Economics hell
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Save me
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
What is subjective and objective
Subjective value, profit
Objective - price, cost
Implicit costs
Explicit costs
sunk costs
implied/implicit cost - oppurtunity cost, it is the value of forgone benefits (that could have been saved)
Explicit costs- actual cost
Sunk cost - irreversible, it has already been spent and cannot be recovered
economic systems
traditional
barter trade system
you consume your own products
little economic progress
command
government owns everything (factors/resources)
it decides what goods or services will be produced
determines methods of productions/wages
provides healthcare/education
market
economic decision is decentralized
services/goods based on demand
private enterprises
How does job specialization increase work efficiency?
1) people can focus on what they do best
2) people can produce more quickly and high quality
3). Businesses can take advantage of ECONOMIES OF SCALE
Level of production increases, the average cost of producing each individual unit declines
Macro vs micro economics
Micro focuses on the economics of families, businesses and workers.
Macro focuses on econs as a whole. Economy of the nation
about issues like growth of production, unemployed people, the inflation increase in prices, trade balance etc.
Fiscal vs Monetary policy
Fiscal -economic policies involving taxes, exchange rates, housing etc
determined by the government
Monetary - altering interests, money supply, government budget
determined by the central bank
what are the factors that ARE and ARE NOT involved in the CIRCULAR FLOW
No:
government intervention (taxes)
foreign trade
savings (loans)
assume that :
all prices are constant
in equilibrium
always full employment
Visualize a circular flow
two main sectors - firms and households
two main markets - goods/service and factors of production (labour)
Formula for opportunity cost
Sacrifices/gains = opportunity cost
Supply demand model
demand - negative slope
supply - positive slope
X axis - quantity
Y axis - price
marginal benefit and marginal cost
MB>MC - good
MB=MC - acceptable
(both above are rational choices)
MB<MC - no good
why would someone pay to much to get so less benefits
What is equilibrium
When demand is equal to supply
No resource is wasted
Supply thing (give the law and definition)
Law of supply
Supply go up
Price go up
(Positive slope)
how much good/service is the supplier willing to supply at a given price
Movement vs Shift
Movement - price change, demand/supply change)
Shift- the price doesn't change, supply/demand change
(affected by non price factors)
Shifts usually affect the other (eg shift in supply, movement in demand)
Example of movement
Discounts, sales
List what affects demand (non price factors)
Income
Price of substitute/complement change
Changing tastes/preferences
Changes in expectations about future
Changes in composition of the population
Inferior product?
Income go down
Demand go up
goods that ppl only buy when they are poor
Elasticity??
Basically how “flexible" a price can be adjusted where ppl can still buy the product
how responsive the people are to the price
Inelastic is not flexible price
Supply shift determinents
Natural and social factors
natural conditions
Input prices (raw materials)
Numbers of sellers
technology
government policies
expectations on future prices
what is elastic, and what is not
elastic - >1
unit elastic - = 1
inelastic - <1
Price floor and ceiling
they are price controls set by the government
price ceiling is at the bottom - maximum price something can be charged
(eg necessities, so people can afford them)
(price ceilings forces shortages)
price floor at the top- minimum price something can be charged
eg cigarettes so people wont buy them
Opportunity cost
the value of the forgone alternative action or decision
what is Scarcity
unlimited human want, and limited resource
“when human wants for goods and services exceed the available supply”
Elasticity formulas (3)
ELASTICITY OF INCOME
Yield (returns to you) -Y
+Ve normal prod. -ve inferior prod
ELASTICITY OF DEMAND/SUPPLY
Price of product - P
+Ve supply -ve demand
ELASTICITY OF CROSSPRICE PRODUCT
Price of another product - X
+Ve substitute -ve complementary
Fixed cost vs marginal cost vs variable cost vs average cost
Fixed cost - cost that doesnt change with the amount produced- rental fee
variable cost - scales with amount produced- Raw materials (?)
factors of production and how they are paid
selling labour - wages
capital :
selling skill- salary
selling machines - interest
selling land - rent
selling entrepreneurial (skills?) - profit
positive vs normative economics
positive - focus on description , explanation, quantification
OBJECTIVE facts, no opinions involved, no judgement
Normative
SUBJECTIVE judgment, value based, ethical considerations etc.
production possibilities frontier
a graphical model illustrating the maximum combinations of two goods or services an economy can produce with its available resources and technology
on the line - optimum
inside the line - not using the resources to its potential
outside the line - not possible or achievable (cuz scarcity and limited resources)
the law of increasing cost
it explains the concave shape of the PPF
cuz if more goods are produced, the opportunity cost for an additional unit increases
firms main objective?
Decrease cost
shortage vs surplus
shortage - too many demand
fix by increasing price to lower the demand
surplus = too many supply
fix by decreasing price to increase the demand
and by fixing them, they return to equilibrium
complementary and substitute goods’
complementary - they go tgt
when good A demand up, the complementary product does the same
positive relationship
substitute - they “replace” the product
when good A demand up, the substitute demand goes down
inverse relationship
what is ceteris paribus
“with other conditions remaining the same, other things being equal”
demand assumptions
constant income (of the buyers)
constant prices of relative goods
unchanging preferences
constant number of buyers
all are normal goods
ceteris paribus
Demand? (law and definition)
LAw of demand
price go up, demand go down
price go down, demand go up
definition
the amount people are willing to buy
Shifting thing (what decreases and increases)
Quantity increase, price decreases - shifts right
Quantity decrease, price increase - shift left
The 4 types of economic structures (?)
Monopoly
oligopoly
monopolistic competition
(the middle 2 = imperfect competition)
perfect competition
Total cost, total average cost thing
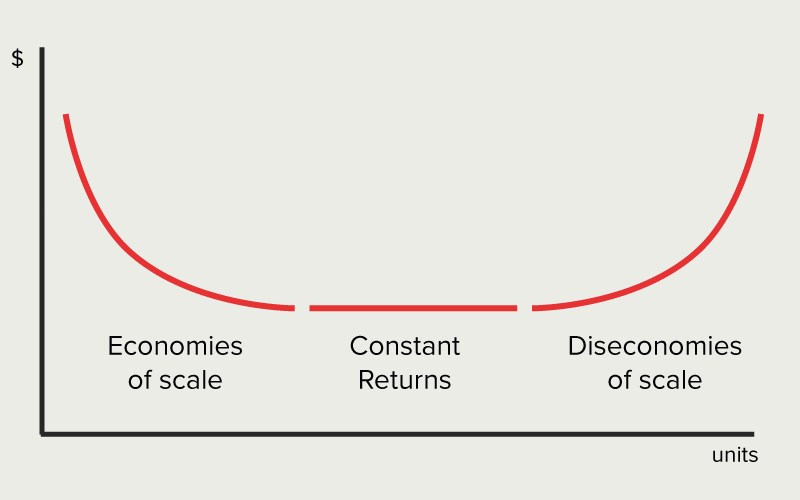
Economies of scale
Economies of scale = increasing returns (average cost gets lower)
constant returns =
Diseconomies of scale = decreasing returns ( average cost becomes higher again)
average cost go up cuz need to afford more machines, hire more ppl to cover the demand to produce more.
total revenue = ?
Total revenue = price x quantity
Profit = total revenue - total cost
Marginal cost
Cost needed to produce ONE MORE UNIT
it gets higher and higher at some point
Diseconomies of scale
Dimishing marginal returns or somethiNG>
Why can't the demand curve be vertical? (Firms charging as high they like
1) income is fixed
2) we will actively seek substitutes
Shut down vs exit
Shutdown
Shutting down a production line, but keeping labour, land and entrepreneurial skills. Basically making another product
Exit
quit everything basically. Selling all resources
Dead weight loss
An area of the graph that is a lose lose situation because it is inside the ppf which means it is underutilized. This only happens in pure monopoly (factt check this)
Monopoly power (?)
Influencing prices
Influencing output
Pricing strategies to prevent or stuffle competition
May not pursue profit maximization - encourage unwanted entrants to the market
Sometimes seen as a case of market failure
Monopolistic characteristics
Large number of firms in the industry
Small price band
May have some element of control over price due to differentiate their product in some way from their rivals - products are therefore close but not perfect , substitutes
Entry and exit from the industry is relatively easy -few barriers to entry and exit
Consumer and producer knowledge imperfect
Price maker and price takers
Price maker set prices, usually the dominating firm does it
Price takers take the price from price makers
Perfect competition caharcteristics
Horizontal demand line
Large number of firms
Products are homogenous - Consumer has no reason to express a preference for any firm
Freedom of entry and exit into and out of industry
Firms are price takers
Each producer supplies a very small proportion of total industry output
Consumers and producers have perfect knowledge about the makert
Predatory pricing
Big firms try to prevent smaller firms from entering by lowering the price (cuz they are price makers) to below their competitors cost.
Oligopoly
Price may be relatively stable across the industry - kinked demand curve (a combo of inelastic and elastic)
Potential of collusion
Behaviour of firms affected by what they believe their rivals might do - interdependence of firms
Goods could be homogeneous or highly differentiated
Branding and brand loyalty may be a poten source
Game theory
kinked demand curve
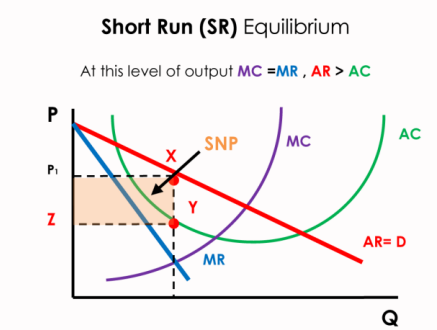
WTH is a supernormal profit ???
Supernormal Profit = Total Revenue - Total Cost
The orange area
the profit a firm earns above and beyond the normal profit, calculated by subtracting both explicit and implicit costs from total revenue. (then why is it called super normal profit??)
Supernormal profit is the excess profit a business makes after covering all its costs, including the minimum amount needed to keep the business running (normal profit). It's calculated by subtracting all total costs (both explicit and implicit) from total revenue. In simple terms, it's the "extra" profit earned above what is just necessary to stay in business. “
often temporary
Imperfect competition
number of independent firms in
Aim of firm is to maximise profits industry
Product differentiation exists.
The products are not homogenous and competitive advertising occurs
Free entry/exit of firms to/from the market
Knowledge is widespread each competitors know what the other is earning
Many buyers of the goods produced in the industry
Concentration ratio
an economic metric that measures the dominance of a few firms in a market by summing the market shares of the largest firms, typically expressed as a percentage.
shows market structure
CR4- Concentration ratio of 4 companies
CR8 - 8 companies , measures market
Long run vs short run
In short run
in long run, many short runs make it up (?) variable cost (uhhh)
Law of diminishing returns
When MPL is more than 0, MPL declines as more labour is hired. (or any marginal product like land, capital)
when MP at maximum and MC at minimum.
Accounting profit vs economic profit
Accounting - minus explicit ONLY
Economic - minus explicit and implicit (oppurtunity cost)
relationship between MC and MP
The relationship is inverse ,both of them slope upwards, but MC gets steeper and steeper while MP gets flatter and flatter.
Why is 1 season a short run?
Short run - at least one fixed input ( factors of production) (capital, labour, land , entrepreneurial skills)
Cuz you fix one to see which is the most efficient (observe what is most optimum)
MIDPOINT FORMULA!!!!
Economics of scale
When minimum points of all possible SRATC (short run average total cost ) become lower as quantity of output
The kinked demand curve - where it appears and what it is
Appears in oligopoly
it has both inelastic and elastic properties (?)
elastic cause drop in price
inelastic causes raised price for revenue
what does macroeconomics examines?
examines Performance and behavior affected by :
government policies
central banks (federal reserve in ‘murican books) financial institutions
Actions of other economies (other countries)
aggregate economics units and phenomena
What are the ceaseless activities?
Activieties that keep happening
recession
inflation
economic growth
unemployment
2 types of GDP
Nominal
real
3 causes of inflation
3 types of unemploment
Frictional quit a job to get another (short term)
Structural (long) (fired!!) - cuz your skills are no longer required (change in industry, technological advancement )
Cyclical - due to recessions
whats NRU
Natural something unemployment
tools of monetary policy
fiscal policy
Constant returns of scale?
The flat part of the long run graph
Diseconomies of scale
definition of inelastic
Inelastic means that a 1% change in the price of a good or service has less than a 1% change in the quantity demanded or supplied.
GDP (definitiions)
gross domestic produce
Market value of all the final goods and services produced within a countries borders in a given period
only final goods (intermediate goods are excluded to prevent double counting)
only legal goods
What is CPI
How to calculate inflation rate from CPI