The Immune system
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Describe how HIV is replicated. (4)
Attachment proteins attach to receptors on helper T cell (lymphocyte)
Nucleic acid/RNA enters cell
Reverse transcriptase converts RNA to DNA
Viral protein/capsid/enzymes produced
Virus particles assembled and released from cell
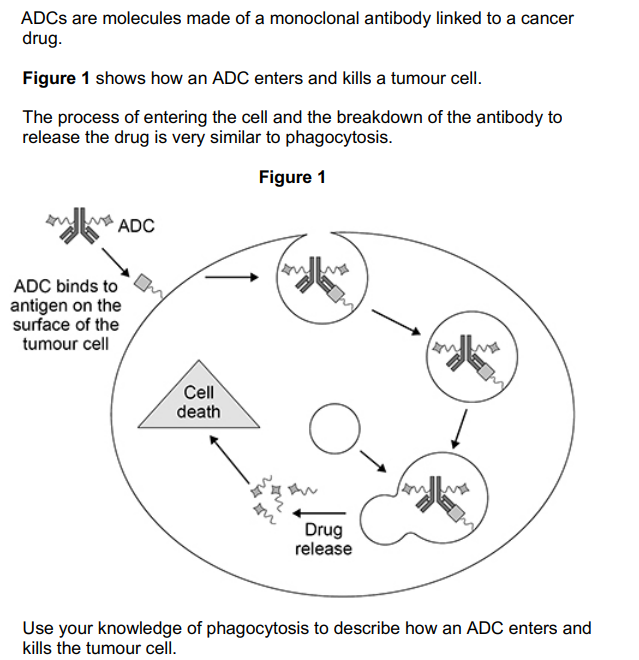
ADCs are molecules made of a monoclonal antibody linked to cancer drug. The process of entering the cell and the breakdown of the antibody to release the drug is very similar to phagocytosis.
Use your knowledge of phagocytosis to describe how an ADC enters and kills the tumour cell. (3)
Cell engulfs (endocytosis) the antibody/ADC
Lysosomes fuse with vesicle/phagosome containing ADC
Lysozymes (hydrolytic enzyme) breakdown/digest the antibody/ADC to release the drug
Describe how HIV is replicated once inside helper T cells. (4)
RNA converted into DNA using reverse transcriptase
DNA incorporated into helper T cell DNA
DNA transcribes into HIV mRNA
HIV mRNA translated into new HIV/viral proteins for assembly into viral particles
Describe how a phagocyte destroys a pathogen present in the blood. (3)
Engulfs (endocytosis)
Forming vesicle/phagosome and fuses with lysosome
Enzymes digest/hydrolyse
Give three types of cell, other than pathogens, that can stimulate an immune response.
(Cells from) other organisms/transplants
Abnormal/cancer/tumour cells
Cells infected by virus
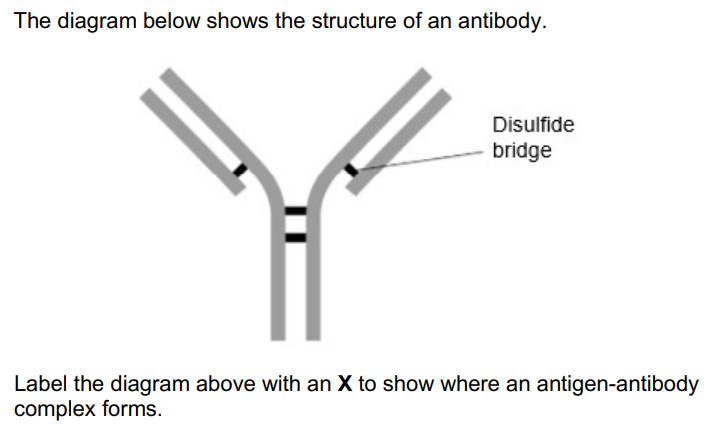
Show where antigen-antibody complexes form (1)
End of both ends of Y shape
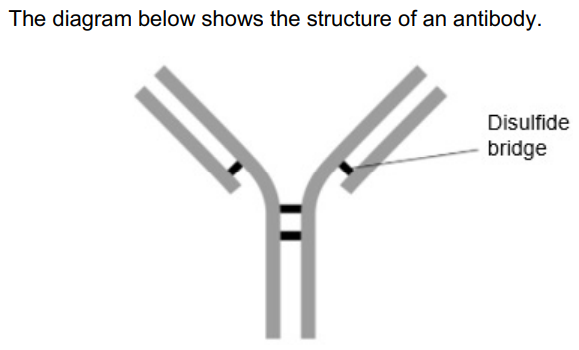
A disulfide bridge is labelled in the diagram above.
What is the role of the disulfide bridge in forming the quaternary structure of an antibody? (1)
Joins two different polypeptides
Explain how HIV affects the production of antibodies when AIDS develops in a person. (3)
Less/no antibody produced
Because HIV destroys helper T cells
So few/no B cells activated/stimulated or few/no B cells undergo mitosis/differentiate/form plasma cells.
In Europe, viruses have infected a large number of frogs of different species. The viruses are closely related and all belong to the Ranavirus group. Previously, the viruses infected only one species of frog.
Suggest and explain how the viruses became able to infect other species of frog. (2)
Mutation in the viral DNA/RNA/genome/genetic material
Altered tertiary structure of the viral attachment protein (antigenic variability)
Allows attachment proteins/virus to bind to receptors of other species
Explain how determining the genome of a virus could allow scientists to develop a vaccine. (2)
The scientists could identify the proteome / proteins that derive from the genetic code
They could then identify potential antigens to use in vaccine
Describe how B lymphocytes respond to vaccination against a virus. (3)
B cell antibody binds to viral specific/complementary receptor/antigen (forms antigen-antibody complex)
B cell divides by mitosis (clones)
Plasma cells release/produce monoclonal antibodies against the virus
B cells/plasma cells produce/develop memory cells
What is a monoclonal antibody? (1)
Antibodies with the same tertiary structure OR antibody produced from identical plasma cells/B cells/B lymphocytes
Give one example of using monoclonal antibodies in a medical treatment. (1)
Targets/binds/carries drug/medicine to specific cells/antigens/receptors OR block antigens/receptors on cells
Describe the role of antibodies in producing a positive result in an ELISA test. (4)
First antibody binds/attaches/complementary (in shape) to antigen
Second antibody with enzyme attached is added
Second antibody attaches to antigen
Substrate/solution added and colour changes
Describe and explain the role of antibodies in stimulating phagocytosis. Do not include details about the process of phagocytosis. (2)
Bind to antigen / are markers
Antibodies cause clumping/agglutination OR attract phagocytes
Tests using monoclonal antibodies are specific. Use your knowledge of protein structure to explain why. (3)
Specific primary structure / sequence of amino acids
Specific tertiary / 3D structure
Only binds to one antigen
Give two ways in which a pathogen may cause disease when it has entered the body.
Releases harmful toxins
Causes cell lysis resulting in damage to cells