alkanes and haloalkanes
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
nucleophilic substitution mechanism definition
-involves a nucleophile, where an atom in a molecule is replaced by another
CFCs
chlorofluorocarbons
harmful to ozone layer owing to release of chlorine atoms on exposure to UV radiation
UV breaks C-Cl bond, forming a Cl. free radical, which destroys ozone molecules, causing hole in ozone layer
uses: propellant in aerosol sprays (volatile), dry cleaning (non-toxic and good solvents)
why are alkanes unreactive
C-H bond is short, strong as nuclei of both atoms are close to shared pair of electrons
and non-polar so other reagants aren’t attracted to them
C-C and C-H have sigma bonds (overlap of s-orbitals directly between bonding atoms)
free radical substitution
alkanes react with halogens in presence of UV light
involves free radicals where atom in a molecule is replaced by another
photochemical reaction brought about by light
homologous series
a series of organic compounds with the same functional group, and therefore similar chemical properties. Each successive member differs by CH2.
There’s a gradual change in physical properties due to increasing molecular size
trends in increasing size of alkane molecules
-boiling point and viscosity increase, molecule gets bigger, number of electrons per molecule increases, induced dipole forces get stronger (more contact surface area), more energy required to break them
-flammability and volatility decrease, less likely to evaporate
Initiation step in free radical substitution
-UV radiation breaks a covalent bond
-CL2 => 2Cl. (2 chlorine free radicals)
propagation step
free radicals are simultaneously consumed and regenerated during the course of a chain reaction
-Cl. + CH4 => HCl + .CH3
-.CH3 +Cl2 => CH3Cl + Cl.
termination step
2 free radicals combine to make a stable molecule
-Cl. + .CH3 => CH3Cl
-Cl. +Cl. => Cl2
-.CH3 +.CH3 => C2H6
why do branched molecules have a lower melting point
-straight chained can pack more tightly together
-branched have less contact surface area
-weaker induced dipole forces
Homolytic fission
covalent bond breaks evenly
one e- from bond goes to each atom
use of haloalkanes
solvents, chemical feedstocks, propellants
why don’t alkanes mix with/dissolve in water
hydrogen bonds need to be broken and form induced dipole forces which are weaker and don’t compensate for hydrogen bonds
steps of UV breaking CFC by homolytic fission
CCl3F => Cl. + .CCl2F OR CF2Cl2 > CF2Cl. + Cl.
.Cl + O3 => .ClO +O2
.ClO + O3 => .Cl (regenerated) + 2O2
-overall: 2O3 => 3O2
Nucleophilic substitution mechanism
-dipole on C-I/F/Cl , c is delta +,
-curly arrow from bond to delta - halogen
-curly arrow from electron pair on OH- to C delta +, forming dative covalent bond
-alcohol + halide formed
-boiled under reflux with aqueous KOH (alkali) solution
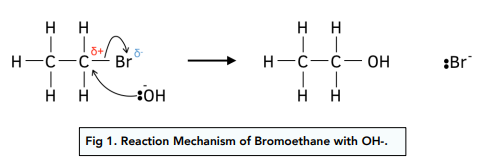
nucleophile
electron pair donor
hydrolysis of haloalkanes
-water or aqueous alkali is nucleophile, curly arrow from e- pair on O to C delta +
-water in presence of ethanol
nucelophilic substitution
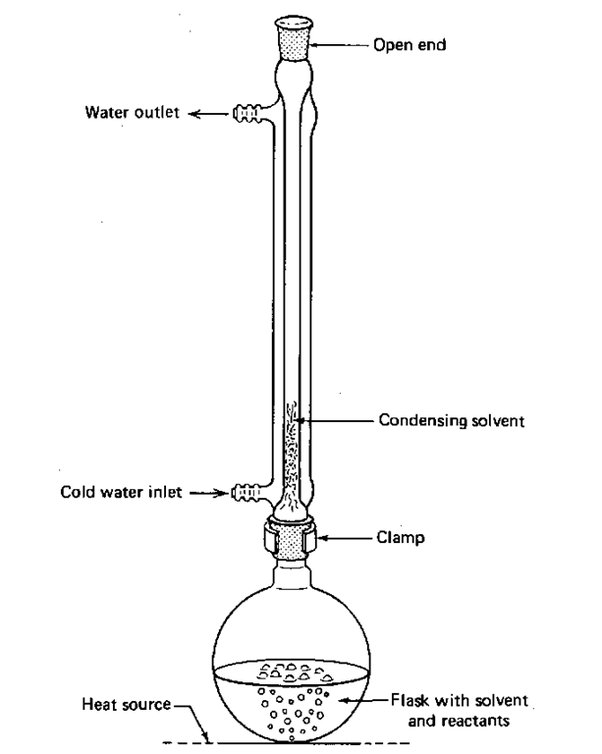
reflux
heating the chemical reaction for a specific amount of time, while continually cooling the vapour produced back into liquid form, using a condenser
why is C-I bond weaker than C-Br, so iodoethane is more reactive than bromoethane
it’s weaker because it’s longer
because I atom is bigger so nucleus further from e- pair, less nuclear attraction
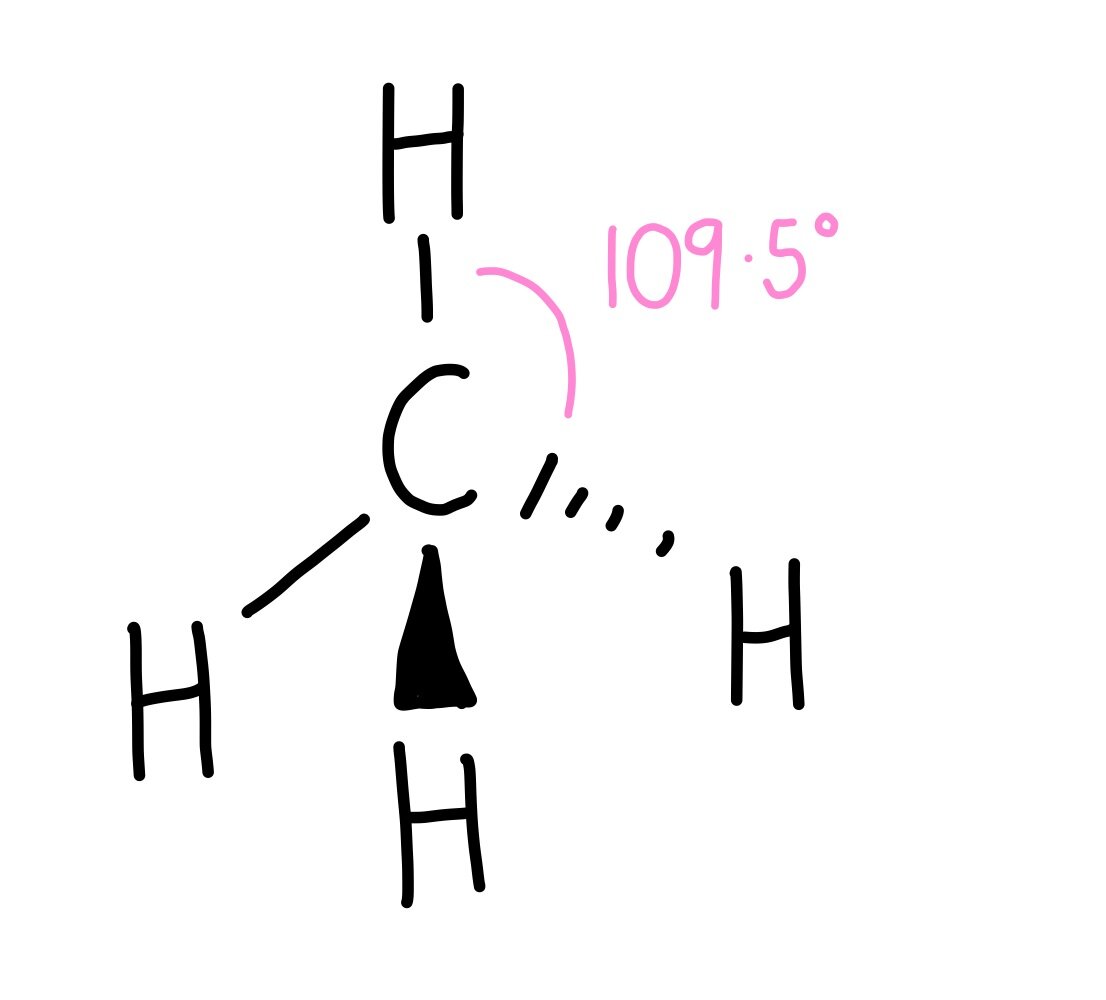
what’s the shape and bond angle around a C in an alkane
tetrahedral
4 bonding e- pairs repel equally
109.5
what’s the reason for incomplete combustion of alkanes
insufficient oxygen supply, making CO
what tests for halogens
silver nitrate (hydrolysis by water in present of AgNO3 and ethanol)
then nitric acid
how would you monitor rate of reactions of iodo, bromo and chloroethane
silver nitrate test
time takes to form precipitate
Ag+ + Cl- => AgCl (s)
why are hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) kinder to the environment than CFCs
contain hydrogen, break down more easily in atmosphere, less harmful to ozone layer
why is water a weaker nucleophile than a hydroxide ion
-doesn’t have as many lone pairs or a negative charge
breakdown of ozone by NO radicals
NO. + O3 = NO2. + O2
NO2. + O = NO. + O2
overall: O3 + O = 2O2
limitations of free radical substitution
-substitutions can happen at different positions on carbon chain
-mixxture of organic products made due to further substitutions
naming haloalkanes
give smallest number to halogen/start with carbon 1 as one with halogen
e.g. 2-bromo-3,3-demethylbutane
alcohol>haloalkane
H2SO4 catalyst
NaBr
reflux