Bone & Joint, Bloodstream & Line
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Bone & Joint infxns comprised of 2 disease processes —>
osteomyelitis
septic arthritis
Osteomyelitis Diagnosis: LABS
+ (3)
Presence of _____ in chronic cases
Cultures → 2
-
+WBC, CRP, ESR
anemia
blood, deep tissue
bone biopsy
Best option to rule in/rule out osteomyelitis?
MRI
Typical pathogen for osteo/periprosthetic joint infxns
staph aureus
Ostoe/Joint DEFINITIVE THERAPY
IV therapy may be converted to PO if there is a clear clinical response after ______
*Patients must have good adherence and outpatient follow-up!!!
7-10 days
OSTEO/JOINT INFXNS definitive therapy
Preferred tx options
MSSA →
MRSA →
Streptococcus →
Enterococcus →
Enterobacteria (GNR) →
Pseudomonas →
Anaerobes →
oxacillin, nafcillin, cefazolin
vanco
PCN or cephalo
pen G, ampicillin
ceftriaxone
ceftazidime, cefepime, zosyn
metronidazole, clindamycin
________ can cause rhabdomyolysis!!!
daptomycin
OSTEOMYELITIS DURATION OF THERAPY
Acute
Chronic
6 weeks
6 weeks IV → 3-12m PO (if indicated)
SEPTIC ARTHRITIS EMPIRIC THERAPY
If culture yields MSSA →
Gram stain negative →
Duration: IV antibiotics _______ follow by PO therapy for a minimum of ______
Longer courses of IV ______ may be needed to treat difficult pathogens such as Pseudomonas
*_______ course recommended for bacteremia and secondary S. aureus arthririts
anti-staph PCN (oxacillin, nafcillin), or 1st gen cephalo (cefazolin)
vanco + GNR agent
2 weeks → +1-2 weeks
3-4 weeks
4 week
PROSTHETIC JOINT INFXN
empiric therapy
If staph is suspected or confirmed …
rifampin
NEVER use ^ as monotherapy
BLOODSTREAM INFECTIONS
Community-acquired → BSI occurring ____ after hosp admission
Hospital-acquired
<48h
>/= 48h
BSI PATHOGENS
Important clinical pathogens → 4
USUAL CONTAMINANT
coag + staph AUREUS, enterobacteria, pseudomonas, candida
coag - staph EPI
BSI Contaminants
When potential contaminant is seen in 1 of 2 blood cultures
We assume it is a pathogen and TREAT it IF:
Same organism in ½ blood cultures and ALSO in _________ (urine, wound, etc)
Presence of organism in ½ blood cultures in the setting of ____________ (infective endocarditis)
Same organism is observed in ________ (2/2)
another culture source
prosthetic heart valves/devices
multiple blood culture
Which is a probable contaminant with 1 of 2 blood cultures being positive?
A. Coagulase positive Staphylococcus
B. Coagulase negative Staphylococcus
C. Candida
D. Pseudomonas
B
Which could be a pathogen and should be treated empirically?
A. 1 of 2 blood cultures AND urine both growing Staphylococcus epidermidis
B. 1 of 2 blood cultures growing coagulase negative Staphylococcus AND PSH includes heart valve replacement
C. 2 of 2 blood cultures growing Streptococcus anginosus
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
D
Management of S. aureus Bacteremia (SAB)
All patients should be treated with ____ antibiotics
Control the ________
Document clearance → __________ after initial + cultures
EMPIRIC coverage → preferred + alt
MSSA (definitive) →
MRSA (definitive) →
IV
source of infxn
repeat blood cultures 48h
vanco AUC/MIC 400-600 → daptomycin
nafcillin, oxacillin → cefazolin (non sev PCN allergy)
same as empiric
DAPTOMYCIN monitoring
CK levels baseline + weekly
SAB SYNERGISTIC Therapy Considerations
currently recommends AGAINST addition of ________
currently recommends AGAINST addition of ________ in the absence of prosthetic devices (can use when present) → NEVER USE AS MONOTHERAPY!
gentamicin
rifampin
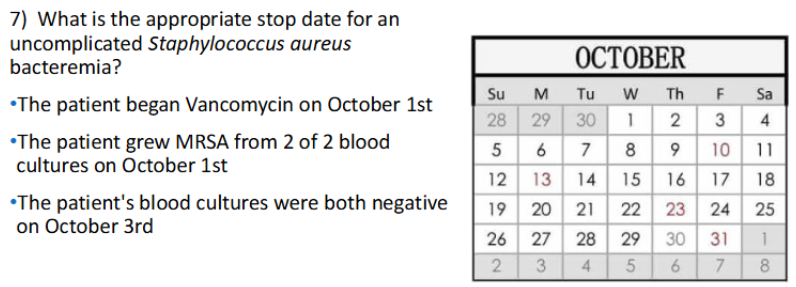
SAB DURATION OF THERAPY uncomplicated
14 days from 1st set of - blood cultures
SAB DURATION OF THERAPY complicated
28-42 days from 1st set of - blood cultures
OTHER GRAM + BSI ANTIMICROBIAL THERAPIES
Enterococcus →
Vancomycin-resistant enterococci VRE →
Streptococcus →
ampicillin, vanco, combo +gentamicin or amp+ceftriaxone
daptomycin
IV PCN or cep
h
Which is the most appropriate therapy for a MSSA BSI?
A. Vancomycin
B. Linezolid
C. Daptomycin
D. Nafcillin
D
Which is most appropriate therapy for a MSSA BSI in a patient with a non-SEVERE PCN allergy?
A. Nafcillin
B. Vancomycin
C. Cefazolin
D. Gentamicin
C
Which is the most appropriate initial therapy for a MRSA BSI?
A. Vancomycin
B. Linezolid
C. Daptomycin
D. Nafcillin
A
Which is the most appropriate therapy for a VRE BSI?
A. Vancomycin
B. Linezolid
C. Daptomycin
D. Nafcillin
C
Which is day #1 of therapy for a Staph aureus BSI?
A. 1st day antibiotic administered
B. 1st day clear blood culture collected
B
Which is TRUE regarding antibiotic monitoring parameters?
A. Daptomycin → platelets
B. Linezolid → creatine kinase
C. Ceftriaxone → serum creatinine
D. Vancomycin → AUC/MIC
D
10/16
gram NEGATIVE BSIs - empiric therapy is based on …
ESBL + BSI tx →
Duration of therapy
source of infxn
carbapenem
7-14d
BSIs: Empiric Pseudomonas coverage is needed WHEN → 4
sepsis w unknown source of infxn
immunocomp
IV abx in prev 90d
hospital-acquired