Parasitology Exam 1 (Ch. 3-4)
1/331
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
332 Terms
T or F: Nematodes are multicellular organisms unlike protozoans
True
What are some morphological features of nematodes?
They are unsegmented and elongated
Round on both ends
Bilaterally symmetrical
The largest nematode known to parasitize domesticated aminals in the ____ the “giant kidney worm” of dogs
Dioctophyma renale
Nematodes are covered by a thin ____. This covers the exterior body service and extends into all its body openings.
cuticle
In nematodes, the ____ is right beneath the cuticle and it is what produces the cuticle
hypodermis
In nematodes the ____ is beneath the hypodermis and it is what allows the nematode to move
somatic muscular layer
What are the most important organ systems for the nematodes?
digestive and reproductive
T or F: Female nematodes have a rectum and males have a cloaca
True
Nematodes are ____, meaning that the species produces both female and male individuals
dioecious
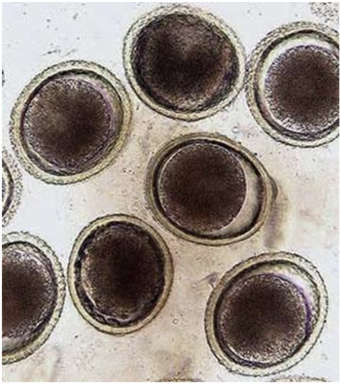
Ascarid/roundworm type (Toxocara canis)
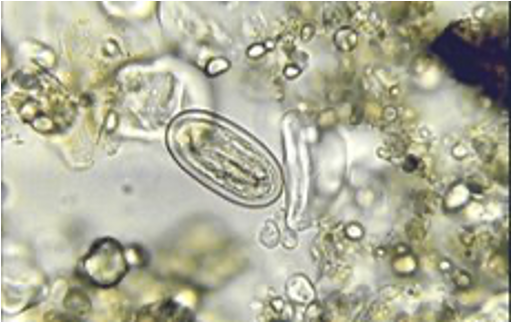
Spirurid type (Physaloptera spp.)
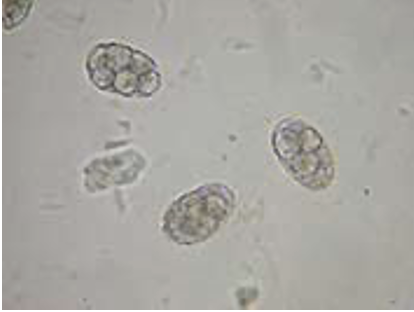
Trichostrongyle/hookworm type (Ancylostoma caninum)
____ - the pre larval stage
Microfilarae
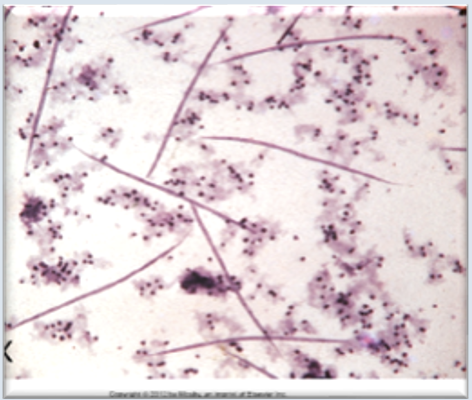
Dirofilaria immitis larvae
____ - have a kinked tail larvae
lungworm larvae
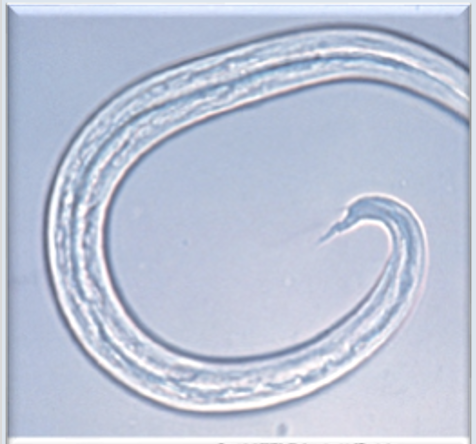
Aelurostrongylus abstrusus larvae
____ - have a long-tailed larvae
Dracunculoid larvae
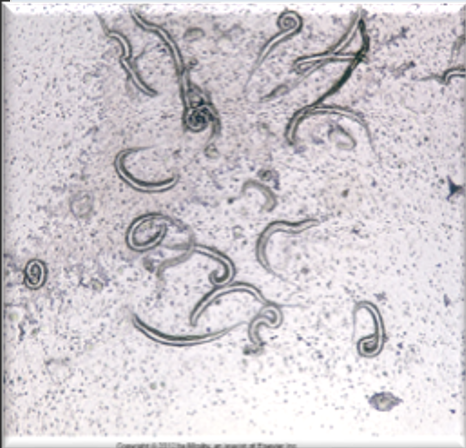
Dracunculus insignis larvae
____ - the eggs produced by these nematodes contain a single-cell stage or a morula stage within the eggshell
Oviparous
____ - the eggs produced by the female nematodes contain a first-stage larva within the eggshell
Ovoviviparous
____ - female nematodes retain their eggs within the uterus and incubate them, then give birth to live larvae
Larviparous
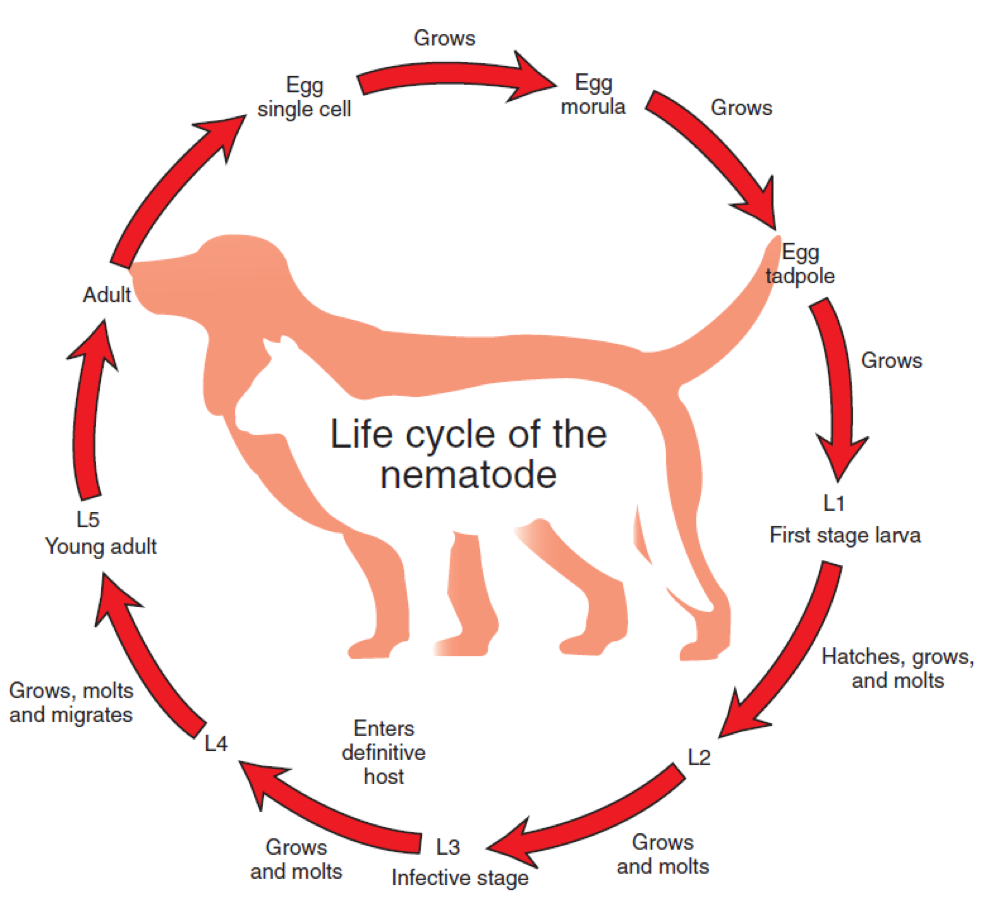
Life Cycle of Nematode
The third stage larva is known as the ____ because it is infective for the definitive host.
infective third-stage larva
Once the infective third-stage larva has been reached, it must return to the definitive host to survive by one of 2 ways:
Direct penetration
Intervention of the intermediate host
____ - this is where there is no intermediate host in the life cycle
direct life cycle
What is an example of the direct life cycle?
Canine hookworms develop to the infective 3rd stage in the external environment. They penetrate dog’s skin and migrate to the small intestines
____ - this is where there is an intermediate host in the life cycle
indirect life cycle
What is an example of the indirect life cycle?
A female mosquito ingests the microfilariae along with her blood meal from the infected animal. The microfilariae develop into the infective 3rd stage larva within the mouthparts of the mosquitoes. When the mosquito feeds again, the infective 3rd stage migrates into the uninfected animal.
What are the hosts for the Physaloptera species?
canines and felines
Where is the Physaloptera species located in adult animals?
the lumen of the stomach or the small intestine
What is the transmission route for Physaloptera species?
ingestion of eggs
What is the common name for the Physaloptera species?
Stomach worm
What does the Physaloptera species feed on?
blood
What are the clinical signs of an animal infected with Physaloptera?
vomiting
anorexia
dark tarry stools
How do you diagnose Physaloptera?
fecal flotation and vomitus
Who is the host of Toxocara canis?
canines
Who is the host of Toxocara cati?
felines
Who is the host for Toxascaris leonina?
canines and felines
What is the route of transmission for Toxocara canis/cati and Toxascaris leonina?
Ingestion of egg with infective larva
What is the common name for Toxocara canis and Toxocara cati?
Canine and Feline Roundworms
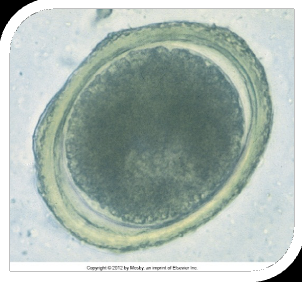
Toxocara canis
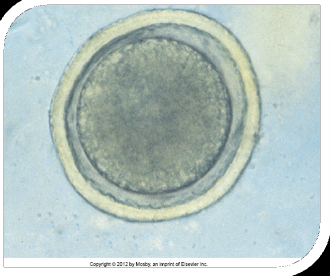
Toxocara cati
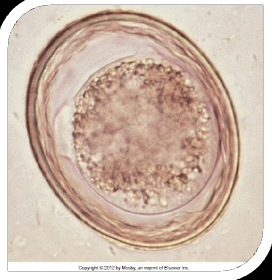
Toxascaris leonina
When Toxocara canis/cati are passed through the feces, the adult worms usually appear ___
tightly coiled
What are the clinical signs of Toxocara canis/cati?
vomiting
diarrhea
constipation
pot-bellied appearance
How do we diagnose Toxocara canis/cati?
fecal flotation
What is the treatment for Toxocara canis/cati?
Vermifuge (Piperazine or Pyrantel)
Vermicide (Thiabendazole or Mebendazole)
How does vermifuge work?
It paralyzes the parasites
How does vermicide work?
It kills the parasites
T or F: Toxocara canis larvae can cross the placental barrier and infect the host’s offspring but Toxocara cati can not
True
Toxocara spp. can also infect humans and it can cause what?
visceral larval migrans
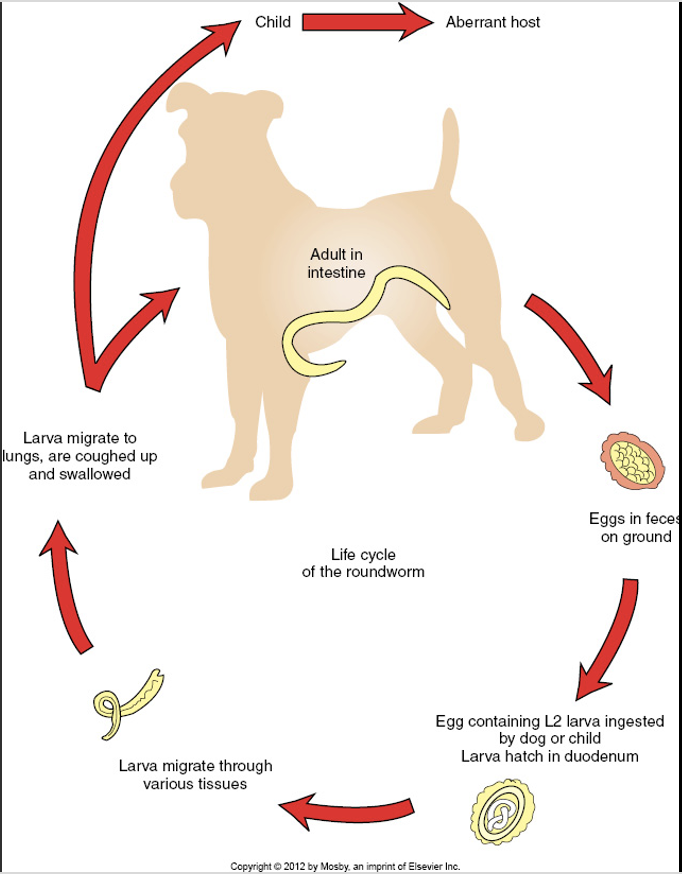
Life Cycle of the Roundworm
Who is the main host for Baylisascaris procyonis?
Raccoon
What is the location of Baylisascaris procyonis within an animal?
small intestines
What is the route of transmission for Baylisascaris procyonis?
Ingestion of eggs
What is the common name for Baylisascaris procyonis?
Raccoon roundworm
How is Baylisascaris procyonis diagnosed?
fecal flotation
T or F: Baylisascaris procyonis is not a zoonotic disease?
False
Baylisascaris procyonis larvae migrate to the central nervous system and they produce a condition known as ____
Neurological larval migrans
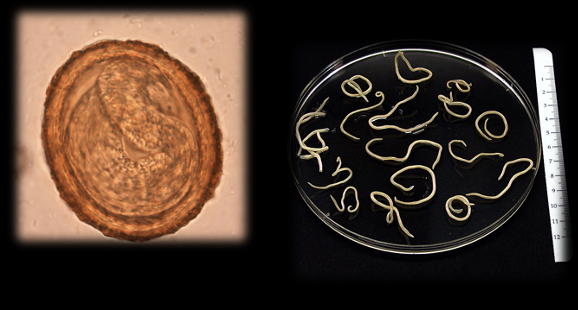
Baylisascaris procyonis
Who is the host for Ancylostoma caninum?
Canine
Who is the host for Ancylostoma tubaeforme?
Feline
Who is the host for Ancylostoma braziliense?
canine and feline
Who is the host for Uncinaria stenocephala?
canine
What is the location for Ancylostoma caninum in adult animals?
the small intestine
What is the route of transmission for Ancylostoma caninum?
ingestion of eggs
through the skin
across the placenta
through the mammary milk
What is the common name for Ancylostoma caninum?
Hookworm
What is the scientific name for Hookworm?
Ancylostoma caninum
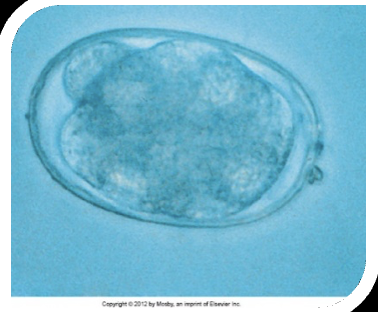
Ancylostoma caninum (Hookworms)
What does the hookworm feed on?
blood
____ feed on blood and secrete an anticoagulant from its mouth. Because of this feeding activity and secondary hemorrhage, they can cause significant anemia
hookworms
What are the clinical signs of Ancylostoma caninum?
black tarry stool
severe anemia in young puppies and kittens
How is Ancylostoma caninum diagnosed?
fecal float
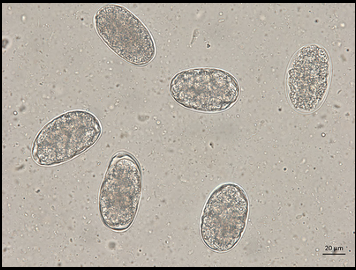
Ancylostoma caninum (Hookworms)
What are the two treatments for Ancylostoma caninum?
Vermicide: this is used when parasite eggs are found on fecal flotation of by other techniques
Prevention: this is accomplished by using once-a-month heartworm preventatives
What are some examples of vermicides used to treat Ancylostoma caninum?
Mebendazole
Fenbendazole
Pyrantel pamoate
What are some examples of prevention used for Ancylostoma caninum?
Heartgard Plus
Ivermectin
Pyrantel
Is Ancylostoma caninum a zooinotic disease?
yes
Ancylostoma caninum can enter the skin of humans, this is known as _____
cutanious larva migrans
What are the two types of Strongyloides species in cats and dogs?
stercoralis
tumiefaciens
Who is the host for Strongyloides spp?
dogs
cats
humans
What is the route of transmission for Strongyloides spp?
Through the skin and through the milk
What is the common name for Strongyloides spp?
Intestinal threadworm
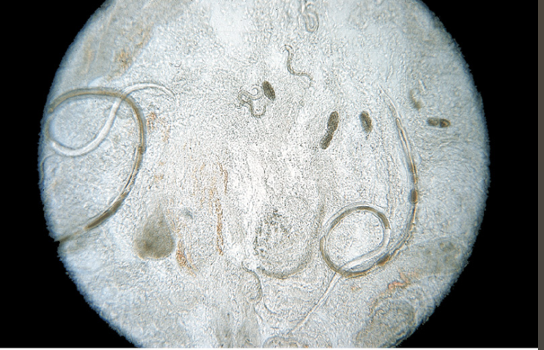
Strongyloides species
T or F: With the Strongyloides species, parasitic males do not exist, the females are capable of producing viable ova without fertilization from a male worm.
True
When a female is capable of producing viable ova without fertilization from a male worm, this is known as what?
parthenogenesis
In the Strongyloides species, in fresh feces, you may see ____ stage larvae
1st
In the Strongyloides species, the larvae go through a free-living stage in the environment before they become the ____ and can penetrate the skin of their host
infective L3
What are the clinical signs of Strongyloides species?
moderate to severe diarrhea in young puppies
Is the Strongyloides species a zooinotic disease?
yes
When humans are infected with the Strongyloides parasite, it is called ____
strongyloidiasis
Who is the host of Trichuris vulpis?
canines
Who is the host for Trichuris campanula?
Felines
Who is the host for Trichuris serrata?
Felines
What is the location of Trichuris vulpis in adult animals?
cecum and colon
What is the route of transmission for Trichuris vulpis?
ingestion of eggs
What is the common name for Trichuris vulpis?
Whipworm
What is the scientific name for whipworm?
Trichuris vulpis
T or F: Trichuris vulpis is a common parasite of cats, but canine whipworms are rare in North America
False, it is a common parasite of dogs, but feline whipworms are rare in North America
The whipworm eggs are passed out in the feces of the host every ___ day.
3rd