CFB 6: Getting Nutrients (Biochemistry)
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Metabolism focuses on _____ molecules.
Small
Different tissues carry out _________ processes.
Different tissues use (and produce) _________ fuels.
Differences can be mediated by _________ enzymes/isozymes.
Different!
Glucokinase vs. hexokinase
Glucokinase: liver/β cells
Hexokinase: ubiquitous
What are pathways?
Series of enzyme reactions that do the chemistry proteins are capable of
T/F: Synthetic (anabolic) and degradative (catabolic) are simply identical sequences of enzymes working in 2 directions.
False
What pathway steps are regulated?
Ones that are out of equilibrium
T/F: Serine synthesis and degradation follow identical paths.
False
Catalysts change ____, NOT ___________.
Change rate, NOT equilibrium
Regulation (e.g. glycolysis) occurs at steps that are close to/far from equilibrium?
Far from
How can you regulate individual enzymes?
1. Inhibition or stimulation by small molecules
2. Covalent modification - inhibition or activation
3. Regulation of amount of enzyme
4. Compartmental separation
Inhibition or stimulation by small molecules (inc. allosteric) has an _________ effect.
Immediate
Covalent modification is often done by what?
Phosphorylation
Allows signaling control, rapid
Example of compartmental separation
Intracellular (transport of fatty acids into mitochondria for oxidation)
Glucose oxidation hormone
Insulin
Glucose synthesis hormone
Glucagon
Insulin is the hormone of the ________ state.
Well-fed
Glucagon is the hormone of the _______ state.
Starved
Epinephrine is the hormone of _____ ______.
Acute stress
Cortisol is the hormone for ______ ____ _________.
Longer term responses
Protein is how many calories per gram?
4 C/g
Fat is how many calories per gram?
9 C/g
How does blood glucose respond to a carbohydrate meal?
Plasma glucose peaks at about 40 minutes then declines
What is glycemic index?
The ability of a food to raise blood sugar
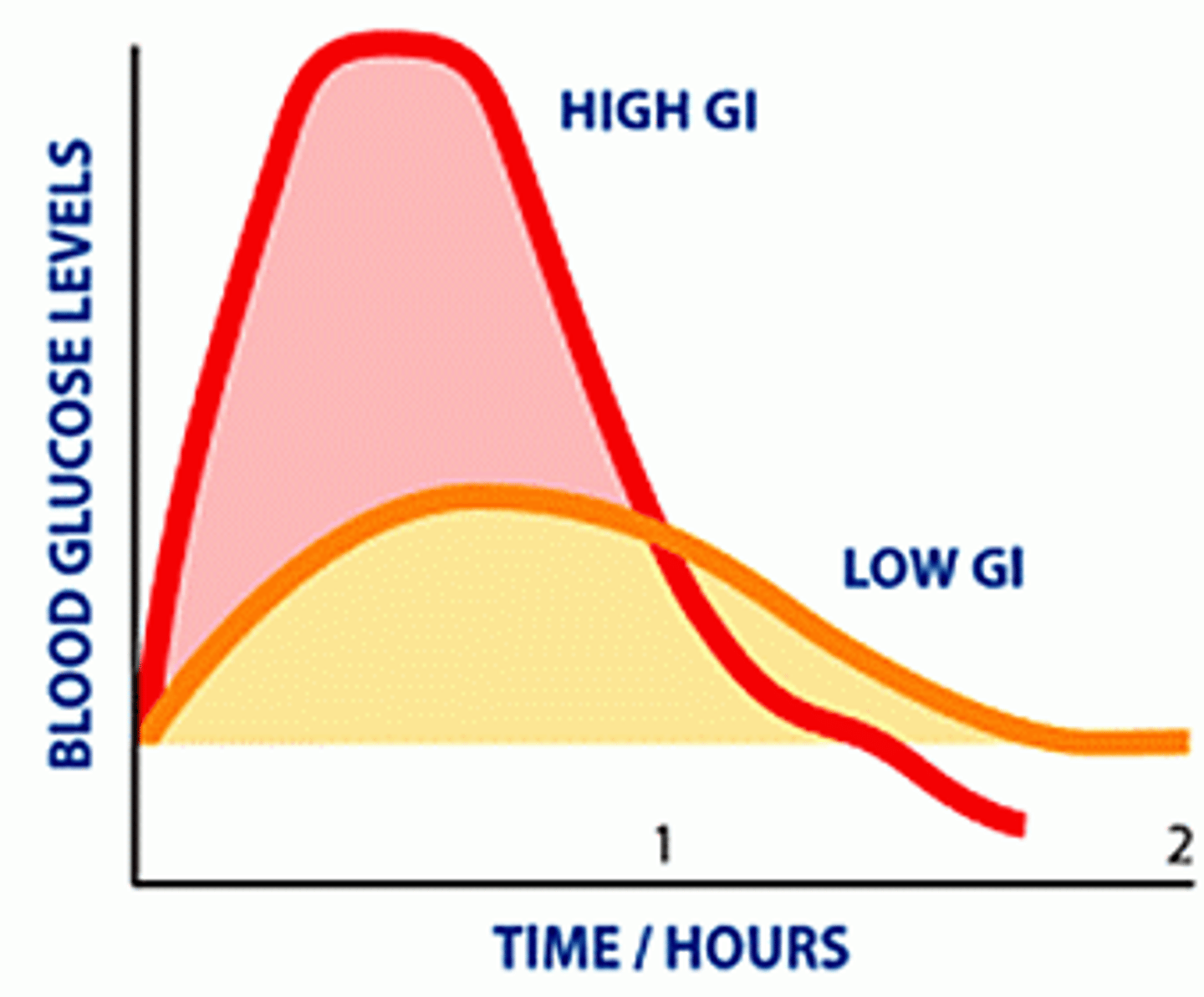
What is the area under the curve?
Blood glucose
Glycemic index varies for what?
Different carbohydrate foods
Glycemic index affects the size of the _______ response.
Insulin
Factors influencing GI
Sugar content (glucose vs. fructose)
Type of starch (amylose vs. amylopectin)
Physical barriers (bran)
Viscosity of soluble fiber (apple)
Fat and protein content (effects gastric transport)
Acid content (affects gastric transport)
Food processing (rolled oats vs. quick oats)
Cooking (al dente spaghetti)
Carbohydrate digestion starts in the _____.
Mouth
Digestion of what yields maltoses and limit dextrins?
α-Amylase
What bonds does α-Amylase break?
α-1,4 bonds
Does digestion occur in the stomach?
No
Digestion continues in the _________ with what secretions and what disaccharidases?
Intestine
Pancreatic secretions
Membrane-bound disaccharidases
What does cholecystokinin (CCK) do?
Stimulates release of bile and pancreatic enzymes (including amylase)
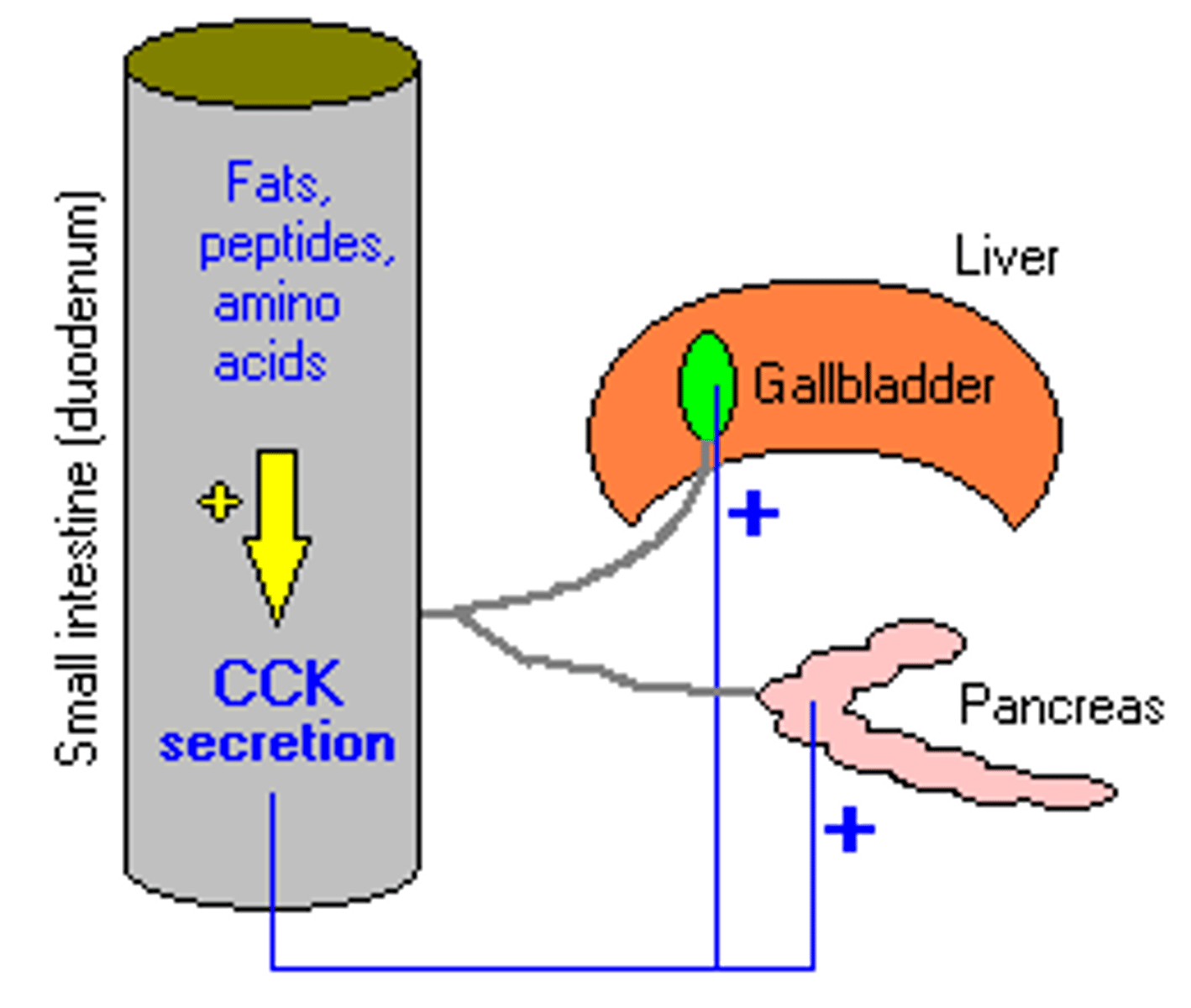
Food reaching the small intestine stimulates I-cells to produce what?
CCK
What is the action of α-amylase?
Cleaves glucose α1→4 glucose bonds but not glucose α1→6 glucose bonds
Brush border CHO enzymes
Sucrase-isomaltase
Maltase-glucoamylase
Lactase
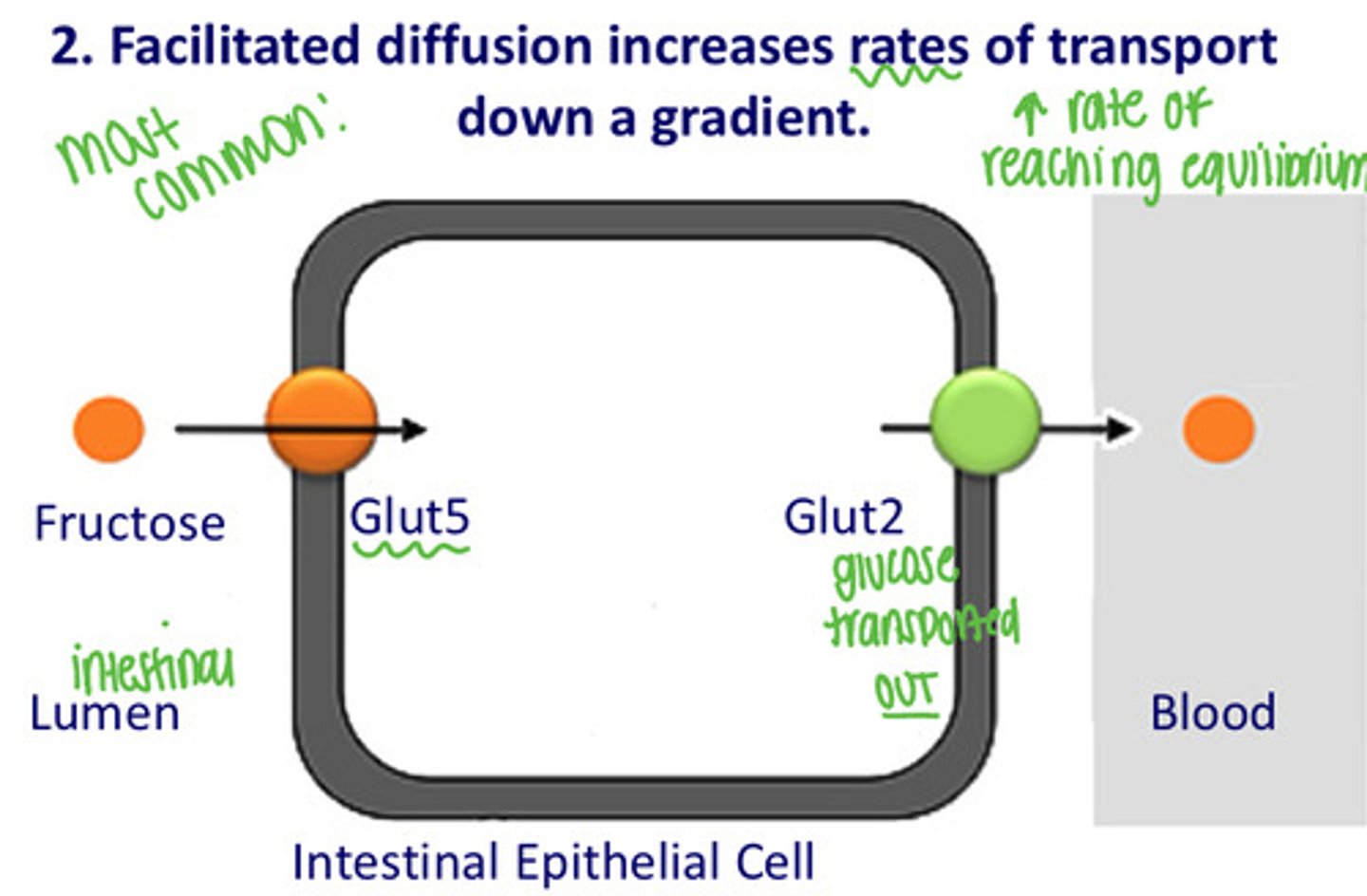
How do monosaccharides generated at the brush border get into the system?
1. Simple diffusion down a gradient
2. Facilitated diffusion
3. Active transport
When is simple diffusion used to get monosaccharides into the system?
Used for "rare sugars" such as arabinose
Least important
Facilitated diffusion increases _____ of transport down a gradient.
Rates
What is the most common method of monosaccharides generated at the brush border getting into the system?
Facilitated diffusion
Active transport increases transport _____, even against a ________.
Rates, even against a gradient
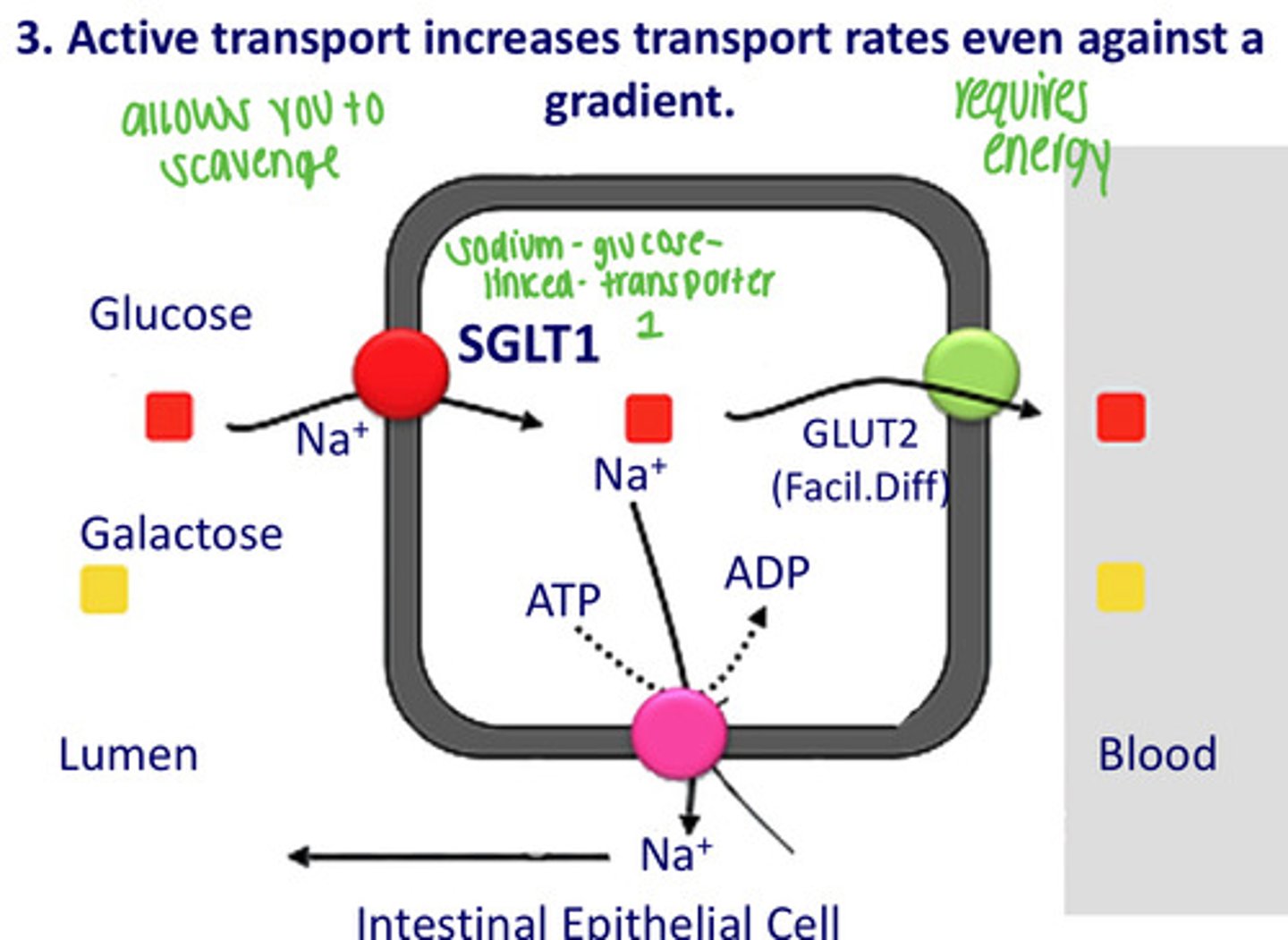
What does SGLT1 do?
Transports glucose and galactose
Sodium-glucose-linked-transporter-1
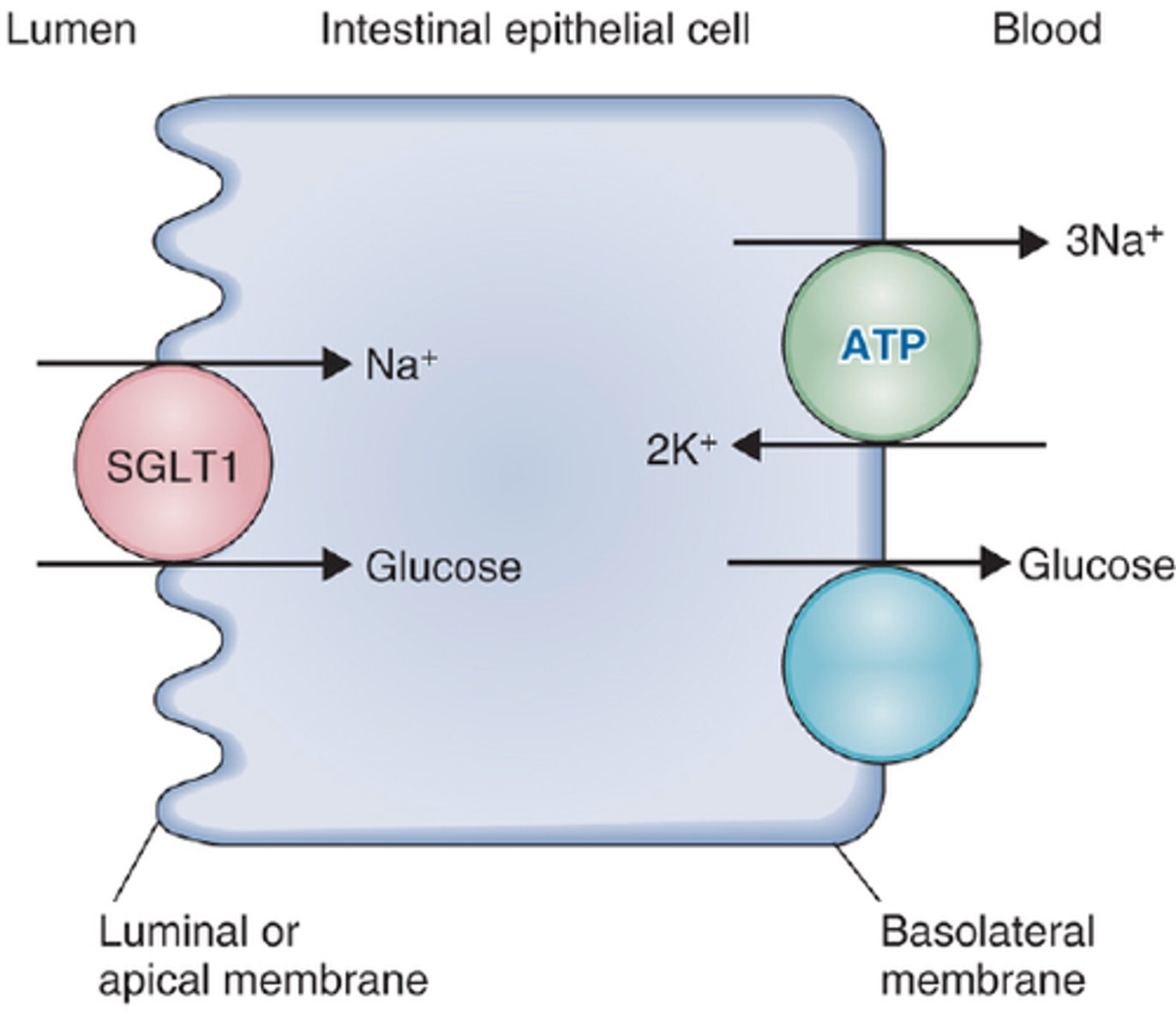
What are the 2 types of SGLTs?
Intestinal mucosa
Kidney brush border (SGLT2)
What are the 3 types of facilitative transporters?
GluT4
GluT2
GluT5
GluT4 is responsive to _______.
Insulin
Which GluT transporters are not responsive to insulin?
GluT2
GluT5
Where is GluT2 found?
Liver, pancreas, intestine
Where is GluT5 found and what does it transport?
Small intestine
Transports fructose
The portal circulation carries glucose from where to where?
Intestine to liver
What is the first organ to see elevated carbohydrates after eating?
Liver
T/F: Once in the circulation, glucose still needs to be transported.
True
Liver removes _______ from the circulation.
Glucose
What might you expect from GluT2 deficiency in the liver?
Fanconi-Bickel Syndrome (liver not filtering glucose)
Post-prandial hyperglycemia
What reduces blood sugar?
Insulin
Insulin reduces blood sugar by doing what?
By stimulating uptake into muscle and fat cells
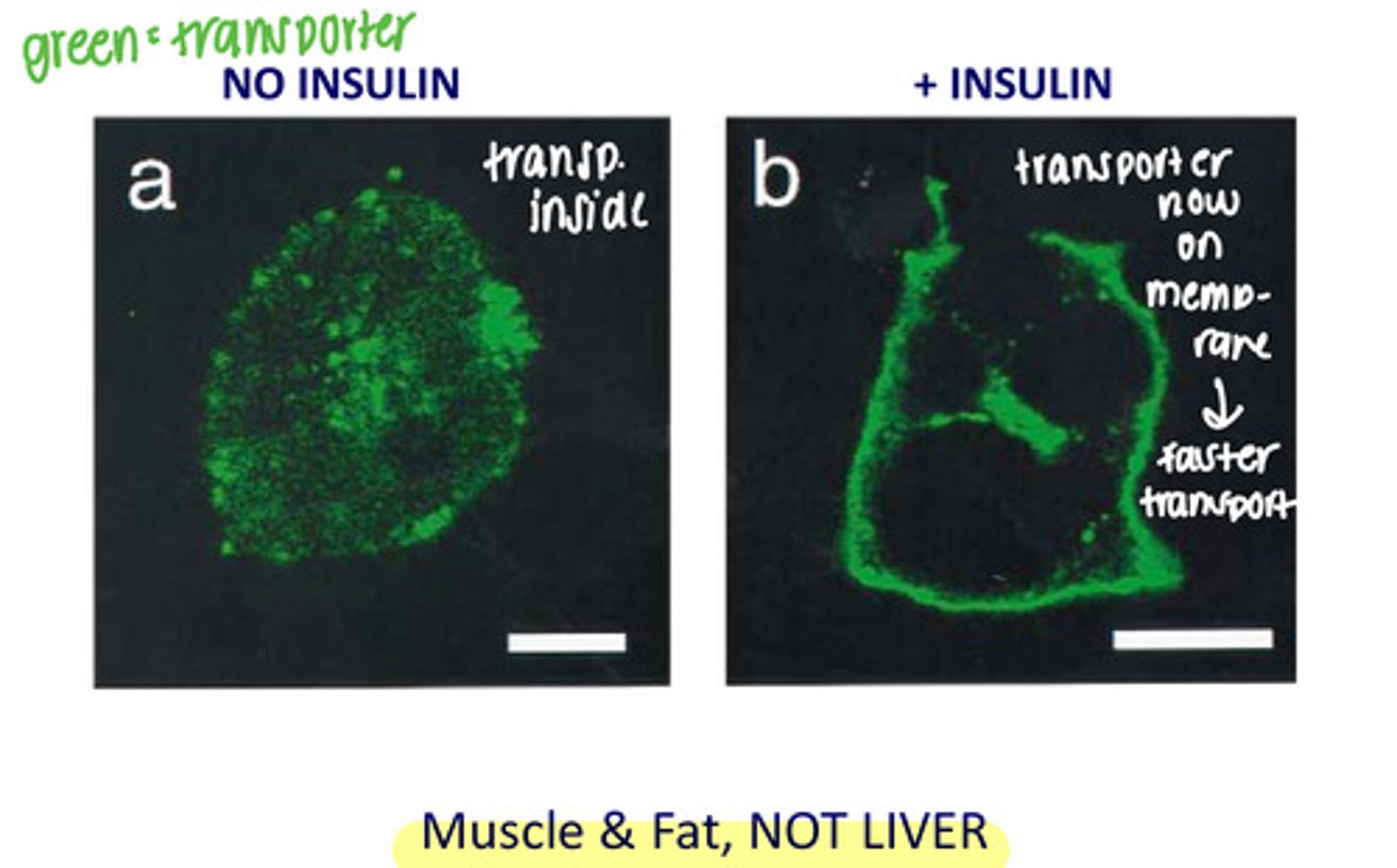
How does insulin stimulate glucose uptake?
Increasing # receptors on plasma membrane
What does SGLT2 in the kidney do?
Prevents loss of glucose to the urine
Humans lack the enzyme to break down _________ sugars found in beans.
Raffinose sugars
What happens if you cannot digest the carb?
Intestinal bacteria metabolize these sugars, giving off hydrogen and carbon dioxide
Lactose intolerance is a deficiency in what?
Lactase
When can lactose intolerance be diagnosed?
Failure to observe glucose increase after lactose challenge
Can observe H2 in the breath
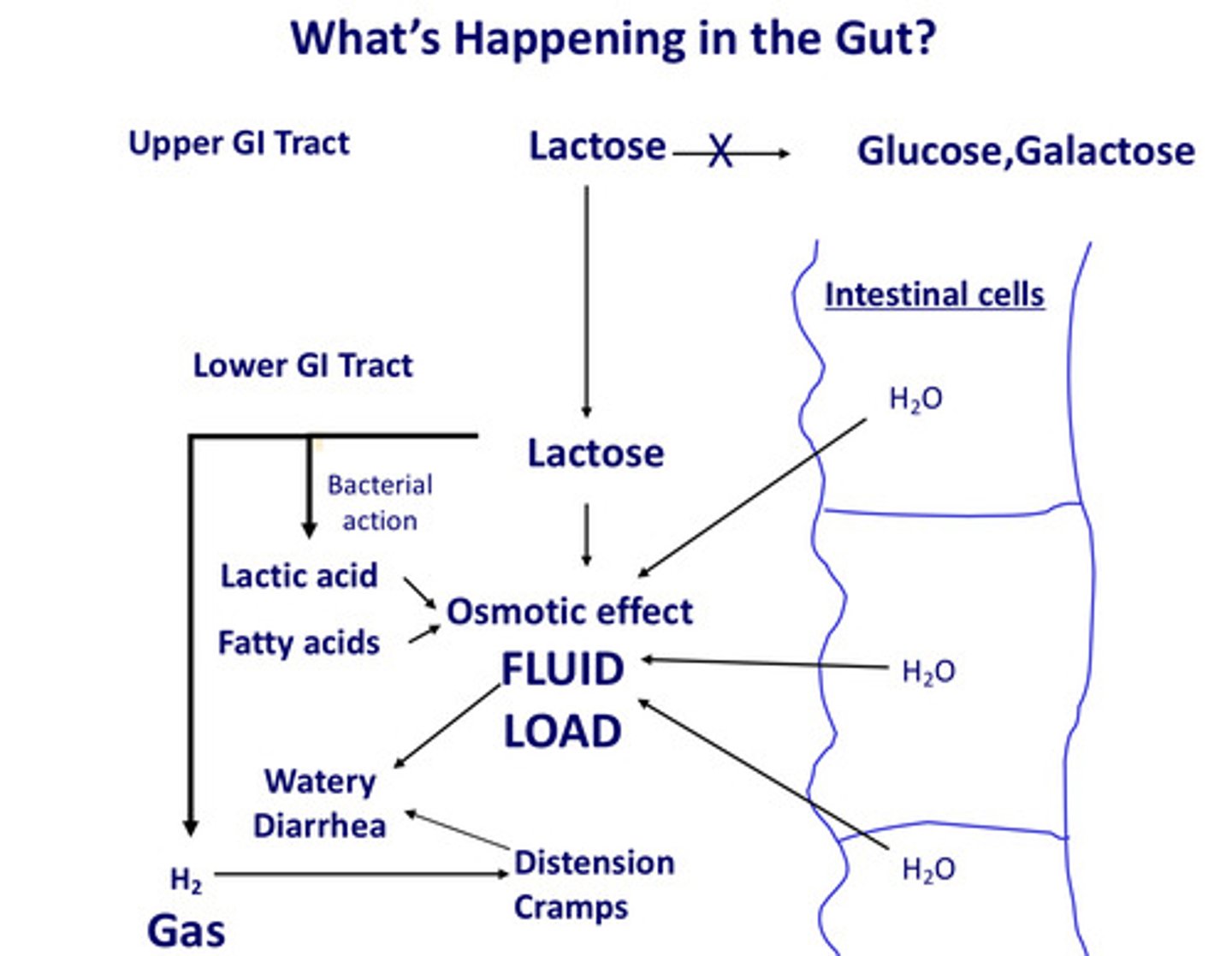
What happens in the gut in lactose intolerance?
Lactose cannot be converted to glucose and galactose
Sources of malabsorption problems
Diet of poorly digestible CHO
Release of pancreatic amylase
Disaccharidases
Absorption by intestinal epithelia
What happens if you cannot release pancreatic amylase?
Pancreatic disease
Cystic fibrosis
What happens if disaccharidases don't work?
Low enzyme levels
-Lactase
-Intestinal illness
Genetic defects
-Sucrose-isomaltase
What happens if absorption by intestinal epithelia is faulty?
Transporter insufficiency
-SGLT1, fructose
Celiac Disease
What are major components of dietary fiber?
Undigested polysaccharides
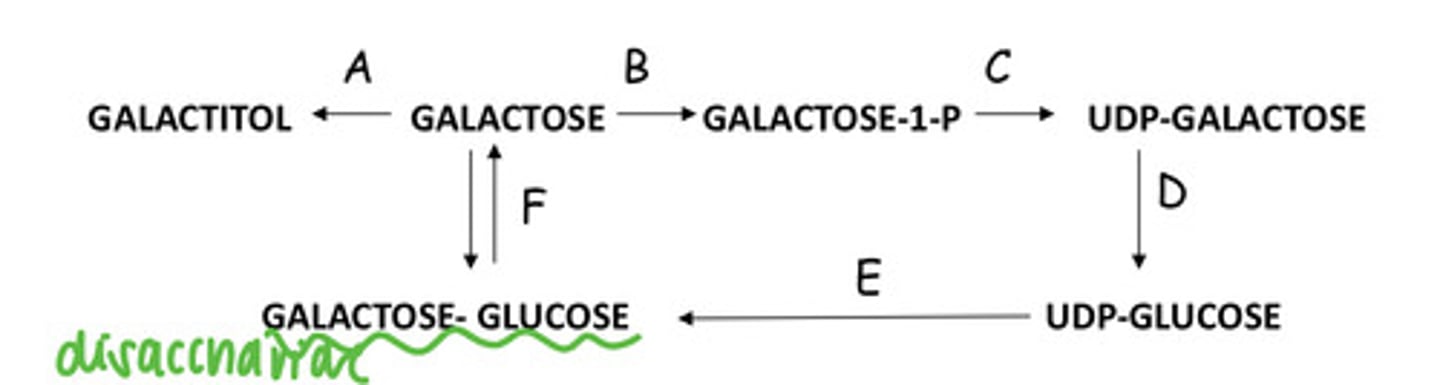
Your infant is recovering from an intestinal virus. She has abdominal distension after feeding. A deficiency of which enzyme causes the problem?
F
Carbohydrate digestion begins in the mouth with which enzyme?
Amylase
Carbohydrate digestion continues in the small intestine with which enzymes?
Pancreatic amylase
Brush border disaccharidases
-Lactase
-Sucrase-Isomaltase
-Glycoamylase/maltase
-α-dextrinase (isomaltase)
What do bacteria in the colon do?
Digest unabsorbed carbs
Active transport of glucose occurs in which tissue?
Kidney to prevent loss of glucose to the urine
Insulin increases the transport of glucose from the blood into...?
Muscle cells