Chapter 20: The Circulatory System: Blood Vessels and Circulation
1/121
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Merged flashcards from Chapter 20, McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
Blood vessel categories
Arteries
Veins
Capillaries
Arteries
Blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart
Capillaries
Blood vessel that connects small arteries to veins, forming a circuit
Tunics
Vessel wall layers; there are three in total:
Tunica interna
Tunica media
Tunica externa
Tunica interna
The innermost tunic that lines the blood vessel with a selectively permeable barrier and chemical secretions for constriction and dilation
Tunica media
The middle tunic consisting of smooth muscle, collagen, and elastic tissue for strength
Tunica externa
The outermost tunic made of loose connective tissue to connect with other organs as an anchor
Artery classes
Three classes:
Conducting (elastic or large)
Distributing (muscular or medium)
Resistance (small)
Conducting (elastic or large) arteries
The biggest arteries (such as the aorta or common carotid) that expand and recoil with the systole and diastole to regulate pressure
Distributing (muscular or medium) arteries
The arteries that distribute blood to specific organs (such as the brachial, femoral, renal, or spenic)
Resistance (small) arteries
Smaller arteries to smaller areas
Arterioles
The smallest of the resistance arteries with a 200mm diameter
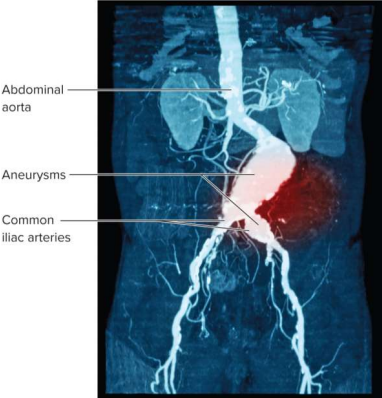
Aneurysm
A weak point in an artery or heart wall that forms a thin-walled, bulging sac that pulses and can rupture or cause pressure
Carotid sinuses
Baroreceptors (blood pressure sensors) in the walls of the internal carotid artery
Carotid bodies
Oval bodies near the branch of common carotids that function as chemoreceptors (chemistry montors) for O2 and CO2 respiration rates
Aortic bodies
The one to three chemoreceptors in the aortic arch
Capillaries
The smaller exchange vessels to allow gasses, nutrients, wastes, and hormones pass between blood and tissue fluid
Capillary types
Three types:
Continuous capillaries
Fenestrated capillaries
Sinusoids
Continuous capillaries
The most common capillaries that allow smaller solutes (like glucose) to pass while blocking large molecules (proteins, blood cells, platelets)
Fenestrated capillaries
Capillaries found in organs needing rapid absorption or filtration (kidneys, small intestine) with filtration pores (fenestrations)
Fenestrations
Filtration pores in fenestrated capillaries that only allow very small molecules to pass
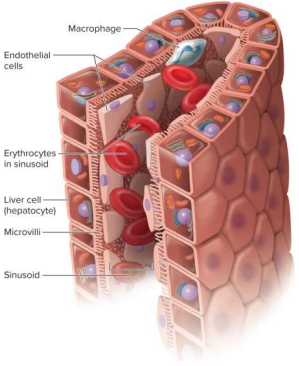
Sinusoids
A type of capillary found in the liver, bone marrow, and spleen for irregularly shaped spaces filled with blood, allowing particles to enter circulation
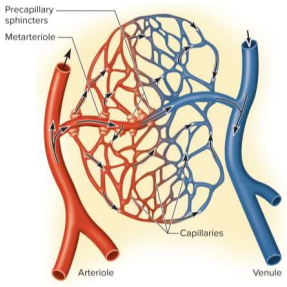
Capilalary beds
Networks of 10 to 100 capillaries - not all are used; 75% of all capillaries are shut down by precapillary sphincters
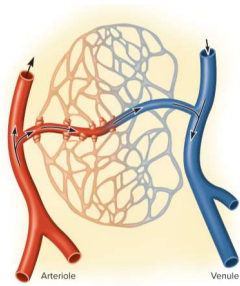
Precapillary sphincters
Controls flow in capillary beds supplied with blood; relaxation allows flow and contraction constricts entry
Veins
The thin-walled, flaccid vessels that collapse when empty and expand easily for steady, low pressure flow back to the heart
Postcapillary venules
The smallest veins with just a tunica interna, some fibroblasts, and pores for fluid exchange
Muscular venules
Veins that recieve blood from the post-capillary venules up to 1mm in diameter with one to 2 layers of smooth muscle
Medium veins
Veins up to 10mm in diameter with thick tunica media, externa, and interna as a result of venous valves while pumped by skeleta muscles
Varicose veins
The failure of venous valves in the merium veins as a result of blood pooling and distended veins; can happen as a result of hereditary weakness, obesity, and pregnancy
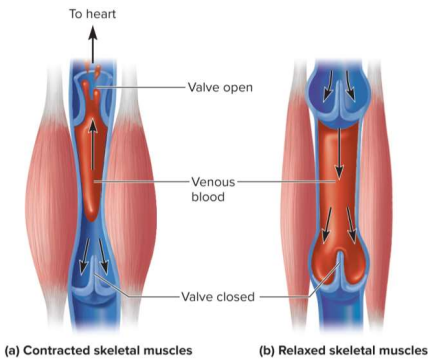
Skeletal muscle pump
Pump that propels venous blood back to the heart using skeletal muscles; found in the gastrocnemius (calves)
Large veins
Veins with a diameter greater than 10 mm with smooth muscle in all three tunics; thick tunica externa - includes the IVC/SVC, pulmonary veins, and internal jugular veins
Hemorrhoids
Varicrose veins of the anal canal
Flow
The amount of blood flowing thorugh an organ, tissue, or blood vessel in a given time (measured in mL/min)
Perfusion
Flow given per volume or mass of tissue in a given time (measured in mL/100g/min)
Hemodynamics
The physical principles of blood flow based on pressure and resistance
Blood pressure (BP)
The force blood exerts against a vessel wall
Sphygmomanometer (blood pressure cuff)
Tool to measure the blood pressure of an indiviudal at the brachial artery, near the left ventricle
Systolic pressure
The peak arterial BP taken during ventricular contraction
Diastolic pressure
Minimum arterial BP taken during ventricular relaxation
Normal blood pressure
120/75 mmHg
Pulse pressure
The difference between the systolic and diastolic pressure to measure force and stress of heart
Blood pressure speed
40 to 120 cm/s
Arteriosclerosis
The stiffening of arteires due to the deterioration of elastic tissues
Artherosclerosis
The build up of liquid deposits that become plaques
Hypertension
A chronic resting blood pressure higher than 130/80 that can weaken arteries, cause aneurysms, and promote artherosclerosis
Hypotension
A chronic low resting blood pressure caused by blood loss, dehydration, and anemia
Blood pressure factors
Three factors:
Cardiac output
Blood volume
Resistance to flow
Peripheral resistance
Opposition to flow in vessels away from the heart
Peripheral resistance factors
Three resistance factors:
Blood viscosity
Vessel length
Vessel radius
Blood viscosity
The ‘stickiness’ of blood, mainly from plasma proteins and RBCs to increase/decrease flow
Vessel length
More of this can cause more cumulative friction, thus decreasing flow
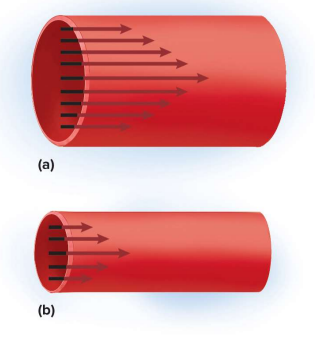
Vessel radius
The radius of a blood vessel; more of this decreases blood-vessel wall contact to speed up flow
Vasomotion
The movement of blood vessel walls, can be controlled:
Locally
Neurally
Hormonally
Local vasomotor control
Done through:
Autoregulation
Vasoactive chemicals
Reactive hyperemia
Angiogenesis
Autoregulation
The ability of tissues to regulate their own blood supply; reacts to wastes with dilation and then reconstricts for homeostasis
Vasoactive chemicals
Substances secreted by platelets, endothelial cells, and perivascular tissues to stimulate vasomotor responses (constriction or dilation)
Reactive hypermia
Reaction to a cut off and restored blood supply with higher flow
Angiogenesis
The growth of new blood vessel; aids hypoxic tissues and can be controlled by growth factors or inhibitors
Neural vasomotor control
Done through:
Baroreflexes
Chemoreflexes
Medullar ischemic reflexes
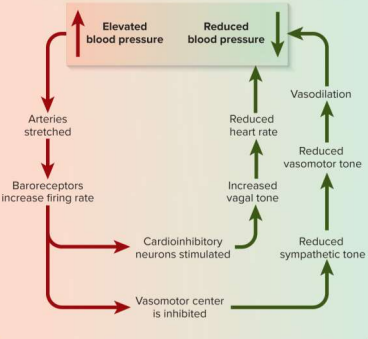
Baroreflex
A neural vasomotor response to changes in blood pressure; aims to stay around set point but cannot correct chronic hypertension due to new set point
Chemoreflex
A neural vasomotor response to changes in blood chemistry, especailly pH and oxygen concentrations, to adjust respiration and vasomotion
Medullary ischemic reflex
Automatic response to a drop in flow to the brain
Ischemia
Insufficient perfusion (flow)
Hormonal vasomotor control
Done through:
Angiotensin II
Aldosterone
Natriuretic peptides
Antidiuretic hormone
Epinephrine and norepinephrine
Angiotensin II
Potent vasoconstictor that raises blood pressure
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Promotes water retention and raises BP; can also act as a vasoconstrictor (hence its alternate name arginine vasopressin)
Vasomotion purposes
Two purposes:
Raising or lowering of BP via centralized control throughout the whole body
Modification of perfusion of an organ for central or local control (exercise or local circulation)
Capillary exchange
The two-way movement of fluid across capillary walls between the blood and tissues; done through either:
diffusion
transcytosis
filtration
reabsorption
Diffusion
The most important form of capillary exchange
Glucose and oxygen diffuse out and carbon dioxide and wastes diffuse in the blood
Capillary diffusion requirements
The membrane must be permeable to the solute or passages must be available to pass through
lipid-soluble substances can diffuse through membranes
water-soluble membranes must go through pores
larger particles are held back
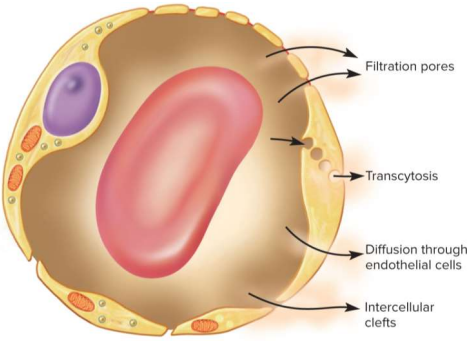
Transcytosis
Vesicle-mediated transport via endo- and exo-cytosis across the capillary wall; very small fraction of solute exchange but crucial for fatty acids, albumin, and hormones like insulin
Filtration and reabsorption
Fluid filters out of arterial end of capillary and osmotically enters venous end in reabsorption, delivering cell materials while removing wastes; can vary like in kidneys (more filtration) vs lungs (more absorption to avoid fluids)
Edema
The accumulation of excess fluid in a tissue; fluid filters in faster than it is reabsorbed and can causae tissue death, suffocation, headaches, or circulatory shock
Venous return
The flow of blood back to the heart, done by:
Pressure gradients
Gravity
Skeletal muscle pumps
Thoracic pumps
Cardiac suction
Pressure gradients
Venous return mechanism where blood pressure draws blood toward the heart
Gravity
Venous return mechanism where blood is drained from the head and neck
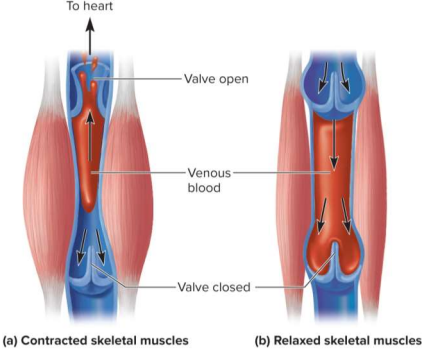
Skeletal muscle pump
Venous return mechanism where limb muscles squeeze blood out of veins
Thoracic pump
Venous return mechanism involving respiration:
Inhalation expands the thoracic cavity
Thoracic pressure on IVC decreases
Abdominal pressure on IVC increases
Blood is forced upward toward heart
Cardiac suction
Venous return mechanism where ventricle contraction pulls valves downwards to expand atrial space, drawing blood in from venae cavae
Venous pooling
The accumulation of blood in the limbs due to inactivity with decreased venous pressure; can be prevented by tensing leg muscles
Circulatory shock
Any state in which cardiac output is insufficient to meet body’s metabolic needs
Septic shock
Type of circulatory shock where bacterial toxins trigger vasodilation and increased capillary permeability
Anaphylactic shock
Type of circulatory shock where a severe immune reaction to a particle increases permeability
Compensated shock
A response to circulatory shock for spontaneous recovery; fainting is an example where blood flow is restored in a horizontal position
Decompensated shock
A response to circulatory shock when compensation fails; life-threatening positive feedback loops can occur and can cause cardiac and brain damage
Brain flow
Done through autoregulation, vasomotion. and spatial allocation at constant 700 mL/min
Brain flow damage
Seconds of deprivation causes unconsciousness, four to five minutes causes irreversible damage
Hypercapnia
The accumulation of CO2 in the brain; triggers vasodilation for more flow due to lowered pH
Hypocapnia
Too low CO2 in the brain; triggers vasoconstriction for less flow due to higher pH
Caused by hyperventilation; can lead to ischemia, dizziness, syncope
Transcient ischemic attack (TIA)
Brief episodes of cerebral ischemia caused by diseased cerebral arterial spasms
Can cause dizziness, vision loss, wekaness, paralysis, headaches, and aphasia
Must be treated as a warning for stroke
Cerebral vascular accident (CVA)
The common name for a stroke, it is the sudden death of brain tissue due to ischemia
Can be caused by artherosclerosis, thrombosis, and ruptured aneurysm
Effects include bindness, loss of sensation, loss of speech, paralaysis, or death
Resting blood flow
Constricted arterioles and less capillary activity at 1 L/min
Working blood flow
Dilated arteries with more muscle metabolistes at 20 L/min; away from digestive and urinary organs
Pulmonary blood pressure
25/10 mmHg; slower for more gas exchange for absorption in capillaries (nearly no filtration)
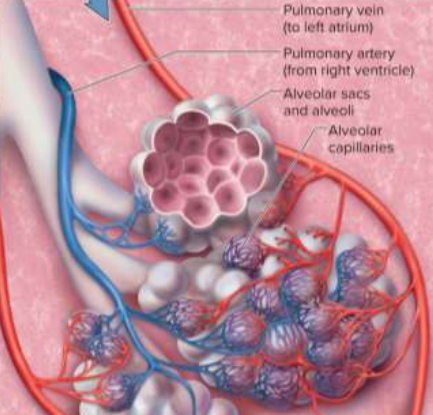
Alveoli
The part of the lung that delivers oxygen to its surrounding capillary beds
Ascending aorta
Where the left and right coronary arteries branch off to supply the heart
Aortic arch arteries
Brachiocephalic trunk (splits into the right common carotid and right subclavian)
Left common carotid
Left subclavian
Right common carotid
Supplies the right side of the head
Right subclavian
Supplies the right shoulder and upper limb
Left common carotid
Supplies the left side of the head