Pedigree Analysis
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Pedigree Analysis
What
Importance
What: Method to study family history to figure out how traits or diseases are inherited
Importance:
To determine if trait is dominant or recessive
To identify deleterious alleles
Shows risk of genetic diseases especially in related families
Dominant Gene Action
Affected individual has
Result of affected individual mating with unaffected individuals
2 affected individuals’ children maybe
2 unaffected individuals’ children are
Skipped generations?
Affected individual has: At least one affected parent
Result of affected individual mating with unaffected individuals: 50% chance of transmitting dominant allele
2 affected individuals’ children maybe: Unaffected
2 unaffected individuals’ children are: Only unaffected
Skipped generations: No, phenotype appears in every generation
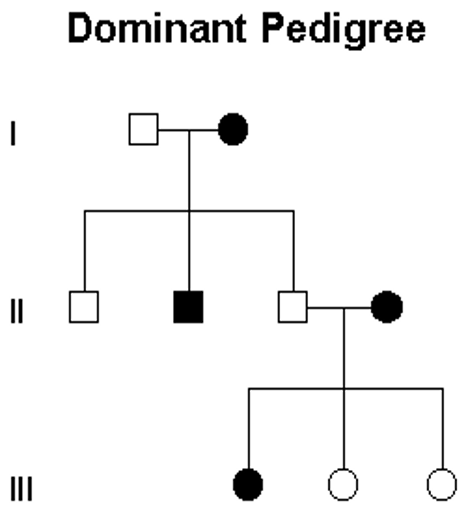
Autosomal Dominant
What
So if heterozygous?
Gender bias?
Affected child means
Unaffected child means
Affected outsiders marrying into family, are assumed to be
Skipped generations?
What: Where a disorder is caused by one copy of a mutated gene on a non-sex chromosome (autosome)
If heterozygous: Shows the disease/trait
Gender bias: No, both genders are affected equally
Affected child: Means at least one parent is affected (homo dominant or heterozygous)
Unaffected child: They are homozygous recessive and have unaffected parents (who cannot pass the trait)
Affected outsiders, assumed to be: Heterozygous
Skipped generations: No, every generation shows trait
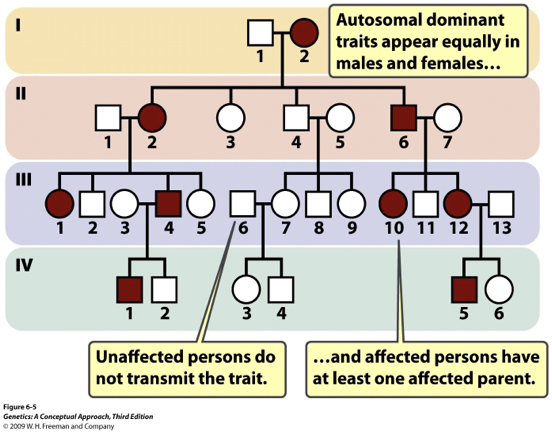
Recessive Gene Action
Affected individual means their parents are
All children of affected individuals are
Affected individual may have a parents that is: Not affected (heterozygous)
All children of affected individuals are: Affected
Autosomal Recessive
All affected are
Unaffected outsiders are
All affected are: Homozygous
Unaffected outsiders are: Homozygous
For sex-linked dominant, mothers and fathers pass their X to?
Mothers = both sons and daughters
Fathers = daughters only
What is co dominance?
When heterozygous shows the phenotypic effect of both alleles fully and equally