Jeppesen Private Pilot Handbook, Chapter 4, Section B Questions
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Describe how runway numbers are determined.
Runways are aligned with the direction of the prevailing wind. Runway numbers correspond to a magnetic north reference. The runway's magnetic direction is rounded off to the nearest 10°, with the last zero omitted. Any runway that is between the headings of 010° and 090° is designated with a single-digit runway number. The number at the end of the runway corresponds to the direction that you are heading when taking off or landing on that runway. For example, a runway labeled 9 on one end is labeled 27 on the opposite end.
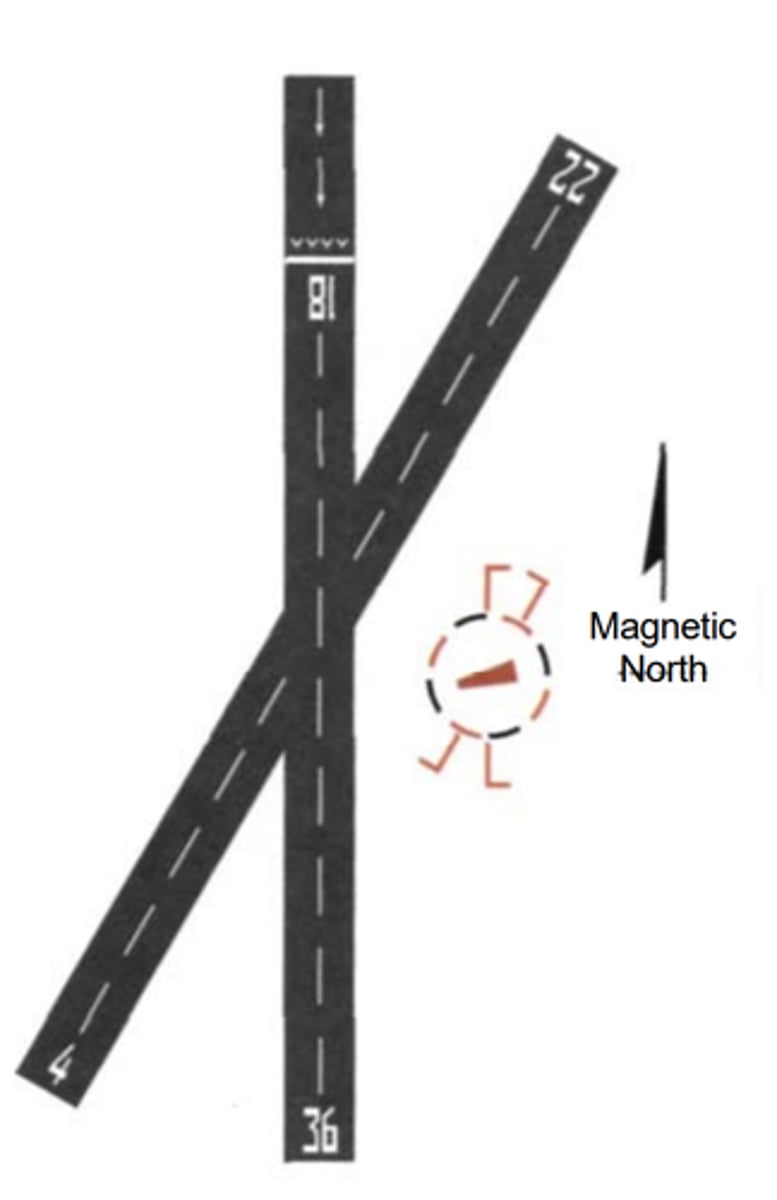
Determine the proper runway and traffic pattern for landing.
A. Left-hand traffic for Runway 36
B. Left-hand traffic for Runway 4
C. Right-hand traffic for Runway 22
B
Explain the purpose of a displaced threshold and the operating limitations associated with it.
Usually, a displaced threshold indicates that there are obstructions such as trees, powerlines, or buildings off the end of the runway. This might prohibit a normal descent and landing on the initial portion of the pavement. Although the pavement leading up to a displaced threshold may not be used for landing, it may be available for taxiing, the landing rollout, and takeoffs.
What marking indicates a closed runway?
A closed runway is designated by a yellow X
Which airplane is on the correct side of the hold line to be clear of the runway?
A

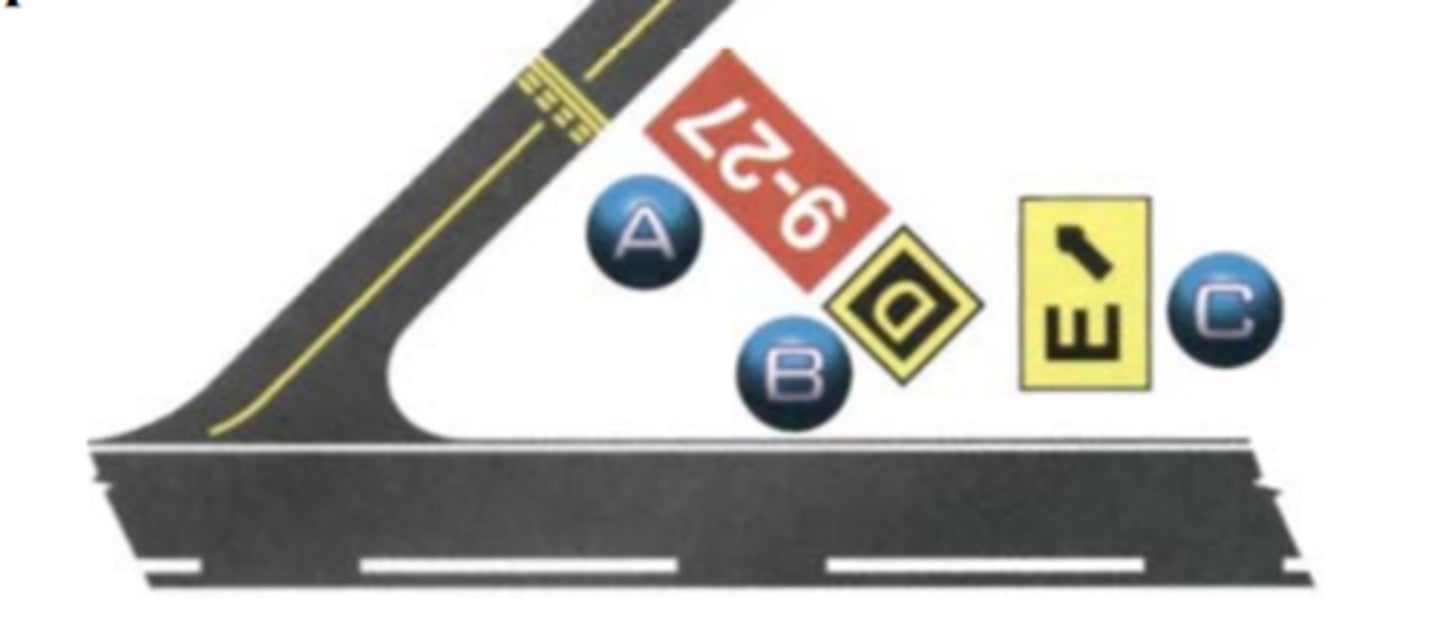
Match the following signs to their descriptions.
1. Direction Sign
2. Location Sign
3. Mandatory Instruction Sign
1. C
2. B
3. A

True/False. Runway incursions are primarily caused by errors associated with clearances, communications, airport surface movement, and positional awareness.
True
Match the following airport beacon light patterns to the appropriate airport.
1. White/White/Green
2. White/Green
3. White/Yellow
A. Civilian land airport
B. Military airport
C. Water airport
1. B
2. A
3. C
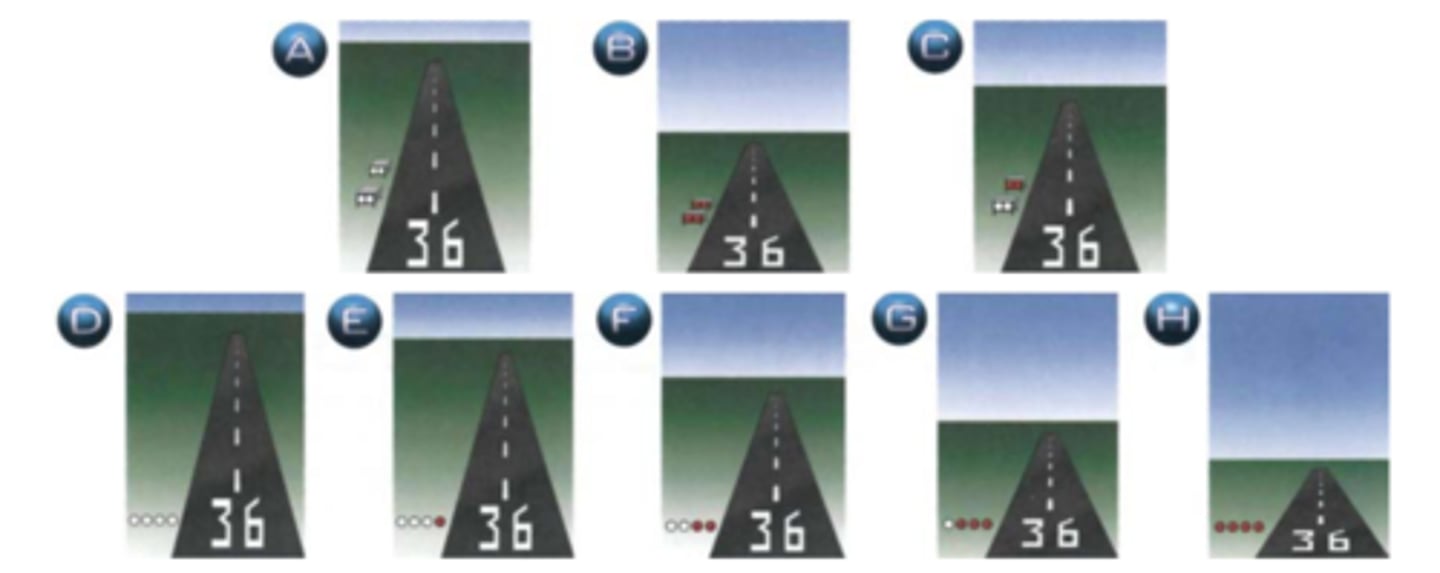
Match each illustration to the correct glideslope description.
1. VASI, on glide path
2. PAPI, slightly high
3. PAPI, on glide path
4. VASI, low
1. C
2. E
3. F
4. B

Describe the procedure for activating pilot-controlled lighting.
To activate three-step pilot-controlled lighting, the mike must be keyed seven times on the specified frequency to turn all the lights on at maximum intensity [HIRLS]. The mike is keyed five times for medium-intensity[MIRLS], and three times for the lowest intensity lighting[LIRLS]. The mike must be keyed the required number of times within a period of five seconds.
At some airports, you will be able to adjust the intensity of the runway lights from either your cockpit by using your radio transmitter or by air traffic controllers.
True/False. Two-way radio is required in both controlled and uncontrolled airports?
False
A two-way radio is required for you to operate in the controlled airport environment only.
At a non-controlled airports, you are not required to have a two-way radio, most pilots use radios to transmit their intentions to other pilots.
How does the wind sock functions?
The stronger the wind, the straighter the extension of the wind sock. Gusty conditions are indicated by back and forth movement of the wind sock.
What are the two purposes of the segmented circle?
1. First, it helps to identify the location of the wind direction indicator.
2. Second, there will be L- shaped extensions on the segmented circle helps you determine the direction of the traffic pattern.
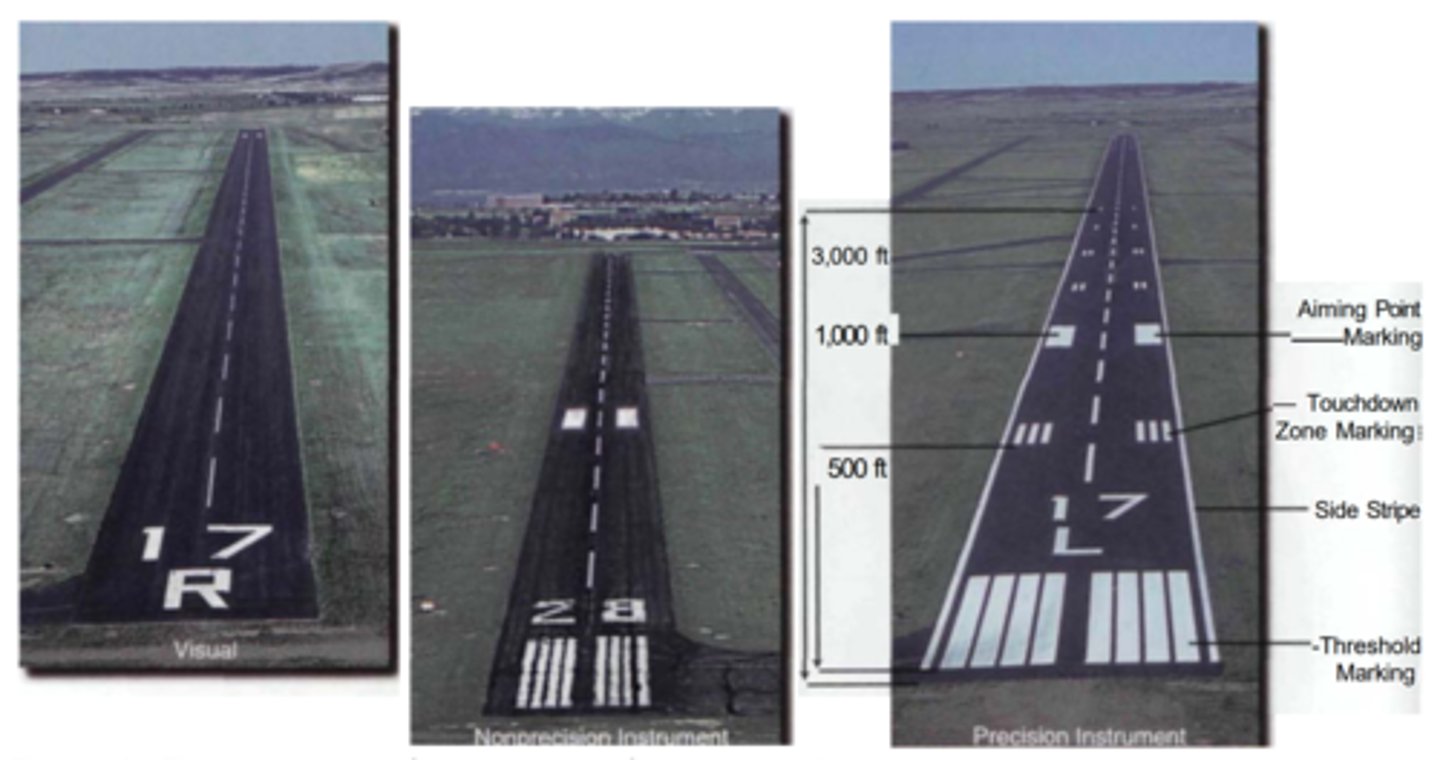
Runway markings vary between runways used solely for VFR operations and those used in conjunction with IFR operations. Explain.
1.A visual runway usually is marked with only the runway number and a dashed white centerline.
2.When a visual runway is used in conjunction with a nonprecision instrument approach, threshold and aiming point markings are added.
3. A precision instrument runway also includes touchdown zone markings.
What does a rotating beacon operating during daylight hours indicates?
It normally indicates that weather at the airport is below basic VFR minimums. When the ceiling is less than 1,000 feet and/or the ground visibility is less than 3 statute miles.