Lab 12: Williamson Ether
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What is the mechanism of the reaction? What kind of substitution is it?
Two mechanistic step for the Williamson ether synthesis
SN2 Substitution
Summary
base catalyzed formation of the metal alkoxide/phenoxide
Nucleophilic substitution to form the ether
Detailed
Start with 4-bromophenol
Tetrabutylammonium bromide will be the phase transfer catalyst (PTC); this is necessary to allow for the interaction of water soluble phenoxide and water insoluble alkyl halide at the interface of the two phases
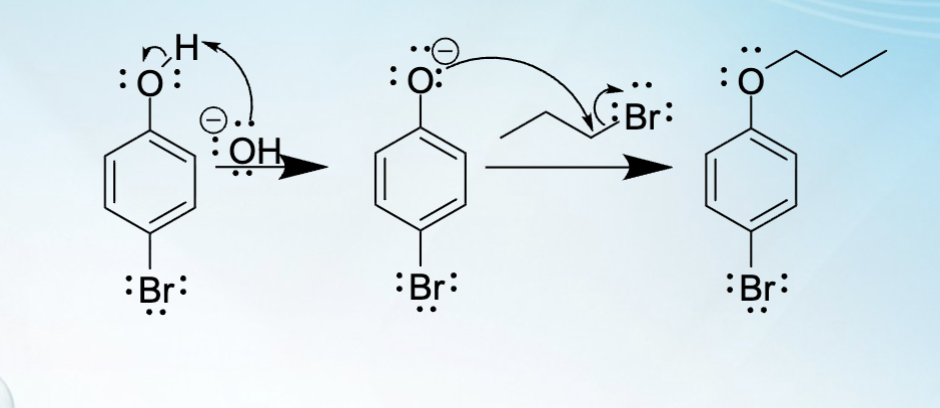
What geometry must the alkoxide and alkyl halides be in for this reaction to occur?
The alkoxides and alkyl halides used for this reaction must
be 1º or 2º
If it is 3º, alkoxides/halides will result in elimination rather than
substitution
What does the microwave do?
allows the reflux period to shorten from 30 mins to 60 mins
What is the difference between extraction and washing?
Extraction: product will dissolve in the newly added solvent while impurities will stay in the original solvent (product into new)
Washing: impurities go in newly added solvent and the product will stay in the original (getting rid of impurities_
What is the protonated product soluble in? What about the deprotonated product?
Protonated
-insoluble in water
soluble in ether
Deprotonated
-soluble in water
-insoluble in ether
What does the column do?
Purify your product (column chromatography)
What is the purpose of this experiment?
We are going to generate a stable, Williamson ether product from a base catalyzed reaction between 4-bromophenol and an unknown alkyl halide
Then, we will use FTIR and HNMR for identification purposes
Balanced equation
See photo

Describe the extraction procedure
Solution from microwave vessel (add 10 mL of DI water and 10 mL of ether)
Separate organic from aqueous
Take aqueous and add ether
Combine the two organic layers
Add KOH to organic layer
Take the organic layer and wash two more times (this is when we will have the product in the original solvent and impurities in new solvent)
General procedure
Microwave
Take TA prepared solution and add to Teflon microwave vessel
Add TBAB and your unknown
Perform microwave procedure for 30 mins
Extraction (this is when our product will be in the new solvent and impurities in the old solvent)
Add mixture to separatory funnel
add DI water and diethyl ether and mix
separate organic and aqueous layer
return aqueous layer to separatory funnel and extract with diethyl ether
combine the organic layers
wash the organic layer three times with KOH (aka you will get aqueous layer out and organic layer will still be left; then add more KOH to that left organic layer)
draw organic (ether) layer with KOH
Column Chromatography
column will be prepared by TA
make sure column in packed (aka add steady amount of methylene chloride) and that methylene chloride is passing through column (we do not want it to become dry=level of the liquid must never be lower than the layer of sand at the top)
add product to column with a pipette
then add more methylene chloride to make sure all product is collected
Solvent Removal and Thin Layer Chromatography
boil off solvent (do not evaporate product)
other partner spot 4-bromophenol dissolved in methylene chloride and your alkyl bromide onto a TLC plate, leaving room for a third spot for your purified product
once solvent has been removed, spot your purified product (helps see if your reaction went to completion because you have your product on one spot and reactant at the other spot)
Experimental techniques used
Thin layer chromatography
Column chromatography
Liquid-liquid extraction
Reflux
IR Spec
NMR Spec
Glassware used
separatory funnel and beaker
Table of reagents
4 bromophenol
potassium hydroxide
1-bromopentane
1-bromo-3-methylbutane
1-bromobutane
Tetrabutylammonium Bromide
diethyl ether
methylene chloride
water
sodium sulfate
Possible unknowns
see photo
