Biological Molecules
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Nutrients
Chemical substances in food that provide energy and materials needed by the body
Condensation Reaction
Condensation is a chemical reaction whereby 2 or more simple molecules are joined together to form a larger biological molecule with the removal of water
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis is the splitting up of a complex biological molecule into its component units with the addition of water molecules
Carbohydrates
Made up of the elements carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
General formula Cm(H2O)n
Hydrogen and oxygen atoms are present in the ratio 2:1
Monosaccharides
Glucose, fructose, galactose
sweet tasting
soluble in water
able to lower water potential of solutions
Disaccharides
maltose, lactose, sucrose
Maltose | Glucose + Glucose |
Lactose | Glucose + Galactose |
Sucrose | Glucose + Fructose |
Glycosidic bond
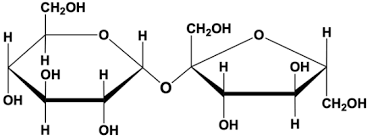
Polysaccharides
Storage polysaccharides:
Starch (plants)
Formed from the condensation reaction of large number of glucose molecules
Can be in long straight chains or branched chains
Glycogen (animals)
Formed from the condensation reaction of large number of glucose molecules
glucose molecules joined up in highly branched chains
Structural Polysaccharides:
Cellulose
Formed from the condensation reaction of large number of glucose molecules
glucose molecules that forms cellulose are bonded differently as compared to starch, hence giving cellulose a different property
Insoluble in water
Starch and glycogen are suitable storage materials because:
insoluble in water so they do not affect water potential in cells
too large to diffuse through the cell membranes, so they stay in the cells
compact shapes which occupy lesser space than all the individual glucose molecules that make up a glycogen or starch molecule
can be easily hydrolysed to glucose when needed
Function of cellulose cell wall
provide mechanical support for plant cell and to the plant, especially for herbaceous (soft stem) plants
resist expansion when water enters by osmosis, ensuring integrity of plant cell and to provide turgidity
General functions of carbohydrates
Glucose- as a substrate for respiration to release energy for all cellular activity
Deoxyribose sugars- Used for the formation of nucleic acids
Forms lubricants
Forms nectar in some flowers
Cellulose- To form supporting structure
Lipids
contains carbon, hydrogen and oxygen with much lesser oxygen as compared to carbon and hydrogen
insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvent
Triglyceride
consists of 3 molecules of fatty acids and one molecule of glycerol
Fatty acid
is a long hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl function group
hydrocarbon chain can be unsaturated (contains carbon carbon double bond) or saturated (no carbon carbon double bond)
hydrophobic
Ester bond
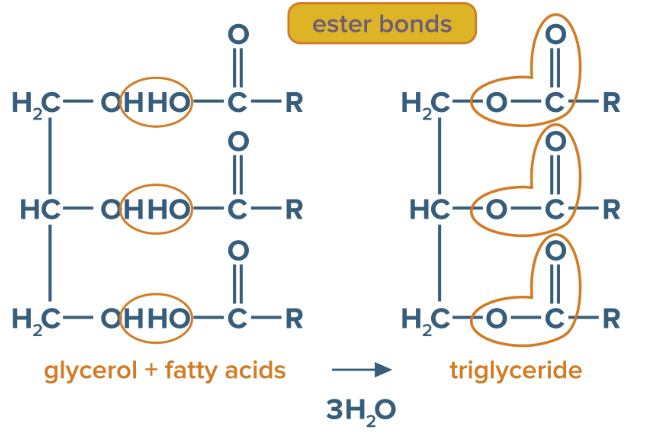
Properties of triglycerides
Oil
at least one carbon-carbon double bond
lower melting point and molecular weight
Fats
absence of carbon-carbon double bond
higher melting point and molecular weight
Insoluble in water
Stored as droplets inside of specialised fat cells, known as adipose cells, because they are insoluble and do not affect water potential in cells
Functions of triglycerides
Energy storage
one gram of triglyceride yields about twice as much energy than one gram of carbohydrates
Heat insulator
Buoyancy in animals
Less dense than water
Protective layer
Ability to absorb shock
Important component of the myelin sheath
Acts as electrical insulator
Provides metabolic water
Oxidation of triglycerides produce metabolic water
Triglycerides release twice as much water as carbohydrates when oxidised during respiration
As a solvent
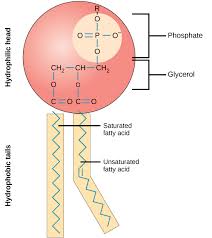
Phospholipids
Phospholipids are a group of compound lipids that contain two molecules of fatty acid, one molecule of glycerol and a phosphate group
hydrophilic phosphate group attracted to water molecules and hydrophobic fatty acid tail repelled by the water molecules
Function: major component of biological membranes
Proteins
Made up of carbon, oxygen, hydrogen and nitrogen
unique 3 dimensional shape
denatured when heated
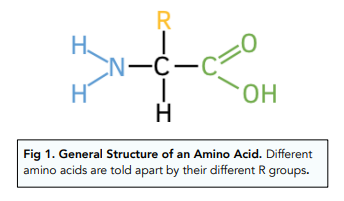
Amino acid
NH3-amino group
COOH- carboxyl group
hydrogen atom
R group
Peptide bond
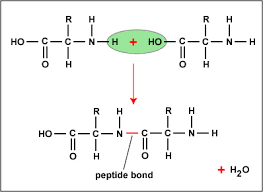
Bonds in protein structure
Peptide bonds join amino acids to form a polypeptide chain
Polypeptide chain folds into a particular 3 dimensional shape
Functions of Proteins
synthesis of new cells, for growth and repair of worn-out cells
Biological catalysts
Chemical messenger
Transport proteins
Structural proteins
Defence of the body
Kwashiokor
form of protein deficiency disease
caused by malnutrition, children have swollen stomachs
skin crack and become scaly