PBS 1.2 Heart Labeling
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
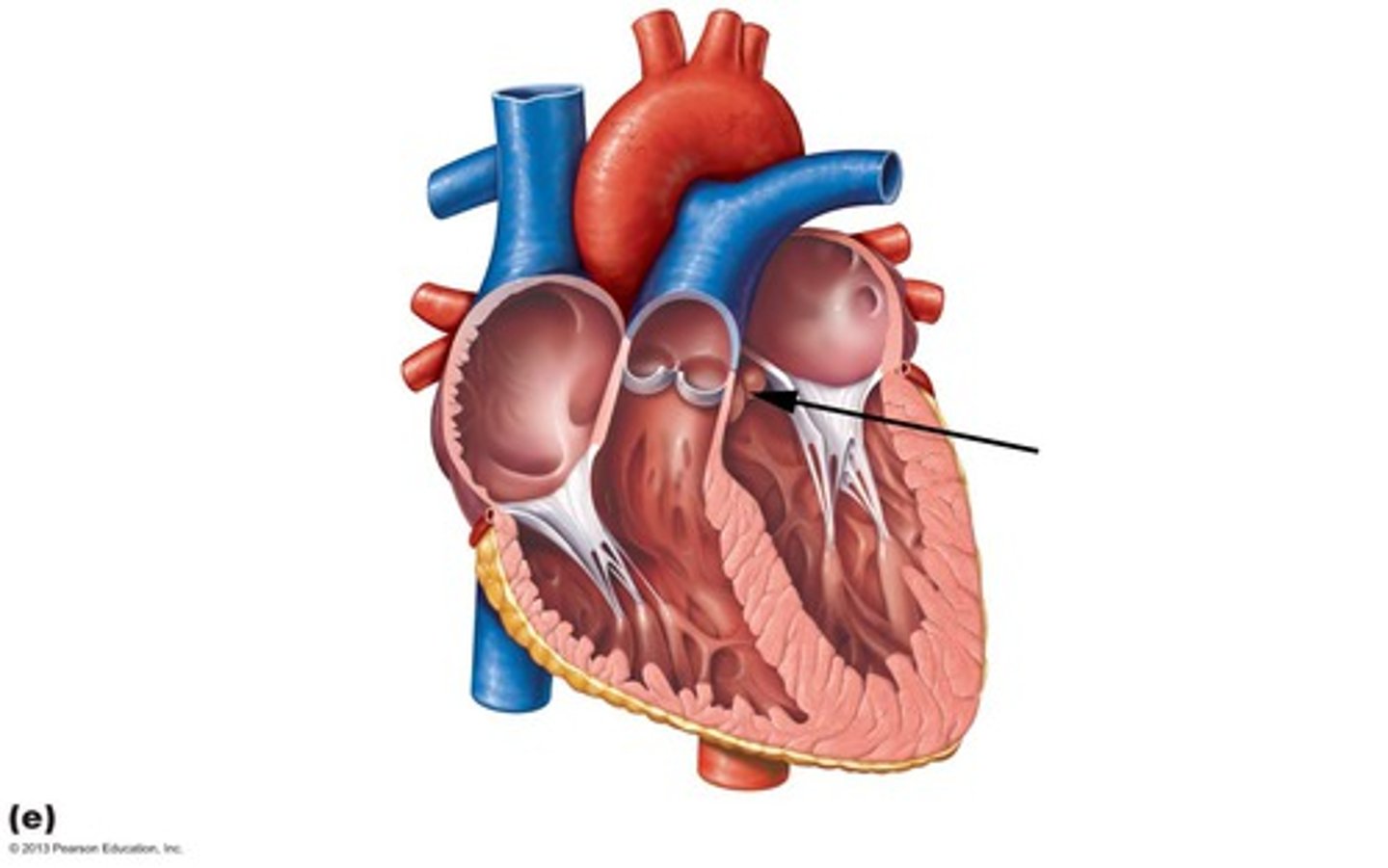
Valves of the heart
mechanical devices that permit the flow of blood in one direction only
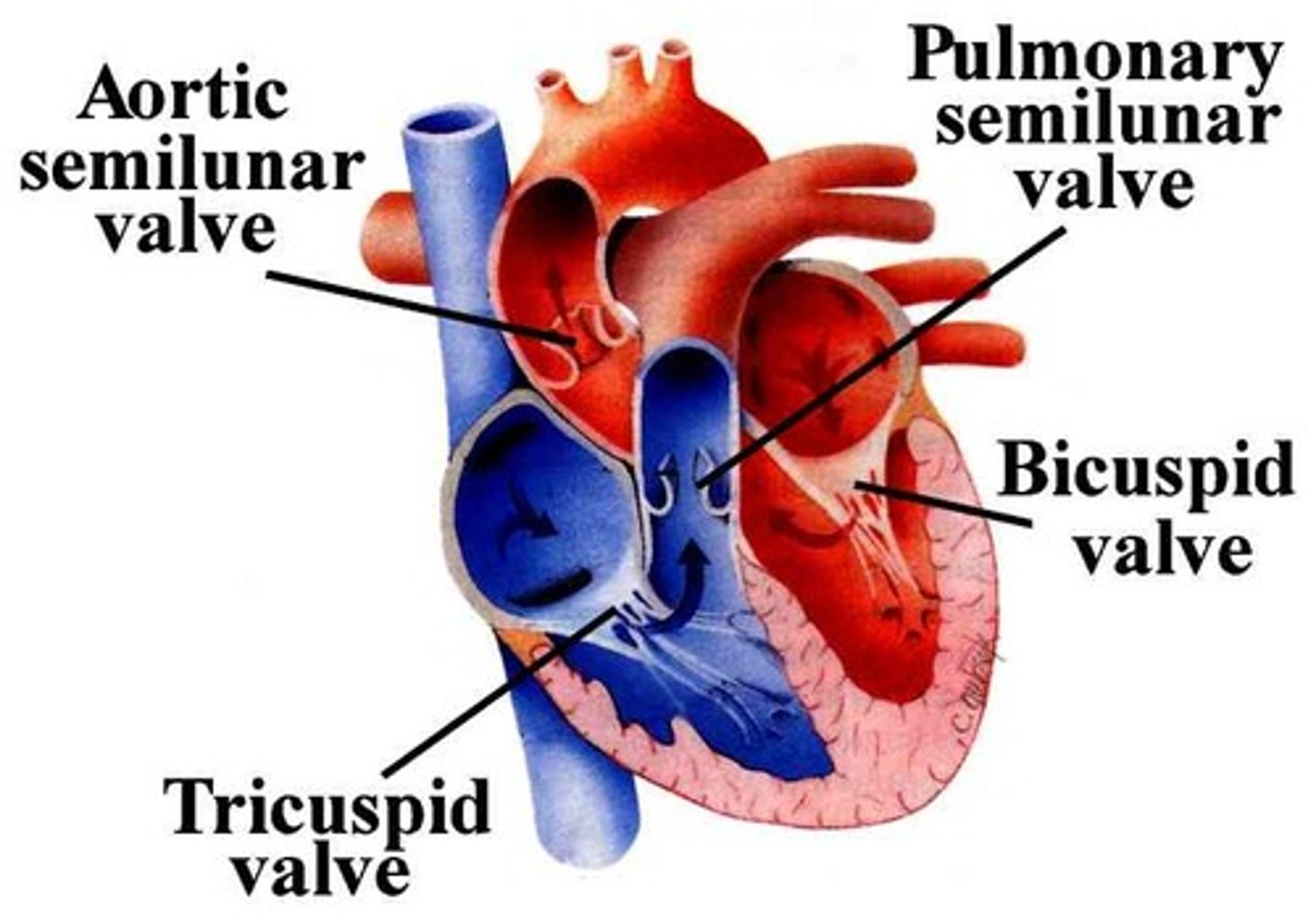
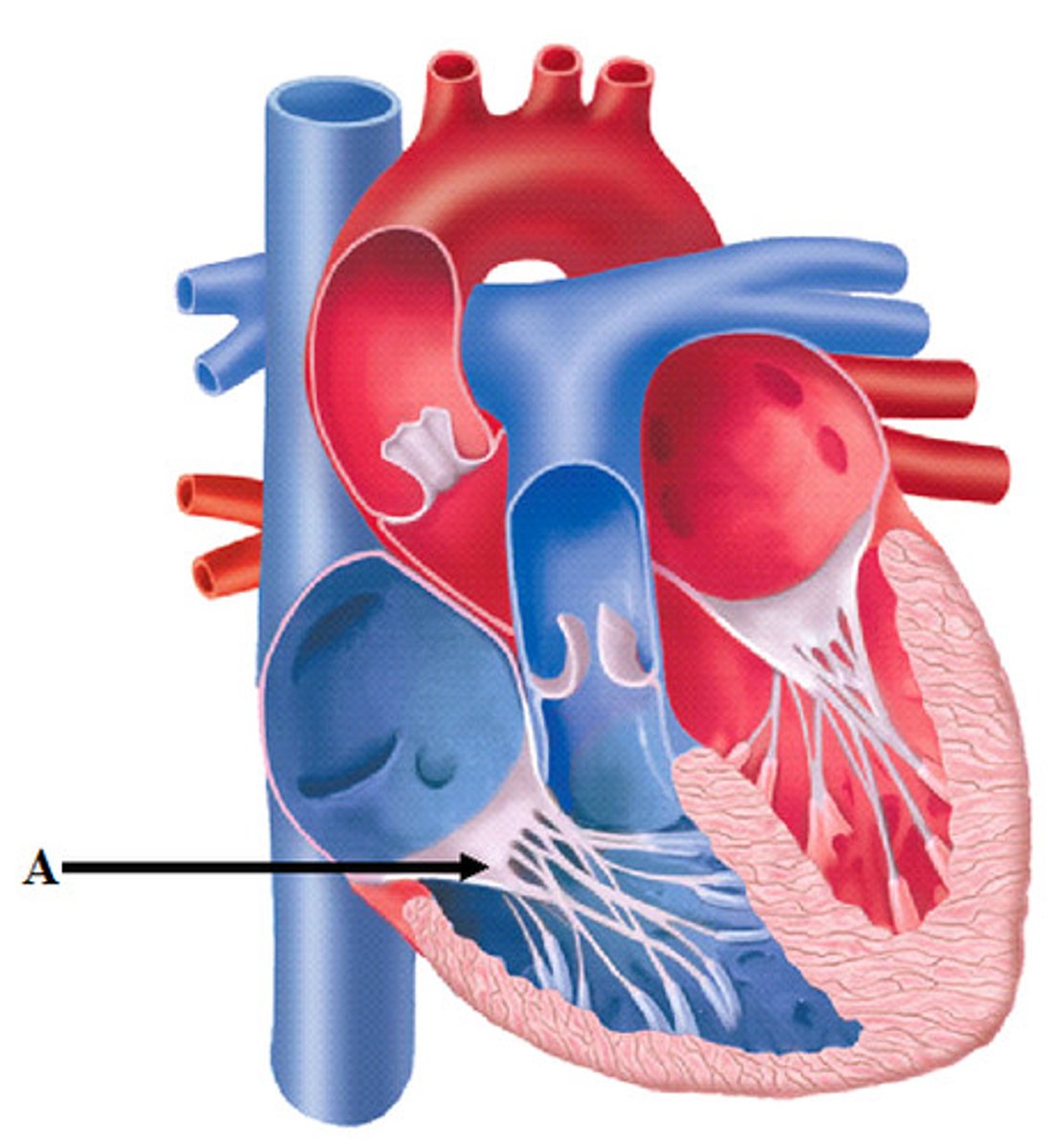
Tricupsid Valve
valve between the right atrium and the right ventricle
Mitral Valve
valve between the left atrium and the left ventricle; bicuspid valve
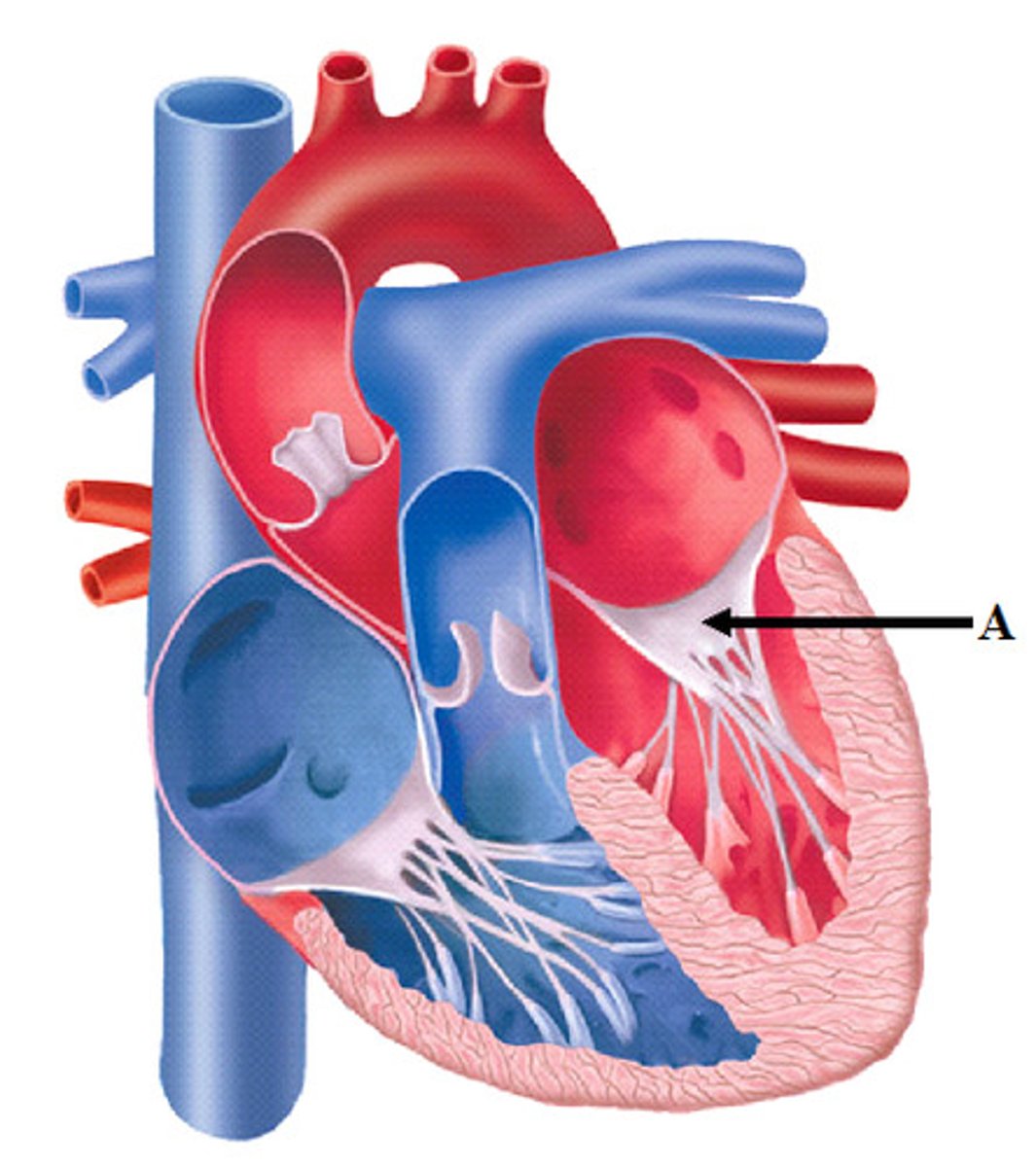
Pulmonary Valve
valve positioned between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery
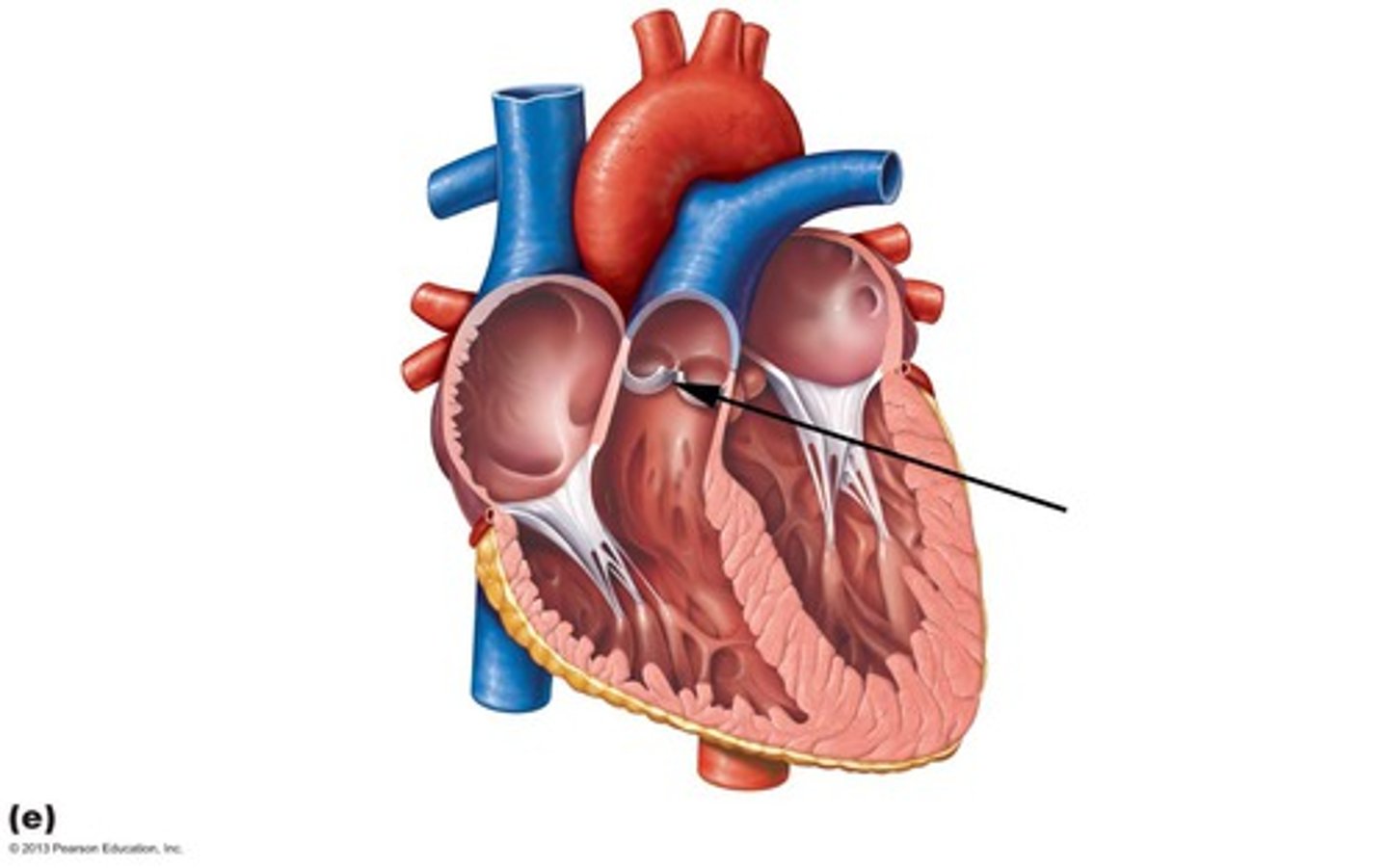
Aortic Valve
The semilunar valve separates the aorta from the left ventricle and prevents blood from flowing back into the left ventricle.
Arteries
carry blood away from the heart
Veins
Blood vessels that carry blood back to the heart
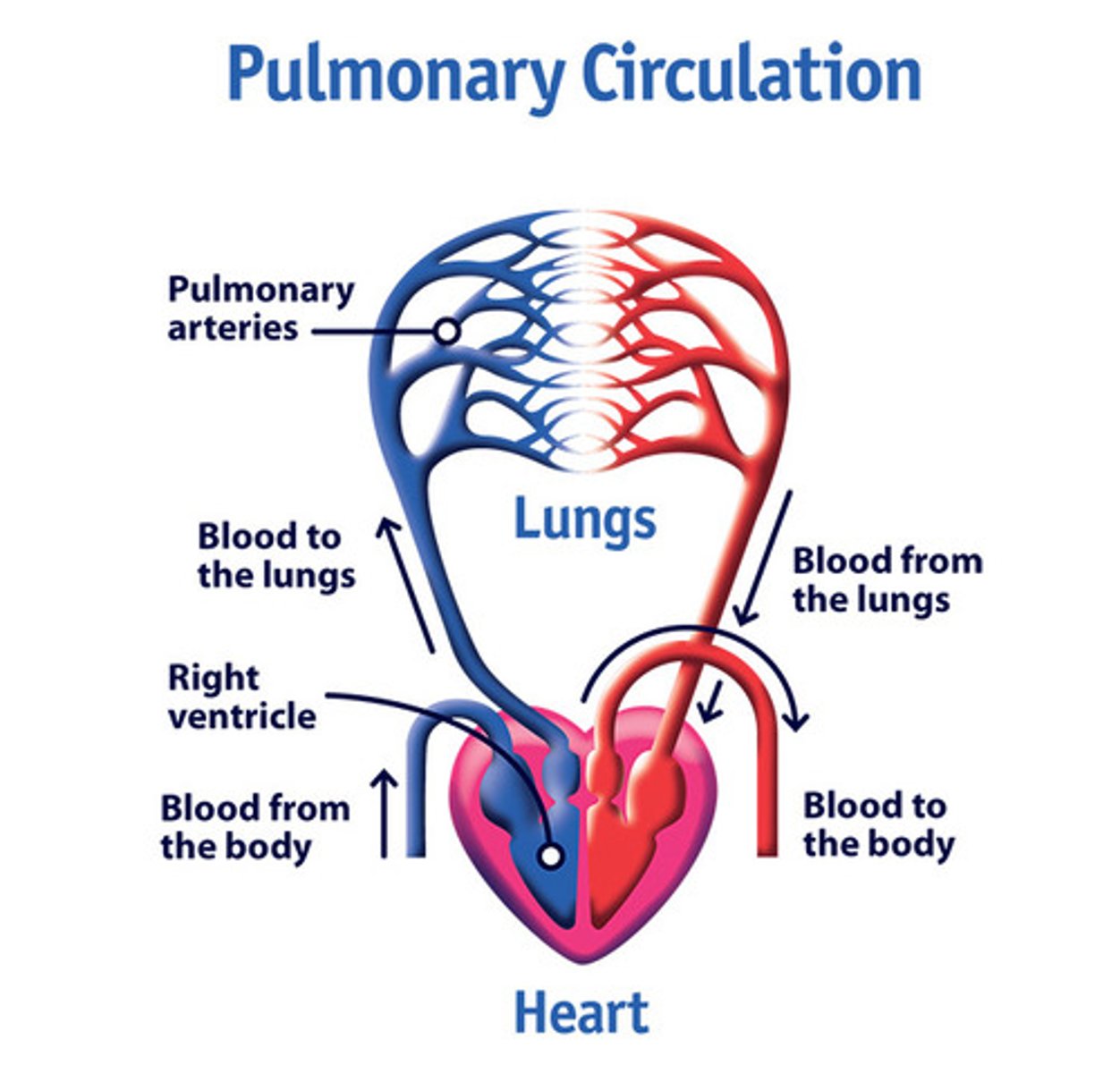
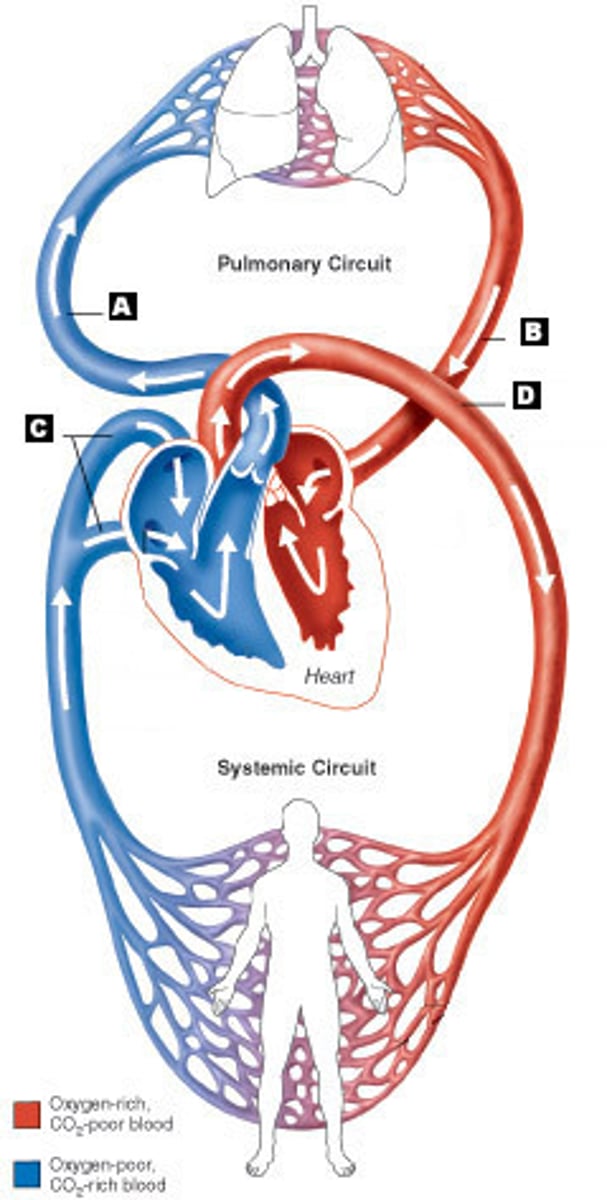
Pulmonary Circulation
flow of blood from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart
*right side of the heart
Systemic Circulation
circulation that supplies blood to all the body except to the lungs
blood from the heart to the body and back to the heart and is controlled by the action of the left side of the heart.
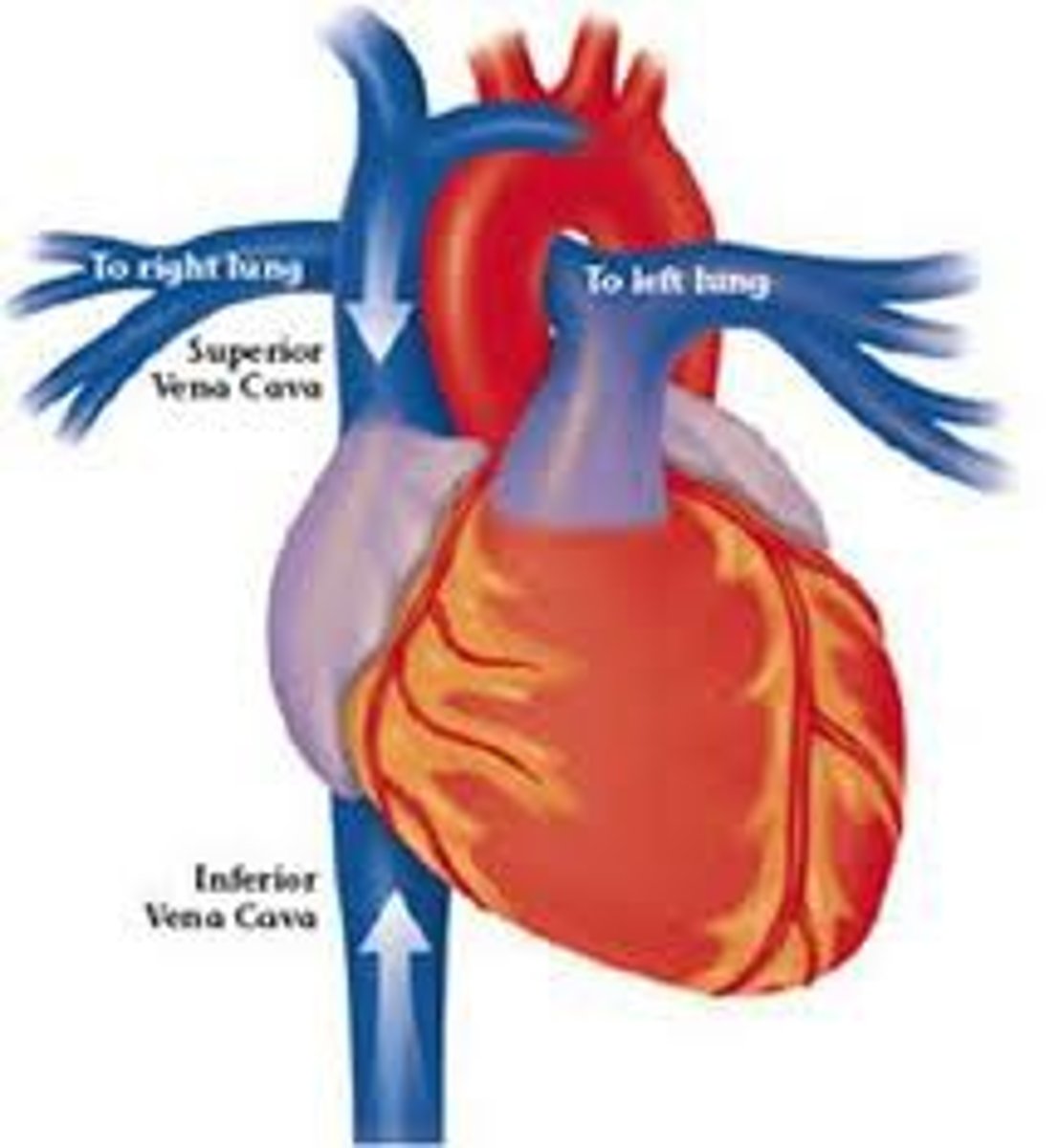
Superior and Inferior Vena Cava
veins that carry deoxygenated blood to the right atrium from the systemic circuit
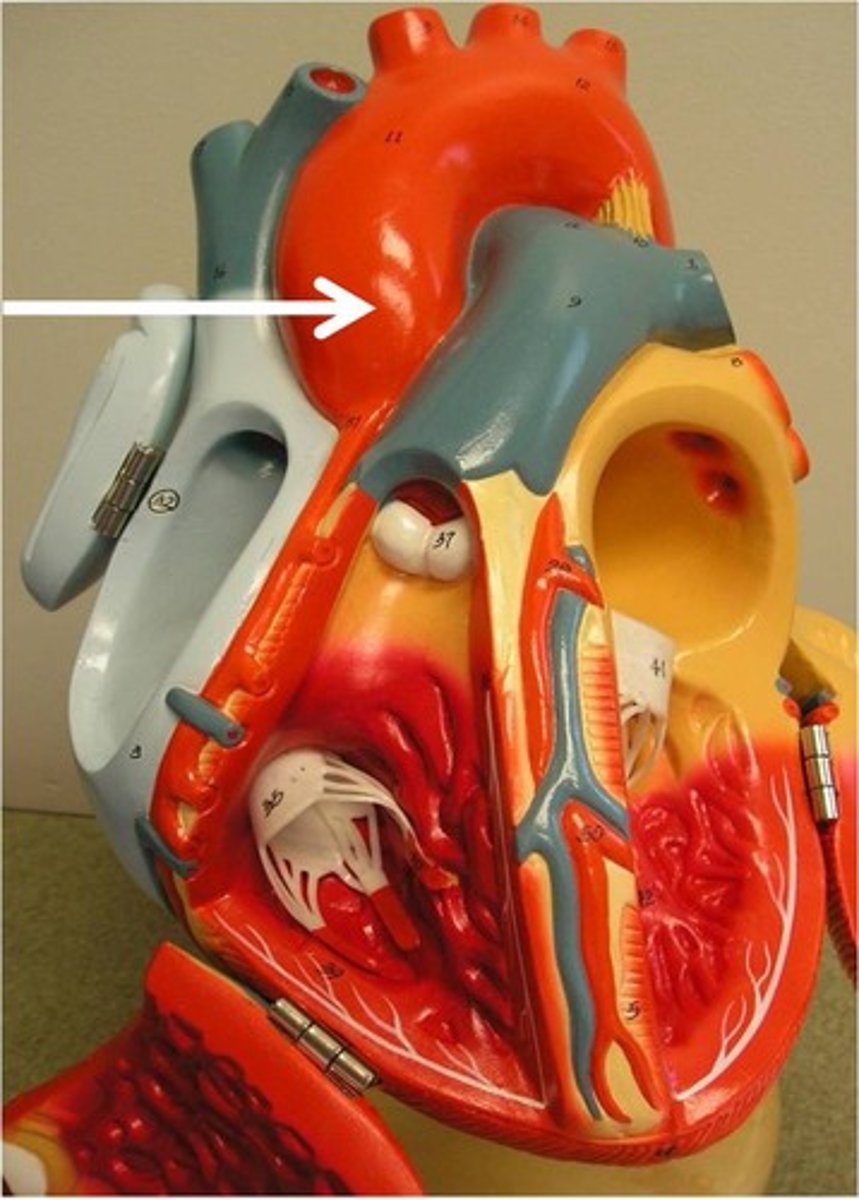
aorta
Largest artery in the body
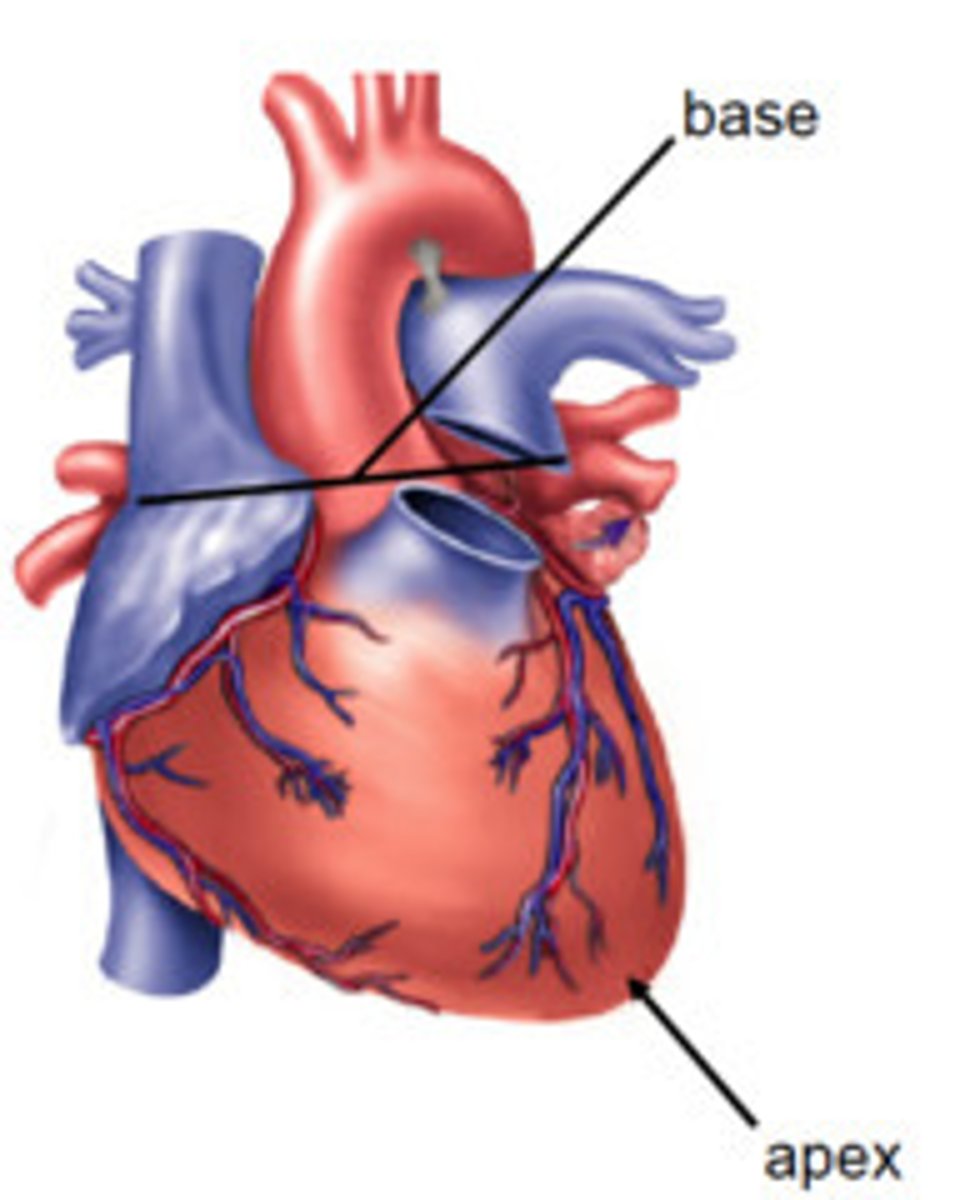
apex of the heart
lower tip of the heart
auricles
"flaps" on the atria to increase the volume of the chamber
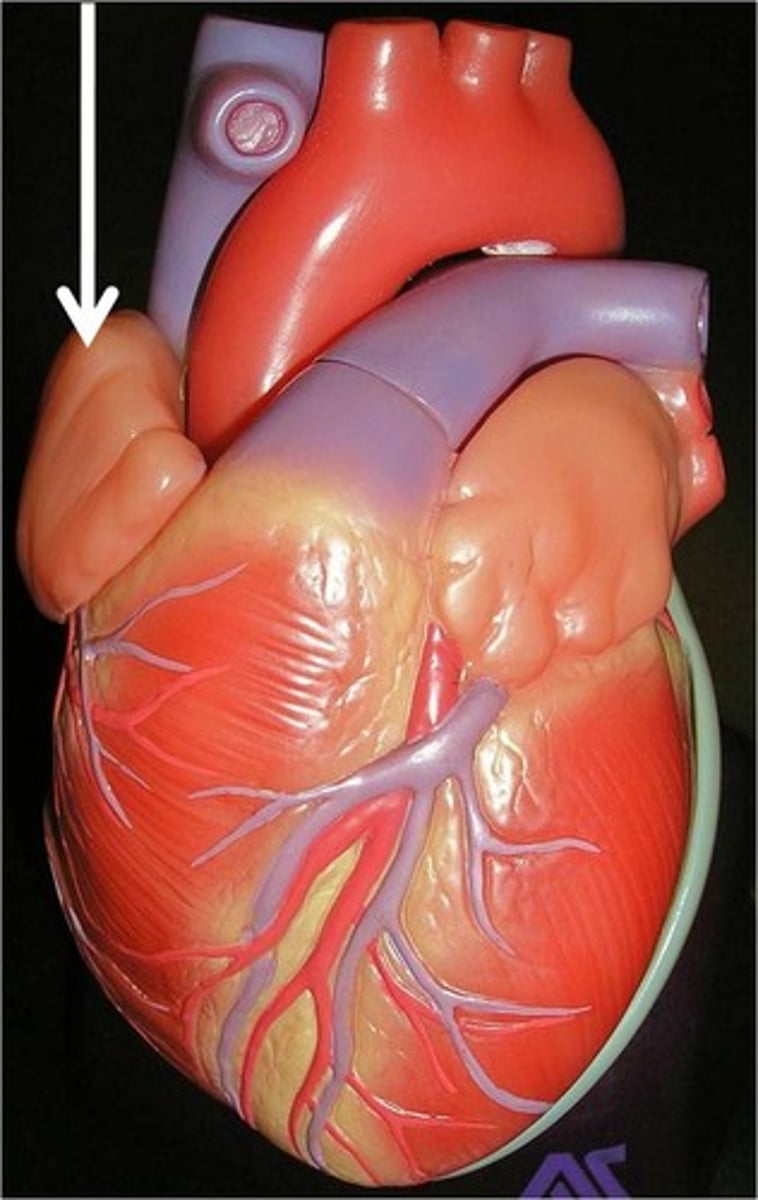
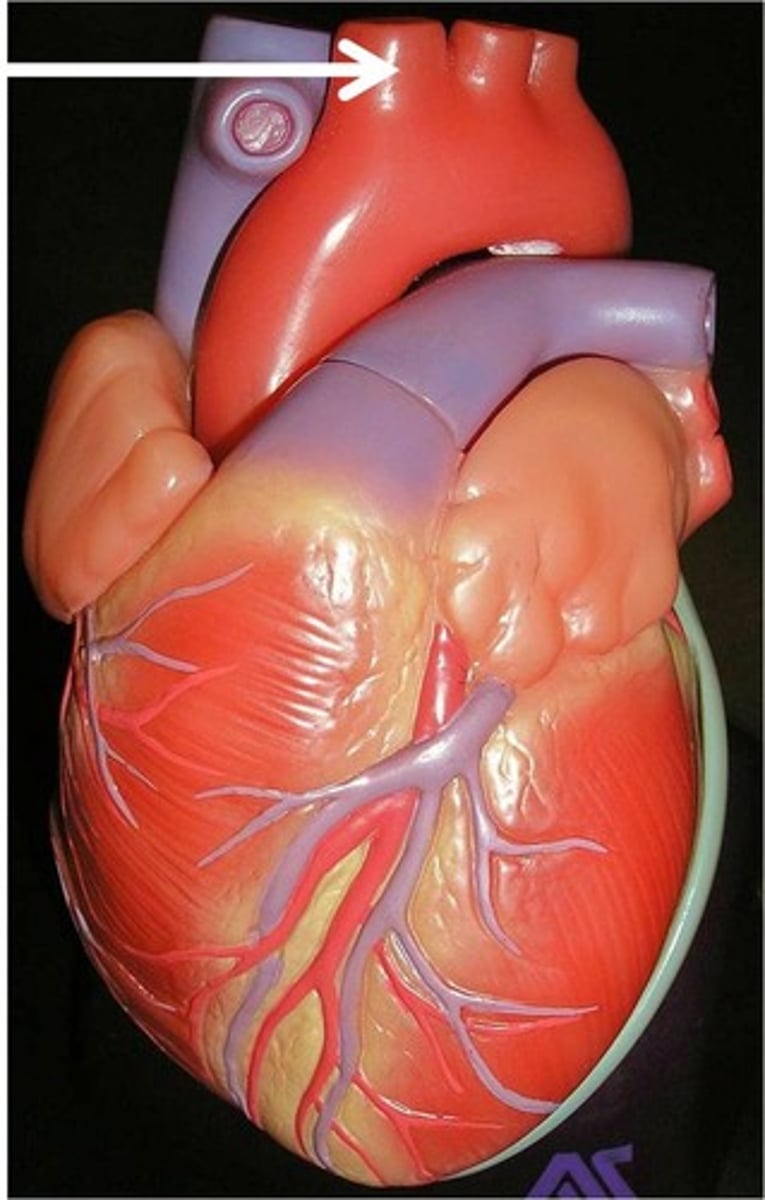
brachiocephalic artery
The first major branch off of the aorta and the major artery to the forelimbs and head.
chordae tendineae
thin bands of fibrous tissue that attach to the valves in the heart and prevent them from inverting
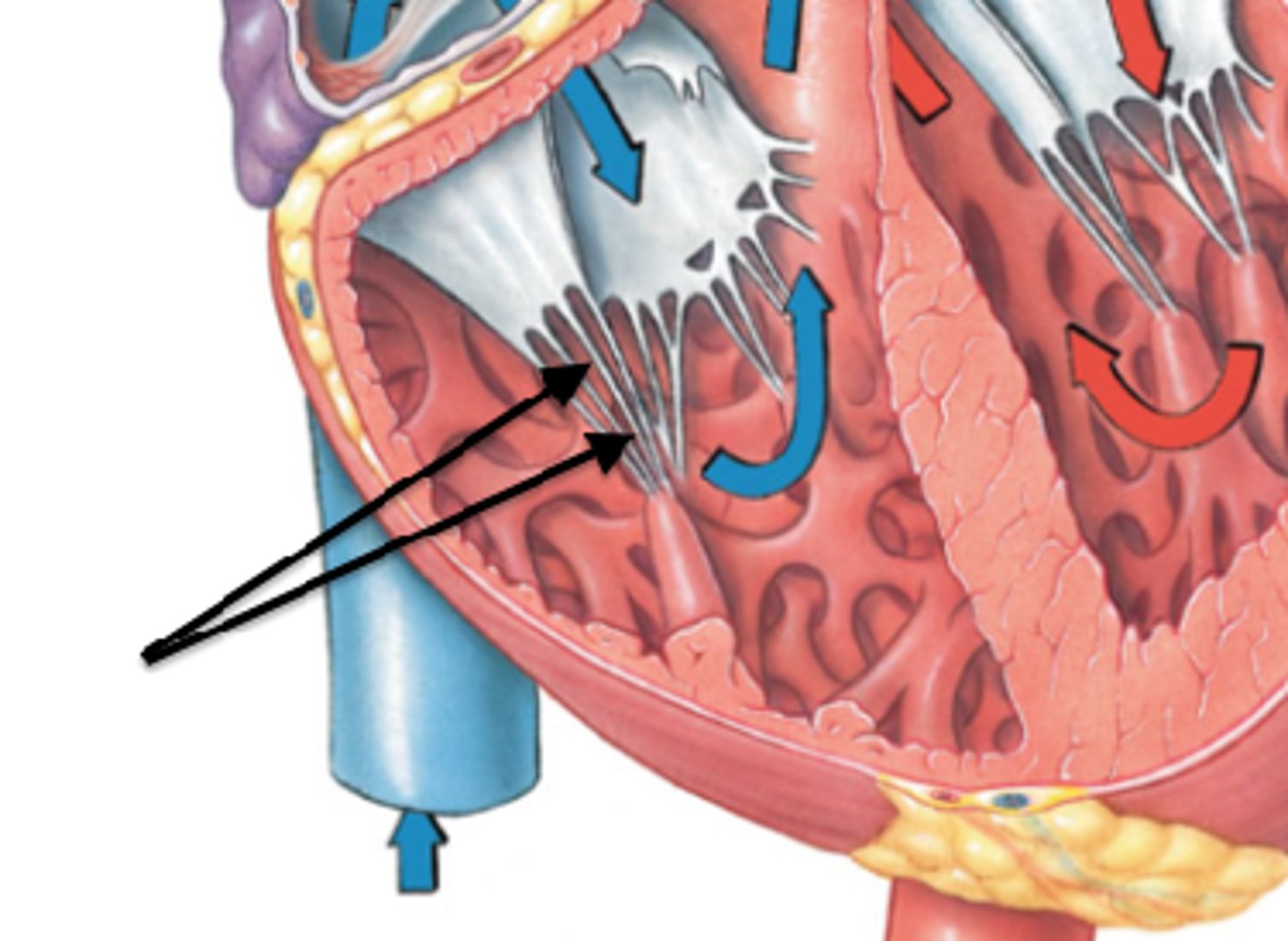
papillary muscles
responsible for pulling the atrioventricular valves closed by means of the chordae tendineae
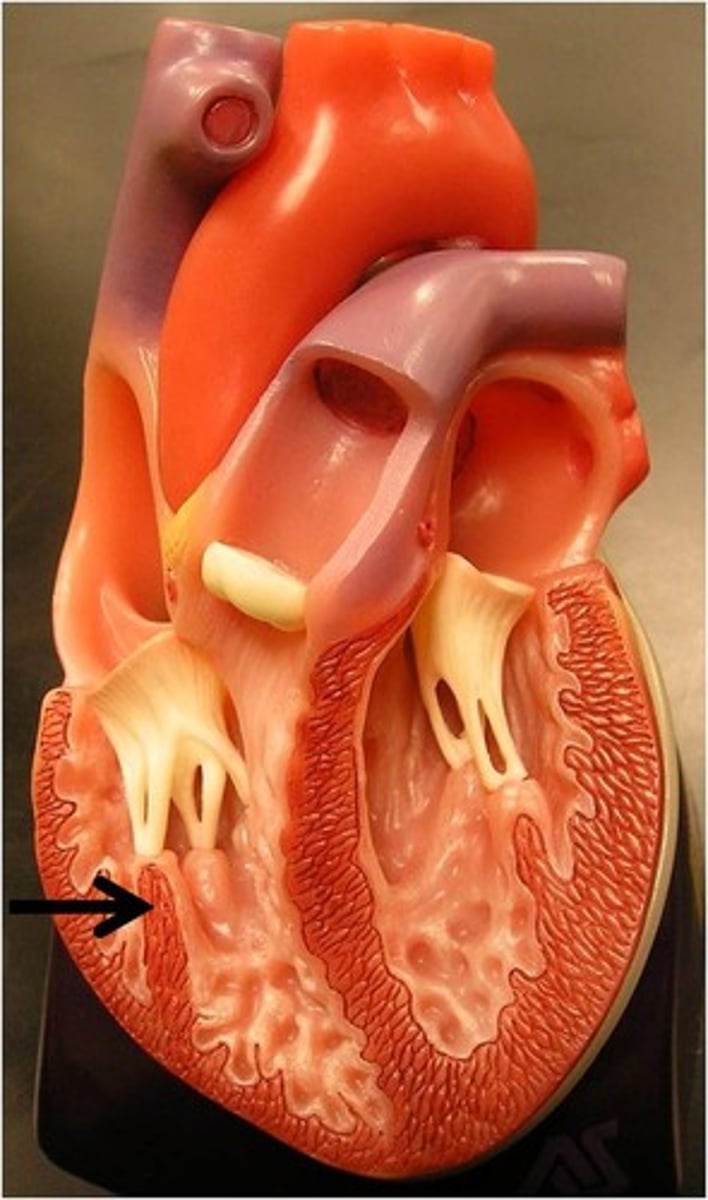
coronary artery
The artery that supplies heart tissue with blood
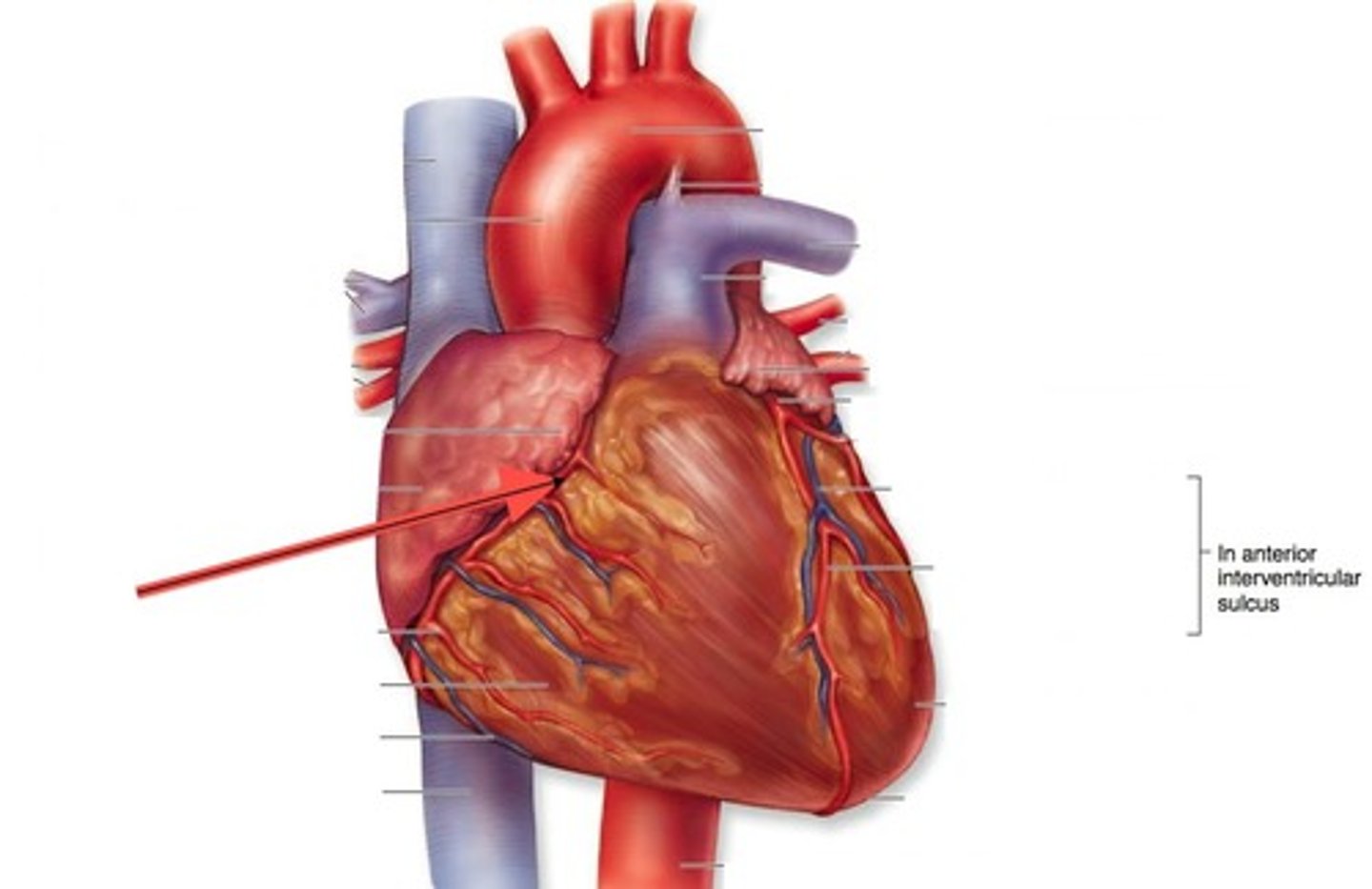
left ventricle
pumps oxygenated blood to the body, thickest of the 4 chambers
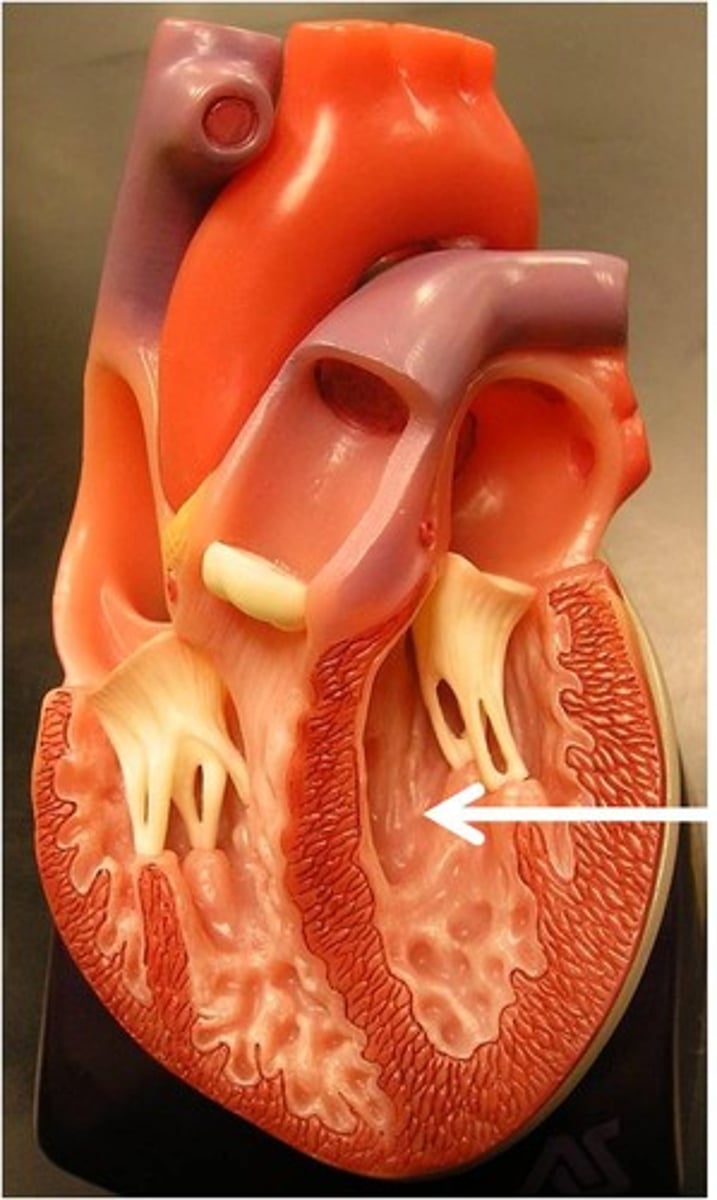
left atrium
receives oxygenated blood from the lungs
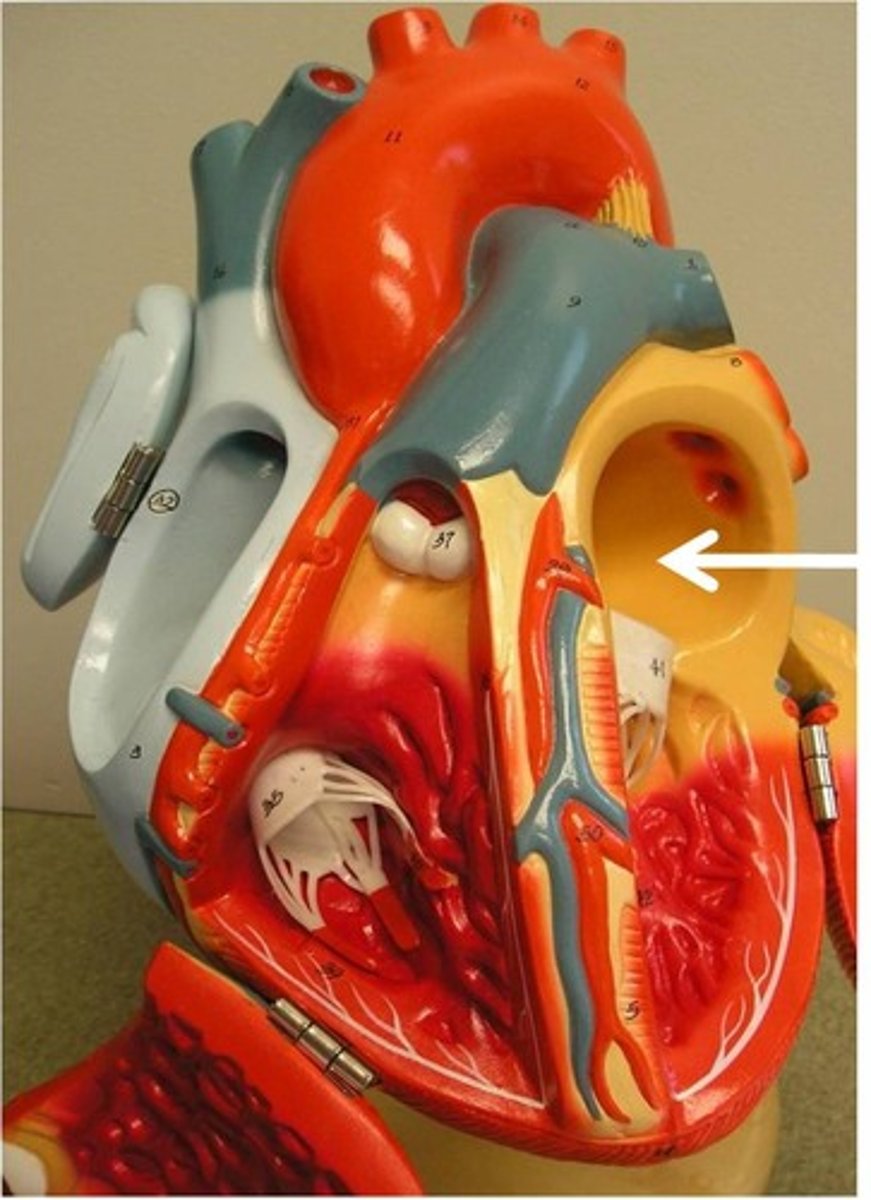
right atrium
Receives deoxygenated blood from the body
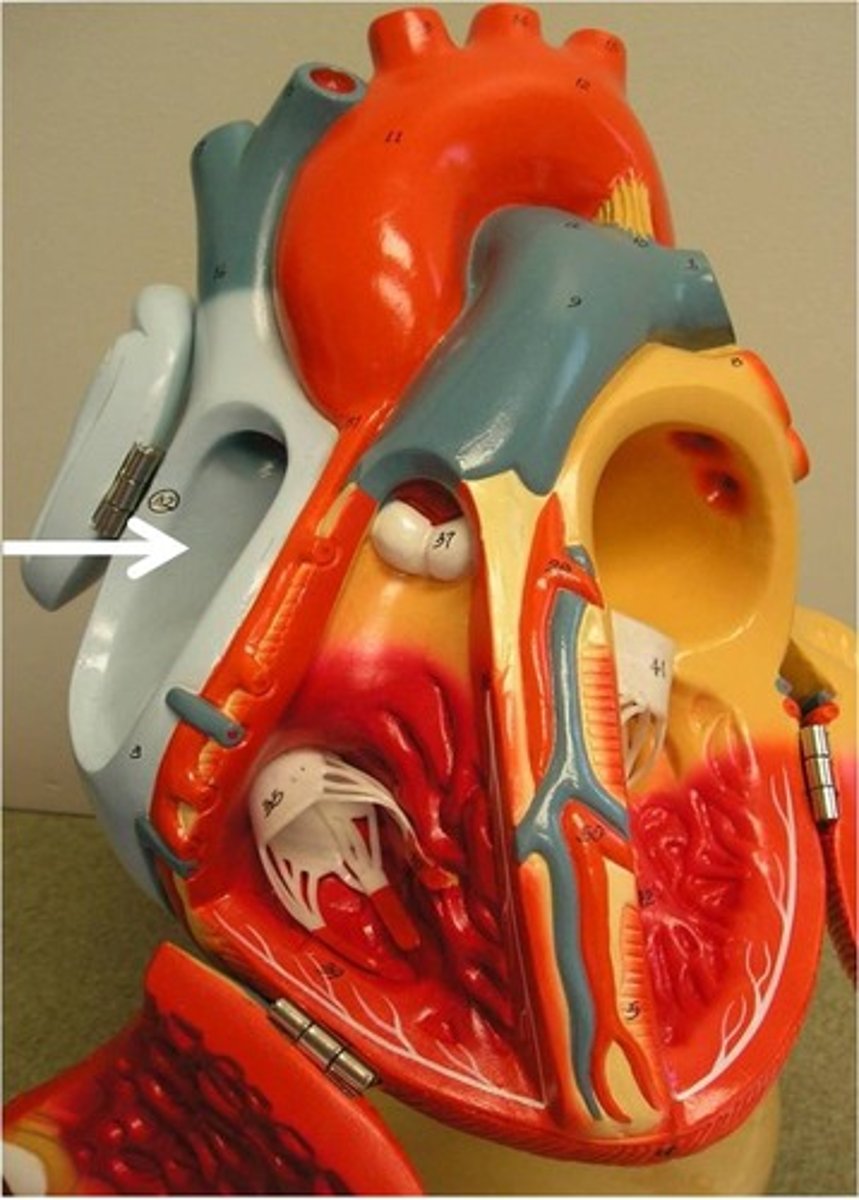
right ventricle
pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs via the pulmonary artery
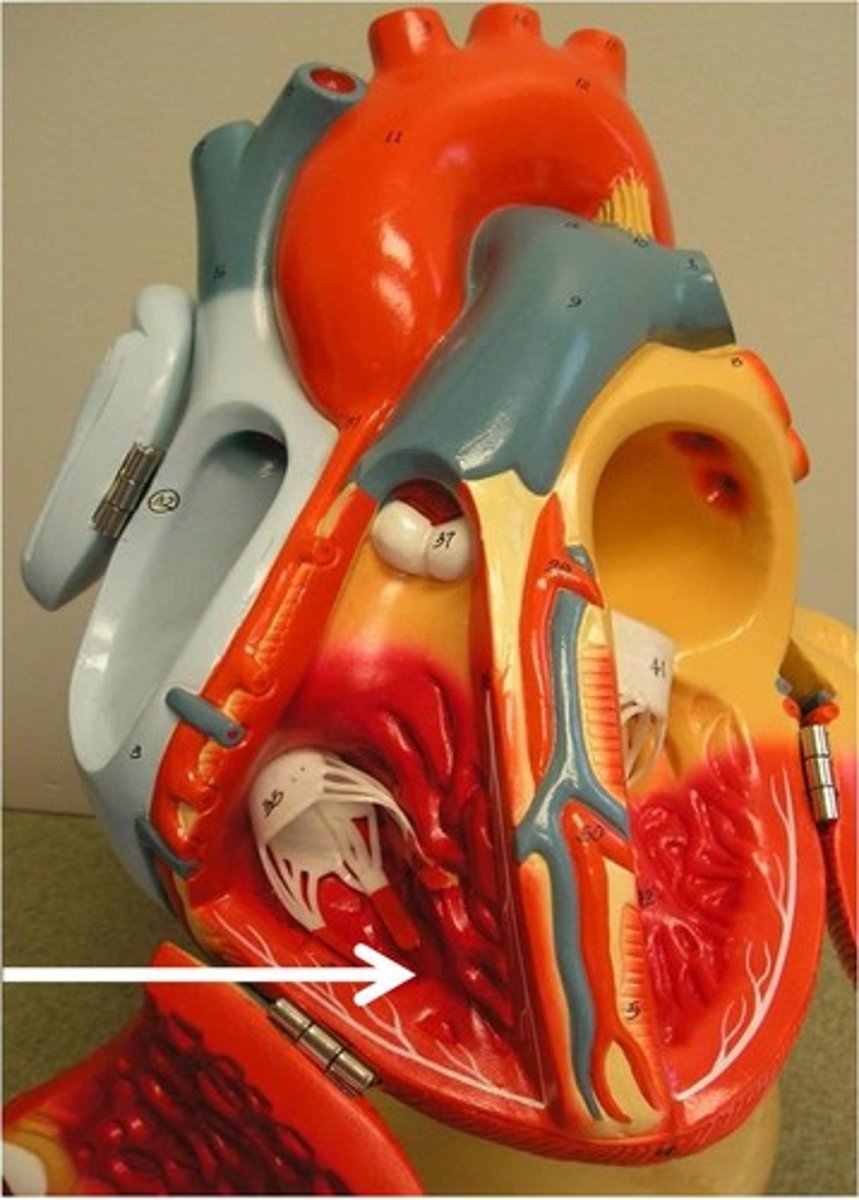
pulmonary artery
artery carrying oxygen-poor blood from the heart to the lungs
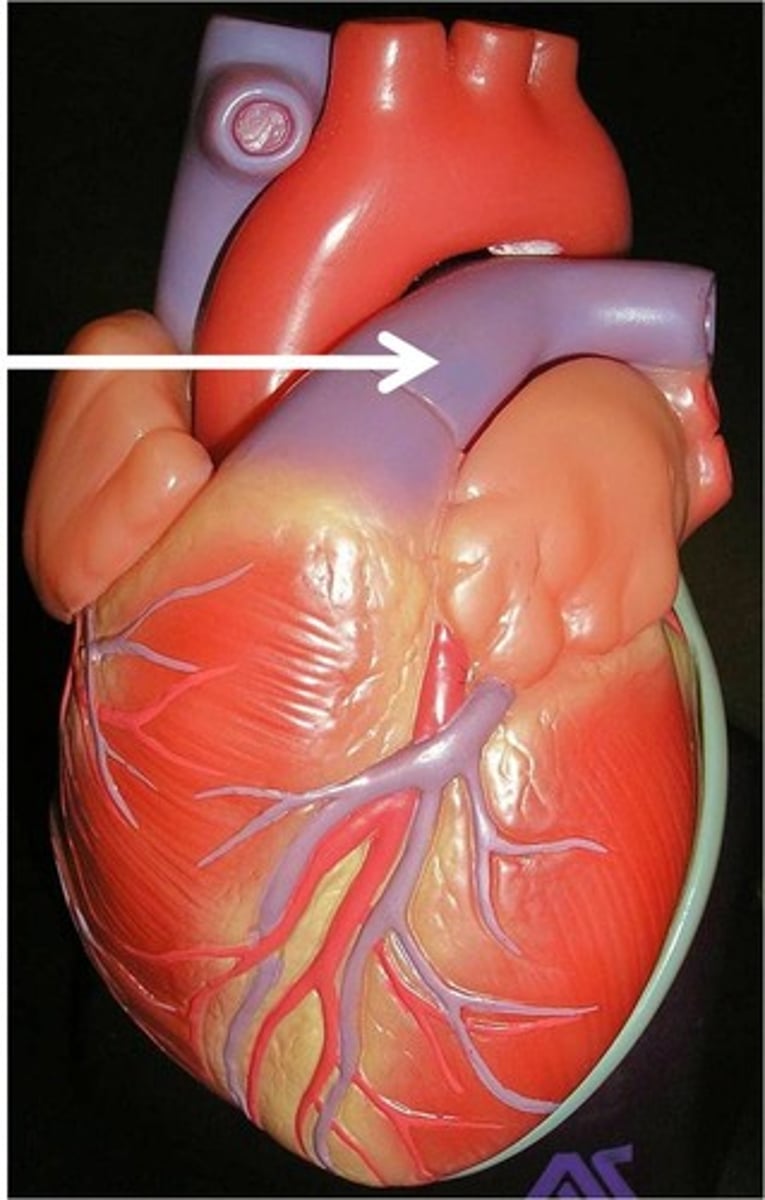
pulmonary vein
one of two pairs of vessels carrying oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart
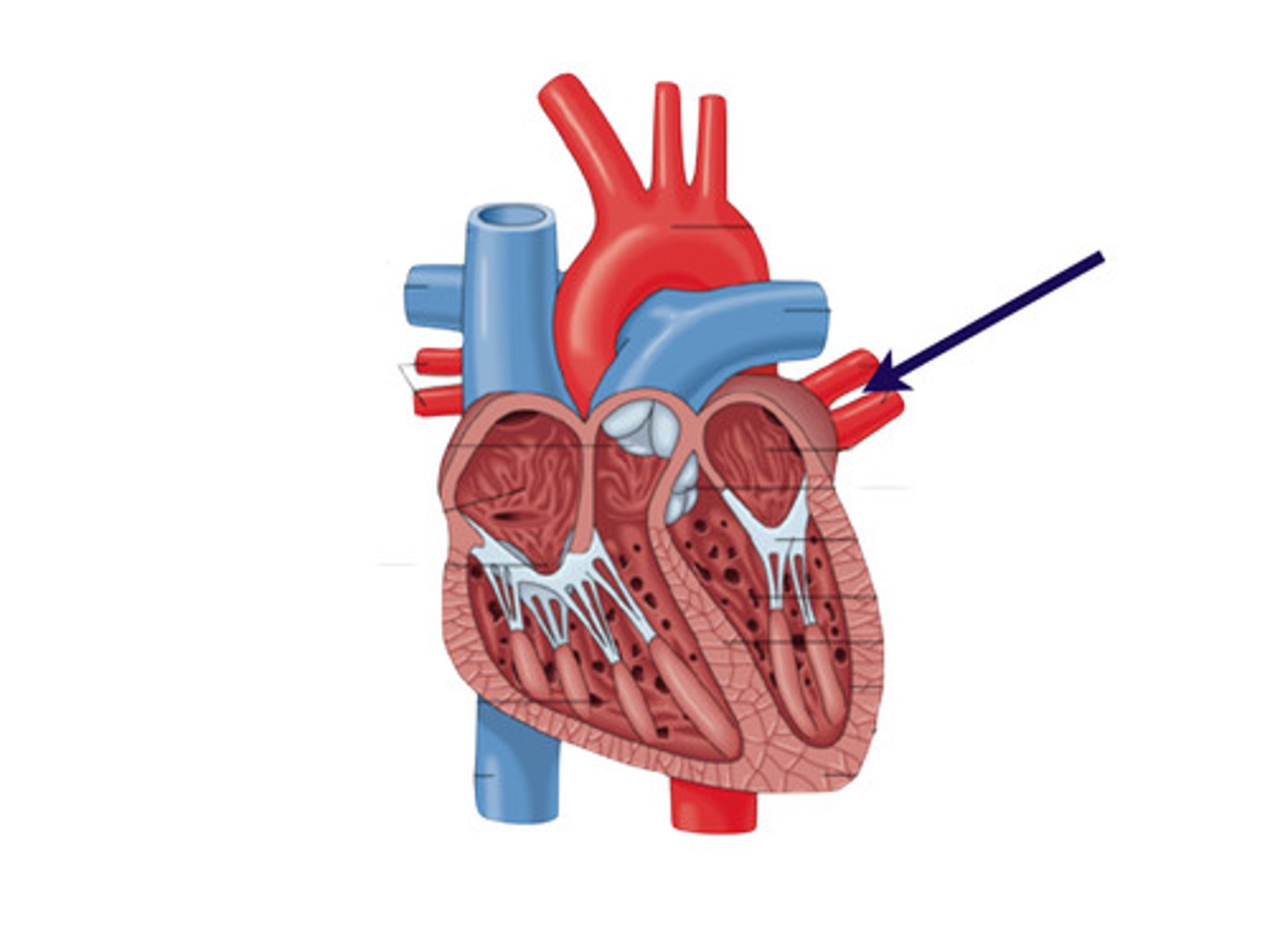
Septum
muscular wall dividing the heart into right and left sides to prevent oxygenated and deoxygenated blood from mixing
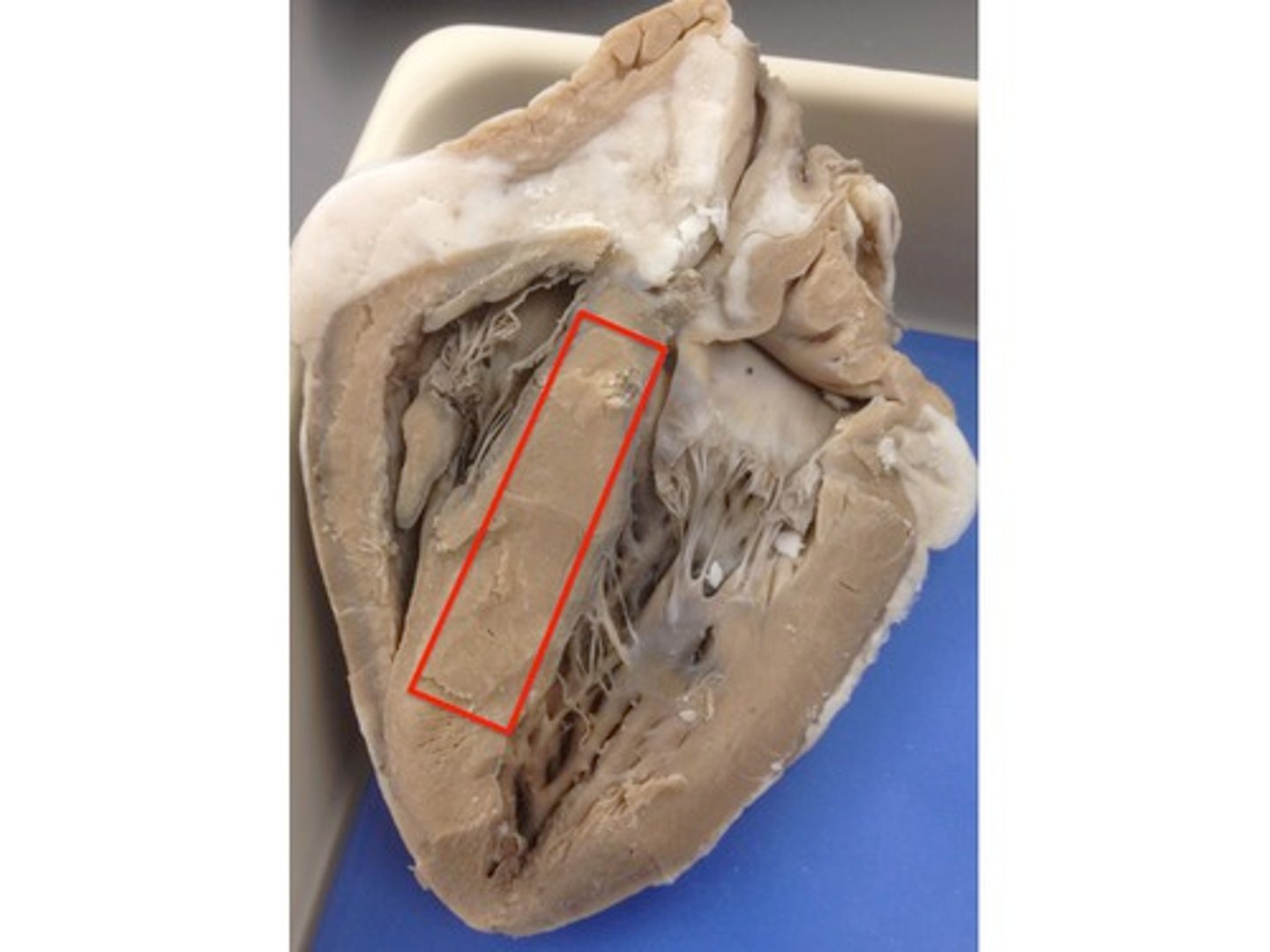
Heart murmur
an abnormal sound from the heart produced by defects in the chambers or valves