Rad Theory W4
1/93
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapters 9, 10, 11, 22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
Image
refers to a picture of an object (tooth)
Receptor
receives image when irradiated
Components of Dental X-ray Film
Film Base
Adhesive layer
Film emulsion
Protective layer
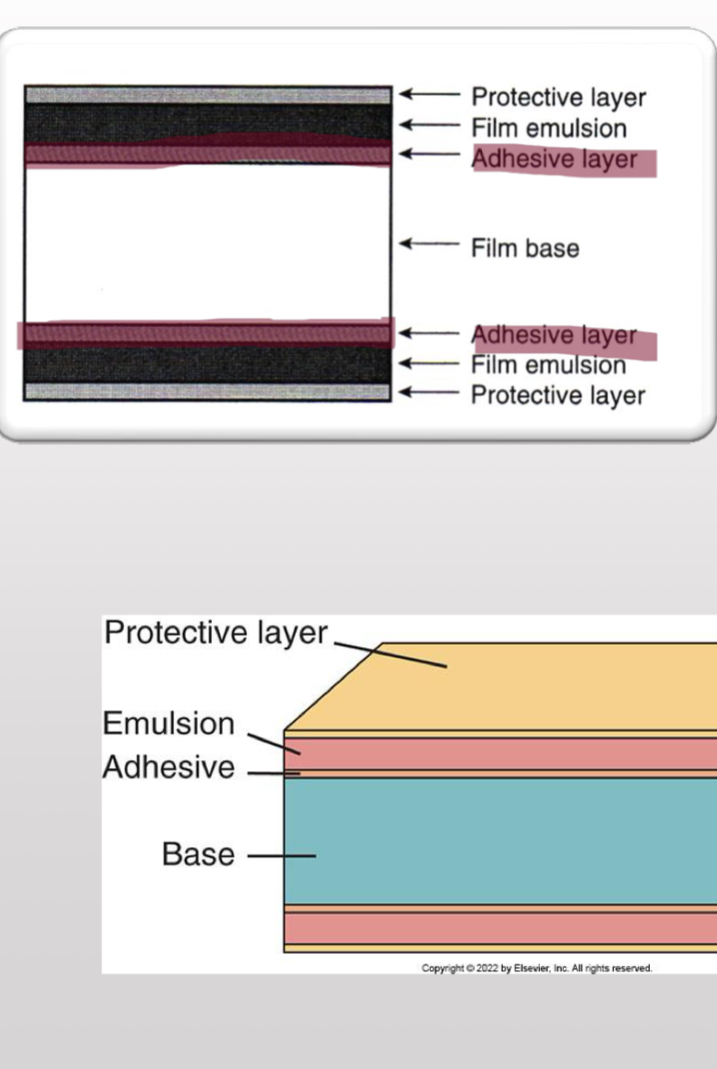
Film base
flexible piece of polyester plastic (0.2 mm in thickness)
What component provides support for the emulsion
Film base
Adhesive layer
attaches the emulsion to the base
Film emulsion
attached to both sides of the film base by the adhesive layer
Film emulsion consists of
gelatin and silver halide crystals
Silver Halide Crystals
absorb radiation during x-ray exposure and store energy from the radiation
Emulsion
80-99% silver bromide crystals & 1-10% silver iodide
Protective layer
thin, transparent coating placed over the emulsion
protects emulsions from damage and manipulation
Latent Image
invisible image (invisible until film is processed)
Types of Dental X-ray Film
Intraoral
Extraoral
Duplicating
Intraoral film
placed inside the oral cavity during x-ray exposure
Types of Intraoral x-rays
perapical, bitewing, occlusal
Types of extraoral x-rays
panoramic, cephalometric
Periapical films
peri = around tooth apex = end of tooth
Horizontal bitewings are useful for?
diagnosing interproximal caries and bone level
The ______ the crystals, the faster the film speed
larger
Which film is the fastes?
F film is fastest (the larger crystals and an increased amount of silver bromide)
Does a fast speed film require more or less radiation?
Less
Faster film creates images that are
less sharp due to LARGE crystal size
FAST-LESS-LARGE
Slower film created images that are
more sharp due to SMALL crystal size
SLOW-MORE-SMALL
The tube side of an intraoral film packet must always face which way?
The teeth and the x-ray tubehead
The label side of the intraoral film packet must face which way?
the patient’s tongue (white in sight)
Screen films
placed between 2 special intensifying screens in a cassette
sensitive to fluorescent light rather than direct exposure to x-radiation
Cassette
holds extraoral film and intensifying screens
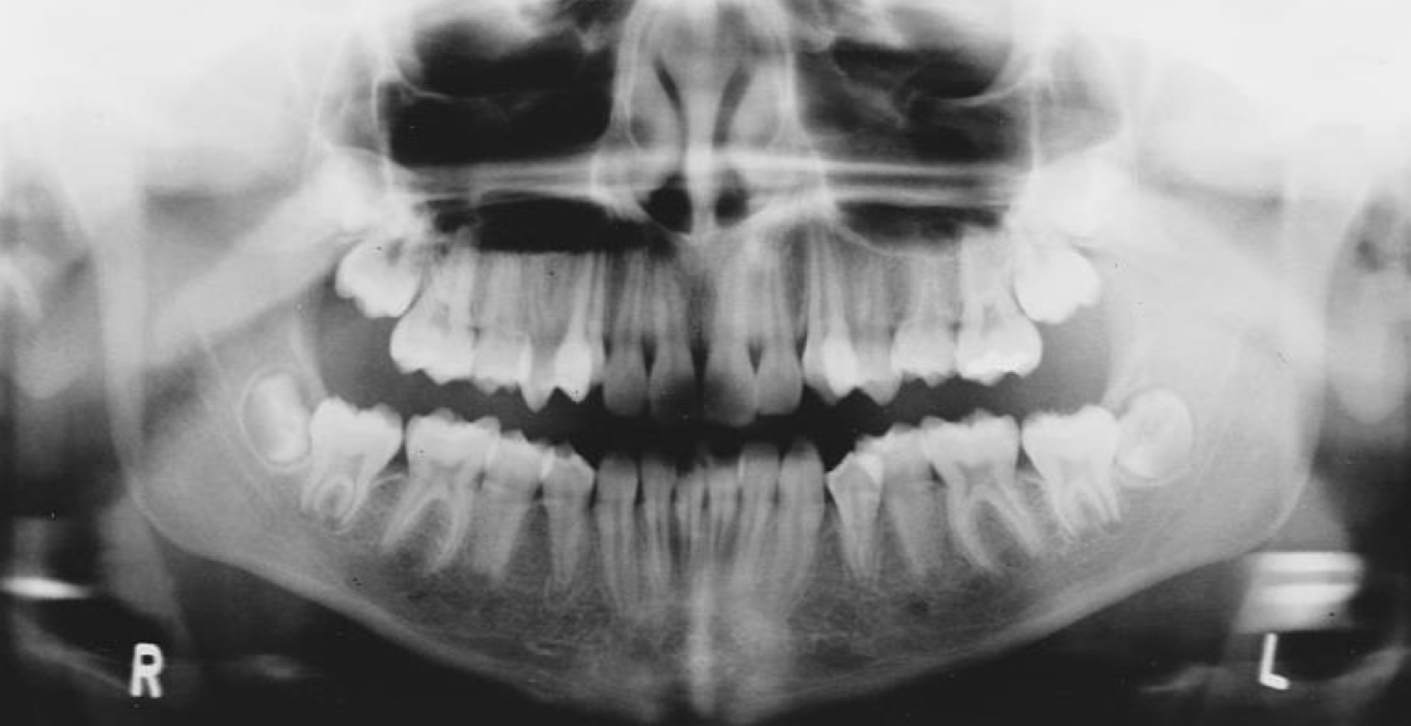
Panoramic Film
shows all teeth in the mouth
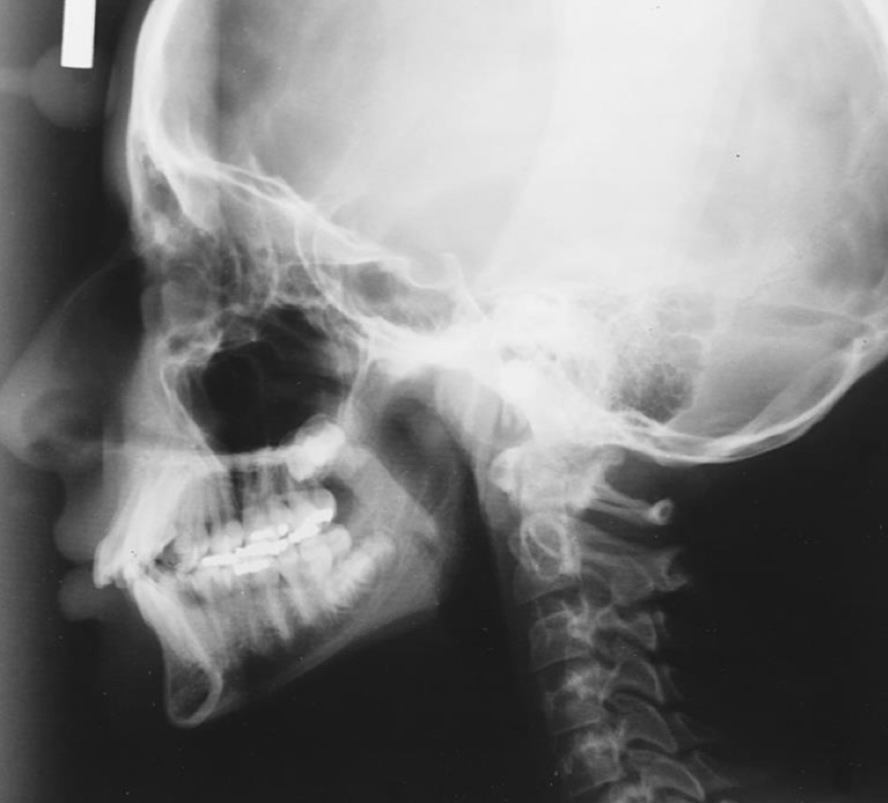
Cephalimetric Radiograph
used for oral surgery and ortho
shows the side profile and spine
Duplicating machines
like a photocopier for x-rays
(used for insurance companies)
Film should be stored in
a cool dry, place
away from radiation
What are the basic steps for manual processing?
Developement
Rinsing
Fixation
Washing
Drying
Development
emulsion is soften; silver halide crystals reduced to black causing dark or black images on a radiograph
Rinsing
film is rinsede to remove developer solution and STOP the developing proces
Fixation
removed unexposed silver halide crystals, creating white/clear areas on a radiograph; emulsion is hardened
Washing
remaining chemical solutions are removed in water bath
grey areas =
latent image produced by exposure
What are the 2 chemical solutions necessary for film processing?
developer and fixer
Developer composition
developing agent
preservative
accelerator
restrainer
Developing agent
Hydroquinone
producing black tones and contrast in the image
temp sensitive
Elon/Metol
produces many shades of grey
not temp sensitive
Preservative
extends the life of developer
accelorator
activates developing agent (alkaline environment)
Restrainer
prevents fogging
Fixer composition
fixing/clearing agent
preservative
hardening agent
acidifier
FIxing/clearing agent
removes all unexposed, underdeveloped silver halide crystals from the emulsion
ex. sodium thiosulfate
Preservative
Prevents deterioration of the fixing agent
ex. sodium sulfite
Hardening agent
-hardens and shrinks the gelatin in the emulsion
Acidifier
neutralizes the alkaline developer; provides necessary acidic environment required by the fixing agent
Darkroom
must be sealed off from any light leakage
Light film
underdeveloped film = low density
caused from insufficient developing time, low developer temps, contaminated dev solutions, inaccurate timer and thermometer
Dark film
overdeveloped film = image very dark
caused from excessive developing time, high developing temps
Reticulation
Film appears cracked
caused from a sudden change between dev and water bath temp
Developer spots
dark spots on film
caused from developer solution coming into contact with film before processing
Always ensure a clean working area
Fixer spots
white spots on film
caused from fixer solution coming into contact with the film before processing
Always ensure a clean working area
Yellow-brown stain
film appears yellowish-brown
caused from exhausted processing solutions, insufficient fixing/rinsing
Developer cut off
a straight white border appears on the film
caused from insufficient developer solution
Fixer cut-off
a straight black border appears on the film
caused by insufficient fixer
Overlapped film
2 films come into contact with each other during processing
Air bubbles
white spots caused by air is trapped on film after placed in processing solutions
(gently agitate film rack after placing in processing solutions)
Fingernail artifact
black, crecent shaped marks on filim
caused by rough handling of films
use finger pads and only handle the edges
Fingerprint artifact
a black fingerprint on film
Caused from touching the film with contaminated fingers of developer or fluoride
work in a clean area
Static electricity
film has thin black branching lines
caused by opening a film packet too quicklly prior to touching another object(carpeted area)
Scratched Film
white lines appear on flim
caused when film emulsions is removed form the base by a film clip or hanger
Light leak
exposed area appears black
caused from white light exposure or defective film packets
Fogged Film
film appears grey, lacks detal and definition
Film mounting
provides a systematic approach for viewing and evaluating radiographs
cardboard, plastic or vinyl
may be opaque or clea; opaque is preffered
What is the importantance of sequence?
efficiency and accuracy
FFP
faulty film placement
fix: move film accordingly
BB
Teeth not on bite block
fix: bite
FDP
faulty dot placement
1/8” IOES
+/- 1/8” inadequate occlusal edge space
OPNP
Occlusal plane not parallel to edge of film
HA
Horizontal angulation (closed contacts)
fix: center ray to go through the contacts
CC
Cone cut
fix: center PID over film
AC
Apex cut off
fix: move PID up, chair through window (XCP rinn)
RD
radiographic density
fix: set x-ray machine at 8 impulses, hold button long enough
FD
film damaged
fix: grab new film
VA
vertical angulation
(too much or too litlle angulation > foreshortening or elongation)
fix: correct angulation
FR
Film reversed
(lookes like tire tracks)
fix: put film in correct way
PP
Processing pitfall
fix: fill solutions properly, keep area clean
unexposed film
film appears clear
fix: expose film
Film appears black
film accidentally exposed to white light
Overexposed film
film appears dark
too much exposure time, kVp, or mA
Underexposed film
film appears light
insufficient exposure time, kVP, or mA
Phalangioama
finger appearing on film
patient holding film
Double exposure
film exposed twice
Penumbra
blurred images on film ‘
movement of client
Ghost image
metallic objects not removed before a panoramic film
Lead apron artifact
lead apron too high up and shows on film
Curve of spee
natural curvature of the teeth
Reverse smile line
clients chin is tipped up
not biting down properly
Curve too steep
chin too low
teeth anterior to the focal trough
client’s teeth are positioned too far forward on the bite block or anterior to the focal trough
anterior teeh appear narrow and out of focus