Set 6 - Cultural and Traditional Learning
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
Emperor Penguins
Recognize each other in the dark through sound, and the males hold their babies between their feet until the females return
Seagulls
Recognize their nest on a cliff but not eggs or sedentary chicks
Animals have innate learning biases from
Higher chance of making certain associations based on prior and current knowledge to infer
Memory
Neuronal representation of information
Meadow Voles Males Territory
Includes all of his mates territories
Prairie and Pine Voles Territory
Shared with their mate
Meadow Vole vs Prairie Voles Navigation
Meadow voles consistently make less errors in mazes than both females and prairie
Place Cells
Cells in the hippocampus that through activity creates a map of space
Males have
Large hippocampi from travelling farther, and have bone structure that can handle increased mechanical loads for greater range
Men Psychology Reflect
Fitness benefits of taking risks
Women Psychology Reflect
Fitness costs of harm
In Twe
Increased range size in men, associated with more children
More spatial anxiety in women
Men more likely to travel alone
Higher Testosterone in Utero
Better spatial memory
Taxi Drivers
Have increased hippocampus size after experience
Extensive GPS use
Decreases hippocampus size because decrease learning leads to decreased neuronal tissue devoted to spatial memory
Drivers using GPS
Ignorant to surroundings, failing to notice where they are or that they’ve passed somewhere twice
Alzheimer less common in
People who heavily rely on spatial memory
Associative Learning
New neuronal representation linking stimulus + state, or action + consequence
Non-Associative
Sensitization and habituation
Sensitization
Increase response to something after a prominent stimulus
Habituation
Decrease response to stimulus after repeated stimulus
Test for Associative Learning
CS predicts US
No association at all
CS never predicts US
Each Associative Learning Group must have
Same proportion of CS with US and CS with no US
Same number of dissociated CS and US presentation
Bayes Theorem
Calculates probability that a test is positive, even when they might not actually have it
Uncertainty
Lack of knowledge about future occurrence of something or form
Coping with Uncertainty
Caution, alertness, sharing resources
Coping with Variation
Learning, sampling, accepting
Rescorla Wagner Model
Measures the chance in strength of association betwen CS and US
Rescorla Wagner Equation
Vt = a(x-Vt)
Weakness of Traditional Approaches to Learning
Reflects lab protocols, not nature
Ignores cognition
Anticipatory Learning
Associating cues with even to adjust physiologically
People will unfamiliar drinks
Gets more intoxicated because there are no familiar cues to physiologically counteract effect
Tandem Runs
Ants run in pairs for leader to show new food source, with follower tapping leader’s leg and they learn how to get to food faster
When follower was removed from leader
Leader would wait to keep going, especially if they were further into run
Japanese Monkey Imo
Washed sweet potatoes and wheat in water before eating, which peers learned through (maybe) social learning/imitation
Young Macques
Play with stones after eating, from females macaques who stacked rocks and knocked them down
Juvenile Monkeys Engage in
Short bouts of play involving vigorous action
Adult Monkey Engage in
Fewer, longer bouts of stone play, helping slow down cognitive degradation
Motor Training Hypothesis of Play
Stone play facilitates development of perceptual and cognitive skills
Local Enhancement
Model draws attention to environment by action that happens and observer learn on its own
Social Facilitation
Presence of model, regardless of what they’re doing, facilitates learning for observer (not social learning)
Capuchin Monkeys
More likely to eat novel food if other capuchins eating food too
Blue Tits and Milk Bottles
Watched others to open milk bottles, and preferred bottle caps with the same colour foiled they observed (local enhancement)
What brain areas are active during imitation?
Inferior frontal gyrus, dorsal and ventral premotor cortex
Correspondence Problem
Knowing what to move to imitate model
Perspective Taking
Interpreting what to move based on POV
Male Elephants more likely to raid crops if
Individual is associated with crop raiders, even if its 2nd closest association and older
Copying
Observer repeats what it sees model doing, where copies is rewarded for behaviour, doesn’t have to be new
Females Fish are likely to
Copy mate choice of another female
When Mice observe mice being bitten by mice
They will have a fear response to stable flies on the first encounter by burying themselves
NMDA Receptor
Plays a role in neural plasticity
Blocking NMDA Receptor
Mice observers don’t show any fear response
Tradition
New behaviour emerging becomes common within group from social learning
Meerkat Demonstrator and Landmark
Temporarily preferred the landmark that demonstrator showed, but eventually explored other ones
Great Tits and Puzzle Box
Great tits taught over 400 birds to access food to solve the puzzle box, and they preferred the method that the demonstrator taught
Teacher
Change behaviour in presence of naive student, given a cost but benefits students in that they learn information faster than they otherwise would get it
Mother Cheetahs use Maternal encouragement for hunting by
Knocking prey for kittens to teach
Carrying back live prey
Running slower to allow kittens to reach
Helpers in Meerkat Foraging Groups
Remove danger from food then present it to pups, and gradually wean them off
Proof Helpers Taught Pups
Spent time monitoring pups after giving food
Retrieve prey when pups lost food
Modify scorpion after lost but later retrieved by pups
Nudged pups to eat
Fairy Wren Mother
Emit vocal password to eggs to minimize food to parasitized youngs
Fairy Wren Call Tradeoff
More emittance creates a more accurate call, but increases nest predation
Opportunity Teaching
Teachers actively place students where they can learn new skills
Coaching
Teaching directly alters behaviour of student by praise or punishment
Modes of Cultural Transmission
Vertical: information is transmitted across generation from parents to offspring
Oblique: transfer of information across generation from adults not their parent
Horizontal: transmission between same aged peer
Beaching in Shark Bay
Dolphin comes out of water, onto beach to catch fish and return to water
Beaching in US
1-6 dolphins isolate group of fish and herd them to the shore to catch them
Sponging
Only female bottlenose dolphins use marine sponges to prove the seafloor for fish
Spongers associate with
Other spongers, young females learn from moms
Exposure to Adult Rhesus Monkeys showing fear from snakes
Young monkeys show similar fear response, which lessens if they see an adult showing on fear from snakes
Guppies will
Follow path to food source which they were taught by peers
Medium and Cactus Finches don’t interbreed
From different mating calls that they learn from their father through cultural transmission
Female Finches avoid
Calls similar to their fathers
Guppies will copy mate choice if
Orange colour is less than 40% difference, if higher they prefer the more orange males
Birds with higher brain size to body ratio
More likely to thrive in new environments, and increased rate of innovation
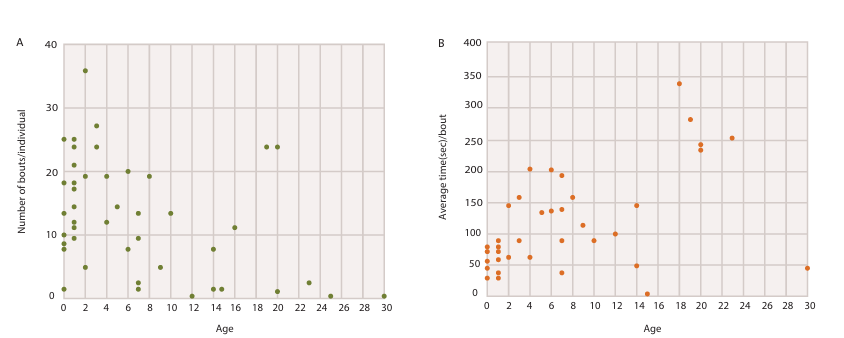
What’s the main message?
Stone play sessions decrease but average time increases with age
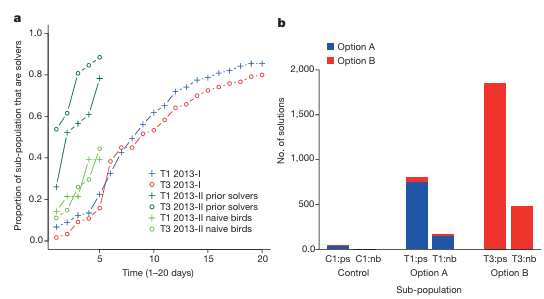
What’s the main message?
Great tits preferred the solution their demonstrator used, and when it came back, birds still employed the same method
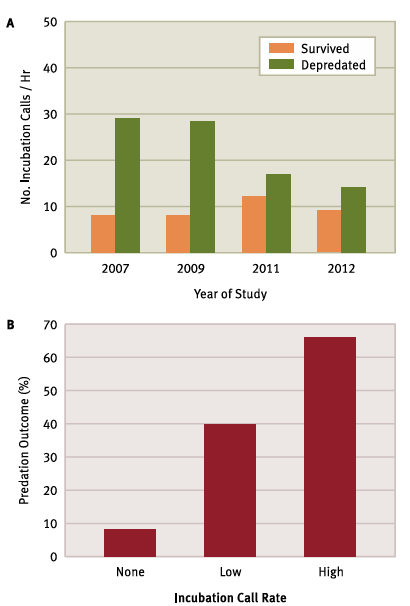
What’s the main message?
High cost for incubation calls
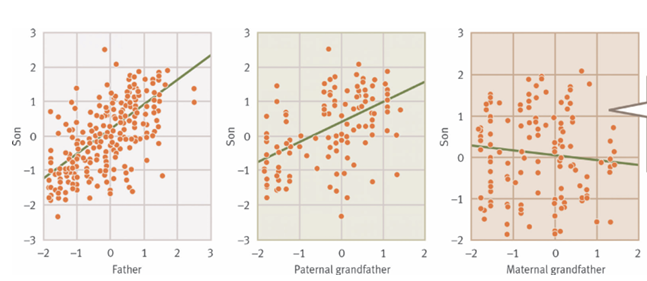
What’s the main message?
Male finch songs are positively correlated with their father and paternal grandfather
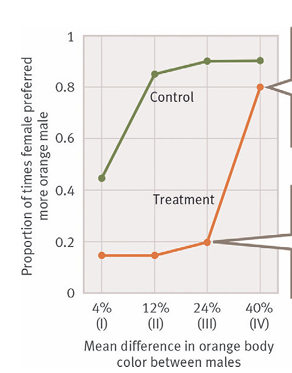
What’s the main message?
When males differed by small amounts of orange, copying other female’s mate choice overrode female’s innate preference for more orange
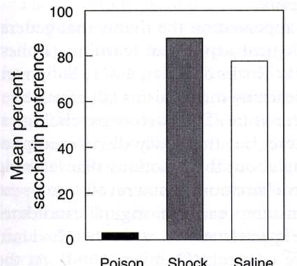
Poisoned rats avoided the tasty water, shock didn’t learn from tasty water
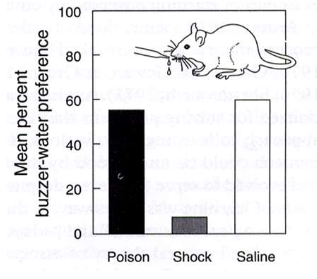
Shock rats avoided noisy water, poison didn’t learn from noisy water
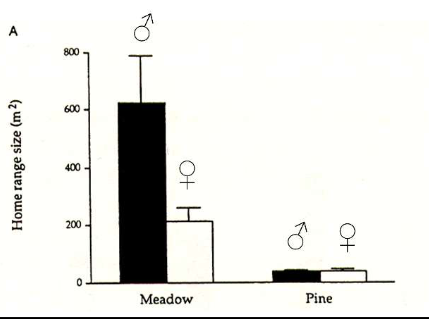
Meadow voles have a much larger home range size than meadow females and pine
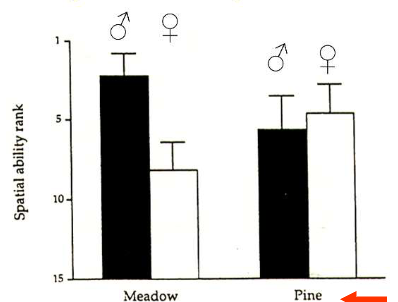
Meadow voles have better spatial abilities than pine voles

Male meadow voles have bigger relative hippocampus size than pine voles
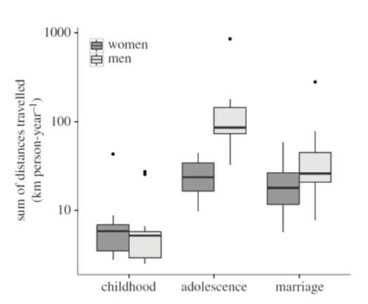
Bolivian males tavel more per year in adolescence and marriage
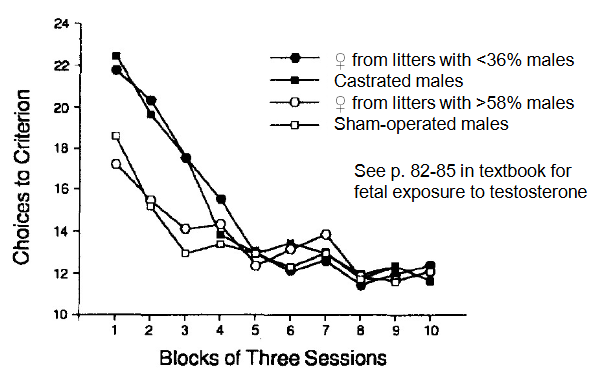
Females with more testosterone on utero were better at maze performance
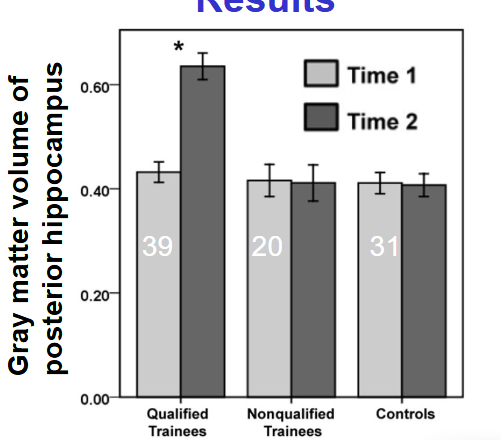
Qualified taxi drivers hippocampus grew after training, but non qualified drivers didn’t
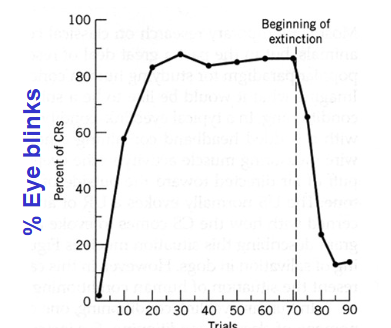
Conditioning a tone with an air puff, causing eye blinks that quickly extincts
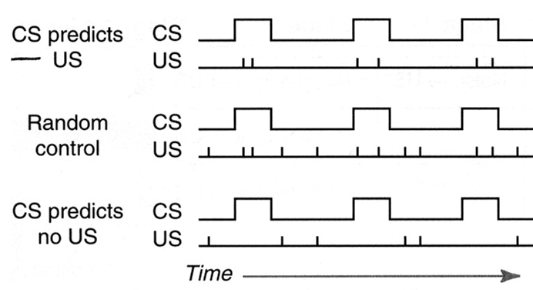
All trials must have the same proportion of US and CS, but the conditional probabilities can vary 50/50 for random, and 100 for CS doesn’t predict US
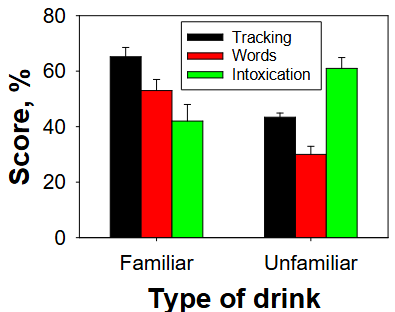
Unfamiliar drinks makes them more drunk, worse at tracking and word search