Quiz 1 Study Guide - Vocabulary Flashcards (Science, Life & the Cell, Biochemistry)
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key terms from the notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Anecdote
A personal story or example used as evidence; not proof.
Expert opinion
A trained person's view; helpful but not definitive proof.
Research data
Measurements from studies used as evidence.
Observational
Study that watches and records without changing conditions.
Experimental
A study that changes one variable to test its effect; includes control and treatment groups.
Peer‑reviewed studies
Research evaluated by other scientists; stronger when many studies agree.
Control (in an experiment)
The baseline condition that is not exposed to the manipulated variable.
Variable
A factor that can be changed or measured in an experiment.
Bias
A systematic error or preference that affects results.
X-axis
Horizontal axis on a graph; often the variable being changed or time.
Y-axis
Vertical axis on a graph; what is measured or observed.
Pattern (on a graph)
A trend in data (upward, downward, or no change).
Scale
The range or size of values shown on a graph.
Units
The standard quantities used on axes (e.g., seconds, meters).
Cells
The basic unit of life; can be single or many cells.
Metabolism
All chemical processes that extract, transform, and use energy. Component of Life
Homeostasis
Maintaining internal balance (stable conditions) despite external changes. Component of Life
You get hot → you sweat to keep your body temperature near 98.6°F.
Growth and development
Increase in size and maturation over time. Component of Life
Reproduction
Creation of offspring or new cells. Component of Life
Response to environment
Moving toward/away from
Example: You touch a hot pan → you pull your hand away.stimuli; adapting to surroundings. Component of Life
DNA
Genetic material with instructions to build and operate an organism. Component of life
Evolution
Change in populations across generations over time. Component of life.
Prokaryote
A cell with no nucleus; DNA in a nucleoid; smaller; no membrane‑bound organelles.
Eukaryote
A cell with a true nucleus; larger; contains membrane‑bound organelles.
Nucleus
Membrane‑bound organelle containing DNA; control center of the cell.
Nucleoid
Region in prokaryotes where DNA is located (not membrane‑bound).
Organelles
Any specialized parts inside a cell that do jobs (builders, shippers, power plants, etc.).
Membrane‑bound organelles
Organelles enclosed by membranes (present in eukaryotes, absent in prokaryotes).
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
ER with ribosomes; synthesizes and folds proteins.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)
ER without ribosomes; lipid synthesis and detoxification.
Golgi apparatus
Packages, sorts, and ships proteins and lipids.
Mitochondria
Powerhouses of the cell; produce ATP energy.
Chloroplasts
Site of photosynthesis in plants; makes sugar from light.
Lysosomes
Recycling center; breaks down waste and cellular debris.
Peroxisomes
Break down fats and detoxify harmful substances.
Vacuoles
Storage compartments; large central vacuole in plants maintains turgor.
Cytoskeleton
Frame and tracks for support and movement inside the cell. Consists of 3 protein filaments. Microtubules (Transportation and Structure), Microfilaments (Movement), Intermediate Filaments (Mechanicle Support), Centrioles (Cell Divison)
Vesicles
Small membrane‑bound sacs for transport and delivery.
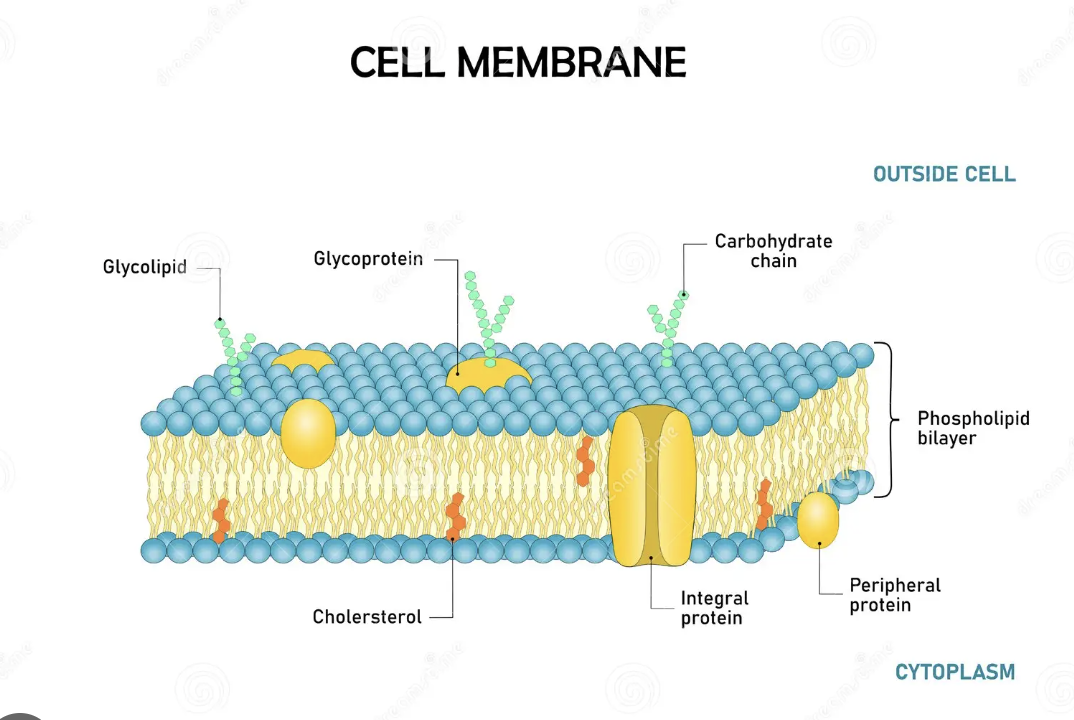
Plasma (cell) membrane
Smart barrier that controls what enters and leaves the cell.
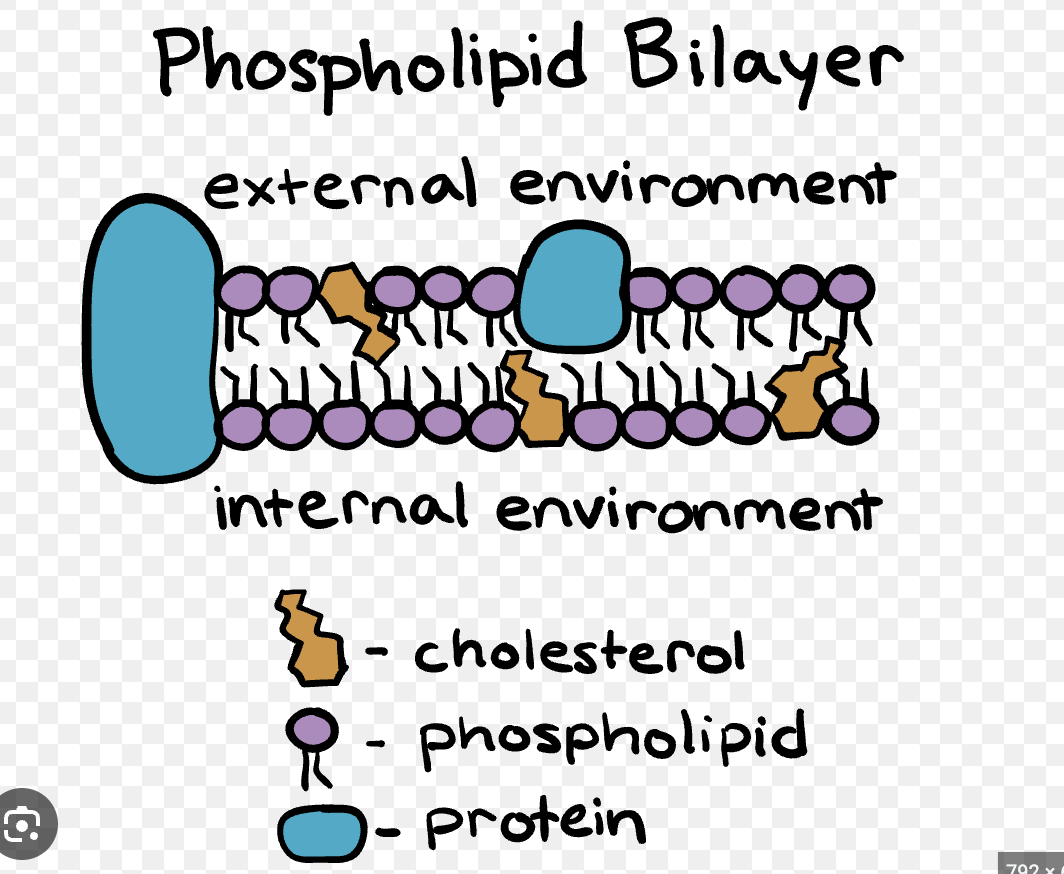
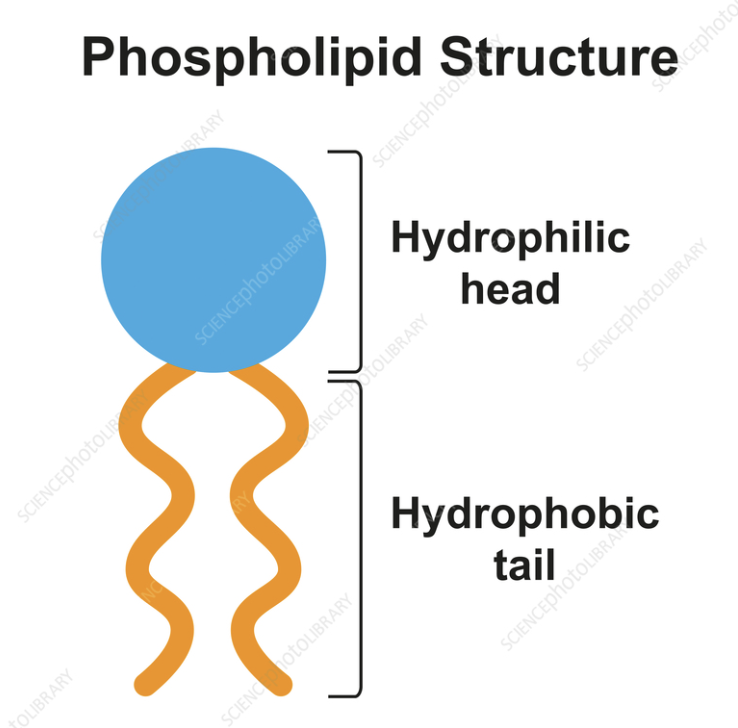
Phospholipid bilayer
Two layers of phospholipids with hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails.
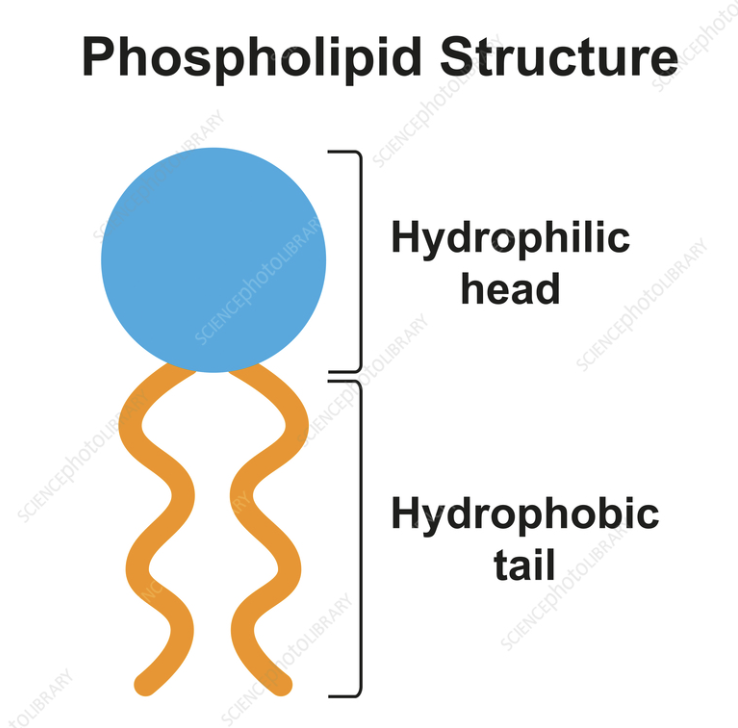
Hydrophilic head
Water‑loving part of a phospholipid face toward water. (Phosphate functional Group) Polar)
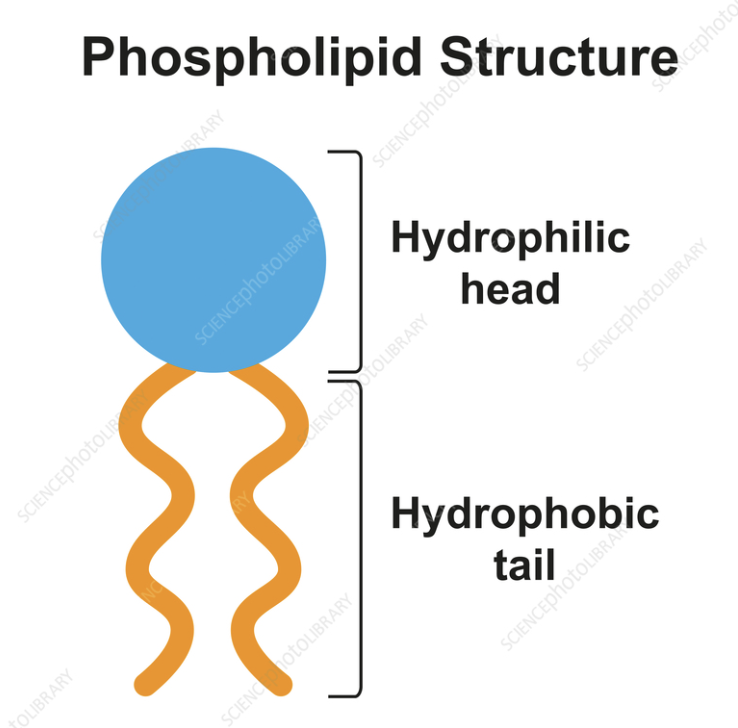
Hydrophobic tail
Water‑fearing part of a phospholipid that avoids water. (2 Fatty Acid hydrocarbon chains) (Nonpolar)
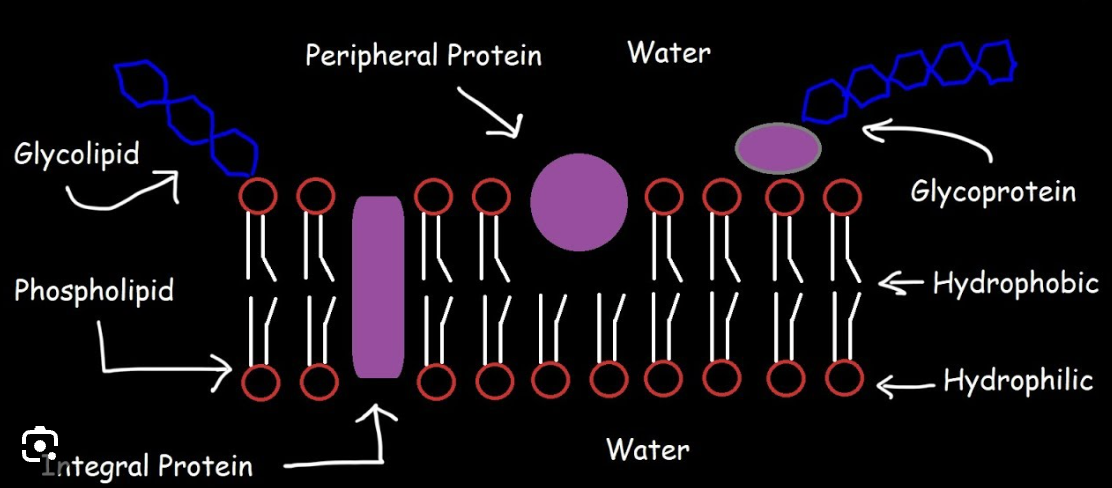
Integral protein
Proteins that span the membrane and act as channels or pumps.
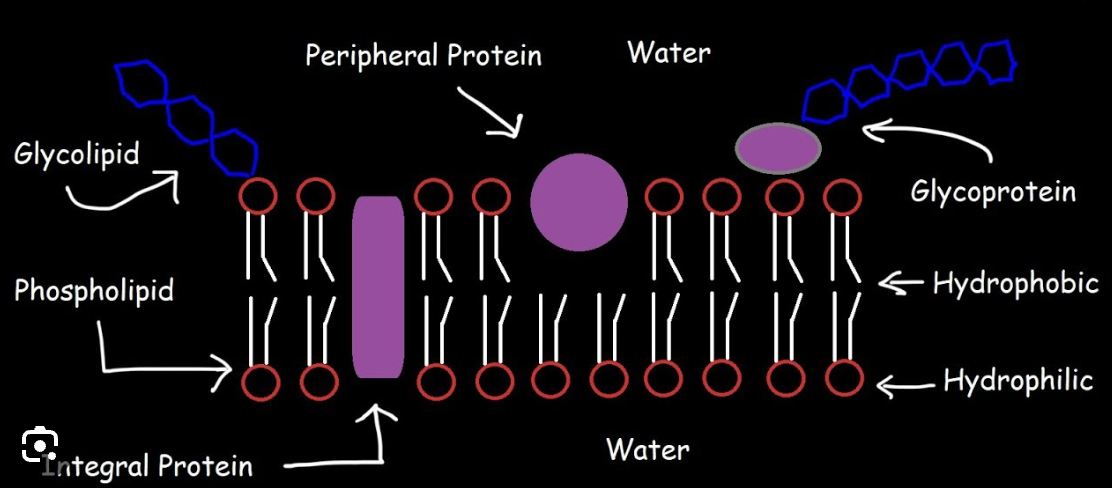
Peripheral protein
Proteins on the membrane surface that assist with signals or support.
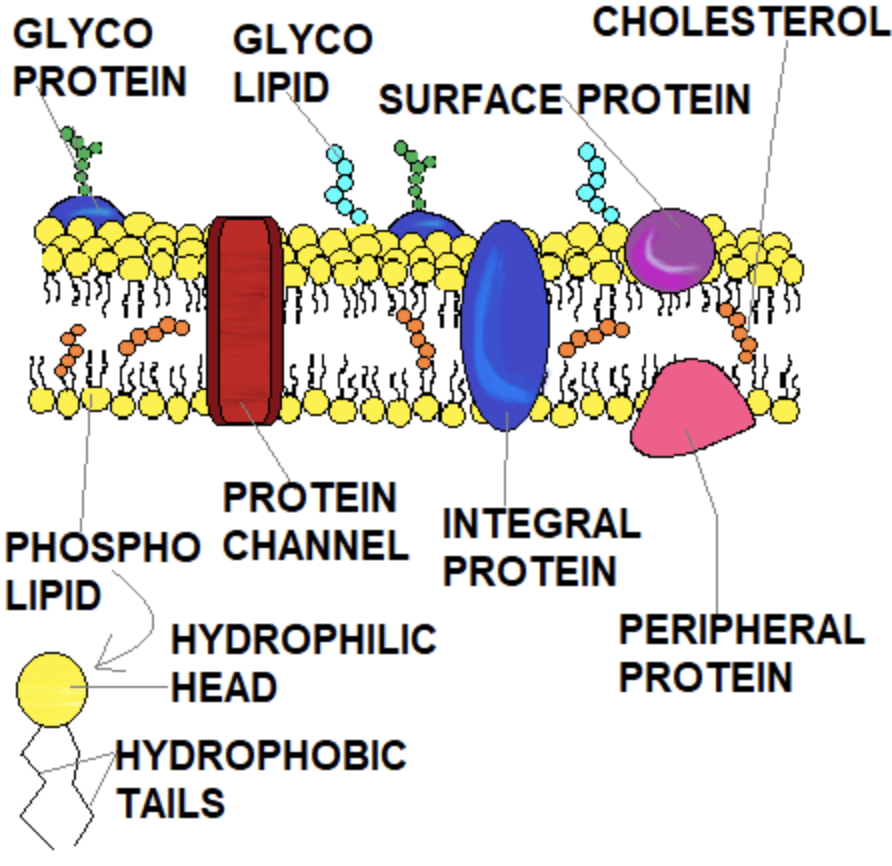
Cholesterol (membrane component)
Sterol in the membrane that helps regulate fluidity.
Carbohydrates (in membranes)
ID tags on proteins/lipids used for cell recognition (glycoproteins/glycolipids).
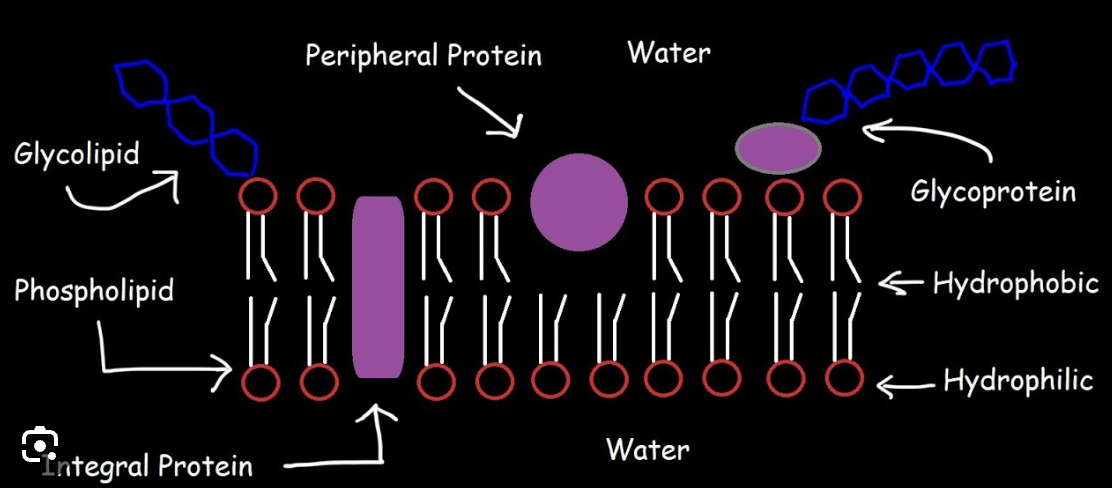
Glycoprotein
Protein with carbohydrate chains used for cell recognition. (ID Tag in the plasma membrane)
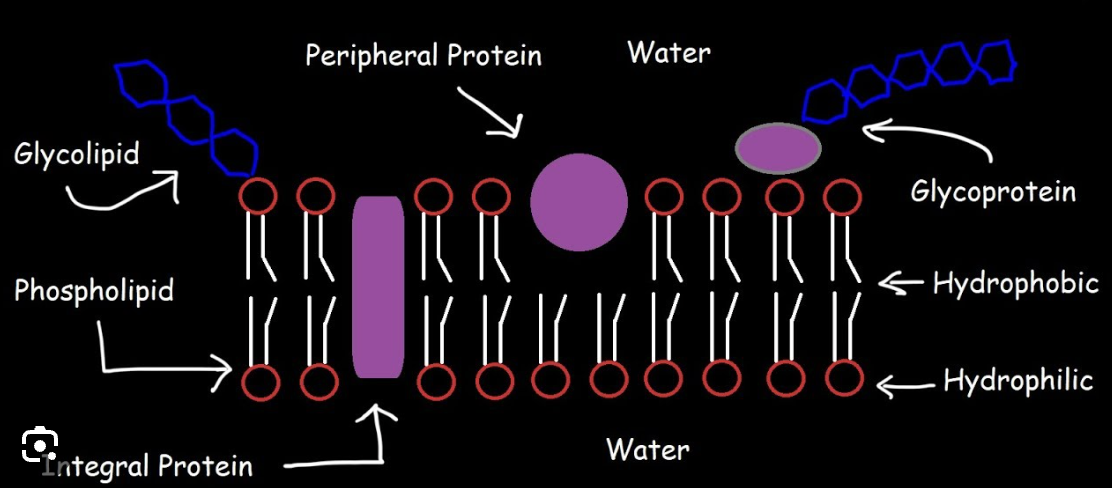
Glycolipid
Lipid with carbohydrate chains used for cell recognition. (ID Tag in the plasma membrane)
Self‑assembly
Molecules spontaneously organize into structures like membranes.
Liposome
Spherical vesicle formed by a phospholipid bilayer.
Tiny phospholipid bilayer bubble with a watery center (often used to deliver drugs)
Amphipathic
Molecule having both hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts.
Triglycerides
Fatty acids attached to glycerol; energy storage.
Glycerol
Backbone of triglycerides to which fatty acids attach.
Fatty acids
Long hydrocarbon chains that attach to glycerol in fats.
Saturated fats
Fats with no double bonds; typically solid at room temperature.
Unsaturated fats
Fats with one or more double bonds; typically liquid at room temperature.
Phospholipids
Similar to triglycerides but with a phosphate head; amphipathic and form membranes.
The Tail is hydrophobic, and Head is hydrophilic
Steroids
Lipids with four fused carbon rings (e.g., cholesterol, hormones).
Waxes
Long‑chain lipids that are waterproof and protective.
Membrane permeability (ion crossing)
Ions have difficulty crossing the hydrophobic core of the bilayer.
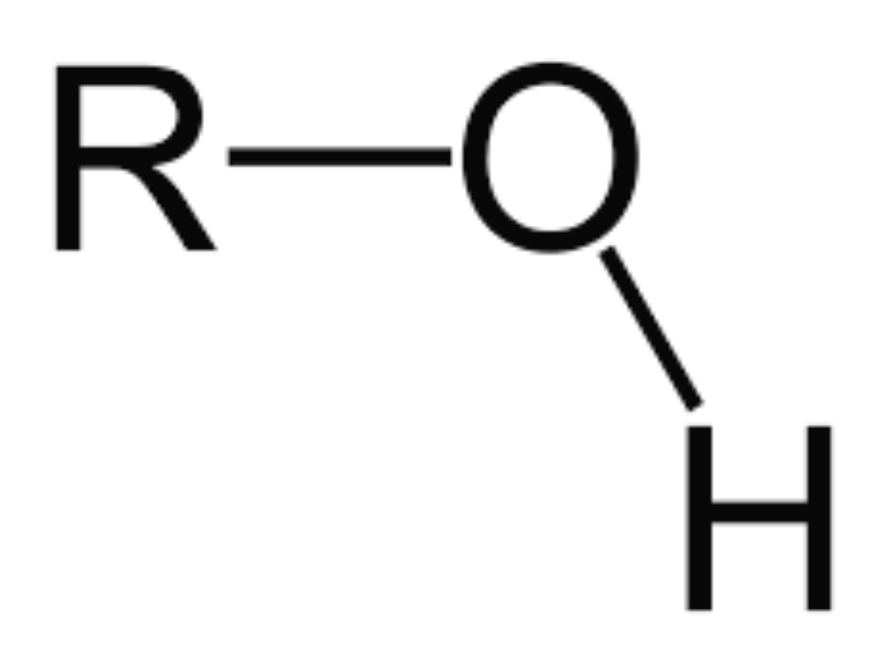
Hydroxyl
Turns Molecule into an alcohol; functional group consists of
‘O-H’
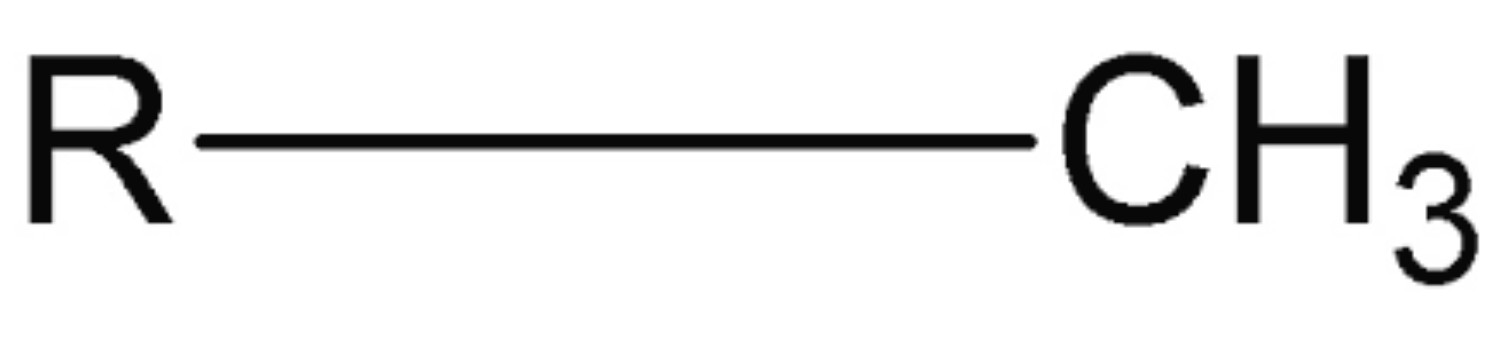
Methyl
Hydrophobic; Functional Group CH3
Nonpolar
Carbonyl
Functional group with a double bond between carbon and oxygen
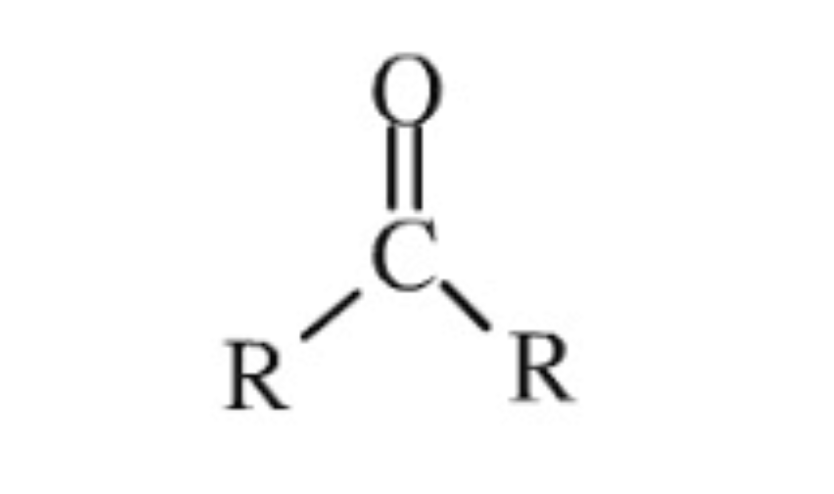
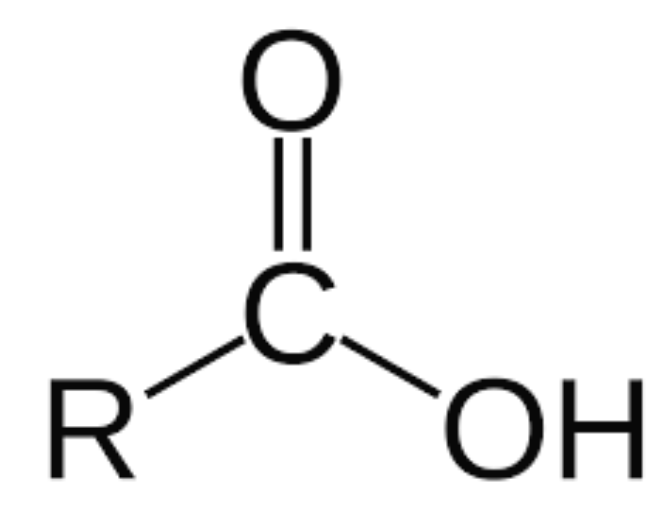
Carboxyl
Functional group with both a carbonyl + hydroxyl group, typically represented as -COOH. Can also be Ionized as COO-. And it’s acidic
Nonpolar molecules are hydrophobic
Are Nonpolar molecules hydrophobic (Don’t like water) or hydrophilic (Like Water)?
Polar molecules are hydrophilic
Are Polar molecules hydrophobic (Don’t like water) or hydrophilic (Like Water)?
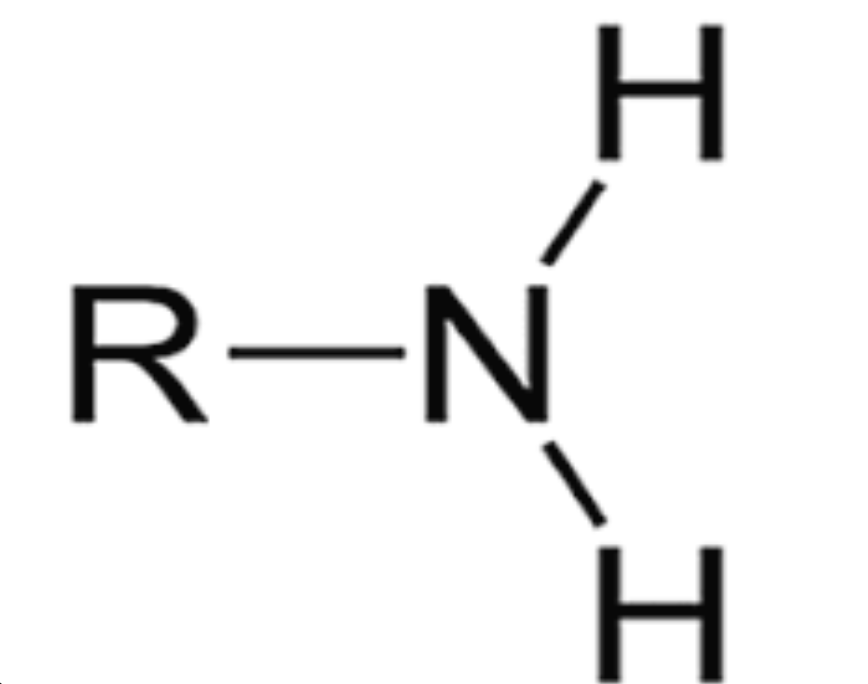
Amino
Acidic functional group that contains NH2. Can be ionized for NH3+
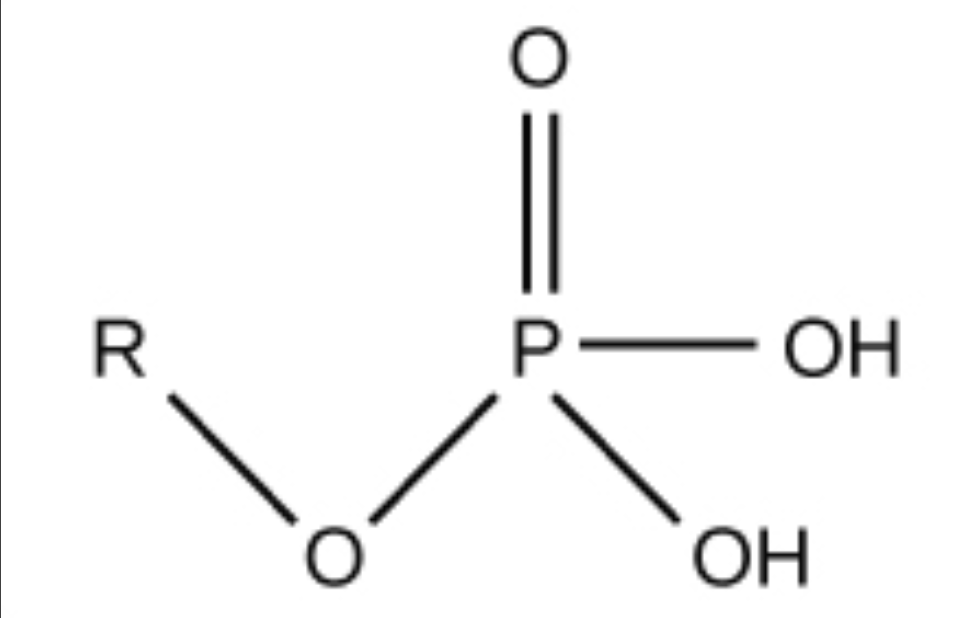
Phosphate
OPO3Hs, acidic, can be ionized as OPO3-
Sulfhydryl
S-H; Sulfar bonded with hydrogen, Polar, Thoil group
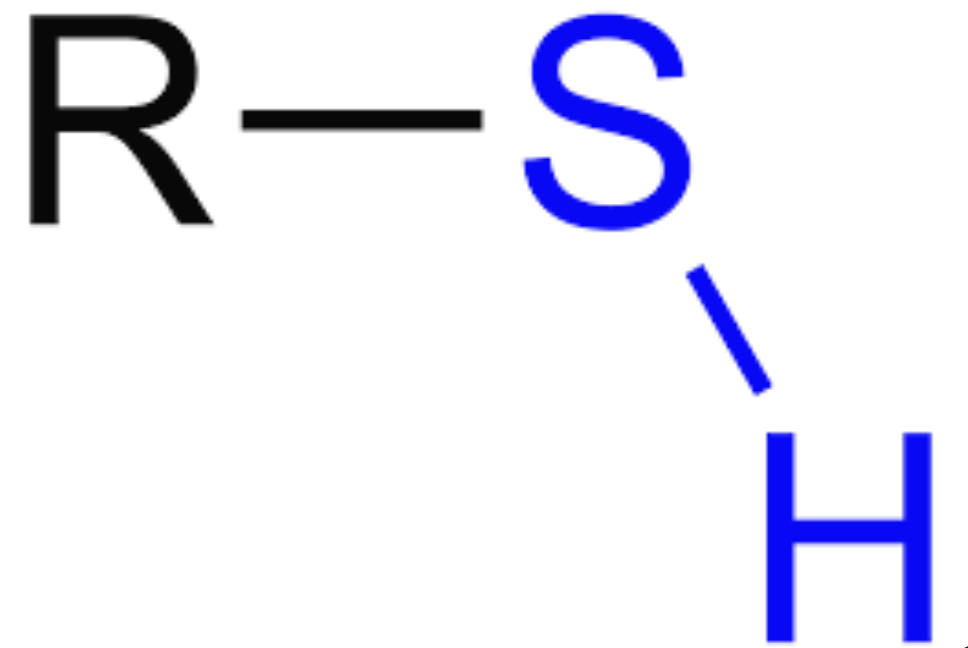
Endosymbiotic Theory
Mitochondria and chloroplasts began as free-living bacteria that a larger cell engulfed; they lived together until they became permanent cell parts.
Movement of Proteins
Nucleus -> RNA moves through pores -> Rough ER -> Golgi Proteins move w/ vesicles -> Plasma membrane
Rough ER (makes + folds proteins) → vesicle (bubble box) → Golgi (sorts + adds address tags) → new vesicle →plasma membrane
Endomembrane System
A team of membranes (nuclear envelope, ER, Golgi, vesicles, lysosomes, plasma membrane) that makes, modifies, and ships proteins and lipids.
Connected membranes (ER → Golgi → vesicles → membrane/lysosome) that make, tag, and ship proteins & lipids.
Intracellular Structures
The cell’s inside parts (nucleus, ER, Golgi, mitochondria, lysosomes, cytoskeleton, etc.) that build, power, clean, and move things.
All inside parts of a cell (the whole factory), including the shipping department and everything else.
Intercellular Structure not bound by a membrane
Cytoskeleton, Cytosol, Ribosomes, Chromosomes
Chromosomes
Intercellular Structure in the Nucleus consisting of DNA
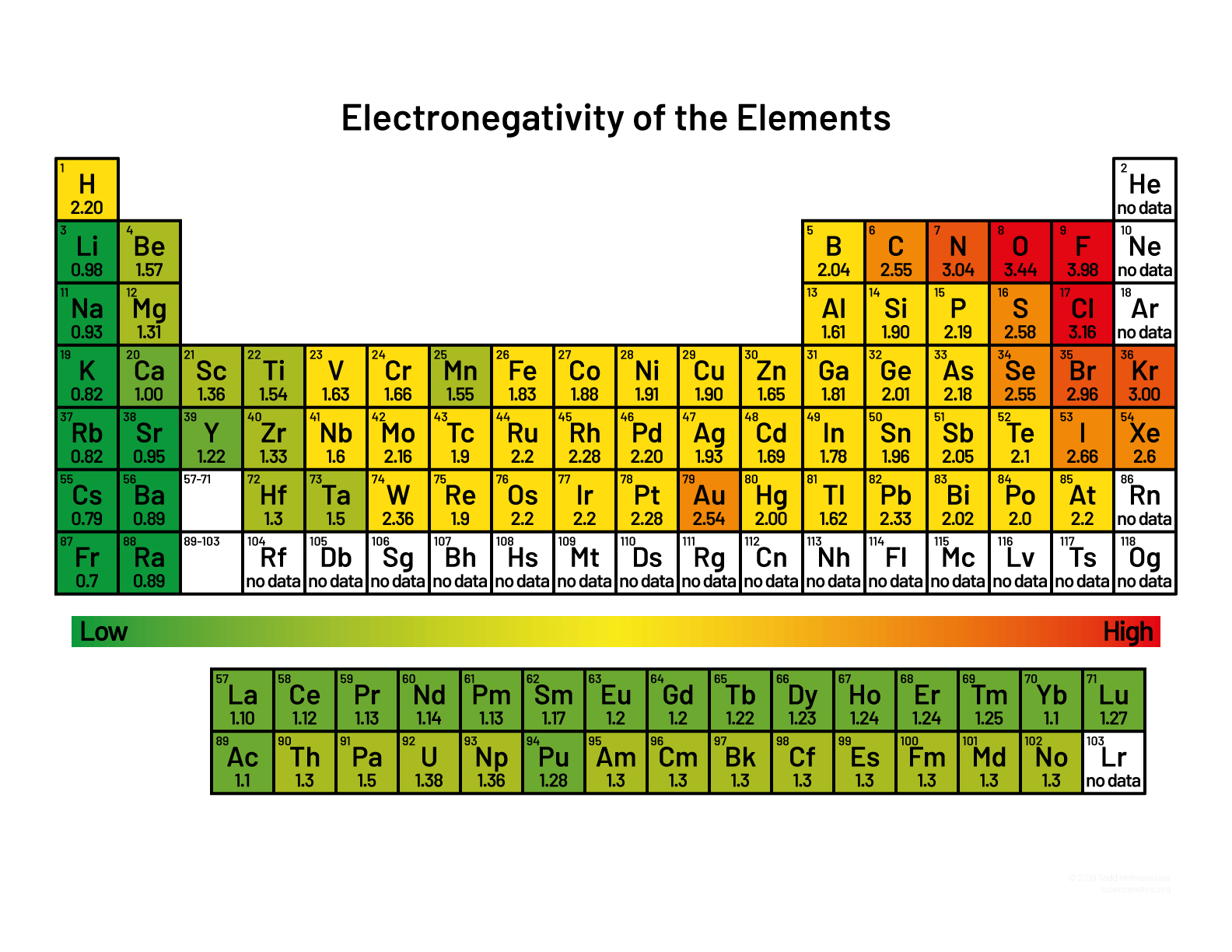
Electronegativity
Energy of an element when bonding.
Increases when going up and right on PT
Polar Covaelmt
Unequal sharing of elections
NOT neutral
Nonpolar Covalent
Equal sharing of election
Neutral
Organic Molecule
Life bonding molecules; contain Hydrogen and Carbon Bonds
Ionic Bond
Transfers Electron
Between Metal and Nonmetal
Covalent Bond
Sharing of electrons between 2 bonds
Inrganic Molecule
chemical compounds that typically lack carbon-hydrogen (C-H) bonds
Ribosome
Tiny rRNA-protein machines (free or on rough ER) that read mRNA (from nuculous) and link amino acids to make proteins.