bio II final - johnson's section - unit 1
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
DDT was once considered a “silver bullet” that would permanently eradicate insect pests. Instead, DDT is largely useless against many insects. DDT resistance in insects would not have evolved if:
The insect pests did not have genetic variations that resulted in DDT resistance
Which of these conditions are TRUE of populations evolving due to natural selection?
A) The population must vary in traits that are heritable.
B) In different species, structures that share the same function must share an evolutionary origin.
C) Heritable traits that increase reproductive success are more likely to be passed on to the next generation.
D) Individuals pass on most traits that they acquire during their lifetime.
E) Two of the above (A-D).
F) Three of the above (A-D)
E
Ras, a small G protein-like protein, is often mutated in different types of cancer. Activation of Ras normally signals to a cell that it should divide. Cancer cells divide uncontrollably. Which of the following changes to Ras would you expect to see in a cancer cell that has a mutated form of Ras?
A mutation that means Ras cannot hydrolyze GTP to GDP
Which of the following statements correctly describes inositol trisphosphate (IP3) as a second messenger?
IP3 binds to an IP3-gated calcium channel, causing the release of calcium ions from the endoplasmic reticulum
The hypothalamus produces a signal that induces the adrenal medulla to release hormones that control short term stress. The process by which the hypothalamus sends a signal to the adrenal medulla involves:
A) Endocrine signaling
B) Autocrine signaling
C) Paracrine signaling
D) Neural signaling
E) Portal blood vessel signaling
F) More than one of the above types of signaling (A-E)
D) Neural signaling
Which of the following statements about lipid-soluble (hydrophobic) hormones is true?
A) They most often act by affecting the transcription of genes
B) They act by producing second messengers
C) They bind to receptors on the plasma membrane
D) They enter the cell and directly bind DNA
E) They open ion channels
F) They dephosphorylate proteins
A) they most often act by affecting the transcription of genes
Which of the following occurs in Meiosis II but not in Meiosis I ?
A) Pairs of homologous chromosomes align together at the metaphase plate
B) Crossing over occurs
C) Independent assortment of chromosomes occurs
D) Random fertilization occurs
E) Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles
F) Cytokinesis
E) sister chromatids separate and move to opposite plates
To generate a reliable “karyotype” of a cell for assessing chromosome number abnormalities, it is important to test a cell at a phase when the chromosomes are maximally condensed AND have the complete number of chromosomes for a diploid cell. If a cell that is undergoing meiosis is prepared for a karyotype analysis, what is the optimal meiotic phase at which to test the cell?
metaphase II
What is the correct sequence for the life of sperm that are ejaculated out of these choices?:
epididymis
Urethra
Vans deferens
ejaculatory duct
seminiferous tubules
Seminiferous tubules, Epididymis, Vas deferens, Ejaculatory duct, Urethra
In humans, where does the fertilized oocyte begin to divide (cleave) ?
oviduct/fallopian tubes
during fertilization, the cortical granules
Trigger the formation of the fertilization envelope
The process of cellular differentiation is a direct result of:
A) Different genes being expressed in the cells of different tissues
B) Totipotency
C) Cell division
D) Apoptosis
E) Activation of master regulator genes
F) More than one of the above (A-E) are correct
F/A,E
Thalidomide, now banned for use in pregnant women, was used in the early 1960s by many women in their first trimester of pregnancy to lessen nausea ("morning sickness"). Some of these women gave birth to children with arm and leg deformities, suggesting that the drug most likely influenced:
Morphogenesis (the biological process that allows a cell, organism, or tissue to develop its shape)
The “primitive streak” in a bird embryo is the functional equivalent of:
The blastopore in a frog embryo
Cells move to new positions as an embryo establishes its three germ-tissue layers during:
gastrulation
Which of the following processes will be disrupted if the apical ectodermal ridge is surgically removed from a chick embryo?
Outgrowth of the limb bud would be disrupted
In the process of neurulation
The neural plate rolls into a cylinder to form the neural tube
What is the MyoD protein?
a transcription factor that binds to and activates the transcription of muscle-related genes
The embryos of complex multicellular animals must establish spatial coordinates for development to progress. An important reference coordinate for developing frogs is the . .
A) location of the vegetal pole
B) location of the animal pole
C) point of sperm penetration
D) two of the above (A-C)
E) three of the above (A-C)
F) none of the above (A-C)
E
What type of cell surface receptor protein phosphorylates itself after it binds to an extracellular ligand?
receptor tyrosine kinase (kinases add phosphate groups)
What ligand opens an ion channel on the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum?
IP3+ or Ca2+
What protein becomes activated when a GTP binds and displaces a GDP?
G-protein or Ras
Which enzyme in the epinephrine to glucose pathway is inhibited by caffeine?
Phosphodiesterase or cAMP phosphodiesterase
What kind of receptor activates the alpha subunit of another protein?
G-protein coupled receptor/GPCR
What is a key protein in the Ca++ signaling pathway that undergoes a conformational change upon binding Ca++ ions?
Calmodulin or PKC or RyR
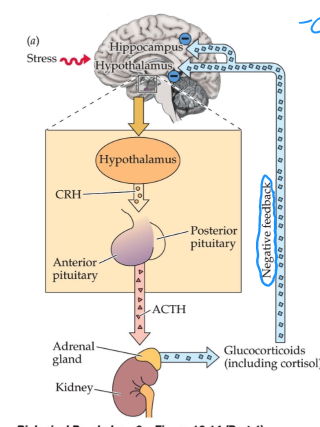
What pituitary hormone stimulates the secretion of steroid hormones from the adrenal gland?
Adrenocorticotropic hormone/ACTH
Which endocrine gland secretes a hormone that regulates functions related to light/dark cycles and seasonality, and promotes sleep?
pineal gland (light inhibits hypothalamus which inhibits pineal gland)
If blood calcium levels drop, what hormone is released?
Parathyroid hormone
A person with abnormally high metabolism may produce too much of which hormone?
Thyroid hormone/thyroxine/T3/T4
. If a person becomes dehydrated, a hormone is released from the . . .
Posterior pituitary
It is well known that morphological structures in different species can appear to be similar because of evolutionary “homology,” but sometimes structures in different species can appear to be similar and have equivalent functions by “analogy,” where the structures in the different species do not share common ancestral structures. An example of analogous structures is the wings of birds vs. insects. These analogous structures can arise in evolution by . . .
A) punctuated equilibria
B) convergent evolution
C) evolution of antibiotic resistance
D) vestigialization of organs
E) developmental channeling through an epigenetic landscape
B
Which of the following are NOT necessary for terminating the effect of glucagon on liver cells:
A) phosphatase activity
B) phosphodiesterase activity
C) synthesis of cGMP by guanylyl cyclase D) the regulatory subunit of protein kinase A
E) spontaneous hydrolysis of GTP by the a subunit of the G-protein
C

What endocrine gland secretes a non-tropic hormone that manages long-term stress responses, including suppression of the immune system (CORTISOL)?
Adrenal cortex/gland
What endocrine gland secretes a tropic hormone for the management of long-term stress?
Hypothalamus OR Anterior Pituitary
In a target cell, where are the receptors for steroid hormones located?
Cytoplasm (and/or nucleus)/intracellular receptor
What hormone secreted by the pancreas promotes the breakdown of glycogen and the release of glucose into the blood?
glucagon
What hormone acts on the kidney and bones to increase Ca++ levels in the blood?
PTH or parathyroid hormone
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) is released in response to an increase in blood osmolarity. When blood osmolarity returns to normal, ADH release is inhibited. What kind of feedback regulation is this?
Negative Feedback
What is the name of the type of gene that finally/ultimately defines the identity of a segment (for example, a leg)?
Hox gene OR Homeotic gene
What developmental process is driven by caspases?
apoptosis
What is it called when a cell reaches the point where it is irreversibly committed to become a particular cell type?
Determination OR Cell Determination
Many cells are structurally & functionally different but contain the same DNA. What is this concept that all cells have the same DNA called?
Genomic Equivalence OR Totipotency
Suppose you were told that a newly discovered dominant mutation in a gene in Drosophila called gutless results in an embryo lacking an abdomen. You are also told this is a maternal-effect gene (therefore, it acts by a mechanism that is similar to that of bicoid). Based on this description you could reasonably conclude:
a female carrying the mutation in this gene would not produce viable offspring
Suppose you put the nucleus of an adult brain cell into an egg that has lost its own nucleus. This cell develops into a complete organism. This experiment and its result specifically support which of the following statements?
Nuclei of adult cells contain a complete genetic “blueprint.”
Imagine a male has a mutation in his gene encoding inhibin, such that inhibin is not made or secreted. What impact might this mutation be expected to have in this person? (inhibin inhibits the release and production of FSH; so without it, spermatogenesis would go unregulated)
spermatogenesis is OVER-activated.
In humans, fertilization stimulates . . .
the second meiotic division of an oocyte contacted by a sperm.
The genes BRCA2 and HTR2A are on human Chromosome 13. Imagine you received different alleles for these two genes from your mother vs. your father. If the combinations of these alleles of BRCA2 and HTR2A on your chromosomes are different in you than in either your mother's or your father's chromosomes, what phenomenon is most likely to be responsible?
recombination
Imagine a male has a mutation in his gene encoding inhibin, such that inhibin is not made or secreted. What impact might this mutation be expected to have in this person?
spermatogenesis is OVER-activated