Lecture 18
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Intellectual Development Disorder
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Binet, Simon
The first IQ test was developed in France by Alfred _______ and Theophile ______
Eugenicists saw IQ testing as a way to identify people who they thought shouldn’t be allowed to have children → those who had lower intellectual functioning were put in institutions and sterilized without their consent
More likely to be Black , Indigenous or poor
IQ tests developed were racist, testing culturally based knowledge and test-taking proficiency
How was the pseudoscience of eugenics connected to intelligence/IQ in the past?
Cognitive abilities: mental processes representing your actual abilities, and they improve and degrade throughout life
Intelligence: measured quantity/score that summarizes a person’s ability to apply knowledge and skills
What’s the difference between cognitive abilities and intelligence?
Crystallized intelligence | Fluid intelligence |
The number of facts you know, using the knowledge you acquired throughout your life | Your processing power, using your mind to solve new problems |
Increases throughout life | Increases, peaks in young adulthood, decreases in older age |
What’s the difference between crystallized and fluid intelligence?
Mental age is the level of age graded problems someone is able to solve, vs. chronological = your actual age
What is someone’s mental age and explain the difference with chronological age?
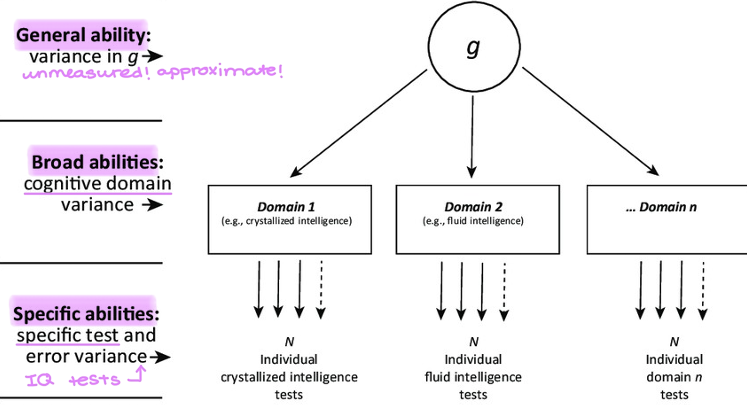
General abilities → unmeasured, approximate
Broad abilities → cognitive domain (ex: crystallized/fluid intelligence)
Specific abilities → specific test (ex: IQ test)
Explain how the psychometric approach uses a hierarchical view of intelligence?
pre-schoolers
6-18
adults
Wechsler Scales:
WPPSI-III for ______-______
WISC-V for kids between ___-___ years old
WAIS-IV for _______
Verbal
spatial
reasoning
Working
speed
The 5 domains of intelligence assessed with Wechsler Intelligence Scales for Children:
______ comprehension
Visual ______
Fluid _______
_______ memory
Processing _____
normal
→ representative
Test norms are the standards of ______ performance expressed as average scores and the range of scores
→ They are based on the performance of a large, ______ sample
70, 130
3
3
IQ and standard deviations:
95% have scores between ___ and ___
Less than ___% have scores of 130+ → criterion of giftedness
Less than ___% have scores below 70 → indication of impaired intellectual functioning
4
→ childhood
Around age ___, there is a fairly strong relationship between early and later IQ
→ BUT many children show ups and downs in their IQ scores over the course of ______
stable
For kids with very low levels of cognitive functioning, they are more likely to stay ______ in adulthood
increases
As children age, the stability across re-tests ______
Biases in tests
Environmental differences among groups (ex: racial-ethnic minorities = lower SES, lower quality access to services, higher exposure to stigma/discrimination)
Stereotype threat
What are the 3 causes of racial-ethnic disparities in IQ scores?
decrease
→ persist
When you account for environmental factors in IQ, Black-White disparities ______
→ BUT differences still _______ and it may be due to other factors
visual-spatial
There are culture differences in processing of _____-______ information, which may partly explain the discrepancies in IQ between racial-ethnic groups
well, norms, research
Overall, IQ tests are great because they work very _______, _______ are very good, and they have been continuously refined based on copious _______
working, speed
The General Ability Index (GAI) is an estimate of general intellectual ability that is less reliant on _______ memory and processing _______