Recognized basic atomic structure (TEAS 7)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
atom
the fundamental constituent of matter that retains the properties of an element. it is the smallest unit that has a unique identity
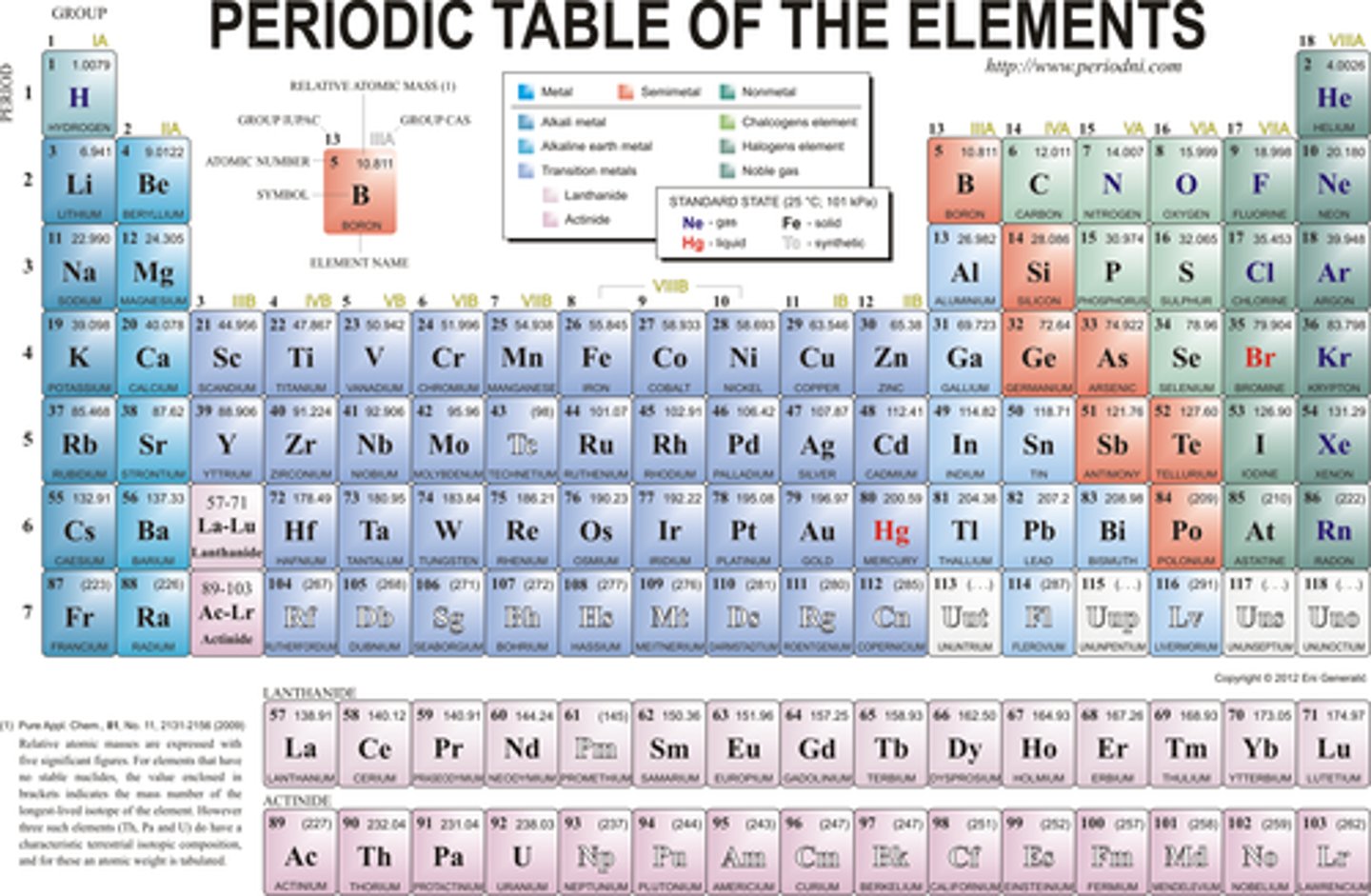
periodic table
the table of elements is expressed as columns and rows
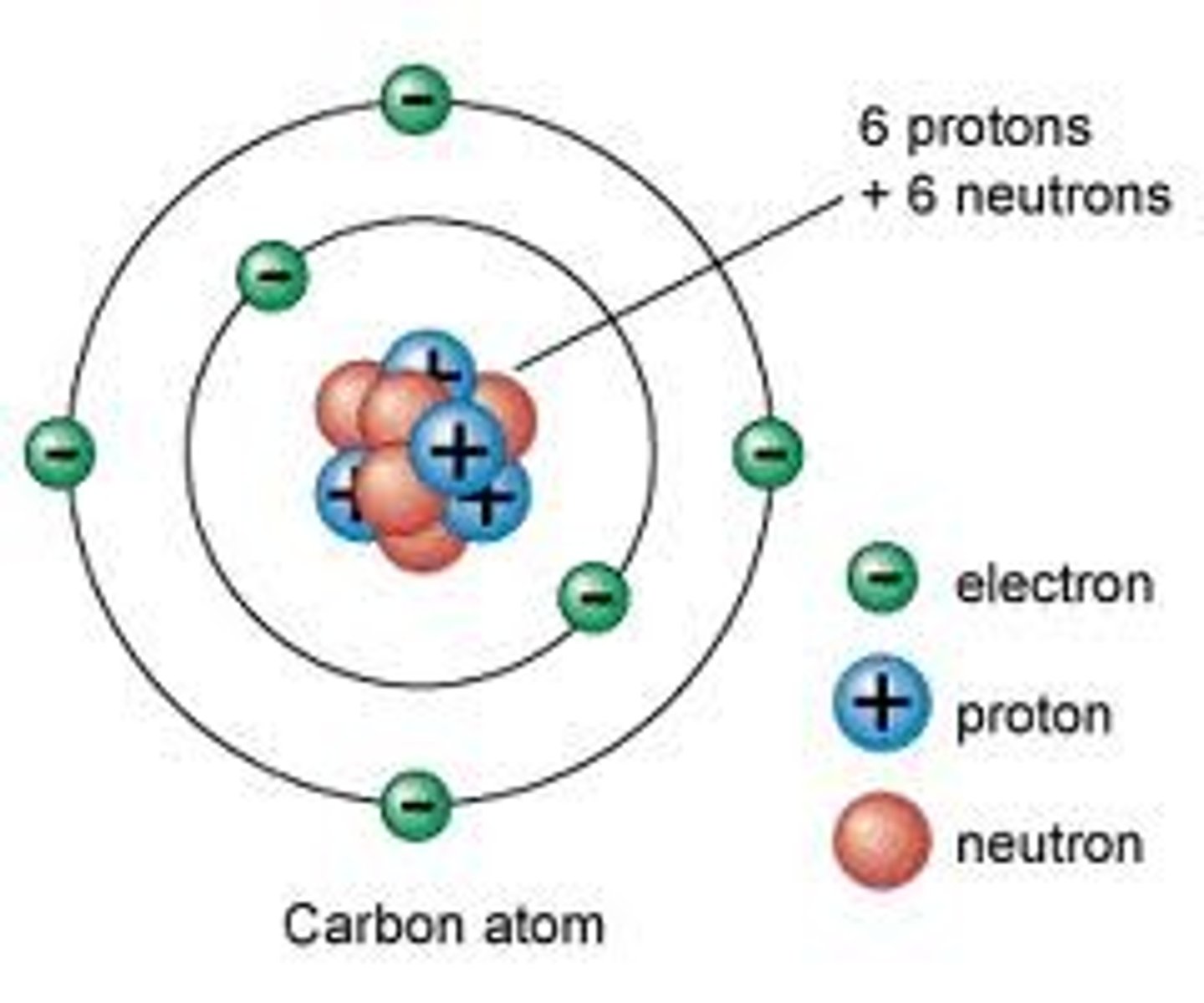
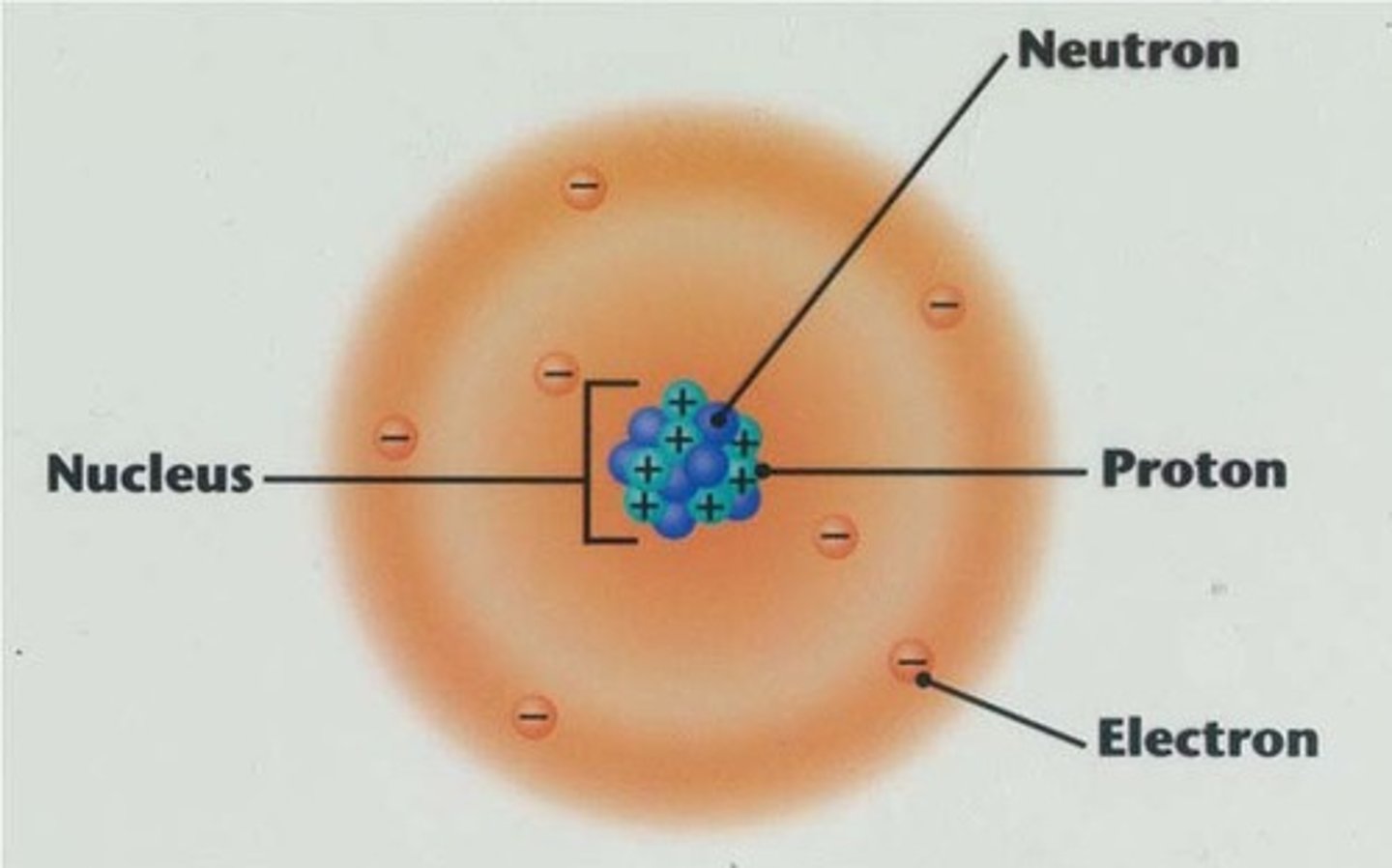
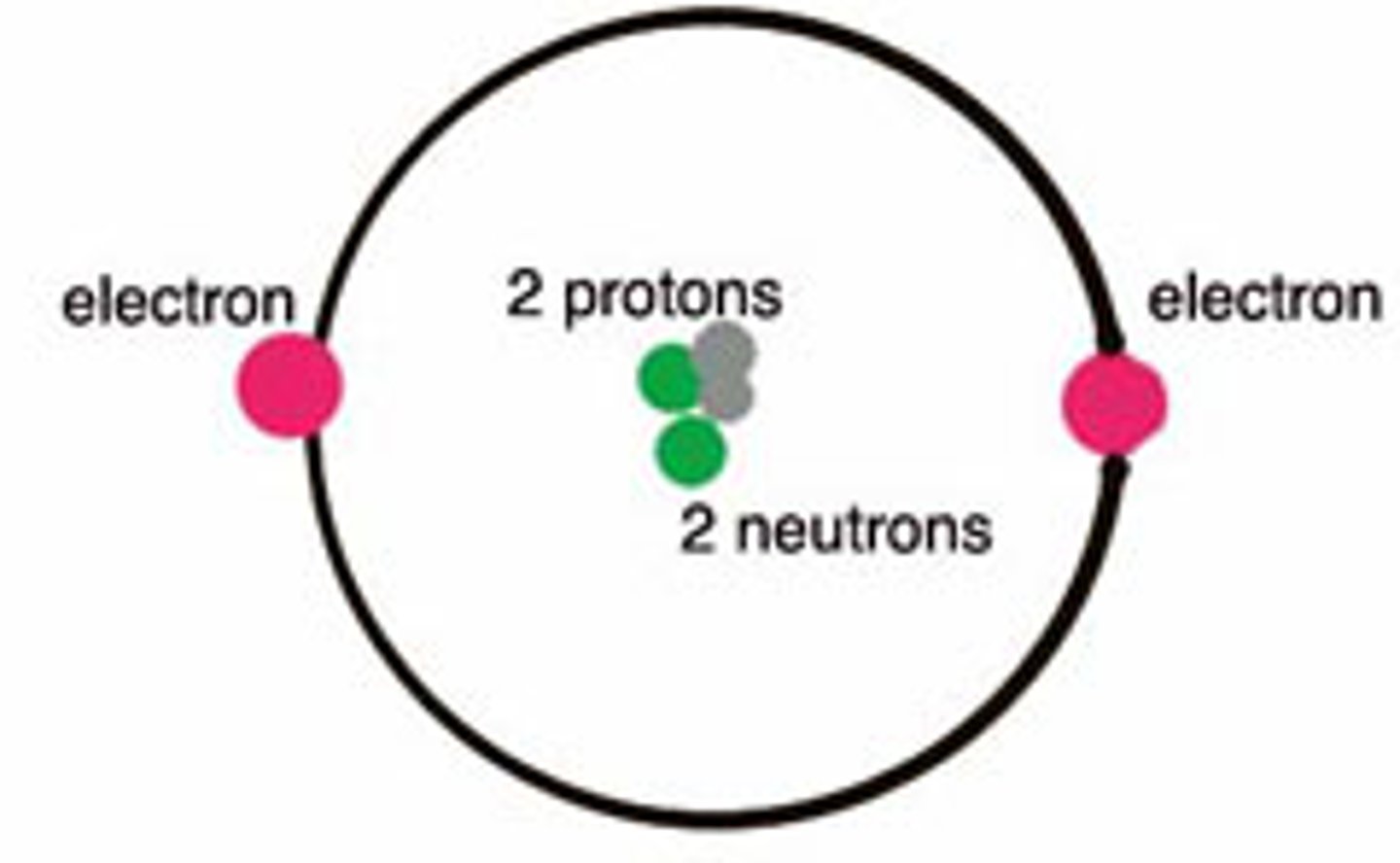
proton
positively charged atomic particle

neutrons
an atomic particle with no electric charge

electron
a negatively charge atomic particle

nucleus (atom)
The central part of an atom that contains the protons and neutrons.
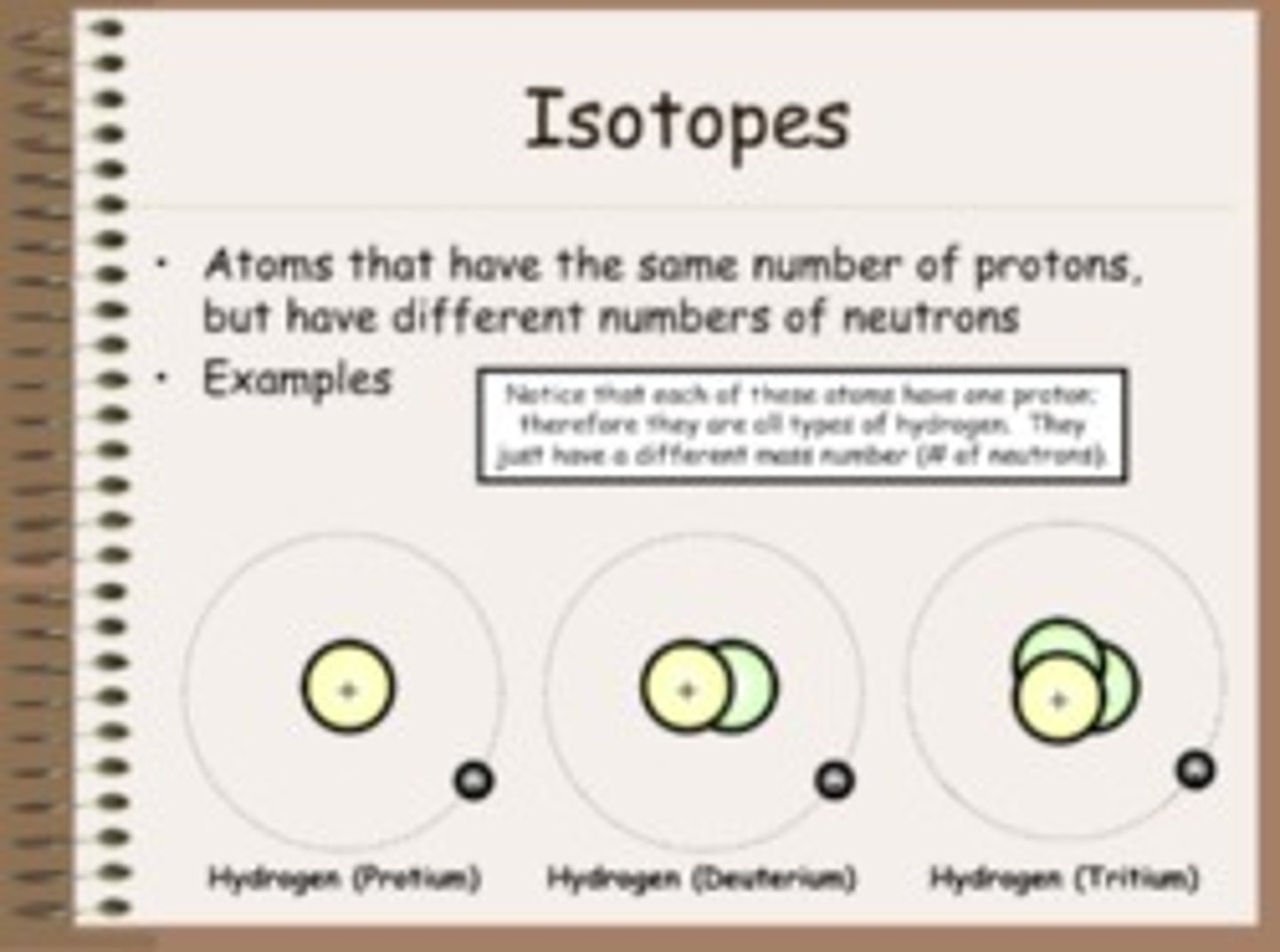
isotopes
atoms of the same elements that have different numbers of neutrons but the same number of protons and electrons
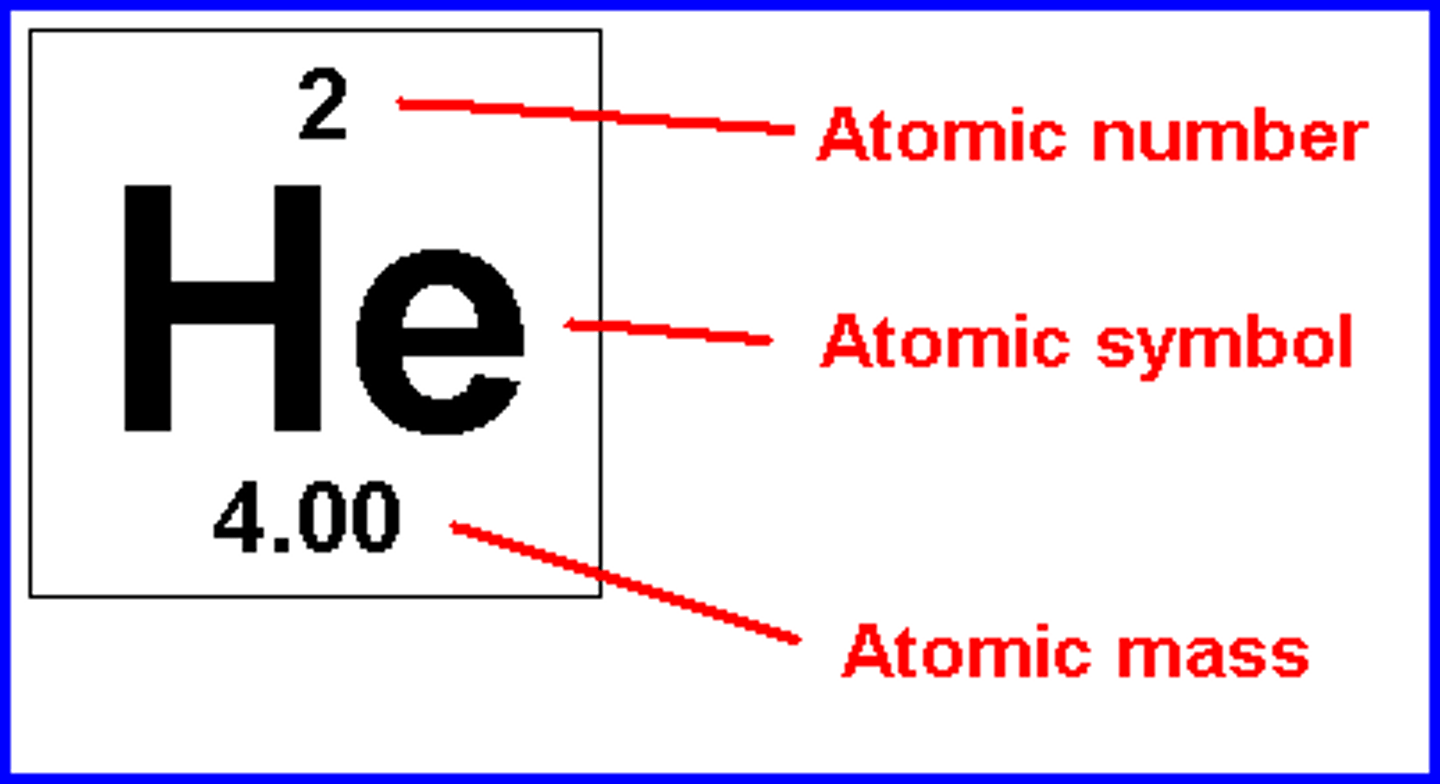
atomic mass
the sum of the masses of protons and neutrons in one atom of an element
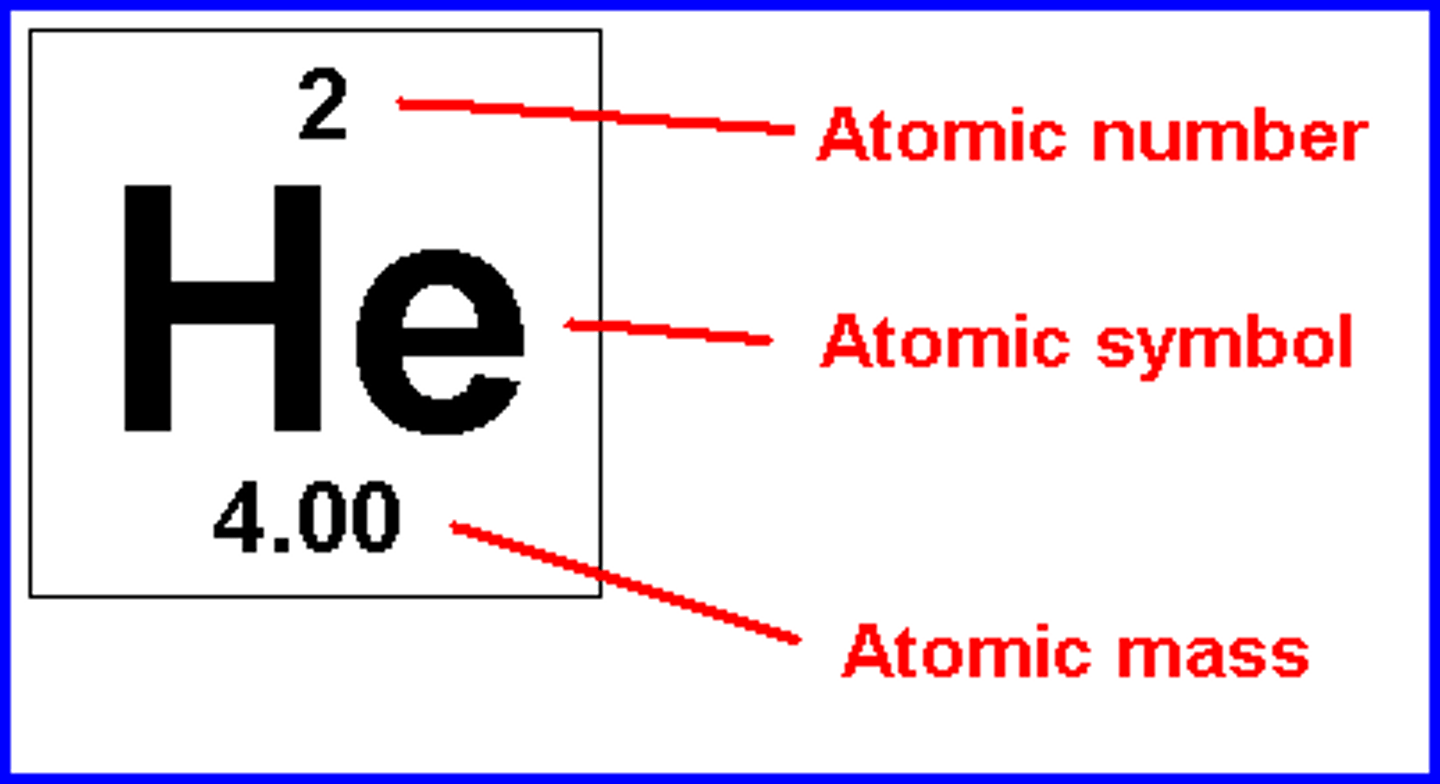
Atoms undergo chemical reactions by
gaining or losing electrons to achieve stability
an atoms properties relate to the
number of valence electrons in the atom's outermost shell
each type of atom will always have
the same number of protons.
atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
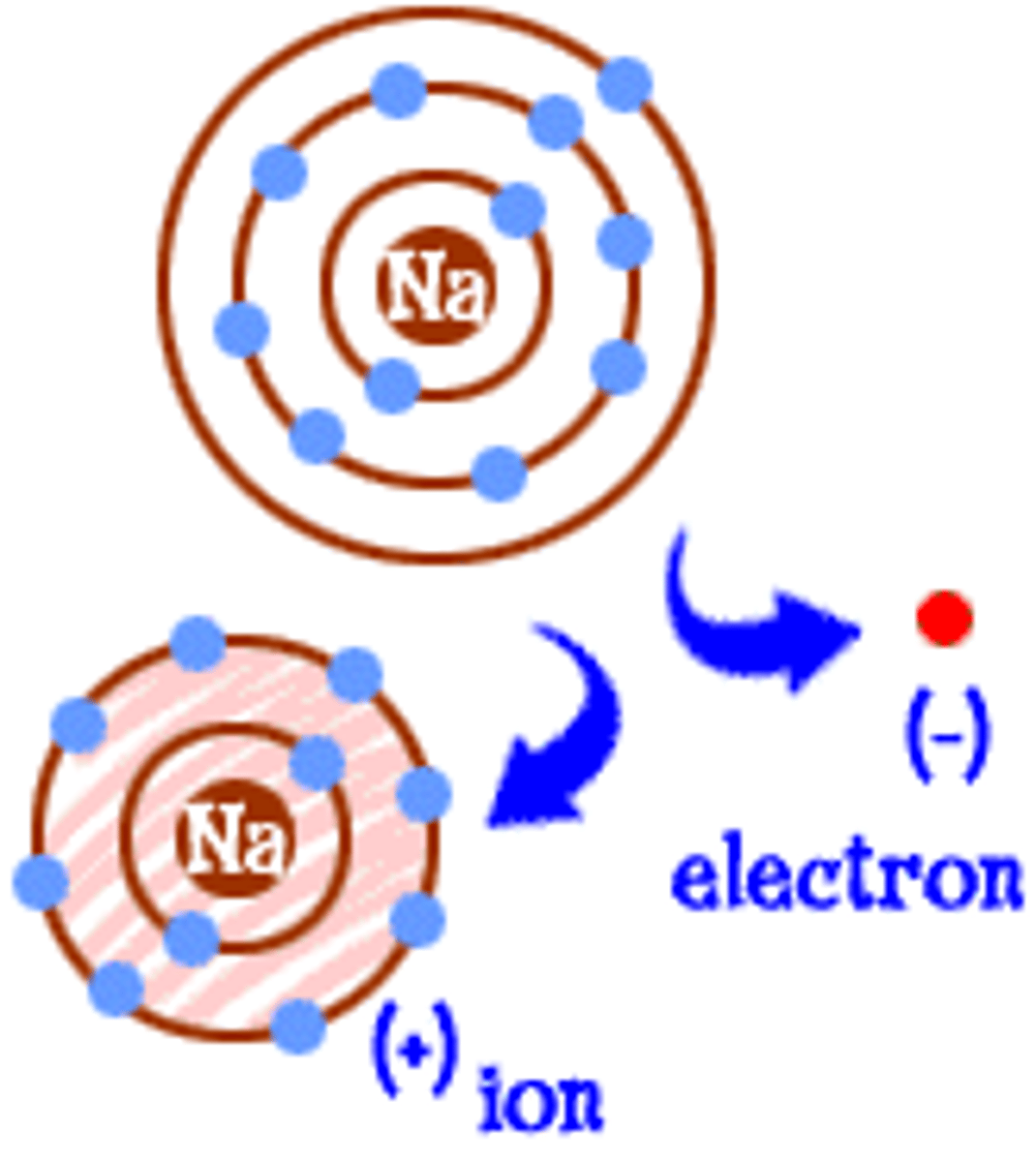
ion
positively and negatively charged atoms or molecules
YOUTUBE HOW IONS WORKSatom
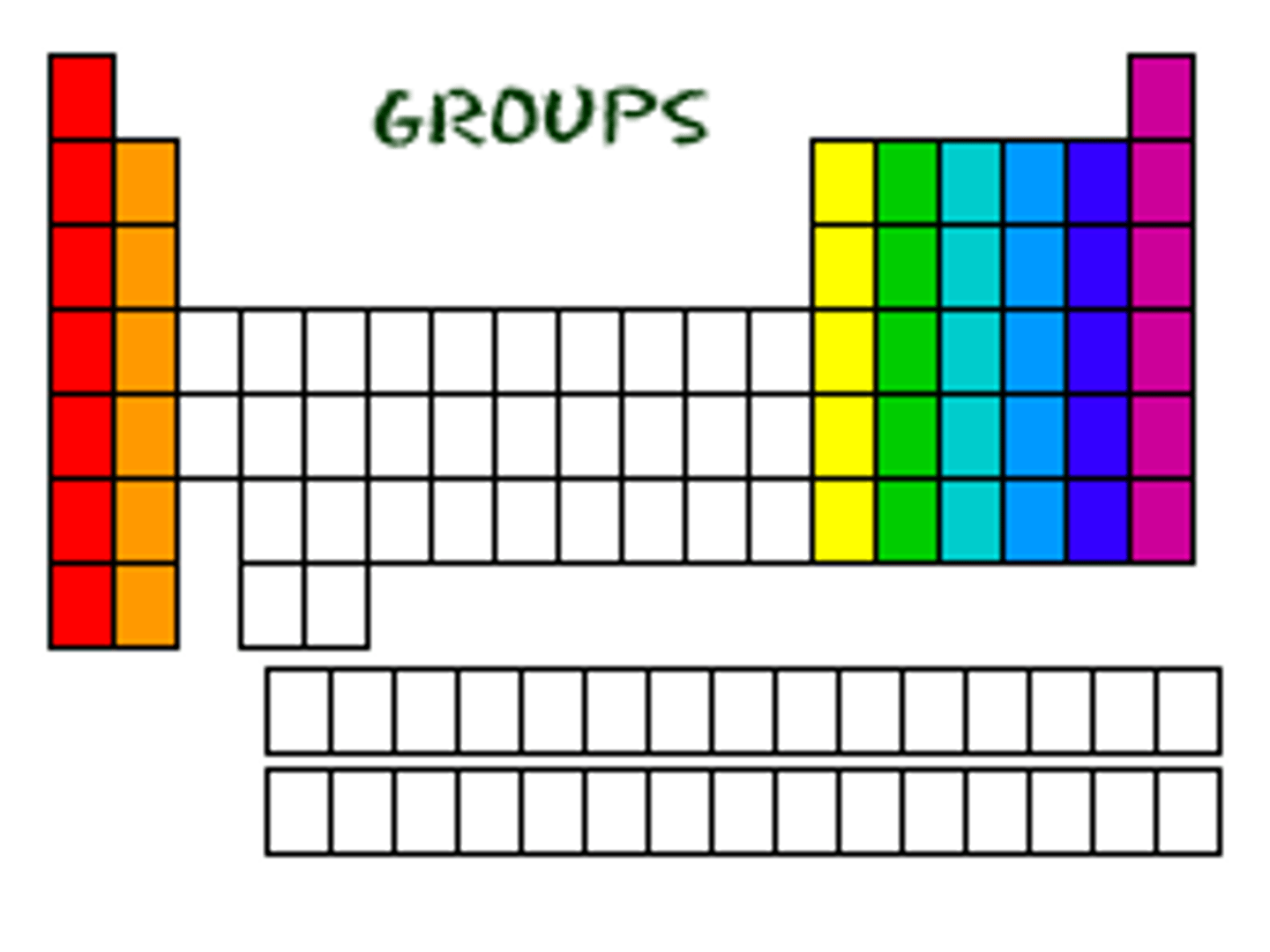
group
a column of elements in a periodic table
-fact that the elements in each group have the same number valence electrons
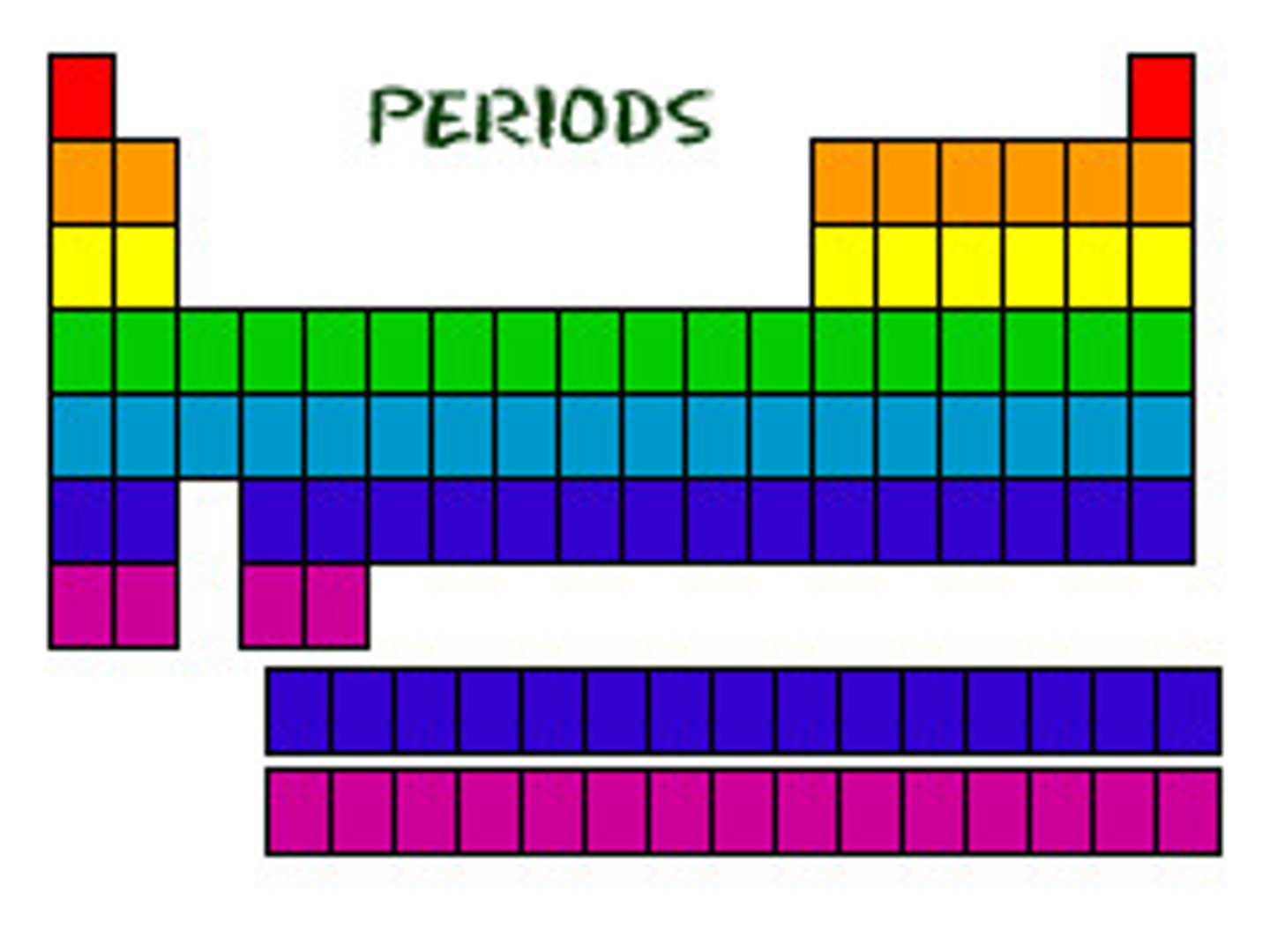
period
one of seven horizontal rows in the periodic table;
they indicate outermost shell of an atom.
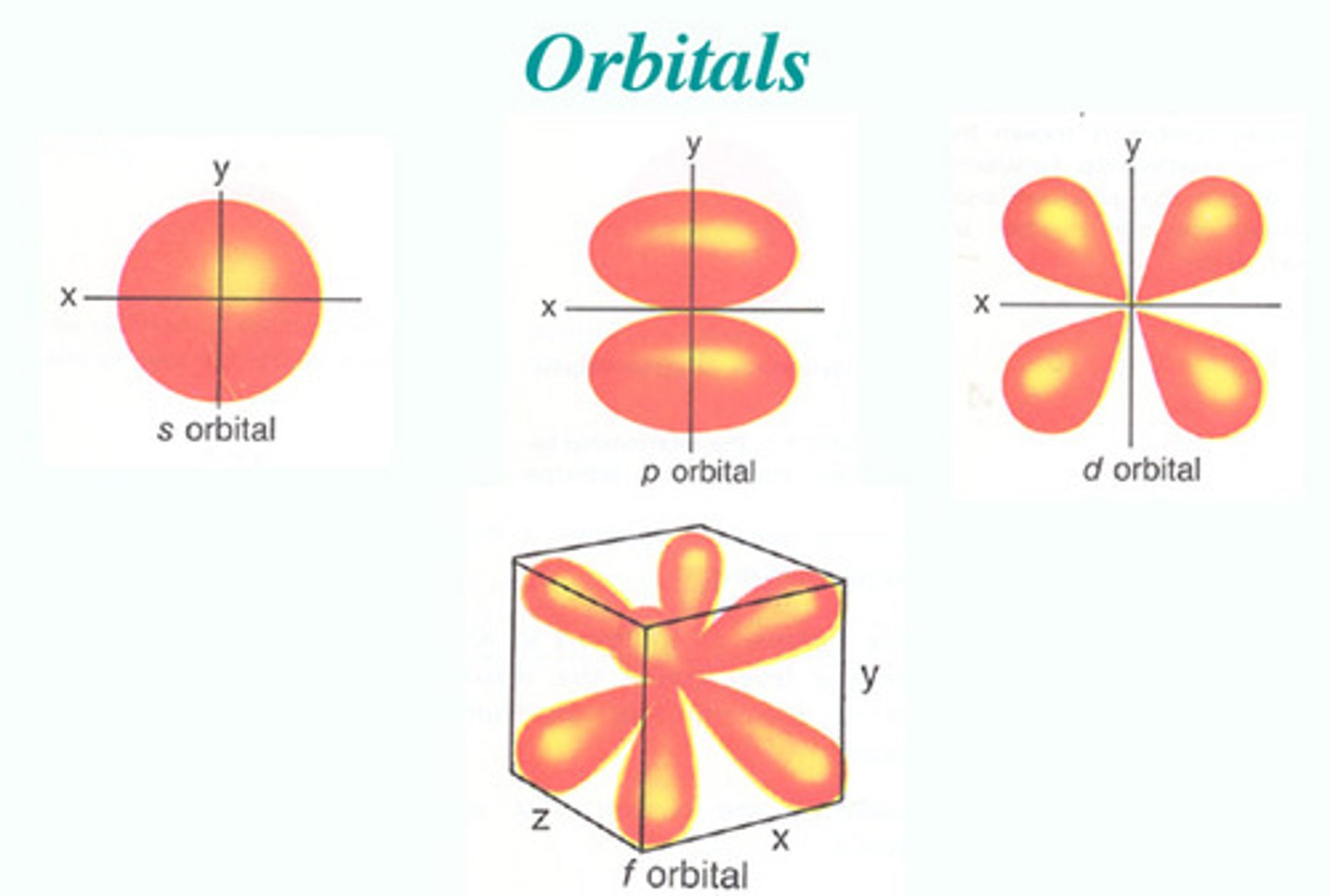
orbital
An area around the nucleus where an electron can be found
atoms are neutral, so
the number of protons equals the number of electrons
the atomic number is an integer in the periodic table so to identify the number of electrons and protons, look at the
integer shown with the element.
atomic masses on the periodic table are shown in decimals form to
account for the natural abundance of the element's various isotopes.
s orbital can accommodate
a maximum of two electrons at a time and its the closest to the nucleus;
-hydrogen and helium only have an s orbital that can hold a total of two electrons
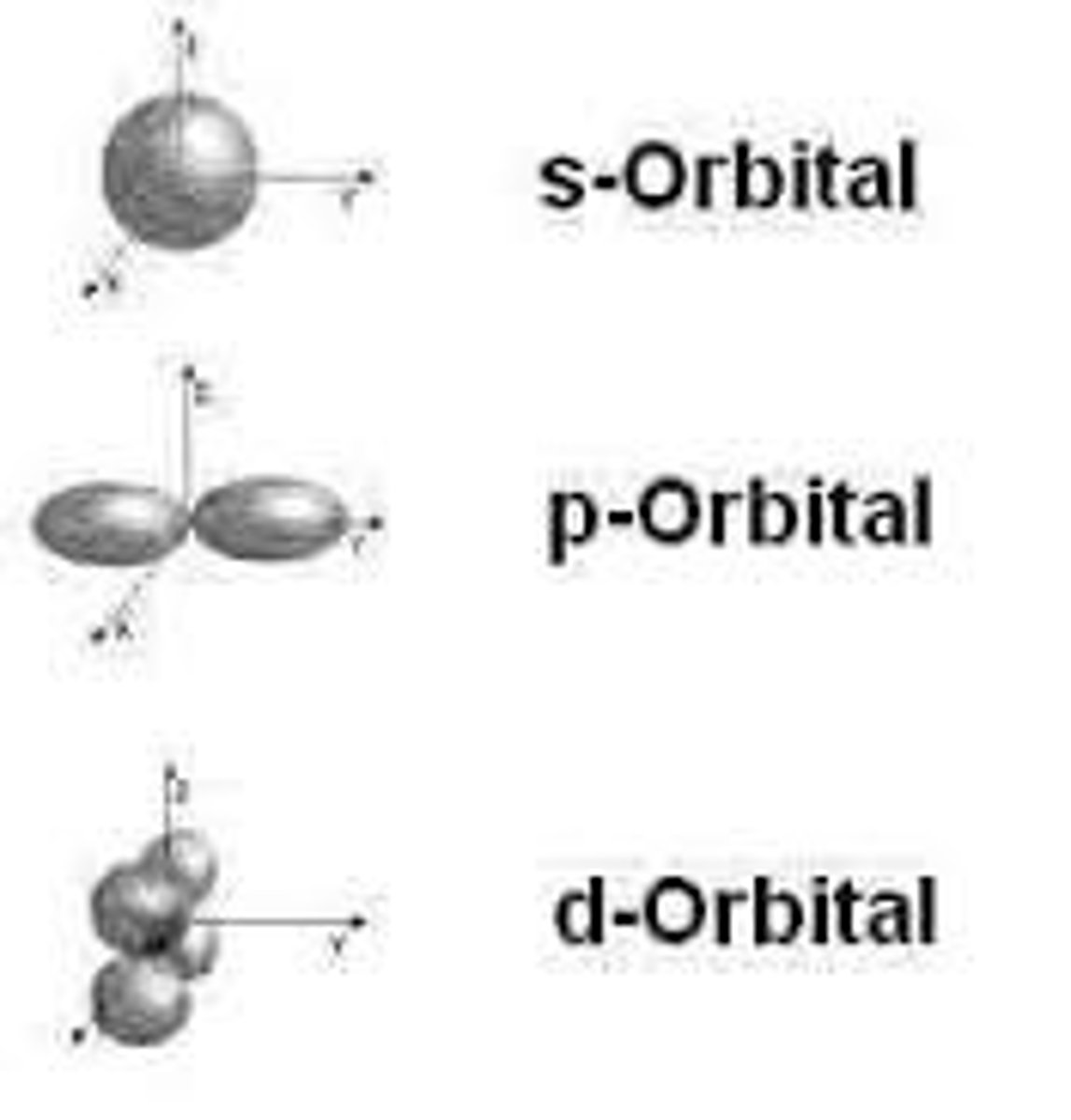
p orbital
6 electrons, dumbbell shaped;
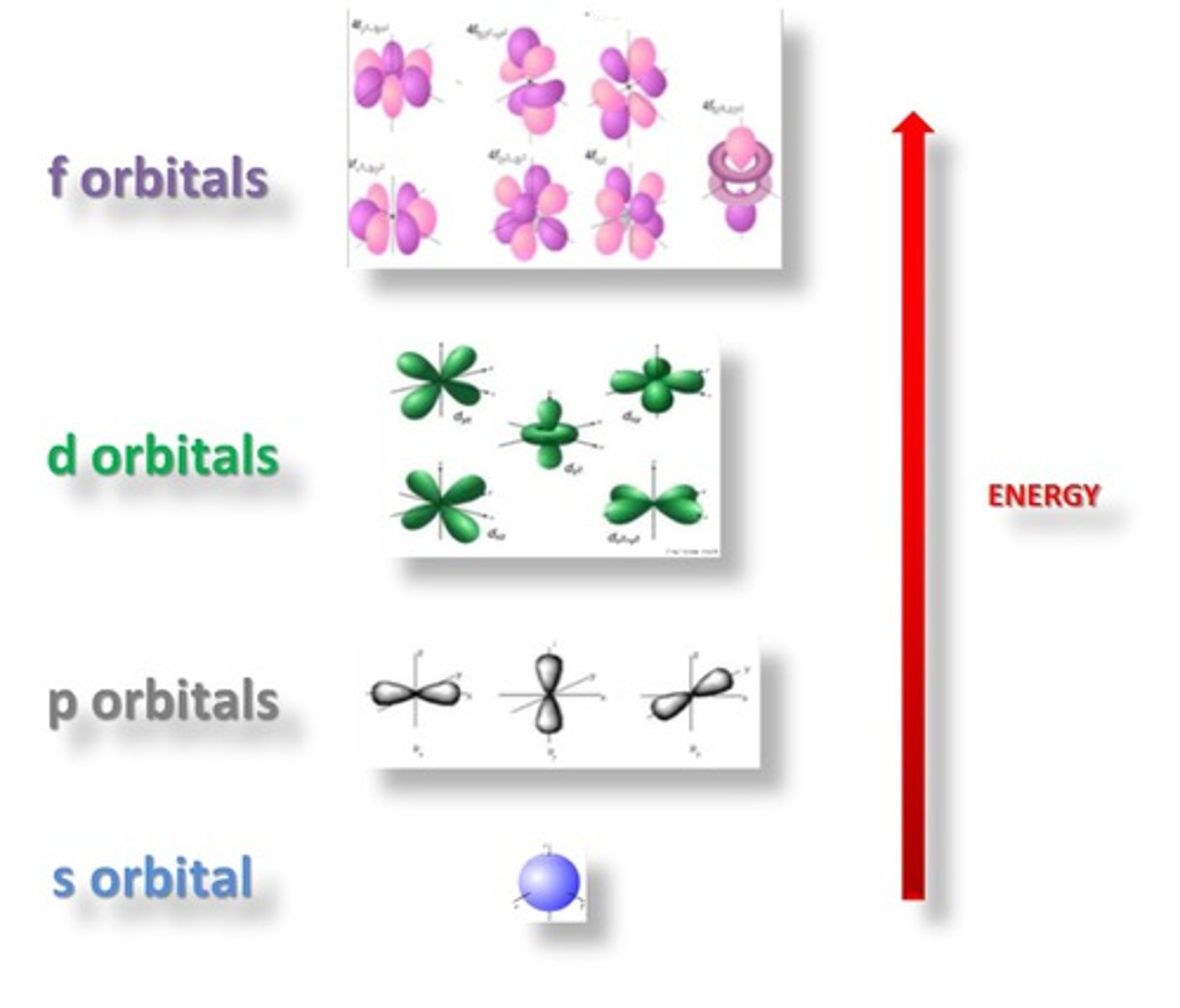
d orbital
10 electrons, clover shaped
f orbital
7 orbitals, 14 electrons, daisy shaped
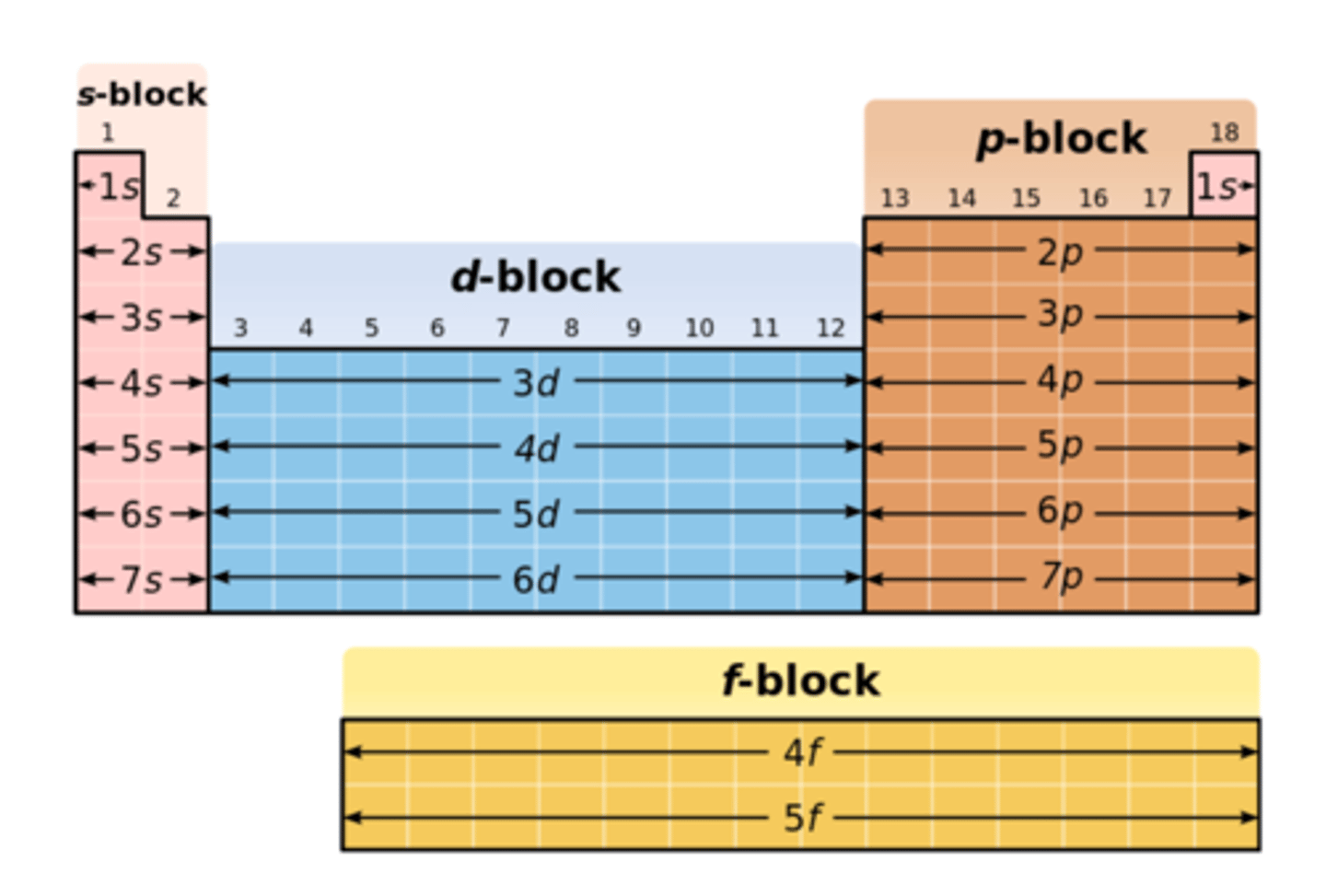
STUDY PERIODIC TABLE
!! To familiarize with atomic mass, atomic number, orbitals, and periods.
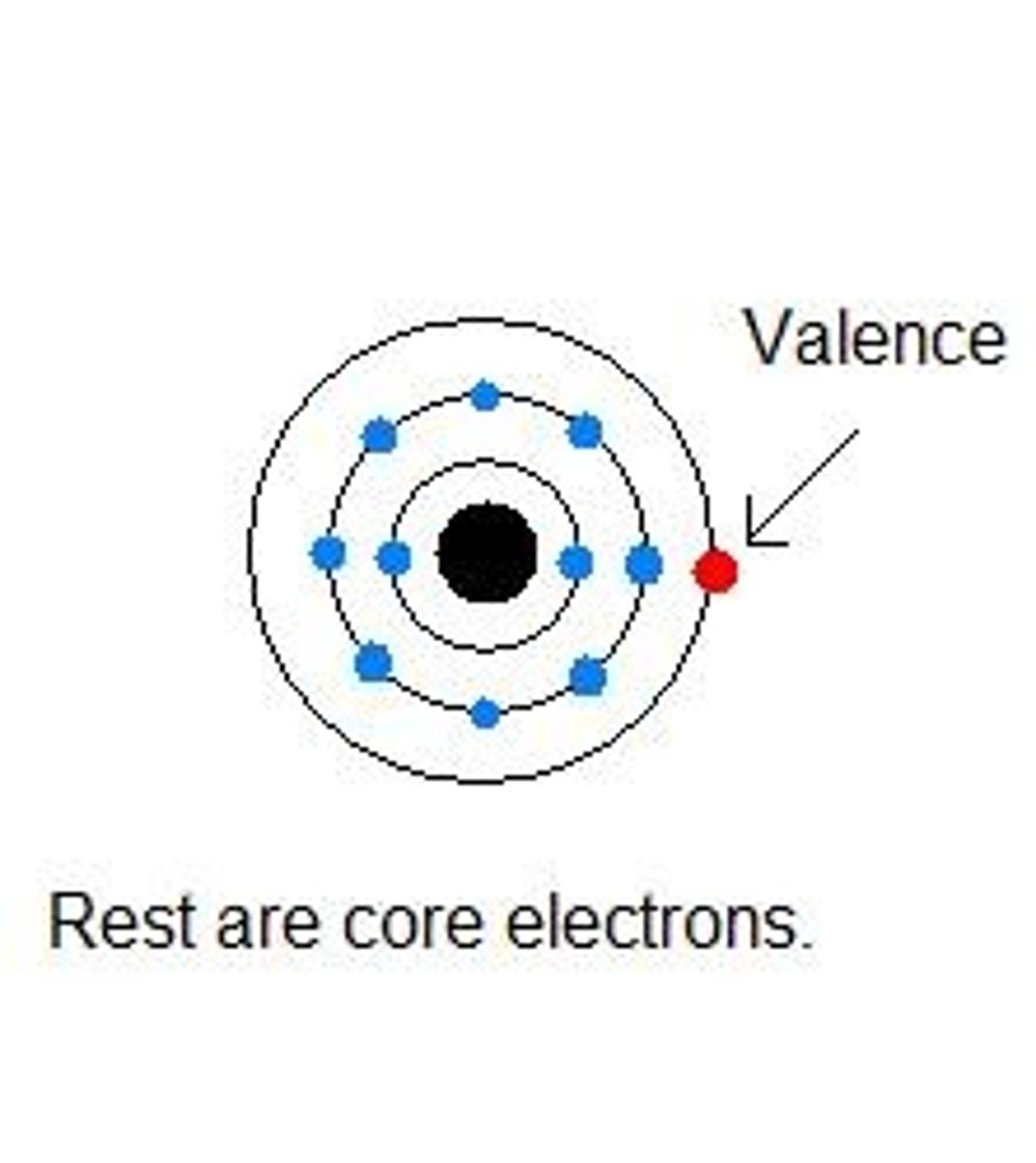
valence electrons are in the
outermost shell of an atom and participate in chemical reactions.
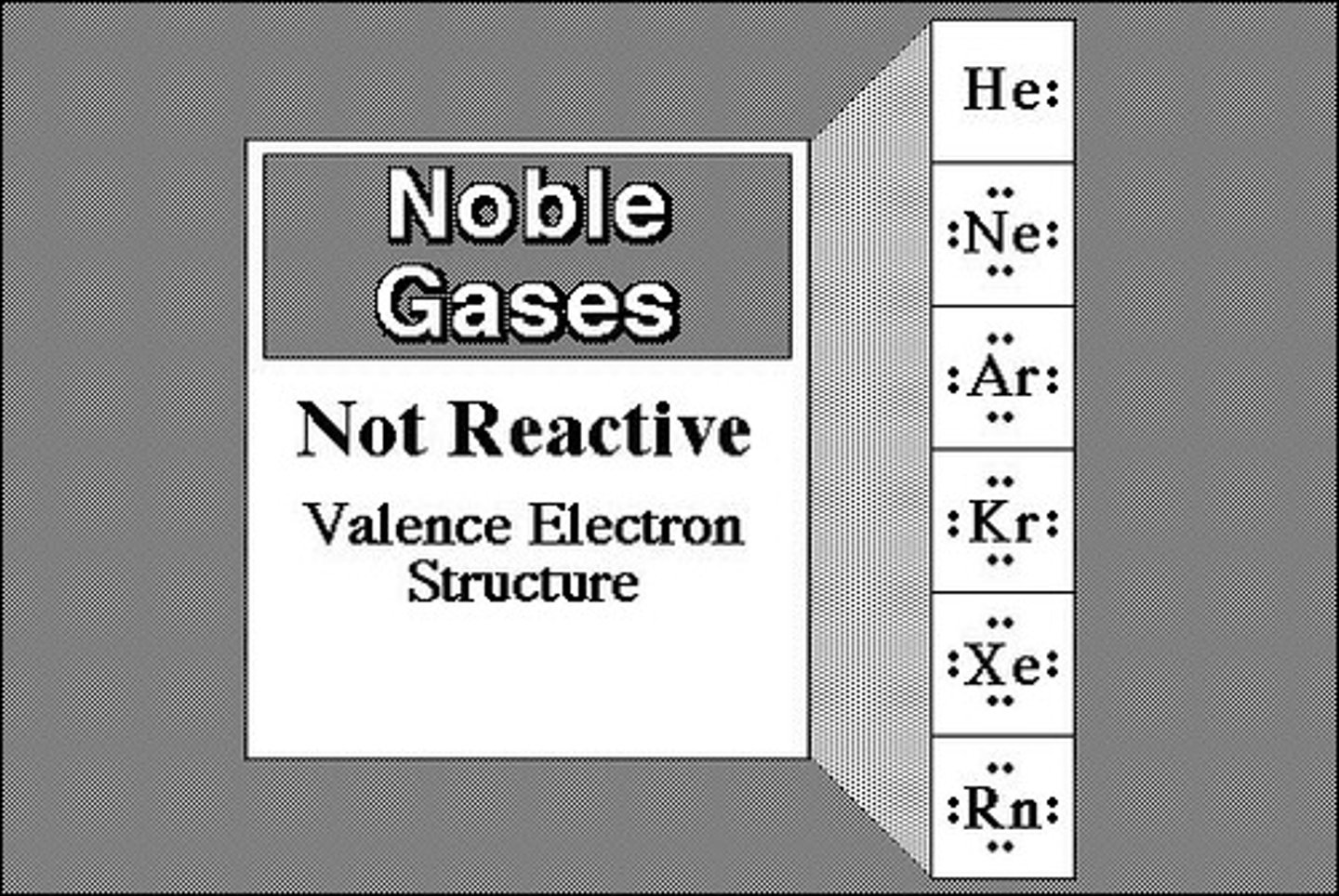
noble gases or inert gases, like helium and neon, have
full shells and are quite stable. they do not react with other atoms because they are stable.
nonmetal
any element or substance that is not a metal
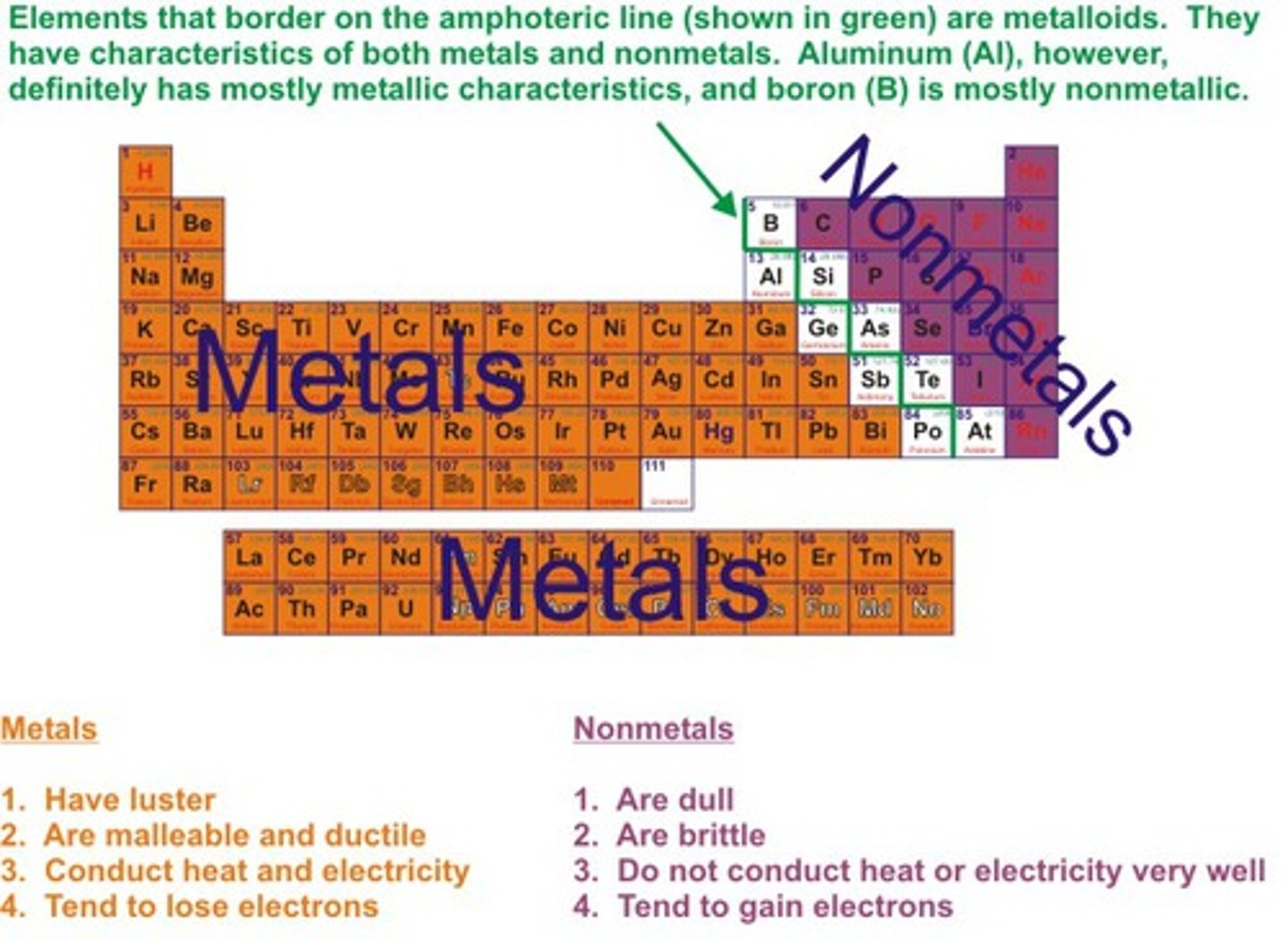
metal
a substance that is a good conductor of electricity and heat, forms cations by loss of electrons, and yields basic oxides and hydroxides.
anion
A negatively charged ion
cation
A positively charged ion

ionic bond
the bond between two oppositely charged ions.
compound
a substance made of two or more elements
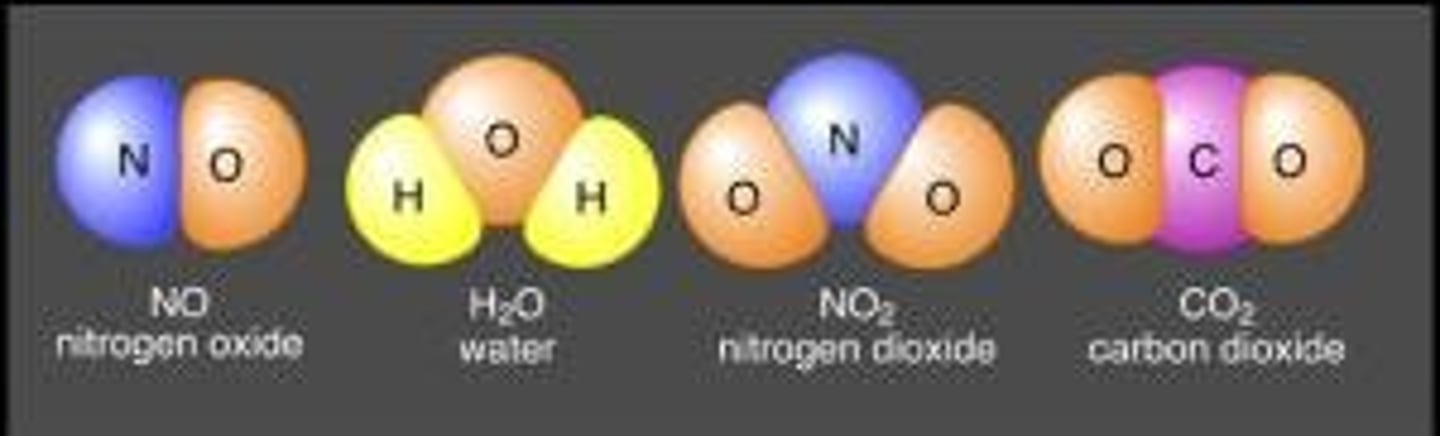
covalent bond
a chemical bond in which electron pairs are shared between atoms
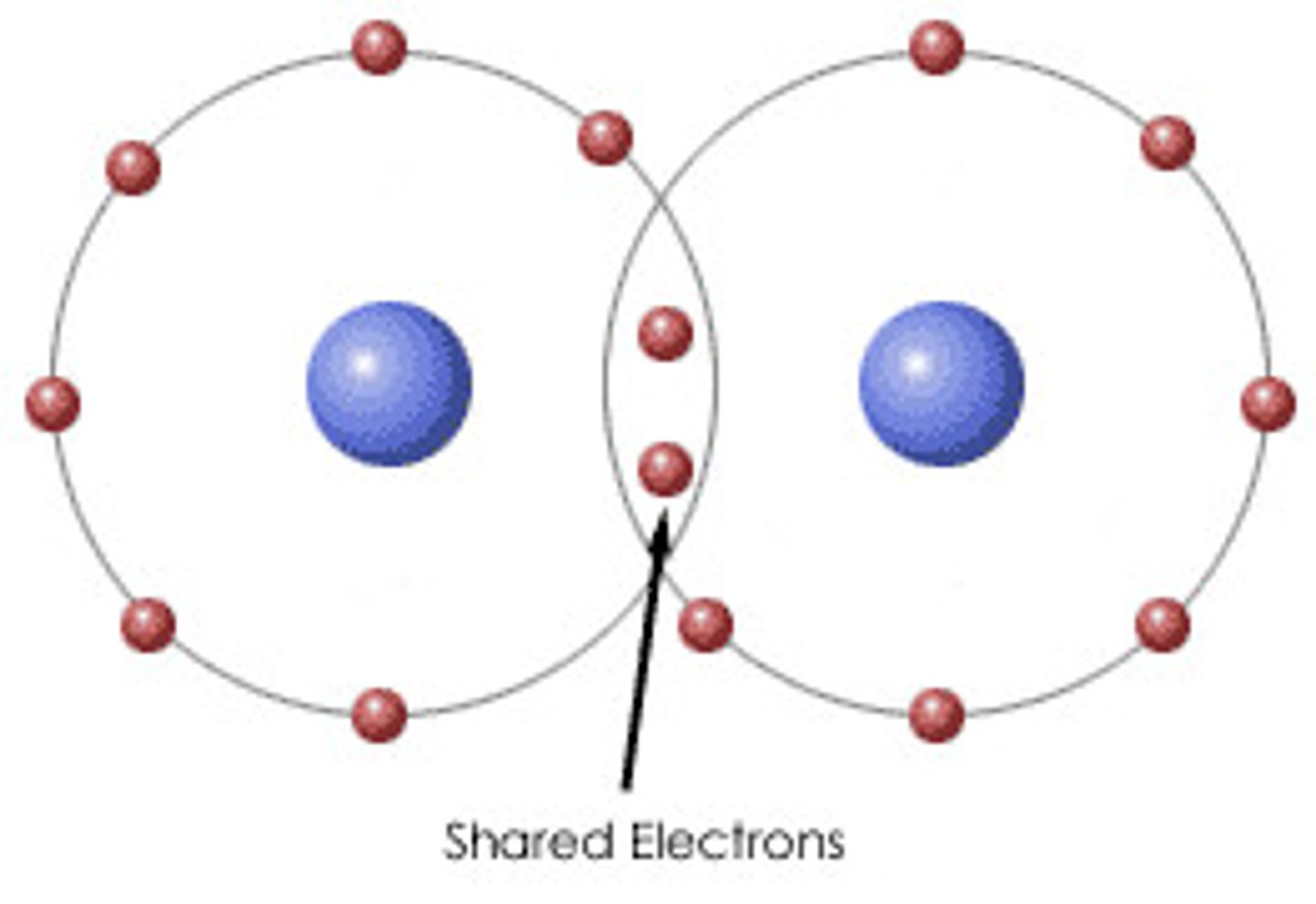
gaining electrons typically happens in
atoms with valence electrons greater than 4; usually nonmetals
losing electrons typically happens in
atoms with valence electrons less than 4; usually metals.
STUDY OTHER CHEMISTRY TEAS
OR YOUTUBE