in which one part is removed. You’re given six options that best complete the design
Simultaneous processing test
What is Cognitive Assessment System (CAS)?
Das and Naglieri
Verbal and non-verbal tests that measure basic cognitive functions
5-18 years of age
Battery of tests
Can be used to remedy cognitive deficits of children with learning problme
What is intelligence a product of?
Nature and Nurture
Correlation of intelligence of diff samples
Identical Twins separated together correlate .90
Identical twins separated in childhood .72
Fraternal twins reared together .6
Siblings reared together .5
Siblings reared apart correlate .25
Last one supports environment
Who intelligence is more similar to the one of an adopted child?
Biological parent not adoptive patent
It gets closer to adoptive parents as they grow
How are nature and nurture combined?
Heredity sets a range within which individuals development is set by environment
Most common aptitude test
DAT (Differential Aptitude Test) 8 sub test
Verbal Reasoning
Numerical Reasoning
Abstract Reasoning
Clerical Speed and Accuracy
Mechanical Reasoning
Space Relations
Spelling
Language Usage
Who made an Indian Adaptation of the DAT?
J.M. Ojha
What is first successful attempt to formally measure age?
1905, Alfred Binet and Theodore Simon
Measure of person’s intellect development relative to their age
When did Mental age come?
1908
What is Chronological Age?
Biological Age
What is MA?
Mental age
Measure of person’s intellectual development relative to people of their age group
How did Binet and Simon classify smart kids?
Is MA is more that CA the kid is bright
A dull kid’s MA is less than CA
A retarded kid’s MA is 2 years less that CA
What is IQ?
1912, William Stern, German Psychologist
Mental Age divided by chronological age and multiplied by 100
IQ = MA/CA * 100
What is the normal curve?
Most people’s IQ tends to be in the middle. Bell curve
Mean IQ =100
90-110 is normal intelligence
<70 = Intellectual Disability
>130 = exertional talent, intellectually gifted
IQ range
130 - Very Superior 2.2 Intellectual Gifted
120-130 Superior 6.7
110-119 High Average 16.1
90-109 Average 50.0
80-89 Low Average
70-79 Borderline
Below 70 Intellectually disabled
How is Intellectual Disability defined?
AAMMD views intellectual disability as “significantly sub-average general intellectual functioning existing concurrently with deficits in adaptive behavior and manifested during the developmental period
IQ < 70
Deficits in adaptive behavior
Observed during developmental period (0-18)
How is intellectual disability classified ?
55-70 IQ = mild
35-55 IQ = moderate
20-40 IQ = severe
Below 20-25 IQ = Profound
Mild can hold jobs and families
Gets worse as it goes down
People with Severe Disability are incapable of managing life and need constant care for their entire life
What is Giftedness from teachers point of view?
exceptional talent in wide areas
high ability,
high creativity
high commitment.
What is Talent?
Remarkable ability in specific field known and prodigy
When did to the study of gifted Individual begin?
1925 by Lewis Terman
Who are prodigies?
Highly talented people
Characteristics of Gifted Children during infancy and childhood
Larger Attention Span
Good recognition memory
Preference for novelty
Sensitivity to environmental change
Early appearance of language skills
Characteristic of gifted children?
Advanced logical thinking, questioning
and problem solving behaviour.
• High speed in processing information.
• Superior generalisation and discri
mination ability.
• Advanced level of original and creative
thinking.
• High level of intrinsic motivation and
self-esteem.
• Independent and non-conformist
thinking.
• Preference for solitary academic
activities for long periods.
What other source help us understand gifted childre?
Teachers’ judgment, school achievement record, parents’ interview, peer and self—ratings in combination with intellectual assessment
What do gifted children require?
Special attention
different educational programmers to sharpen children’s skills in productive thinking, planning, decision-making, and communication.
Types of Intelligence Tests
Individual/Group Test - Administrator is sensitive to feelings in Indvidual test by not in group test. Individual test can answer orally, group test have to give MCQ
Verbal, Non-Verbal, or Performance Tests - RPM is Nonverbal test, Kohls’ Block Design Test is performance test.
In verbal test requires to give answer orally or in written. Can be only given to literate people
If person is not literate or has language gaps. They are given a non-verbal test. RPM
In performance test you actually manipulate the objects. Can be conducted across culture. Culture-Fair test. Kohls’ Block Design Test. Wooden blocks you have to arrange a pattern in a given time
Culture-Fair or Culture-Biased Tests - Intelligence tests show bias in culture. White middle-class people do better. Hard to make culture fair test
Performance/Projective/ tests can’t be given in group settings
Non Verbal and Performance test help reduce cultural bias
What are some ill effects of Intelligence tests?
Scoring bad may attach a stigma to a child making them lose self-respect and do bad on their test
Might invite discriminatory practices from society
Underestimates the IQ of kids coming from poor backgrounds. Biased to middle and higher class
Don’t capture the creative side of people. They may still succeed
What helps reduce cultural bias?
Non-verbal and performance test
Who made the Hindi Intelligence test?
S.M. Mohsin
What is WAIS (Weschler’s Adult Intelligence Scales)?
Weschler Test
Verbal Comprehension
Perceptual Reasoning
Working Memory
Processing Spees
What is a popular intelligence test in India?
Bhatia’s Battery of Performance tests
Who tried to standardize Binet’s test inn Urdu and Punjabi?
C.H. Rice
Who tried to standardize Binet’s test in Bengali?
Mahanobis
Who prepared a Mental Measurment Handbook of 103 tests in India?
Long and Mehta
Who documents test in INdia?
NLEPT at the National Council of Educational Research and Training and the NCERT
What did Vygotsky say about culture effect of intelligence?
Culture gives a social context to understand the world around them
In less developed societies personal skills are more important while in developed societies achievements founded on abilities are important
What mental functions is different amoung cultures according to Vygotsky?
Elementary mental functions such as crying of attending to mothers voice is the same
Higher mental functions such as problem solving and thinking are culture-produced
What is culture?
A collective system of customs, beliefs, attitudes, and achievements in art and literature
Who theory have some influence of culture?
Sternberg’s notion of Contextual and practical intelligence
What do technologically advanced societies advocate for?
Foster skills of generalization and abstraction
What is technological intelligence?
Attention, observation, analysis, performance, speed and achievement orientation
Used in technologically advanced societies.
Skills of genralisation and abstraction, speed, minimal moves and mental manipulation
Not valued in many Asian and African societies
What is Integral intelligence?
Connectivity with the social and world environment
What is Buddhi?
Mental effort, determined action, feelings, and opinions along with knowledge, discrimination and understanding according to J.P. Das
Knowledge of oneself based on conscience, will and desire
Has affective and motivational components
Facets of Intelligence in Indian tradition/ Integral intelligence
Cognitive and non-cognitive processes
Cognitive capacity (sensitivity to context, understanding, discrimination, problem solving, and effective communication)
Social Competence (respect for social order, commitment to elders, the young and the needy, concern about others, recognizing others’ perspectives).
Emotional competence( self regulation and self-monitoring of emotions, honesty, politeness, good conduct, and self-evaluation).
Entrepreneurial competence (commitment, persistence, patience, hard work, vigilance, and goal-directed behaviours).
What is Emotional intelligence?
Skills that underlie accurate appraisal, expression, and regulation of emotion
Ability to monitor one’s own and other’s emotions, to discriminate among them, and use the information to guide one’s thinking and actions
Who introduced concept of Emotional Intelligence?
Salovey and Mayer
What is Emotional Quotient?
Ability to process information accurately and efficiently
Salvoey and Mayer
What has Emotional Intelligence helped in?
Increasing attention of educators for dealing with students who are affected by stress
Benefits academic achievement
Encourage cooperative behavior
Reduce antisocial activities.
What is Aptitude?
combination of characteristics that indicates an individual’s capacity to acquire some specific knowledge or skill after training.
Aptitude tests
Independant (Specialized) aptitude
Multiple (Generalized) aptitude test
DAT - Verbal Reasoning, (ii) Numerical Reasoning, (iii) Abstract Reasoning, (iv) Clerical Speed and Accuracy, (v) Mechanical Reasoning, (vi) Space Relations, (vii) Spelling, and (viii) Language Usage
General Aptitude Tests Battery
Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery
Landmark research in creativity and IQ
Terman in the 1920s
High IQ does not ensure high creativity
What is Creativity?
Ability of person to think and ponder upon novel and innovating solutions to the given problem and divergent thinking which refers to thinking in a broad and open-minded manner
Divergent (Out of the box)
Broad an open minded manner
Example of the highest level of creativity?
Einstein’s theory of relativity
Are intelligence and creativity intertwined?
Need certain amount of intelligence to be creative
Does not ensure that as intelligence increases creativity increaser
Variations in creativity
Heredity and environment
motivation, commitment, family support, peer influences, training opportunities,
Who made the CIE Verbal Test of Intelligence?
Uday Shankar
Who was the group test of general mental ability?
S. Jalota
Who made Bihar Test of Intelligence?
S.M. Mohsin
Who made Indian adaptation of Stanford-Binet Yest?
S.K. Kulsherstha
Who made test of General Mental Ability in Hindi?
M.C. Joshi
Who made Draw-a-Man test in India?
Pramila Pathak
Who adaped Wechsler Adult Performance Intelligence Scale?
R. Ramalingaswamy
General feature of creative tests
Open ended
Divergent thinking
Ability of produce variety of ideas
New relationships between unrelated things
What is the structure of formal tests?
It is standardized, a complete set of manual and interpretation guide
Only used after extensive training in administration and interpretation of test scores
What is a novel solution to a problem called?
Creativity
What do you need in order to be successful in a particular field?
Interest and Aptitude
Who made creative tests?
Guilford, Torrance, Khatena, Wallach and Kogan, Paramesh, Baqer Mehdi, and Passi.