marketing
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
3C/4P model
The 3Cs (Company, Customer, Competitor) , situational analysis that works to understand the market, used to derive strategy. The 4Ps (Product, Price, Place, Promotion), the Marketing Mix that helps us design and execute strategy created from 3P's.
SBU
Strategic Business Unit - a semi-autonomous unit within a larger organization responsible for particular range of products.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
All strategies for managing interactions to develop, acquire, and retain customers.
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
The predicted net profit attributed to the entire future relationship with a customer.
ADAMS
Accessible: Affordable, Reachable to target. Differentiable: internally homogenous, externally heterogenous among segments. Actionable: Practical. Measurable: Quantifiable outcomes. Substantial.
Customer equity
The total combined customer lifetime values of all the company's customers.
S.M.A.R.T. objectives
Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, Time-bound objectives used for goal setting.
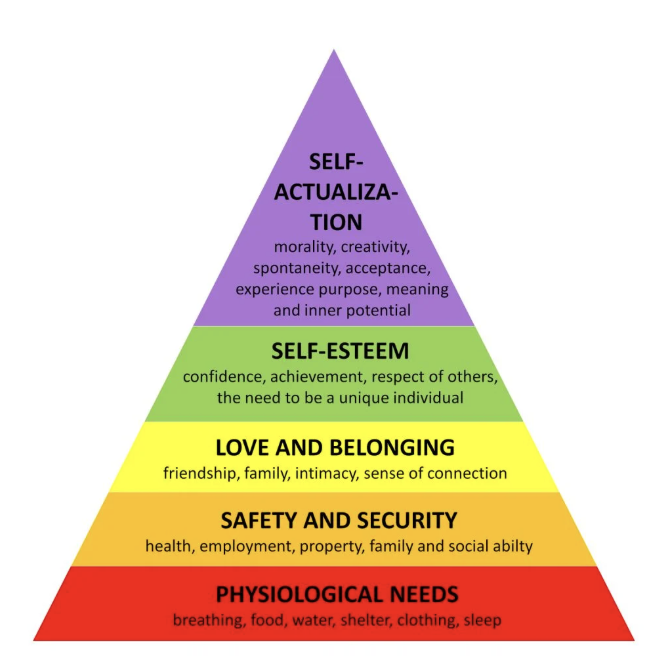
Maslow's hierarchy
A theory of human motivation that arranges needs into a hierarchy, with basic physiological needs at the bottom and self-actualization at the top.
STP (Segmentation, Targeting, Positioning)
Organization model to segment market, select target market, and position its products/services accordingly.
Value proposition
The unique combination of benefits that a company offers to customers. Promise of value.
Portfolio analysis
The process of evaluating the products or services offered by a company and allocating resources accordingly.
Perception process
The process by which individuals interpret and make sense of sensory information.
Exposure → Cognitive Organization (attention)→ Interpretation.
Positioning
The act of designing a company’s offering and image to occupy a clear, distinctive, and desirable place in the minds of the target market.
Marketing mix / 4 Ps
The combination of Product, Price, Place, and Promotion that a company uses to satisfy customer needs.
Key Performance Indicators (KPI)
Quantifiable measures used to evaluate the success of an organization or individual.
Atmospherics
The physical elements of a retail environment that influence the customer's perception and experience.
Perceptual map
A visual representation of how consumers perceive different brands or products in relation to each other.
Marketing myopia
A narrow focus on a specific product or service rather than the broader needs and wants of the target market.
Revenue vs Profit
Revenue is the total amount of money generated from sales, while profit is the amount left after subtracting expenses.
B2C
Business-to-Consumer - transactions between a company and individual consumers.
B2B
Business-to-Business - transactions between two or more companies.
SWOT
Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats - a framework for analyzing a company’s internal and external factors.
PESTEL
An acronym for Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal - macro factors that impact a business environment.
Gross margin
The difference between revenue and the cost of goods sold, expressed as a percentage.
Geodemographics
The study of the demographic characteristics of geographic areas.
Dashboard
A visual representation of key performance indicators and other important data.
5 management orientations
Production, Product, Selling, Marketing, Societal.
Production orientation
(Inside-out) Focus on efficient mass production, economy of scale.
Product orientation
(Inside-out) Innovation focus — “great products sell themselves.” Can lead to marketing myopia.
Selling orientation
(Inside-out) Customers will buy whatever we convince them to buy.
Marketing orientation
(Outside-in) Focus on identifying and satisfying customer needs.
Societal orientation
(Outside-in) Enhances both customer and societal well-being (e.g. sustainability).
4 step marketing process
- Analyze environment 2. Devise strategy 3. Execute via 4Ps 4. Evaluate/Maintain (CRM).
Core components of marketing
Identify Customer Needs, Anticipating Customer Needs, Satisfying Customer Needs, Profitability by adding value
Direct vs indirect competitors
Direct: same products & segment.
Indirect: substitute solutions in different industries. (market or resource similarity)
5 steps of strategic planning
Vision → Mission → Gap analysis → SMART goals → Monitor with KPIs.
Levels of strategic planning
Corporate strategy → Business strategy → Functional strategy.
Mission vs vision
Mission: purpose and priorities. Vision: aspirational, long-term goal.
BCG Matrix
Evaluates business units by market growth rate and market share.

GE Matrix
Evaluates product lines using business strength and market attractiveness.
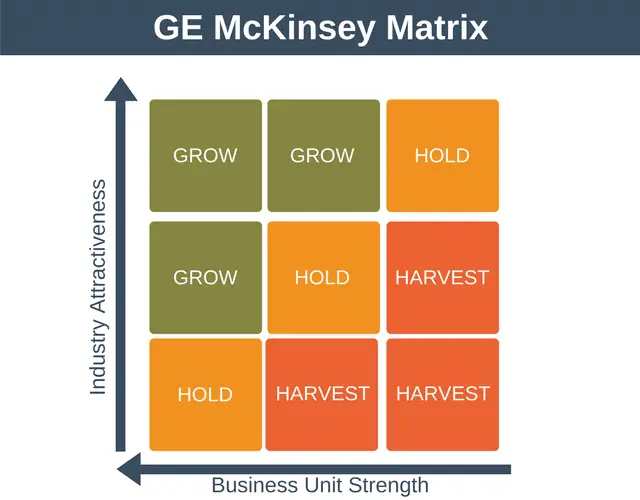
Harvest vs Divest
Harvest: maximize remaining profits with no more investment. Divest: sell or close the unit.
Ansoff Matrix growth strategies
Market penetration, Market development, Product development, Diversification.
Gross profit vs operating profit
Gross: Revenue - COGS. Operating: Revenue - COGS - Operating expenses.
Gross margin
Gross profit / Sales.
4 types of buying behavior
Complex, Variety-seeking, Dissonance-reducing, Habitual.
Maslow’s Hierarchy
Physiological → Safety → Love → Esteem → Self-actualization.
Ernest Dichter
Father of focus groups; used psychoanalysis in marketing.
Fear tactics in advertising
Use with caution, small steps are better than extreme messaging.
Subliminal Advertising
Weak effect, primes only basic concepts, not strong behaviors.
Associative network model
Memories/brands connected like a web, enabling priming and associations.
5 Steps to Complex Decision Making
Need → Info search → Alternatives → Purchase → Post-purchase.
B2B vs B2C Marketing
B2B involves organizations and longer sales cycles, B2C is consumer-focused.
Types of B2B buyers
Producers, Resellers, Governments, Institutions.
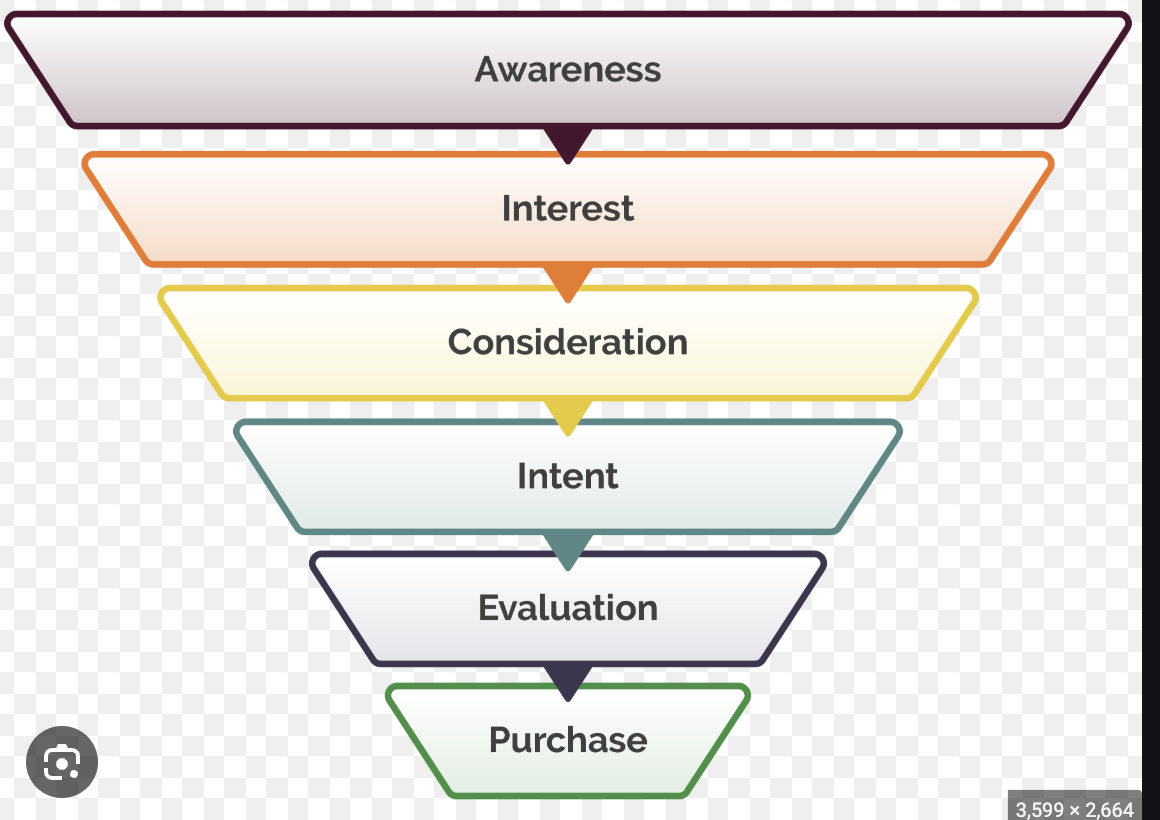
Funnel marketing
Top: Awareness. Bottom: Purchase.
4 segmentation types
Geographic, Demographic, Psychographic, Behavioral.
Behavioral vs Psychographic
Behavioral: usage, loyalty. Psychographic: attitudes, lifestyle.
Differentiated marketing
Different marketing mixes for different segments.
Concentrated marketing
Focus on one target market with a single strategy.
Positioning statement template
For [segment], we are the only [frame] that [value prop] because [support].

Strong brand associations
Color, Price, Endorser, Product meaning.
ABC’s of target selection
Attractiveness, Brand Fit, Competitive Advantage.
Distinctiveness
Economic, Experiential, Functional, or Social differences.
Consumer vs customer
Consumer = uses; Customer = buys.
Marketing intermediaries
Brokers, Wholesalers, Retailers.
Benchmarking
Compare companies based on features, price, etc.
End state metric
Revenue, growth, % from new customers.
Incremental metric
Ad-driven conversions that wouldn’t happen otherwise.
Cognitive dissonance
Discomfort after purchase due to conflicting thoughts.
Reference groups
Groups that influence consumer attitudes/behavior.
Life cycle stage
Stage in life impacts buying behavior (e.g. young adult vs retiree).
Heuristics
Mental shortcuts used to make decisions (e.g., price = quality).
Supraliminal vs Subliminal
Supraliminal is visible with effort; Subliminal is not consciously seen.
Undifferentiated marketing
Single message for the entire market.
VALS
A psychographic model segmenting by values, attitudes, and lifestyle.
Attribute rating method
Consumers rate brands on defined attributes → stats used to map them.
Overall similarity method
Consumers compare brand pairs for similarity → map created using distances.
4Ps decisions
Product: features. Price: min/max. Place: delivery channel. Promotion: where/whom to market.
Porter’s 5 Forces
New entrants, Supplier power, Buyer power, Substitutes, Rivalry.
Subliminal marketing scare
Vickery’s false experiment scared people but had no strong results.
Behavioral segmentation uses
Benefit, usage, occasion.
Concentrated/niche marketing
Useful for low-budget firms targeting a specific group with unique needs.
3 components of Attitudes
Beliefs, Affect (Feelings), Behavioral Intentions
Walter Dill Scott
an early pioneer in advertising psychology, known for applying psychology to marketing and influencing consumer behavior. Pushed the advertising industry to appeal to consumers’ emotions, motives, concerns with social status, not just their “rational brain”
Benefit Segmentation
is a marketing strategy that divides consumers based on the specific benefits they seek from a product or service, focusing on their needs and desired outcomes.
Examples: (different levels of macs, different gym memberships, different types of mattresses)
Levels of Planning