23 - Animal Behavior
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
What is Behavior?
- Change in activity in response to stimulants
- Set of adaptations for survival in environment
What is behavior a result of?
- Natural Selection
What are behaviors meant to do?
They are meant to have organisms should behave in ways that maximize fitness
What is Behavioral Ecology?
- Field of ecology
- Study of ecological and evolutionary basis of behavior
Who is the scientist who helped figure out causes of behavior?
Niko Tinbergen
What are the two categories of questions that are asked to understand animal behavior?
- Proximate causation
- Ultimate causation
What is Proximate Causation?
- HOW does it occur? - "What are the immediate causes?"
What is Ultimate Causation?
- WHY does it occur?
- The answer will almost always be to produce viable, fertile, offspring and survival
Example of proximate causation:
The bluegill sunfish breeds in spring, during which it builds a nest, courts a mate, and mates
- How?
- Stimulus: Increasing daylight hours
- Physiological mechanism: Photoreceptors, they are stimulated longer which triggers neural and hormonal changes --> Leads to breeding behaviors
Example of ultimate causation:
The bluegill sunfish breeds in spring, during which it builds a nest, courts a mate, and mates
- Why?
How does it increase likelihood of survival and reproduction?
- H2O warm and food abundant so offspring grows fast
What is its evolutionary history?
- Fish breeding is spring, will on average have more successful offspring than any other time of year
What did Tinbergen say about action patterns?
Action patterns are fixed
What are Fixed Action Patterns?
- Seq of unlearned behaviors in response to a sign stimulus
- Unchangeable across individuals in species
- Once individual starts this behavior, it WILL complete it
What is a Sign Stimulus?
"the determining feature of a stimulus that produces a response"
Example of a fixed action pattern (Experiment):
Three-spined stickleback fish
- Females: No red belly
- Males: Red belly
Observations:
- Males will attack other males
- Aggressive towards the color red
1. Male in nesting territory and an invader red male is introduced --> Male attacks
2. Male in nesting territory and an invader that was a realistic model with no red underbelly introduced --> Male did not attack
3. Male in nesting territory is introduced to unrealistic models with a red belly --> Male attacks
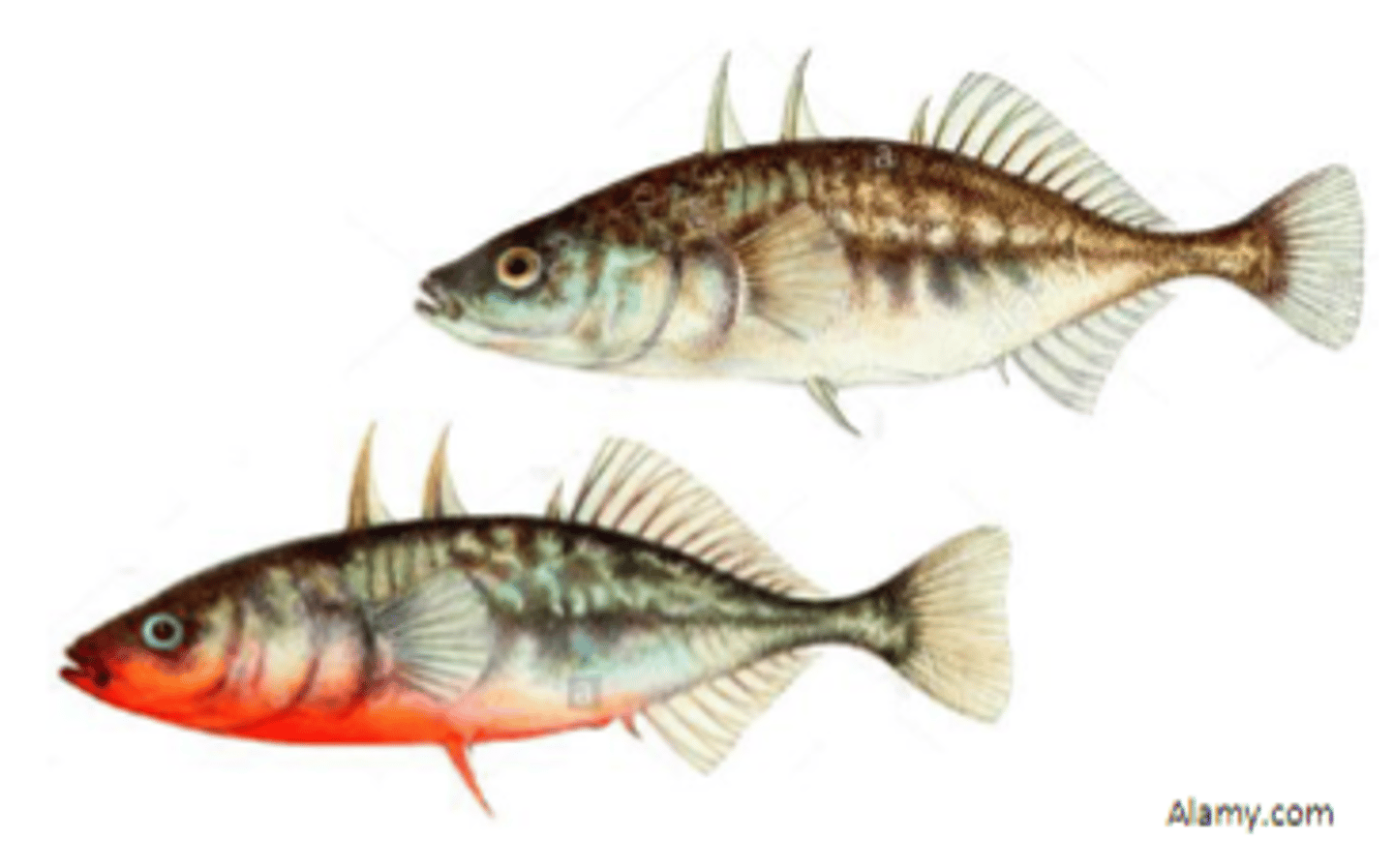
Example of a fixed action pattern (Experiment Conclusion):
Three-spined stickleback fish
- Females: No red belly
- Males: Red belly
Observations:
- Males will attack other males
- Aggressive towards the color red
- Proximate Causation (How?): Red belly, or just the color red, triggers attack behavior (Red belly = Sign Stimulus)
- Ultimate Causation (Why?): Attacks males who invade territory and doesn't attack females (with no red underbelly) because if they survive there is an increase in chances of reproduction success
What is Migration?
Yearly, long-distance movements --> Movement through different environments
How does migration happen?
Usually following exogenous (outside the body) cues, such as the position of the sun
Why does migration happen?
Organism could be migrating to a place with more food, which is important for reproductive success
What is an example of a Behavioral Rhythm?
Circadian Rhythms
What is a Circadian Rhythm?
- Occur over course of a 24 hour period (Occur daily)
- Peak activity at different times, depending on species
What are some examples of organisms and their circadian rhythm?
- Diurnal animals: Daytime (such as us)
- Nocturnal animals: Nighttime (Raccoons)
- Crepuscular animals: Dawn to Dusk (Deers)
How does a circadian rhythm happen?
- Exogenous cues: Such as light intensity
- Endogenous cues: Such as hormones
Why does a circadian rhythm happen?
Possibly because food availability or predator avoidance
What is Communication?
Transmission and reception of mutually recognizable signals
What are Visual Signals?
- Fast
- Transmits lots of information
- Indicate position of signaler
What are some examples of communication?
- Visual Signals
- Auditory Signals
- Songs
- Chemicals
What is an example of a visual signal?
Displays of aggression
What are auditory signals?
- Light is not needed, so it transmits over longer distances
- Calls
What are Calls?
Short simple sounds
What are some examples of calls?
- Bark
- Chirp
What are Songs?
More complex vocalizations
What are some examples of a song?
- Bird songs
- Whale songs
What are Chemicals?
- Pheromones
- Scent marking
What are Pheromones?
- Signals between individuals
- Meant to attract opposite sex/mate
- Alarm signals
What is Scent Marking?
- Urine or feces
- Chemicals from scent glands (in some animals)
What is Learning?
Modification of behavior as result of specific experiences
What are some examples of learning?
- Imprinting
- Spatial Memory
- Associative Learning
What is Imprinting?
- Long-lasting irreversible behavior that occurs in response to a particular individual or object
- Only happens at particular time in an organisms development, called the Sensitive Period (usually when very young)
Why do these organisms imprint?
Organism learns everything from other organism they imprinted on
Why do parents imprint on their young?
- Learns to recognize their own offspring
- Cares ONLY for their own offspring to save energy, time, etc.
Hatchlings of geese and ducks...
- No innate sense of their mother or "gooseness"
- Have innate ability to respond
- Learn and respond with 1st individual with certain characteristics (Loud and walking away), which is usually their mother
How long is the sensitive period of ducklings and goslings?
~2 days and they better have imprinted so they can follow and learn from their mother
Who is Konrad Lorenz?
- Studied newly hatched ducklings and goslings, noticed they followed their mother
- Following behavior critical for parental care (survival of offspring and fitness of parent)
What was Konrad Lorenz's experiment?
- Lorenz started leading the geese when they hatched
- They imprinted on him and would follow him around
What is Spatial Learning?
- All environments vary
- Memory of environment increases an organisms fitness
What did Niko Tinbergen observe about female digger wasps?
- When she leaves her underground nest, she hides the entrance with sand
- When she returns to her nest, she is able to fly directly to it, even though it is hidden
Experiment Niko Tinbergen did with female digger wasps...
1. Tinbergen marked a wasps nest with pinecones. Wasp was able to leave and return without any issue
2. Tinbergen marked a wasps nest with pinecones and moved them once the wasp left. She was returned to where the pinecones were, and not the nest itself
What was the conclusion of Niko Tinbergen experiment?
Female digger wasps use spatial memory to find their nest
What is Associative Learning?
Learning through associations between experiences
What are some examples of associative learning?
- Classical Conditioning
- Operant Conditioning
What is Classical Conditioning?
Association between a normal process and an unrelated stimulus
What is an example of classical conditioning?
Pavlov's experiment with dogs and salivation. In which he would ring an unrelated bell when he served them dinner and eventually, when the bell rang the dogs would salivate without food in their mouths
What is Operant Conditioning?
- Association behavior with rewards and punishments
- Trial and error learning
What is an example of operant conditioning?
Skinners box experiment, in which rats were placed into a box with a lever that would knock a food pellet into the box. The rat would find out by accident that if it hit the lever, it would be rewarded with food and so it would keep hitting the lever.
What is an example of a job that uses operant conditioning?
Animal trainers, they use reward and punishment to teach
What is Cognition?
It is involved in most complex forms of learning
What are some examples of cognition?
- Process of Gaining Knowledge
- Problem Solving
What is the Process of Gaining Knowledge?
- Thinking, processing information
- In Humans: High level functions
What is Problem Solving?
- This is able to happen because of cognition
- Not all animals are able to problem solve
- Ability to create method to overcome obstacles (and ability to create a solution first try)
What is an example of an organism using problem solving skills?
Chimpanzees are able to pile boxes together to reach a banana that is too high for them to reach (not all animals are able to use tools)
What is Social Learning?
Learning through observation of other individuals for how to solve problems
What is foraging?
- It is a feeding behavior
- Organisms need to locate, select, gather, and hunt
What is the Optimal Foraging Model?
- Animals need to make trade-offs
- In a range of possible food, there are costs and benefits that determine the optimal choice to get
What are the two parts for the Optimal Foraging Model?
- Animals make trade-offs
- Prediction follow from trade-offs
What is are some examples of a cost/benefit in the optimal foraging model?
- Amount of energy in the food item
- Travel distance
- Predation risk
What is the prediction that follows from trade-offs?
- Organism will spend the minimum amount of energy for maximum nutritional value
- Maximizes reproduction success
What are some examples of Mating Behavior and Mate Chase?
- Seeking and attracting mates
- Choosing among potential mates
- Competition for mates
- Females chose their mate
What organism is an example of mating behavior and mate chase?
Stalk-Eyed Flies
- Stalks are longer in males than females
- Males with compete for attraction of females
- Longer > Shorter because it correlates to good health
What is Altriusm?
- Behavior that decreases individual fitness but increases the fitness of other individuals in a population
- Unselfish behavior
What are some examples of altruism in nature?
Alarm calls in birds and social rodents
Why is altruism controversial?
Natural selection should favor individuals who maximize their own reproduction, not the populations
What is Inclusive Fitness?
- Not individual fitness
- Evolution does not distinguish between genes that are transmitted directly from offspring and parent and those transmitted indirectly through close relatives