Contact Forces
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Static friction (Fs)
Friction acting on stationary bodies:
Fs ≤ μsFn
This allows us to find the maximum static force. If applied force < no movement. Applied force ≥ then movement.
Dynamic friction (Fd)
Friction acting on moving bodies
To find out how much friction is acting on the moving body use this equation:
Ff = μdFN
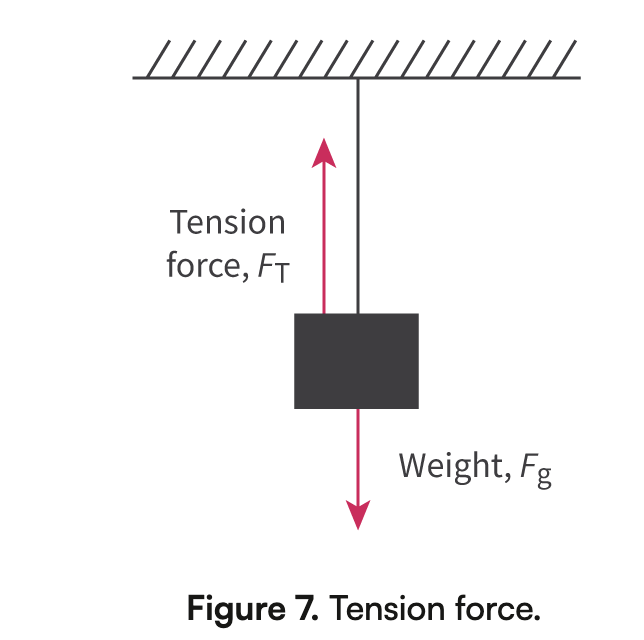
Tension force (Ft)
Same magnitude but opposite direction of the applied force
Ft= mg × ma
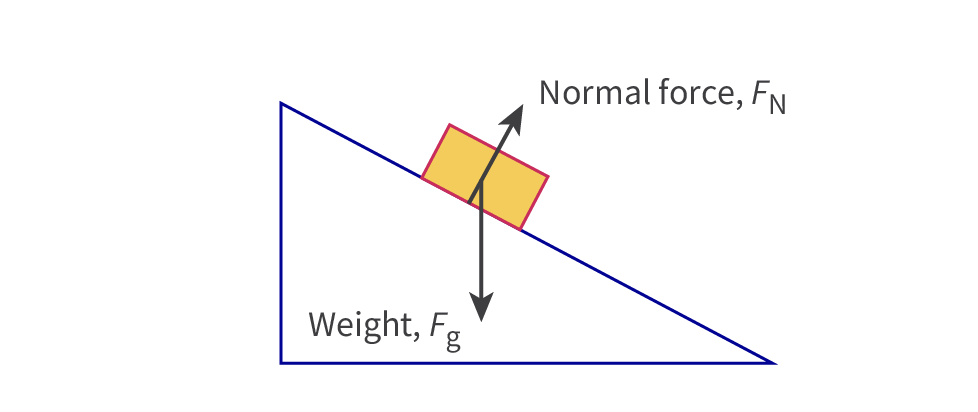
Normal force (Fn)
It is a contact force which happens when to objects in contact push against each other. Normal force acts perpendicular to the surface which is pushing against the body
Elastic restoring force (Fh)
Springs can be either compressed or elongated away from their natural length when they are not touched. The elastic restoring force returns the spring to its natural length. Following Hookes law which states the the force restoring it to its natural length is proportional to the extension of the spring.
Fh= -kx
Viscous Drag Force (Fd)
Force from a liquid or gas that opposes the movement of a body making it a resistive force. Viscous drag is calculated using this equation: Fd=6πηrv. (6π × viscosity of fluid × radius of sphere × velocity of sphere)
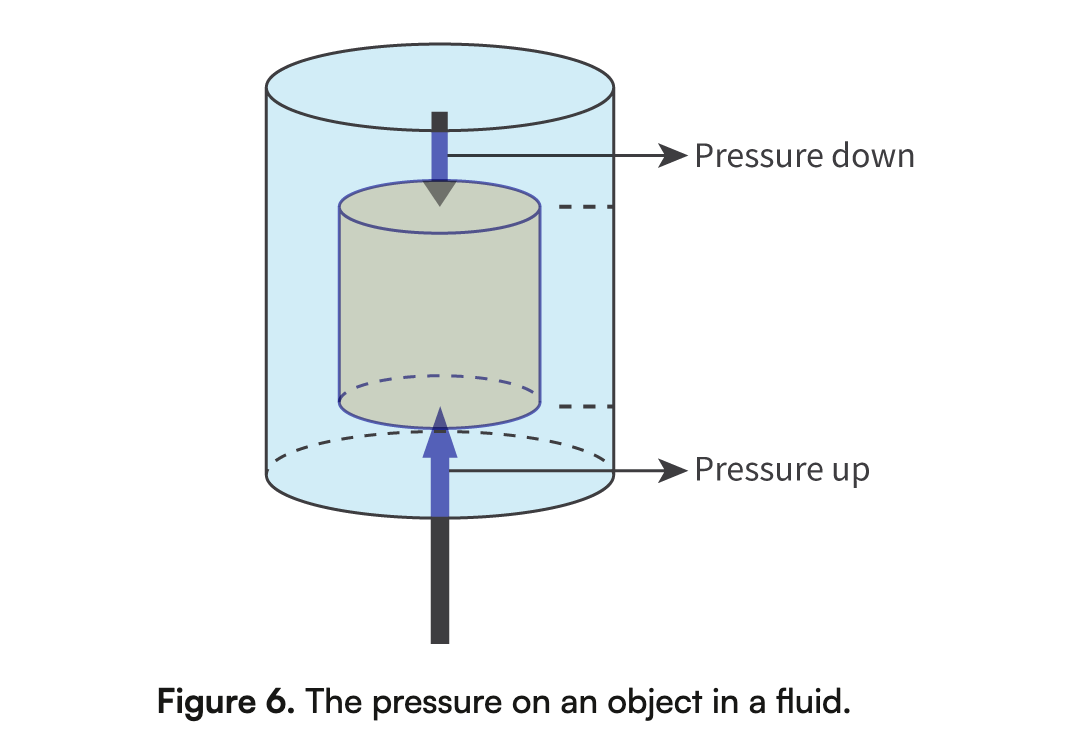
Buoyancy (Fb)
Caused by the differences of pressure between top and bottom of a fluid.
Fb= pVg (density of the fluid × Volume of fluid displaced × 9.8)