DNA ISOLATION AND PURIFICATION
1/200
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
201 Terms
DNA Isolation / Extraction
One of the most critical part in molecular techniques because downstream procedures and analysis relies on the quality of the DNA used for the assay
DNA Isolation / Extraction
It refers to the process of separating DNA from other cellular materials such as proteins and membranes.
• Plasmid DNA
• Viral Nucleic Acids
• Genomic DNA from Blood and Biological Fluids
• Genomic DNA from Tissue and Cells
• Genomic DNA from Forensic Samples
• Genomic DNA from Plant and Fungi
• Genomic DNA from Food and Feed
• Ancient DNA
Sources of DNA
DNA isolation
It requires the removal various cellular materials to free up the DNA material inside the cell.
Inhibit DNA analysis
DNA needs to be separated from other cellular materials because?
Cell lysis / disruption
To expose DNA
It refers to the breaking open of cells.
It is done because?
Detergent
How are membrane lipids removed?
Protease
How are proteins removed?
Ice-cold ethanol or isopropanol
How is DNA precipitated?
Slightly alkaline buffer
Ultra-pure water
Where is DNA resolubilized?
Chelating agents
It binds divalent cations to stop DNAse activities.
Protease
Precipitation by sodium/ ammonium acetate
Extraction by phenol-chloroform mixture
How are cellular and histone proteins bound to DNA removed?
• Lysis of cells to free the DNA material,
• Separation of DNA from other cell components
• Isolation of the DNA
3 basic steps of DNA extraction
Separate WBCs from RBCs, if necessary
Lyse WBCs or other nucleated cells
Denature/digest proteins
Separate contaminants (e.g., proteins, heme) from DNA
Precipitate DNA if necessary
Resuspend DNA in final buffer
Basic steps in isolating DNA
Chemical lysis
It is the simplest and cheapest method that can be employed.
Chaotropic agents
Detergents
Salts
Strong bases
Chemical lysis include what agents / reagents?
Enzymes
Examples include proteinase K and lysozymes which target proteins in the cell or organism to induce lysis.
Lysosomes
Gram positive bacteria (esp. peptidoglycan)
Lysozymes are secreted by?
It targets?
Mortar and Pestle
The most common method of mechanical lysing of cells.
Bacterial spores
Fungal cells
Protozoan oocysts
What organisms are more resistant to lysis?
Histones
Other accessory proteins
The isolation of DNA is prone to protein contamination
due to the presence of?
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
Triton X-100
What detergents can be used to remove proteins from DNA through solubilization?
Chaotropic acids
Guanidine hydrochloride
Guanidinium thiocyanate
What chemicals can be used to denature proteins and employed to lyse bacteria and yeasts?
Serine protease Proteinase K
This is a common protease, originally extracted from the fungus Engyodontium album that breaks down proteins into smaller molecules by cleaving peptide bonds and is thus useful in reducing the protein background as well as in the lysis of cells.
Engyodontium album
Serine protease proteinase K originally extracted from this fungus.
Protease digestion
This removes unwanted proteins.
True
Modified True or False.
Isolation of the DNA
After lysis, the DNA must be isolated from other samples or cellular materials.
Liquid-liquid extraction
Solid-phase extraction
Two separation methods that can be employed in isolation of the DNA.
Liquid-liquid Extraction
This is an organic extraction, which involves liquid phase separation and precipitation
False.
The use of liquid phase extraction is based on the differential solubility of DNA from other molecules in immiscible liquids.
Modified True or False.
The use of liquid phase extraction is based on the differential solubility of DNA from other molecules in miscible liquids.
Phenol
Mixed with Chloroform and Isoamyl alcohol
What are the primary organic solvents used in the Liquid-liquid extraction technique? and is/are usually mixed with?
25:24:1 (Respectively)
Ratio of Phenol, Chloroform, and Isoamyl alcohol (Respectively) in Liquid-liquid Extraction?
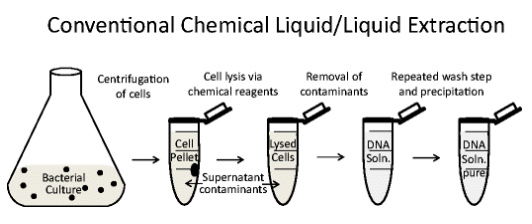
Process of Conventional Chemical Liquid/Liquid Extraction?
False.
The addition of Chloroform or Isoamyl alcohol aids in the partitioning of the different phases and prevents foaming
False
DNA is then precipitated from the aqueous phase using alcohol
True
Modified True or False.
Liquid-liquid Extraction
The addition of Phenol aids in the partitioning of the different phases and prevents foaming
DNA is then aspirated from the aqueous phase using alcohol
Although it is an effective method for DNA separation, it is manual laborious. It poses risks due to the hazards posed by the chemicals used and wastes generated by the procedure.
Precipitation of DNA
This is a liquid phase method that yields a relatively pure product and concentrates the DNA
Ethanol
Isopropanol
This alcohol is usually used to precipitate DNA
High Concentration of Salt (0.1-0.5M)
Sodium chloride
Ammonium chloride
Ammonium acetate
Other mixture/chemical that can also be used to precipitate DNA
Buffer or Ultrapure Water
After precipitation, the sample is centrifuged to concentrate and separate the DNA into pellet and is then dried and resuspended in?
Solid-phase Extraction
This process involves DNA separation either by size or affinity.
Is commonly performed because it is less hazardous, easier to perform, adaptable for automation and suitable for high-volume sample separation.
Less hazardous
Easier to perform
Adaptable for automation
Suitable for high-volume of sample separation
Why is Solid-phase Extraction preferred over Liquid-liquid Extraction?
Lysis
Binding
Washing
Eluting
The basic steps in a solid phase extraction lysis
Gel Filtration
Ion-exchange Chromatography
Affinity Chromatography
Techniques used in Solid-phase extraction
Gel Filtration
This technique separates the components of a mixture on the basis of molecular size, and is the simplest form of chromatography for oligonucleotide purification
Sephadex
What common gel matrix is used in Gel filtration?
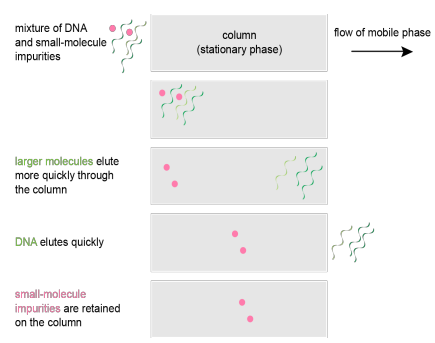
Equilibration
Binding
Washing
Elution
^searched ko lang to^ but refer to the image na lang po
Process of Gel filtration
Larger molecule
DNA
Small-molecule impurities
In Gel Filtration, What is/are
Elutes more quickly through the column
Elutes quickly after the previous asked ^
retained on the column
To the right
What is the flow of mobile phase in Gel filtration?
Ion-exchange Chromatography
This technique is based on the selective binding of negatively charged DNA to surfaces with charged groups.
Charged DNA
This exchange places with ions and bind to the surface by charge and unbound substances are washed away.
Side or walls of the tube
Where does DNA in common anion exchange resin binds/attaches?
Diethylaminoethyl cellulose (DEAE-C)
What is a common anion exchange resin used in Ion-exchange Chromatography?
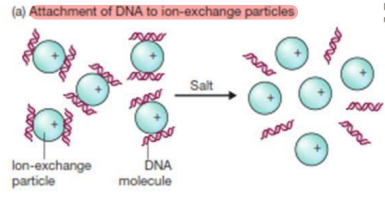
Salt
What separates DNA molecule in Ion-exchange particles?
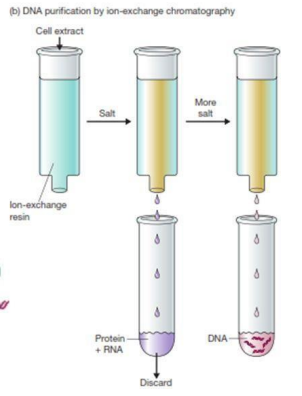
Protein+RNA
What is/are discarded in DNA purification by ion-exchange chromatography?
Affinity Chromatography
This technique uses reversible adsorption of DNA to surfaces such as silica and is the most common method for DNA extraction/isolation
DNA binds to Silica Surfaces
In Affinity Chromatography, when specific binding conditions are met, especially upon addition of chaotropic salts, where does DNA binds to?
True
Modified True or False.
Affinity Chromatography, Is used for many DNA preparation procedures and is commonly used in automated methods.
because of complex hydrogen bond formation between the silica and DNA surfaces in the presence of chaotropic salts or alcohols at high concentration and low pH (below pH 7) resulting to binding
In Affinity Chromatography, Why does Linear DNA adsorbs lengthwise to silica surfaces?
False.
Silica and DNA surfaces are both negatively charged, thus, the binding is due to adsorption in high ionic strength conditions and hydrogen bonding when water is removed from the surfaces
Modified True or False.
Silica and DNA surfaces are both negatively and positively charged, thus, the binding is due to adsorption in high ionic strength conditions and hydrogen bonding when water is added from the surfaces
DNA
What is released when salt or alcohol is removed and the surfaces are hydrated?
Silica-Gel-Membrane Technology
This is based on a simple bind-wash-elute procedure.
Polysaccharides and Proteins
In Silica-Gel-Membrane Technology, what are not adsorb and are removed instead?
Pure Nucleic Acids
In Silica-Gel-Membrane Technology, after wash step, these are eluted under low- or no-salt conditions in small volumes, ready for immediate use without further concentration.
Nucleic acids
Presence of Chaotropic Salts
In Silica-Gel-Membrane Technology, these are adsorbed to the silica-gel membrane in the presence of? which remove water from hydrated molecules in solution.
Fast
Convenient
Economical
No time-consuming phenol—chloroform extractions or alcohol precipitations
Advantages of Silica-Gel-Membrane Technology
Bacteria, Prokaryotes
DNA extraction from different sources:
The simplest cells are composed of a lipid bilayer outer membrane and a cytoplasm containing circular chromosomes, proteins, inorganic salts, metal ions, CHO, and other cellular components.
lipid bilayer outer membrane
cytoplasm containing:
circular chromosomes
proteins
inorganic salts
metal ions
CHO
other cellular components.
DNA extraction from different sources:
Bacteria, prokaryotes, are composed of?
Prokaryotic Cells
Lysis of these releases chromosomal material where DNA can be extracted.
Isolation of genomic DNA from bacteria
This is traditionally achieved using organic extraction of the soluble DNA while the insoluble debris is removed
True
False
Many plant species have a high content of polysaccharides and polyphenols which are not removed by phenol extraction
False
It is much easier to lyse and extract genomic DNA from human and animal cells because of the absence of cell walls and chloroplasts
Modified True or False.
The cell walls of plants for example complicate the DNA extraction process by presenting a barrier that makes it more difficult to lyse the cells
Many plant species have a low content of polysaccharides and polyphenols which are removed by phenol extraction
It is much easier to lyse and extract genomic DNA from human and animal cells because of the presence of cell walls and chloroplasts
True.
False
Another major difference from prokaryotes lies largely on the presence of membrane-enclosed organelles in the cytoplasm
Modified True or False.
Most animal cells do not have a cell wall like microbial cells, and consequently, are easier to lyse and can be lysed using only detergents
Another major difference from prokaryotes lies largely on the absence of membrane-enclosed organelles in the cytoplasm
Resists damage
Neutralizes Nucleases
Preserves integrity
Accentuates lysis of reagents
Why is EDTA preferred over any other tubes in collecting blood samples?
False.
Oral swab typically yields 100 to 1500 ng of DNA per swab while tissue samples may yield 50 to 500 ng of DNA per gram of sample
Modified True or False.
Oral swab typically yields 1000 to 15000 ng of DNA per swab while tissue samples may yield 100 to 2500 ng of DNA per gram of sample
20000ng/mL - 40000ng/mL
250ng/cm2 - 500ng/cm2
150000ng/mL - 300000ng/mL
10ng/swab - 3000ng/swab
1ng/root - 750ng/root
1ng/root - 10ng/root
Typical DNA Amounts that may be extracted from Biological Materials: Amount needed?
Liquid Blood
Blood Stain
Liquid Semen
Post-coital Vaginal Swab
Plucked Hair (w root)
Shed Hair (w root)
1000ng/mL - 10000ng/mL
100ng/swab - 1500ng/swab
1ng/mL - 20ng/mL
3ng/mg - 10ng/mg
50ng/mg - 500ng/mg
Typical DNA Amounts that may be extracted from Biological Materials: Amount needed?
Liquid Saliva
Oral swab
Urine
Bone
Tissue
Plasmid DNA
Used for a number of downstream procedures such as transfection, sequencing, screening, clones, restriction digestion, cloning, and PCR
Transfection
Sequencing
Screening
Clones
Restriction digestion
Cloning
PCR
Plasmid DNA downstream procedures
Antibiotic Resistant Gene
Plasmids are typically designed to contain? allowing selection of bacteria containing the plasmids during growth of colonies or cultures
Extraction of Plasmids
Typically performed from bacterial liquid cultures and there are many methods available for plasmid DNA isolation that are capable of isolating large amounts of high-quality DNA
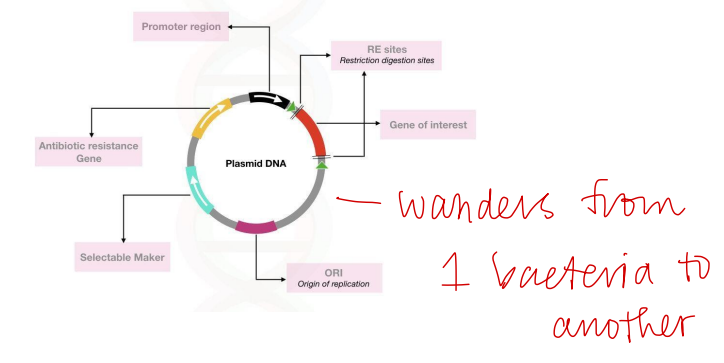
Cycle of Plasmid DNA
Alkaline Lysis Method
Where does the most common method for plasmids are based on?
To take advantage of the alkaline denaturation of plasmid and bacterial chromosomal DNA and the selective renaturation of plasmid DNA following neutralization of the solution
Principle of Alkaline Lysis Method?
The small-scale mini preparation
Plasmid of DNA that is commonly used to screen bacterial clones for the presence of recombinant DNA inserts?
Ficoll-directed Density Gradient Through Centrifugation
Quick Extraction Through Proteinase K and Phenol
DNA Extraction from Whole Blood
Ficoll-Directed Density Gradient Through Centrifugation
Fresh blood is collected in the presence of anticoagulants such as EDTA or citrate
Discarded
Ficoll
Erythrocytes/Granulocytes
Recovered for further analyses
Plasma
WBC
In Ficoll-Directed Density Gradient Through Centrifugation, What is usually discarded and recovered for further analyses after centrifugation of whole blood?
Tris
EDTA
Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)
MgCl2
Proteinase K
Quick Extraction Through Proteinase K and Phenol
For the proteinase K protocol, what are mixed with whole blood in the presence of high salt for overnight digestion at 37C
Proteinase K
This is a broad-spectrum serine protease.
Commonly used in molbio to digest protein and remove contamination from preparations of nucleic acid.
Protease K
Endopeptidase K
Other name of Proteinase K?
False.
The addition of proteinase K to nucleic acid preparations rapidly inactivates nucleases that might otherwise degrade the DNA or RNA during purification.
Modified True or False.
Addition of proteinase K to nucleic acid preparations rapidly activates nucleases that might otherwise degrade the DNA or RNA during purification.
SDS
What denaturant stimulates the activity of enzymes toward native proteins?
SDS
Urea
Trypsin
Chymotrypsin Inhibitors
What chemical/s denature proteins?
Tris-HCl (pH 8)-saturated phenol and water
4hr at room temp
Quick Extraction Through Proteinase K and Phenol
For Phenol Method, Whole blood is mixed with? followed by shaking for how long and what temp?
Aqueous Phase
Quick Extraction Through Proteinase K and Phenol
After centrifugation, what is collected for further standard purification?
Phenol-chloroform extraction
Is a liquid-liquid extraction technique used in molecular biology for isolating DNA, RNA, and protein?
Equal volumes of a phenol:chloroform mixture and an aqueous sample are mixed, forming a biphasic mixture. This method may take longer than a column- based system such as• the silica-based purification, but has higher purity and the advantage of high recovery of RNA
Principle of Phenol-chloroform extraction
Phenol-chloroform extraction
This method relies on phase separation by centrifugation of a mix of the aqueous sample and a solution containing water- saturated phenol, chloroform and a chaotropic denaturing solution (guanidinium thiocyanate) resulting in an upper aqueous phase and a lower organic phase (mainly chloroform).

DNA Extraction from Dry Blood Spots:
Chelex-100 Soaking in Saponin Process?

DNA Extraction from Dry Blood Spots:
Chelex-100 Soaking in PBS Process?

DNA Extraction from Dry Blood Spots:
Chelex-100 No soaking Process?

DNA Extraction from Dry Blood Spots:
InstaGene Matrix Soaking in PBS process?