Art History: Chapter 10 - Roman Art to 330 AD
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Republic Period (509 - 31 BC)
Republic: Power held by citizens to elect leaders
Conquered Italy, including places near the Mediterranean Sea & Atlantic Ocean
Development of temples influenced from Greece
Rose against Caesar, which began a period of civil war
Battle of Actium, Octavian defeats Mark Anthony & Cleopatra the 7th
Octavian renames himself as Caesar Augustus, meaning exalted and sacred
Many Roman sculpture depicted political figures and military leaders
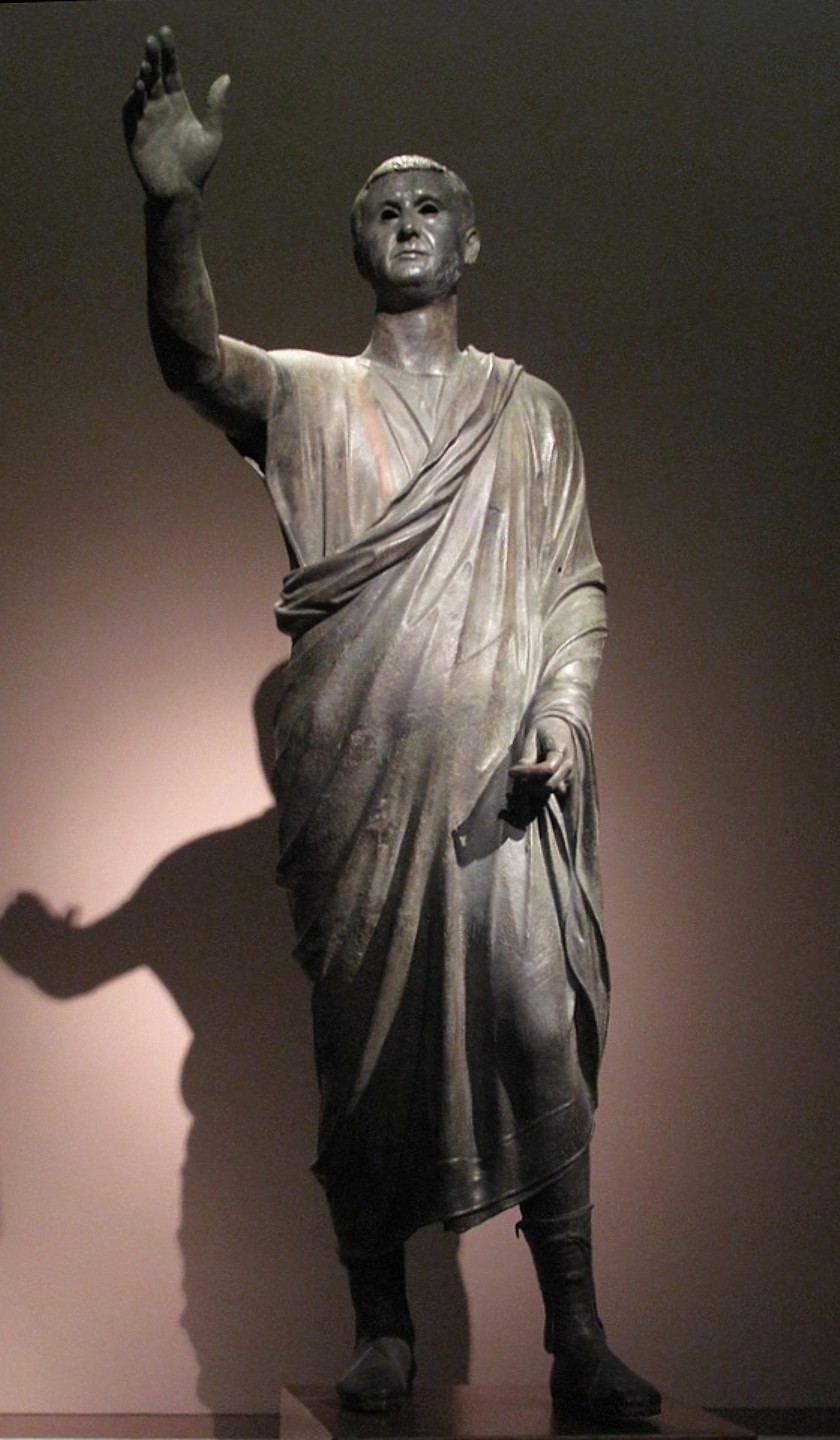

The Orater
Visual
Made of bronze
Depicts lifesized figure stretching his hand out
Is naturalistic and realistic, with wrinkes on his forehead
Neatly folded toga and boots
Inscription of “To (or from) Auli Meteli”
Iconographic
Part of Roman Republic
Age = wisdom
Common features and clothing show he’s an everyday guy
Inscription shows he’s a votive for dieties
Made by Etruscan metalsmith
Used as propaganda to ensure the government was working for citizen’s interests
Showed officials as strong leaders, instilling trust in government capabilities

Capitoline Wolf
Visual
Made of bronze with eyes painted in ivory
Depicts 2 infants and a wolf
Are naturalistic, freestanding, and carved in the round
Infants are in dynamic poses
Iconographic
Part of Roman Republic
Named after Capitoline Museum
Figures are Romulus and Remus, who’re abandoned until a she-wolf allows them to suckle for food
Made using lost-wax casting method
Wolf is Roman symbol
Discovered that the lost-wax casting was done in the Middle Ages
Unknown if the wolf is ancient
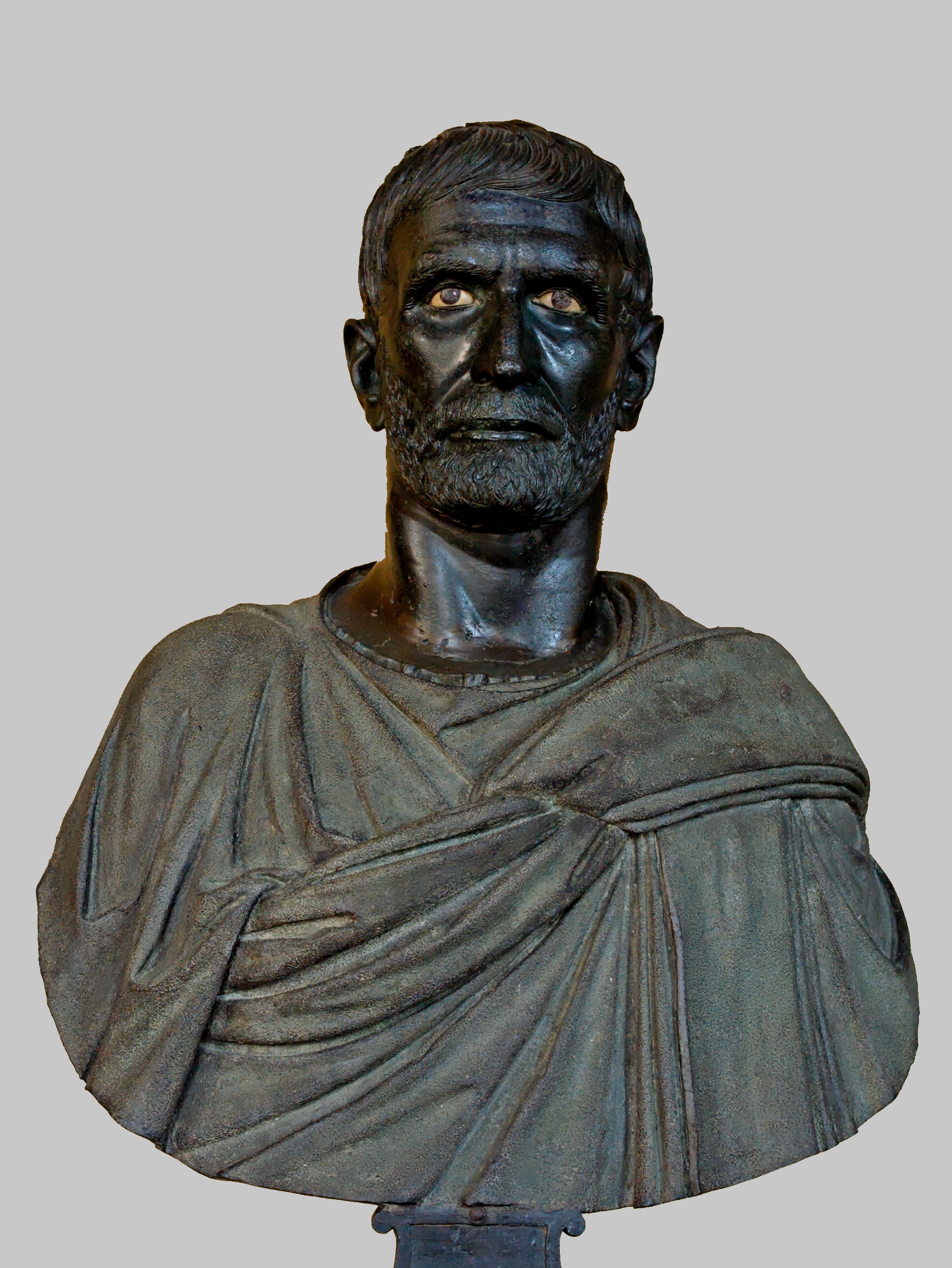

Capitoline Brutus
Visual
Made of bronze with eyes painted in ivory
A portrait bust
Depicts a naturalistic male figure
Brows pushed together, tight jaw, and persed lips show resoluteness
Head inclines downward slightly
Iconographic
Part of Roman Republic
Only original part is the head
Most likely depicting Brutus, the founder of Roman Republic
Was possibly once part of an equistrian sculpture
Likely meant to commemorate an individual
Is meant to look intelligent as wisdom was important for political leadership

Elder of Sccuppito
Visual
Made of marble
Is a portrait head
Is veristic: extreme realism & naturalism
Figure is very wrinkly and has sagging flesh
Iconographic
Part of Roman Republic
Has traces of paint
Figure was a patrician, which is upper class
Is influenced by the earlier practice of death masks to commemorate ancestors
Many were put in atriums of homes as a form of ancestor worship

Head of Elderly Woman
Visual
Made of marble
Veristic and idealistic
Iconographic
Made in Roman Republic
Traces of paint in hair and eyebrows
Fashion was important to Roman women

Tomb of the Scipios
Visual
A subterranean, rock cut tomb
Consists of irregular chambers and connecting corridors to provide niches for burials
Front of tomb decorated with a doric frieze and votive scrolls on lid
Has latin inscription
Iconographic
Part of Roman Republic
Scipio Barbatus is the patriach and most prominent occupant of tomb
Inscription was altered, some of it erased
Held records of Barbatus’ civic career and military achievements
Scipios were keen on maintaining family ties and supporting ancestry
Used for 200 years
Important example of Late Roman Republic funerary culture
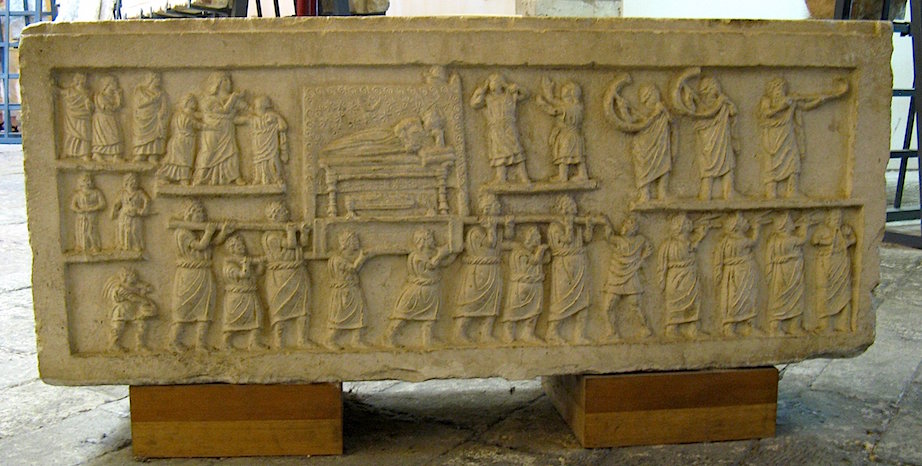

Funerary Procession
Visual
Made of stone
Figures are naturalistic
Depicts male figure resting on a couch with several figures surrounding him
Are being carried away by 8 pallbearers
Figure has lively pose, tilted on his left side
Has chief mourners, paid mourners, and musicians
Has partial inscription
Iconographic
Part of Roman Republic
Inscription suggests tomb was comissioned by a person whose family was formerly of slave origins
Characteristics of “freedman art"
Pompas used to reinforce political and social status
Funerals would hold dramatic displays of mourning, a cleansing of the corpse, then transported to poppa
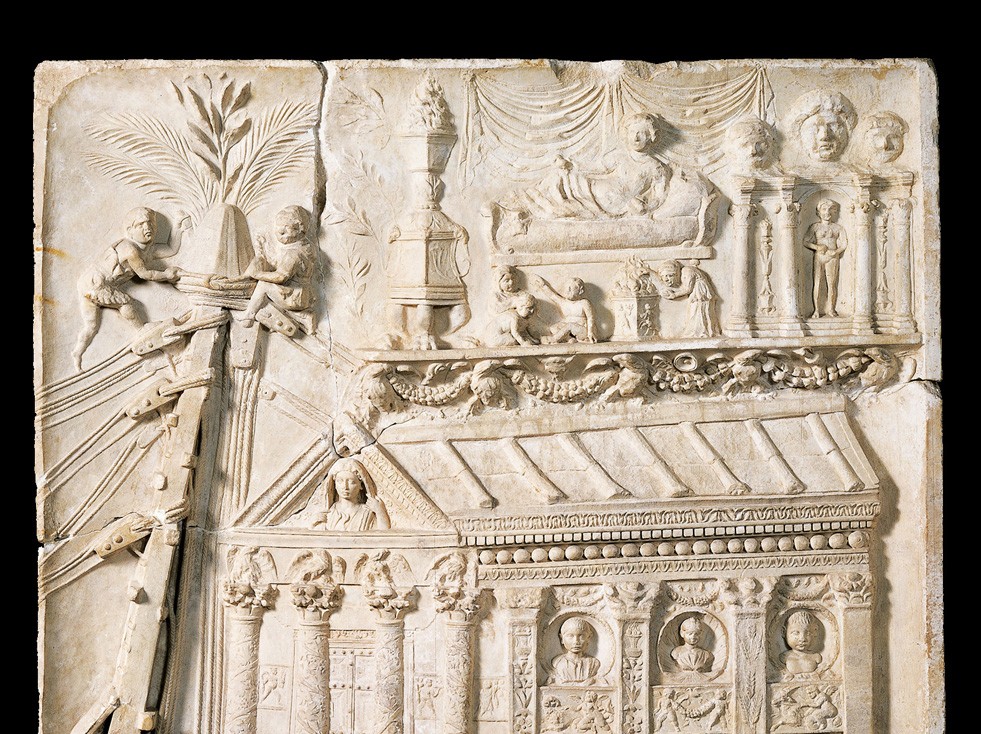

Mausoleum of the Haterii
Visual
Made of limestone and marble
Depicts death of a family matriarch and the family’s source of wealth
First frieze shows woman on funerary bed surrounded by torches, a musician, and mourning children
Newly liberated slaves with pileuses (caps)
Second frieze shows her lounging on couch while children play
Iconographic
Part of Roman Republic
Originally found in pieces
Represents a narrative interplay between death ritual and biography
Conflation of time as we see matriarch dead and alive
Pileus is a cap of freedom, referencing the matren’s liberty
Commissioned by a woman, symbolizing her access to money, which was rare
Haterii were a family of builders that built their own tombs
Final resting places provided an opportunity to document ritual observance, and their success in life and commerce
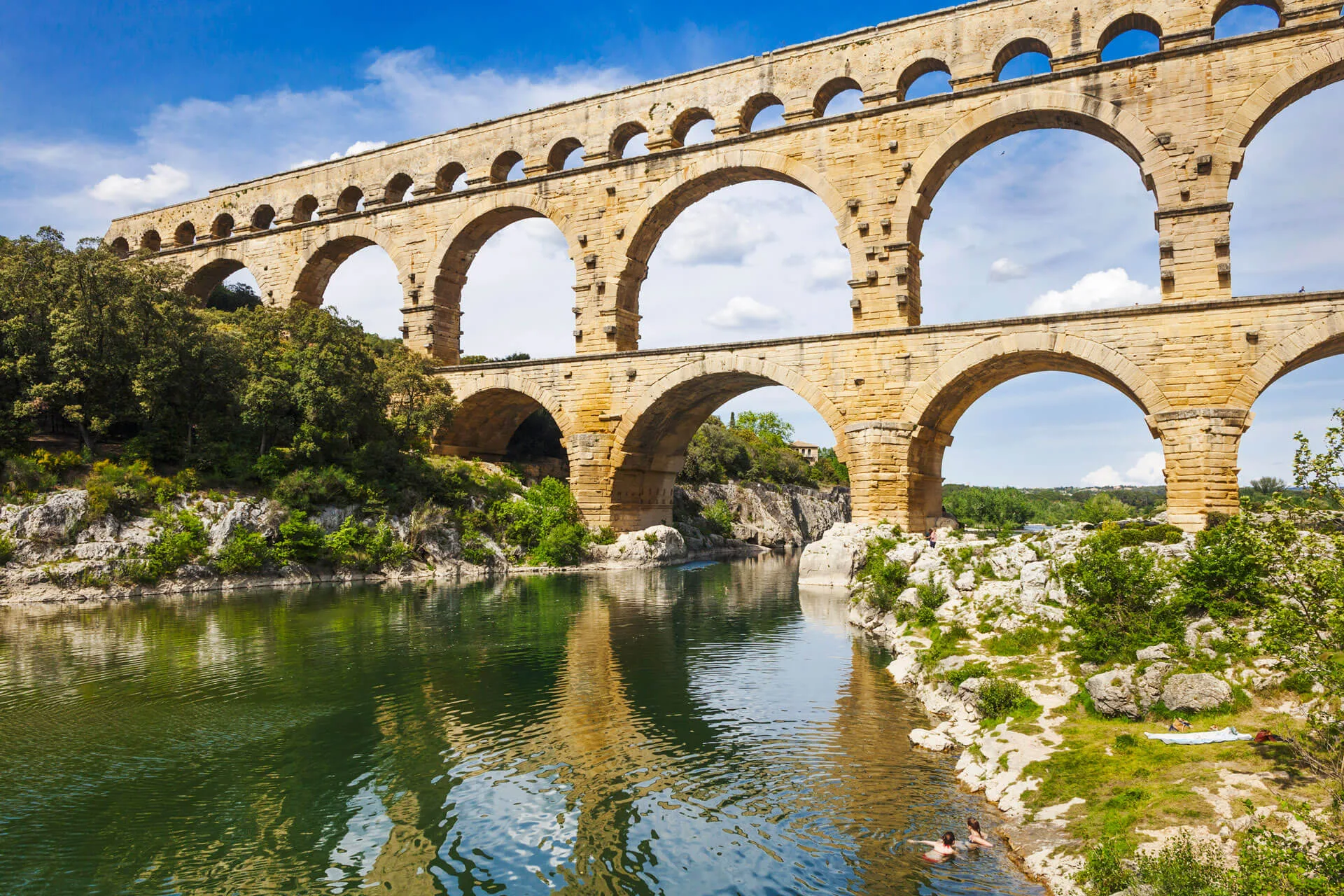

Pont du Gard
Visual
Made of stone
Is in aqueduct
Consists of 3 floors with 52 arches
Iconographic
Part of Roman Republic
Built in Nimes, France
Used to convey water across long distances
Every person in town able to recieve 100 gallons per day for free
Proclaims the wealth of Rome, showing its power and prosperity
Has chiseled grafitti on it

Temple of Portunus
Visual
Made of marble
A rectangular building with a small megaron
Has on-axis approach, high base, and cella with engaged columns
Also has ionic freestanding columns, friezes, and a pediment
Iconographic
Part of Roman Republic
Inspired from Etruscan & Greek temples
Most likely dedicated to Portunus, the god of harbors and piers
Uses post and lintel technique
Reliefs were taken off the friezes
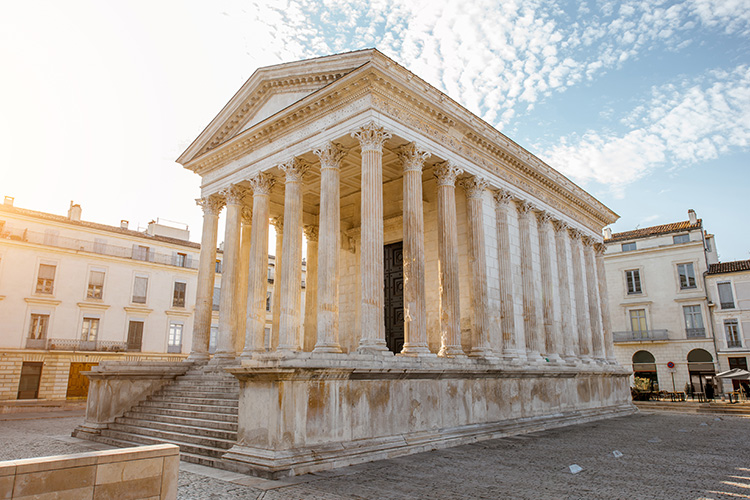

Maison-Carrée
Visual
Made of limestone
Consists of friezes, on-axis approach, deep porch, and corithian engaged columns
Iconographic
Built in Nimes, France
Etruscan and Greek inspired
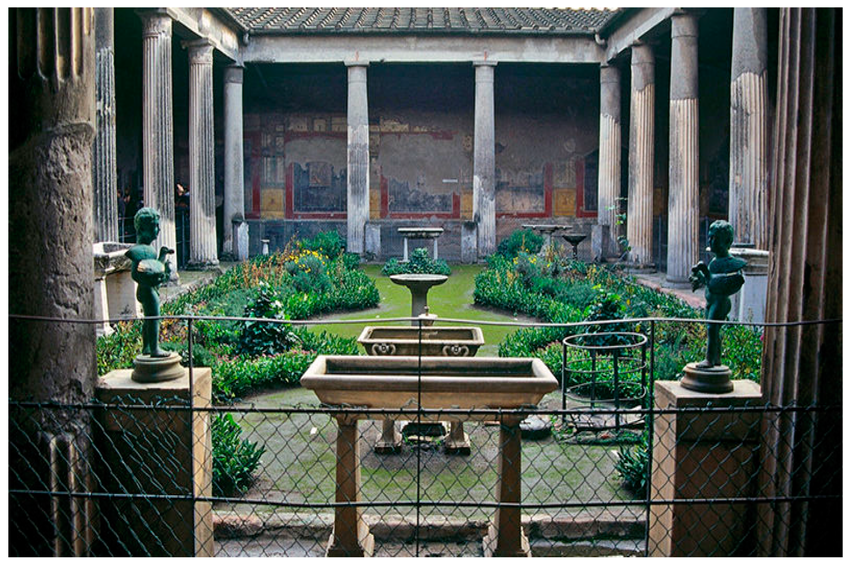

Peristyle Garden
Visual
Consisted of plants, sculptures, and ponds
Contained rooms with buon fresco paintings
Iconographic
Built in Pompeii
Part of House of the Vettii
Is in the atrium of the house, an open central space enclosed by glass roofs/walls
Rainwarer was collected in a pond to help with thirst and cooling off
Allowed light in interior rooms
Traces of paint
Roman Styles of Painting
Classified by August Mau
All paintings are buon fresco
Incrustation Style: Depicts imitation marble and other stones; used in Republic
Architectural Style: Depicts landscapes and figures; used in Republic & Empire
Ornate Style: Depicts flat walls with garlands/borders & scenes; used in Empire
Intricate Style: Combination of all; used in Empire
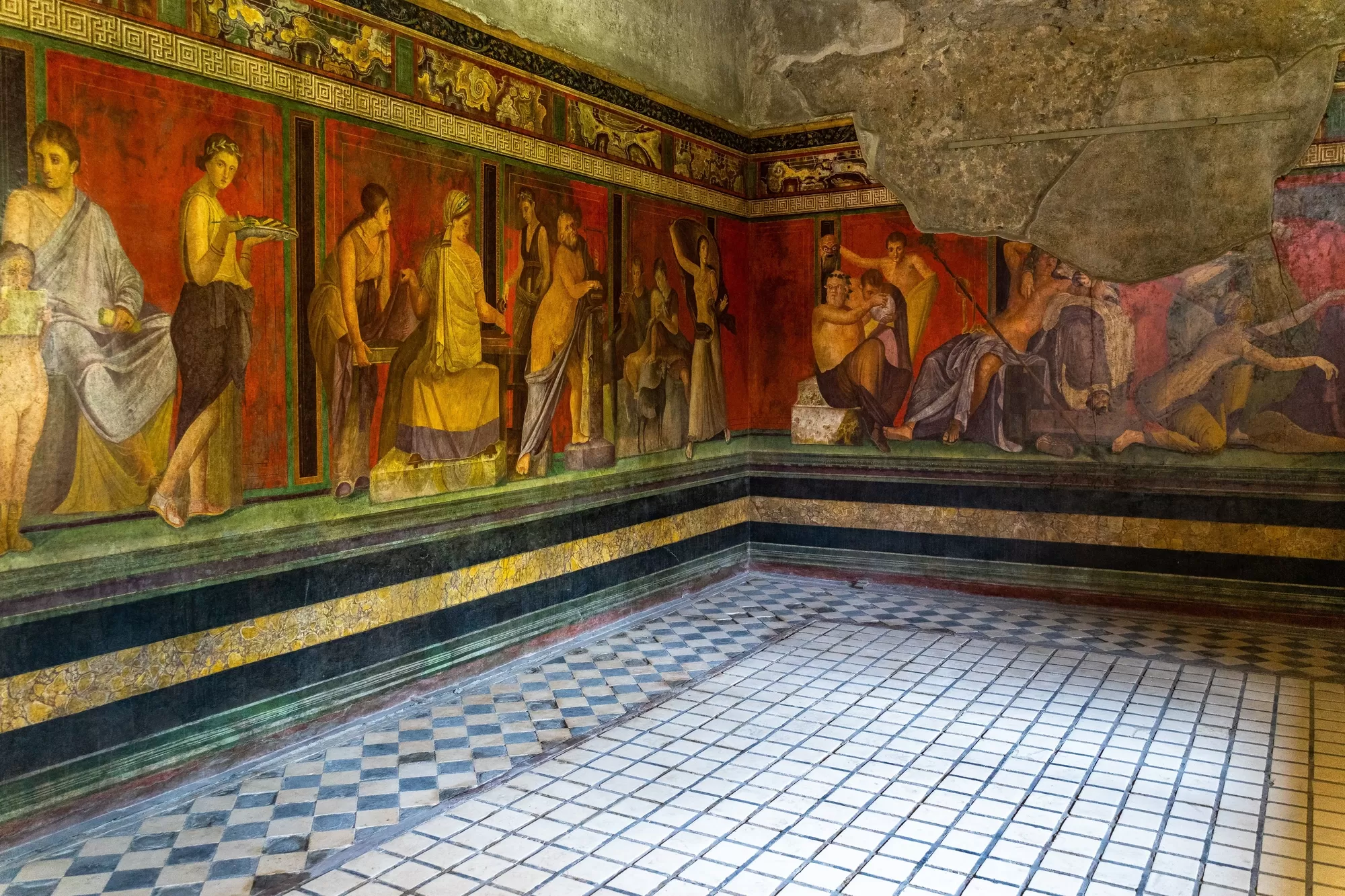

Villa of Mysteries
Visual
High intensity red hue background
Depicts several lifesized figures inside an interior space
Figures are naturalistic and close together as they’re in a tight spcae
Iconographic
Architectural style
Shows initiation ritual into Baccus (god of wine/partying) cult, which included whipping
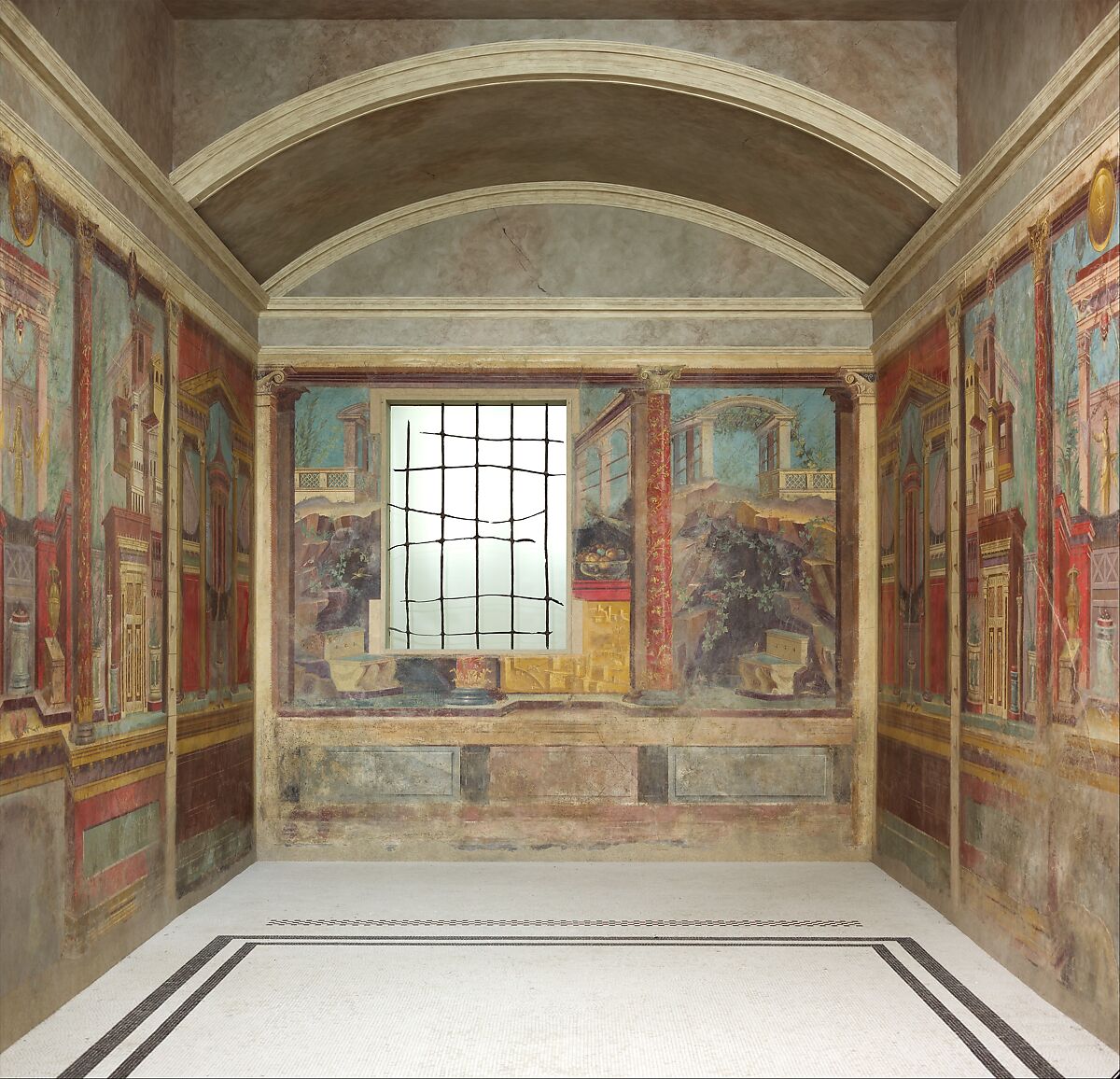

Bedroom One & Two
Visual
Bedroom One depicts several windows and landscape
Bedroom Two depicts 4 scenes of landscape and figures separated by 3 columns/pilaster
Iconographic
Architectural style
In Room M in Villa of P. Fannius
Uses 3-point perspective to continuously shift focus throughout the room

Painted Garden
Visual
Consists of naturalistic trees, plants, and birds
Consists of a yellow fence and pink-grey fence behind it
Birds in active poses
Iconographic
Made in Villa of Livia
Livia is the wife of Caesar Augustus
In architectural style
Room was partially underground, heping to stay cooler
Uses atmospheric perspective for depth and distance
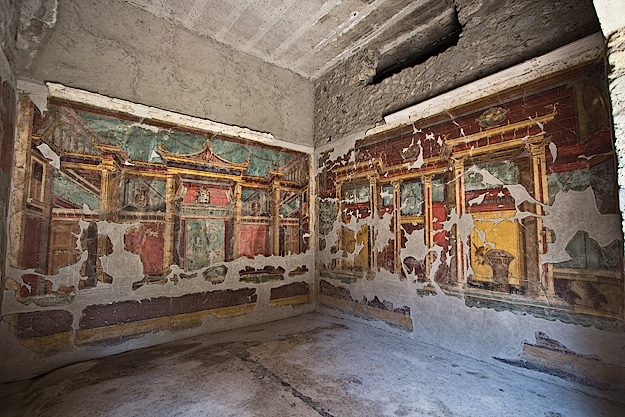

Villa Poppaea Sabina
Visual
Depicts imitation marble and other stones on top and bottom
Depicts columns and windows in various spots
Depicts flat red panels with various scenes
Iconographic
Found in Oplontis
Intricate style
Built for Poppaea Sabina by Emperor Nero as a retreat
Represented their welth and status

Ixion Room
Visual
Depicts imitation marble in the lower, rectangular part
Depicts an illusion of windows with figures inside of them
Depicts paintings with garlands and borders
Iconographic
In House of the Vettii
Intricate style
Excavated in 1800s
Owned by 2 Vettii brothers, who were former slaves that rose to civil office
Important for liberated slaves to show their accomplishments and status through different styles

Portrait of a Married Couple
Visual
Figures are naturalistic and realistic
Depicts two figures close to eachother
Man is wearing a white toga and holds a scroll
Woman is holding a clipboard and pen
Iconographic
In intricate style
Is Terentius Neo and his wife
White toga indicates he’s a freeborn or formerly enslaved man
Found near a bakery complex, so suspected that Terentius was a baker
Served as a public display of their literacy and wealth
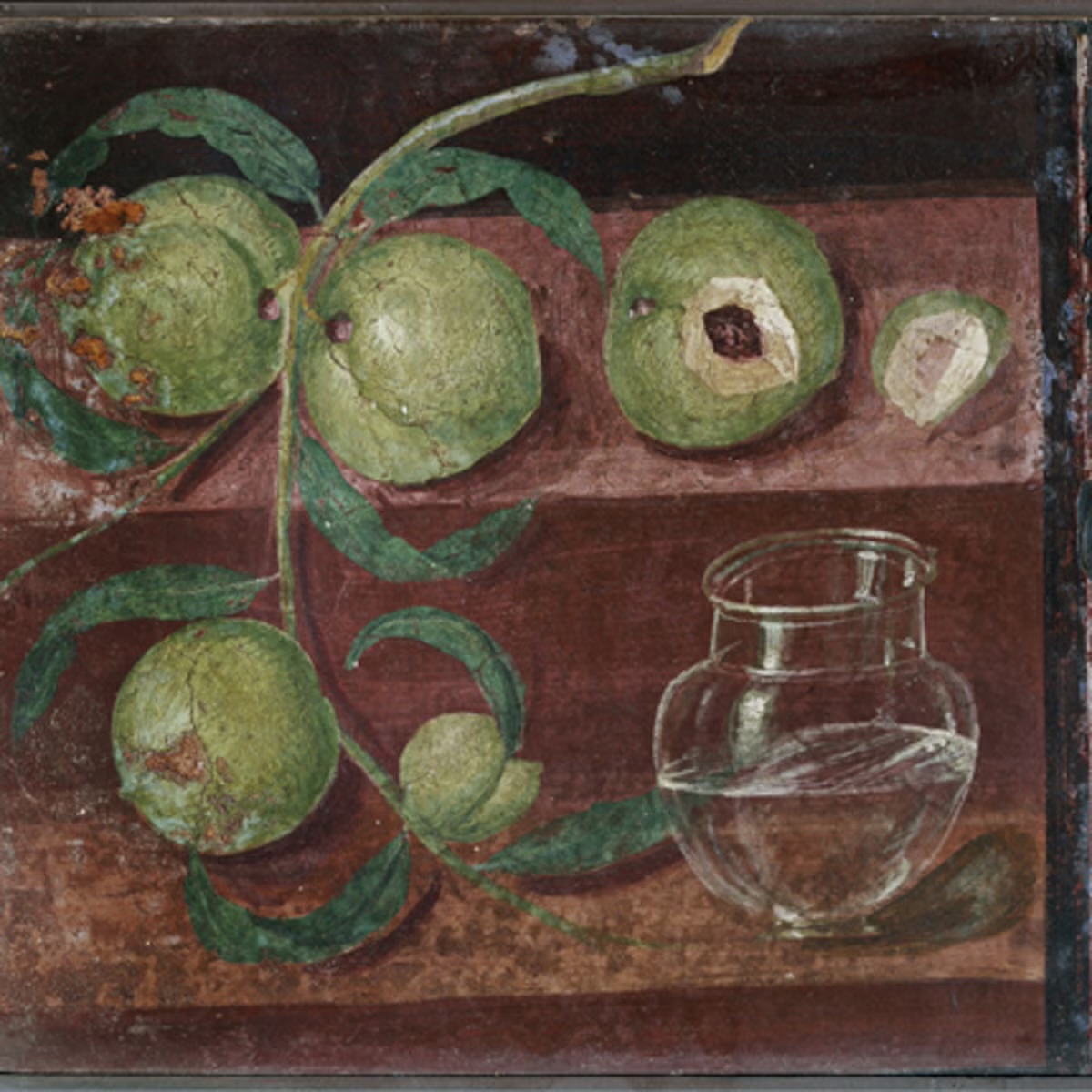

Still Life with Fruit
Visual
Depicts various fruits in cabinets
Are naturalistic
Iconographic
In Villa of P. Fannius Synistor
Romans invented “Still Life” paintings which disappeared until the Dutch revived it
After volcanic eruption, many of these paintings were found
Shows the practice of presenting the hostess gifts
Category of paintings known as Xenia, meaning hospitality

Two Pitchers and a Bowl
Visual
Made of glass
Depicts two pitchers and a bowl (obv)
Iconographic
Romans known for thier glass, as they adapted the glassblowing technique to mass produce and make it afforadble
Would use different types of glass
Became common,everyday objects that replaced ceramics
Had thinner walls, were translucent, and allowed for more shapes
High value was placed on colorless, translucent glass because it mimicked rock crystals
Empire Period (31 - 476 AD)
Julius Caesar extended Rome’s territory
Senators flee after killing Caesar, and 3 slaves carry his body to his wife
Mark Anthony had key to treasury and was the general of the military; joined forces with Cleo the 7th
Both defeated by Octavian (Caesar Augustus) 13 years later
Coins were a form of propaganda
Valued idealism over realism
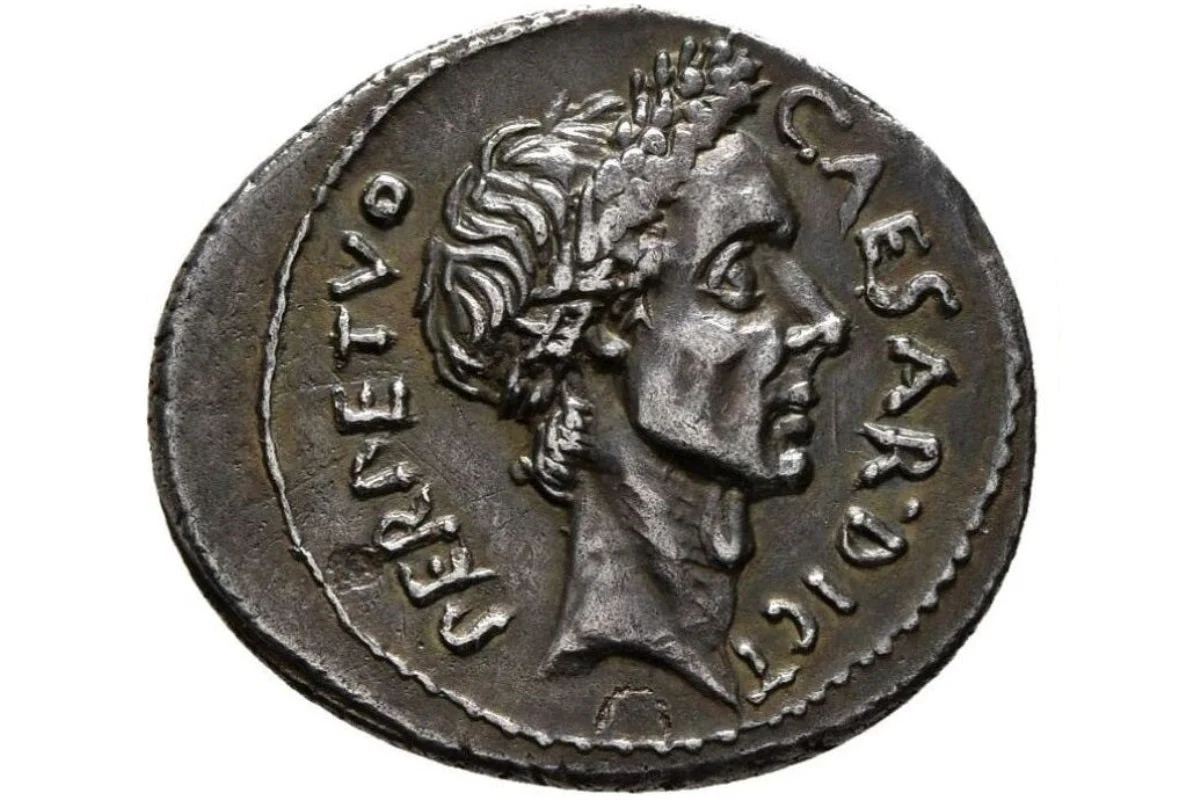

Denarius (Coin)
Visual
Made of silver
Depicts a naturalistic and realistic man with wrinkly skin, baggy eyes, and a possibly receding hairline
Iconographic
Part of Roman Empire
Is a portrait of Julius Caesar, the first to put his face on a coin
Reinforces the Roman view that age is a sign of wisdom
Used to show that he was the absolute ruler, an image constantly visible to the public
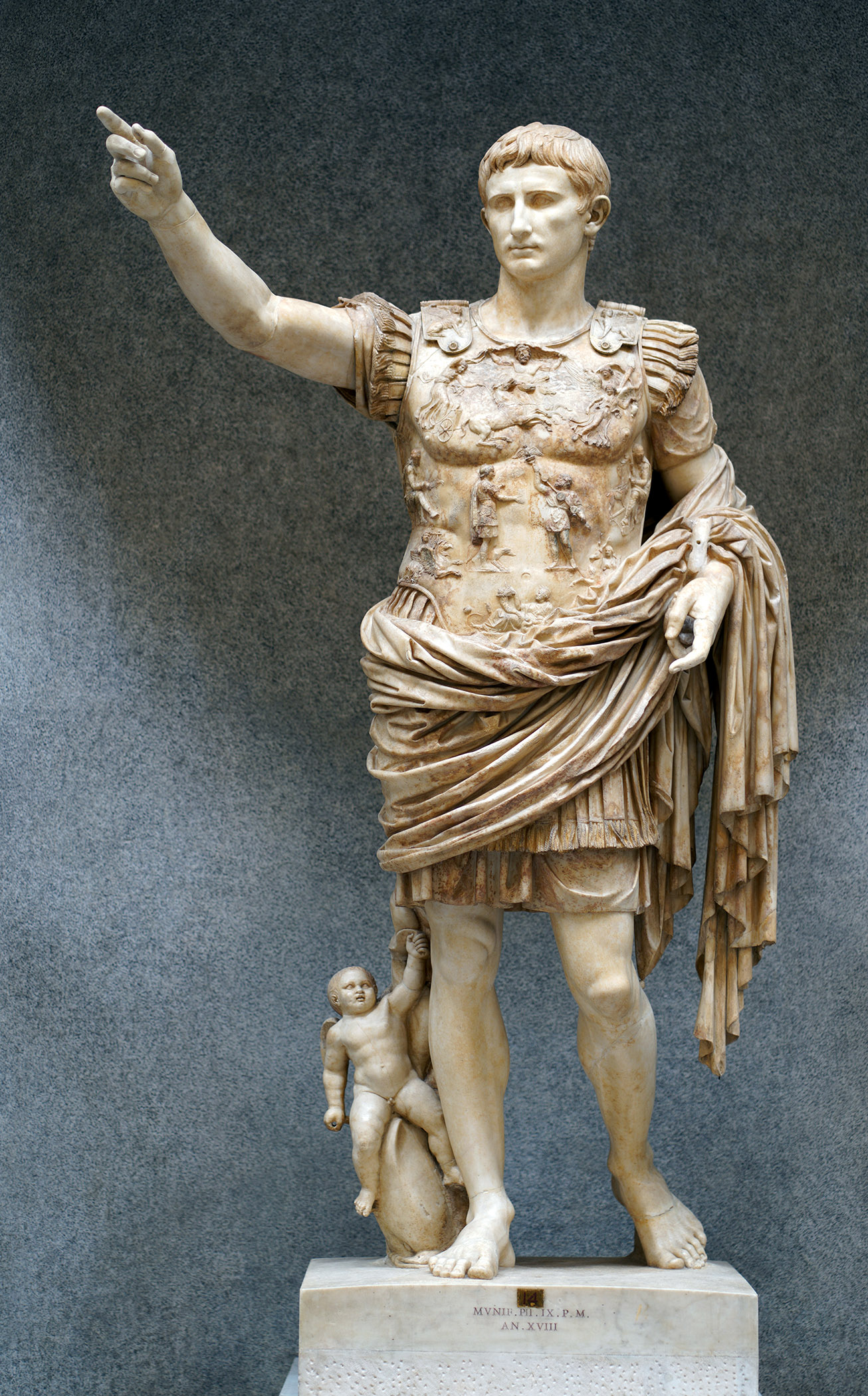

Augustus Primaporta
Visual
Marble copy of a bronze sculpture
Depicts naturalistic and idealistic figure
In relaxed contrapposto stance raising his right hand
Has straight nose, thin lips, and cowlick in hair
Wearing an armored breastplate
Tiny figure near his foot riding a dolphin
Iconographic
Found in estate of Livia
Is Caesar Augustus
Inspired by the Doryphoros statue, implying Augustus brought a golden age to Rome
Cupid’s symbolizes his right to rule because of dietized lieage
All sculptures made him more youthful (contrast of Republican view)
Breastplate represents Augustus’ achievements with divine help
Overall meant to celebrate Augustus’ victory over the Parthians, an enemy that continously beat the Romans

Ara Pacis Augustae
Visual
Made of marble
Has an altar
Lower frieze contains highly decorative relief depicting 50 naturalistic & abstract plant species
Have symmetrical and linear patterns
Animal forms are carved deep in the plants
Sides of the altar is a procession scene, as frieze moves from the back wall up towards the front sides
Figures face the main entrance
Figures in front are high relief while back are low relief
Iconographic
Means “altar of peace”, as it was used to commemorate the peace established by Augustus
Was reconstructed after fragments were discovered under a palace
Ordered by Mussolini, who identified himself with Augustus
Holds political and spiritual signifiance, as Augustus was a priest
Features Augustus’ family members, ministers, and priests with veils on their heads
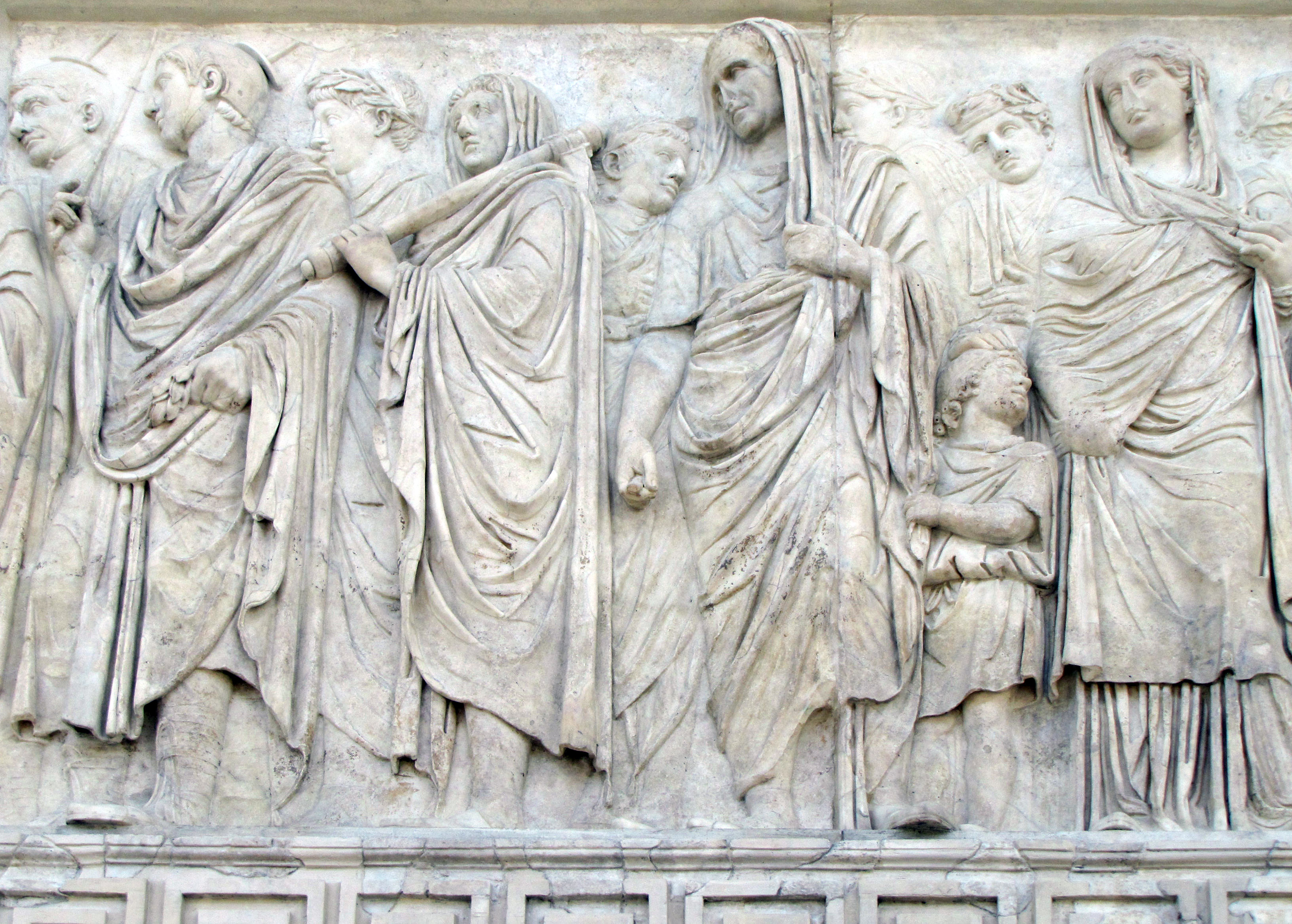

Imperial Procession
Visual
Made of marble
Figures in front are high relief, while back and low relief
Consists of several figures with different roles
Iconographic
On the north and south flanks of the Ara Pacis Augustae
Possibly depicts a celebration of peace
North depicts 46 priests and family members
South depicts Augustus and his immediate family, including Agrippa in a veil
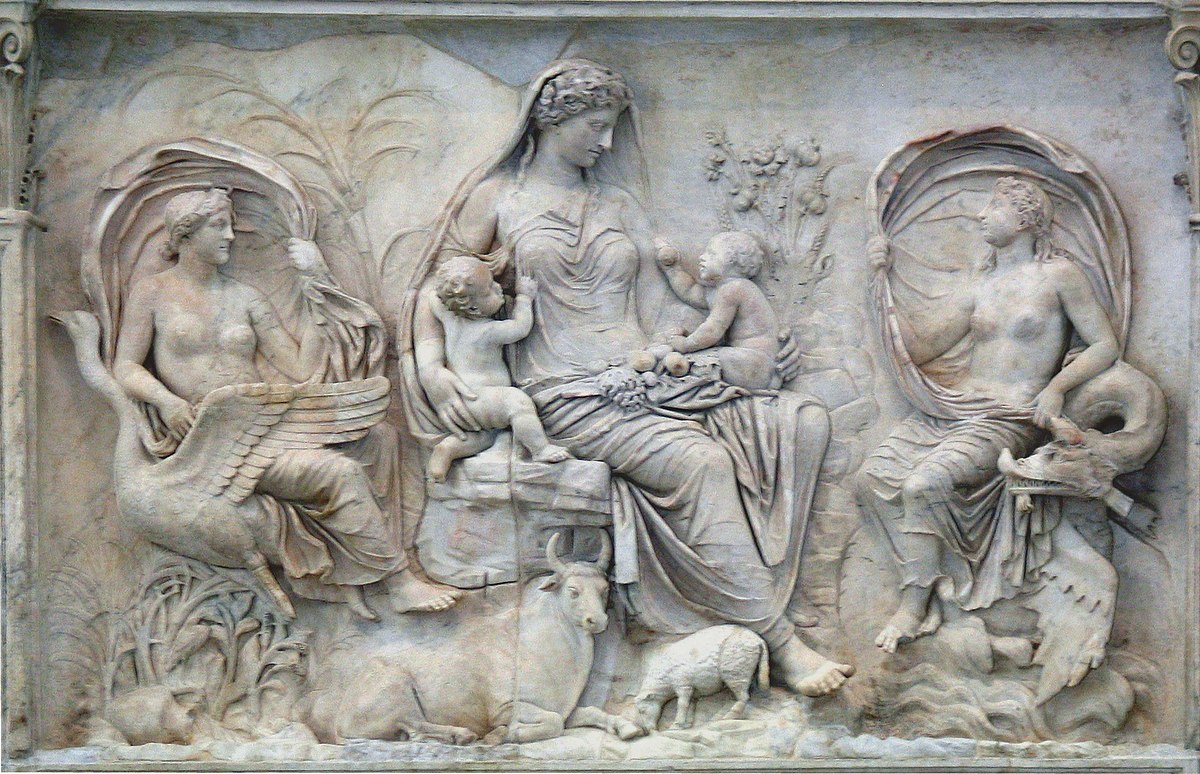
Tellus Panel
Visual
Made of marble
Figures are naturalistic and idealistic
Depicts a woman with clinging drapery
Depicts two children sitting on her lap offering fruit
Depicts ox an dsheep at her feet
Iconographic
On top of the meander at the Ara Pacis Augustae
Children probably represents the winds of the eart and sea
Sense of harmony and peace
Unknown who woman is, but she’s overall a symbol of abundance and fertility
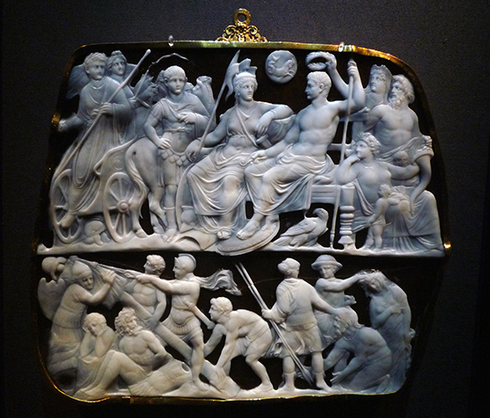

Dioskourides
Visual
Double-layered sardonyx with gold and gold-plated silver
A large cameo
Upper register contains Roma surrounded by Military, Augustus semi-nude holding a scepter, and an eagle near his feet
Personifications of Oikouemene (civilized world), Oceanus (oceans), and Tellus Italaie (Italy)
Lower register depicts captive barbarians and victorious Romans
Iconographic
Private commission by Augustus
Wasn’t seen by a large audience but still had the same purpose
Upper focuses on peace, while lower focuses on the wars that helped maintain peace
Upper register used to symbolize his right of rule, godlike qualities, and devotion to spreading peace through the civilized world
Overall used as a political message of Augustus’ greatest accomplishment and connection to gods
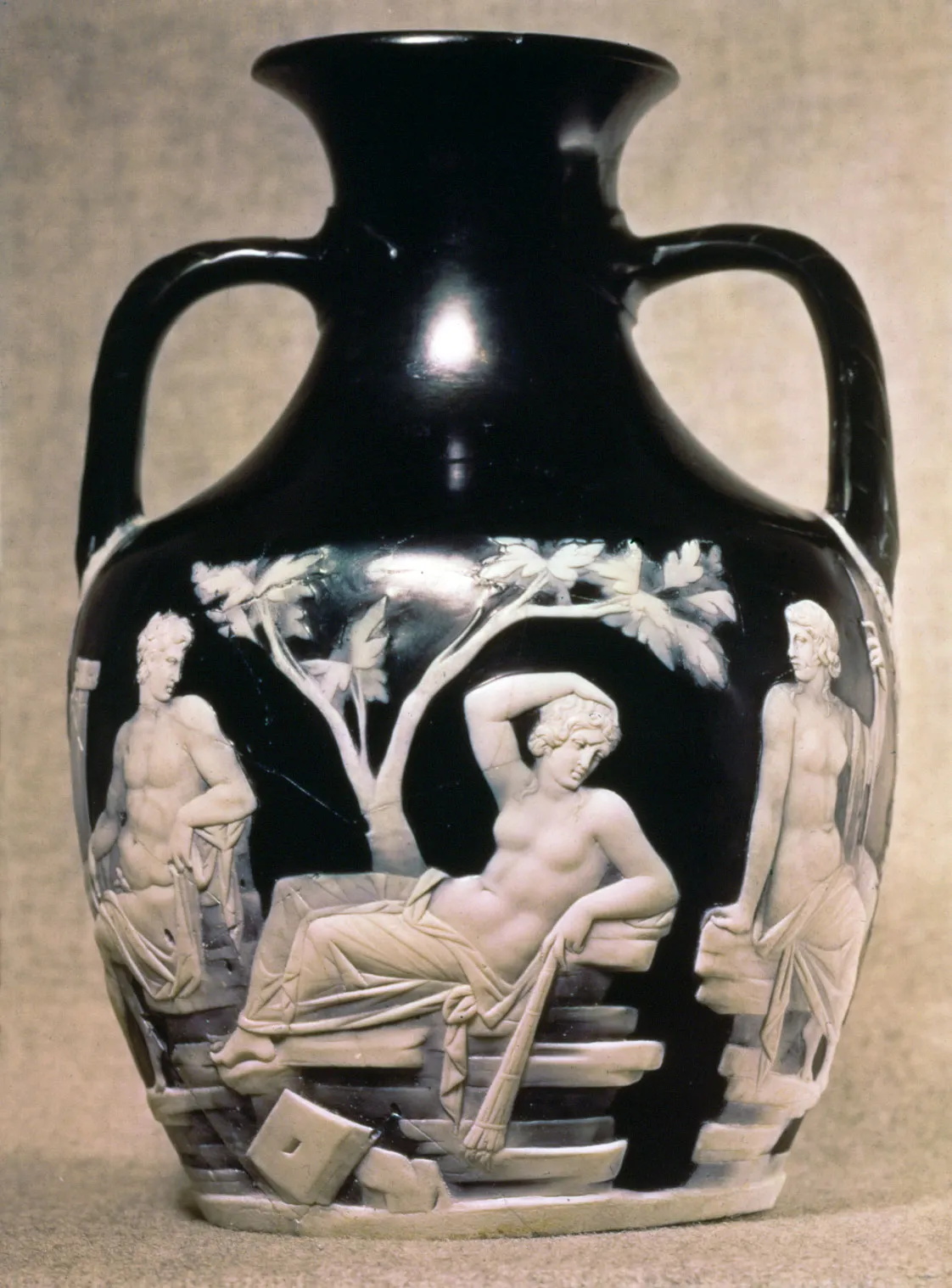

The Portland Vase
Visual
Dark cobalt blue and white cameo glass
Depicts white, naturalistic figures on a blue background
Wedding of the hero Peleus and Thetis the sea goddess
Iconographic
An amphora pot
Used cutting glass technique
Smashed in 1895, but put together by conservators
Missing a bottom
Is an important example of Roman vessels
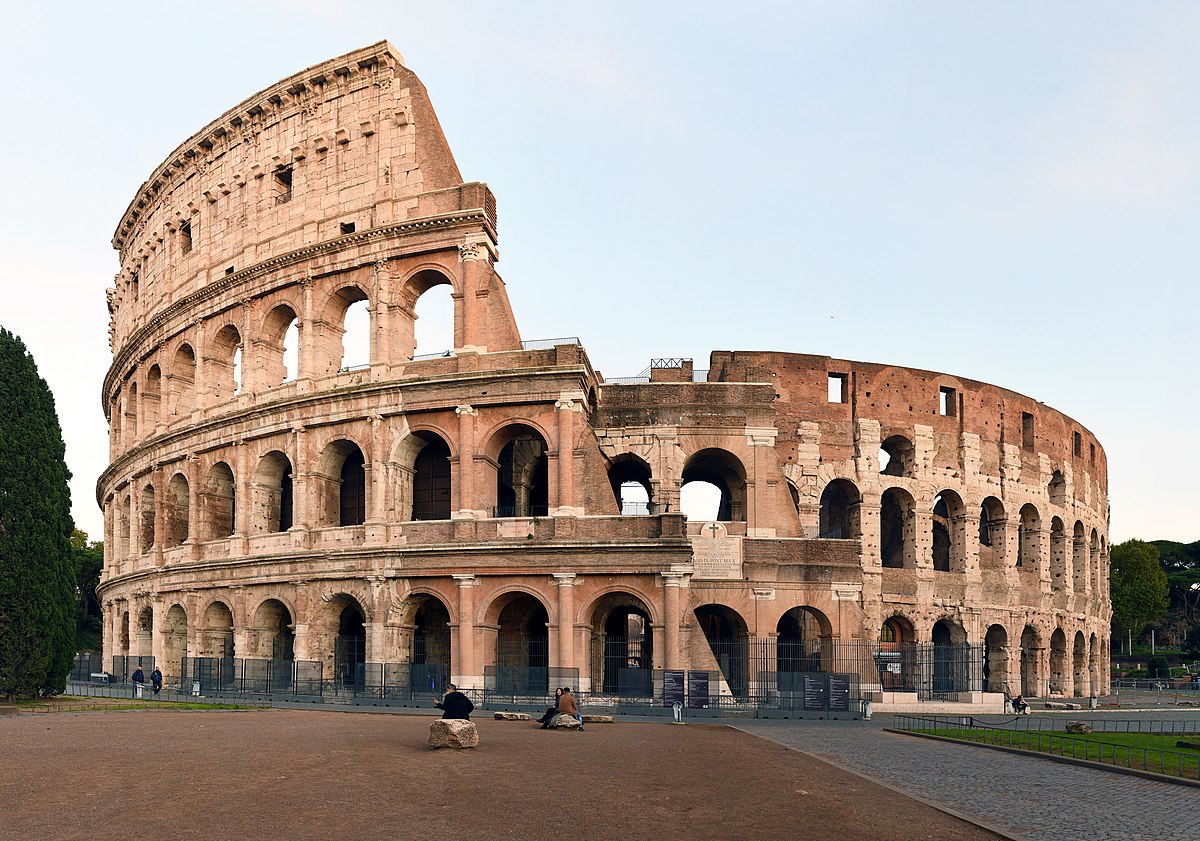

Flavian Amphitheater
Visual
Made of marble
Consists of a complex interior and simple exterior, which is three archades ontop of eachother
Iconographic
Built on order by Emperor Vespasian
Symbol of Flavian dynasty’s power
Marble seats given to the elite while wood seats given to everyone else
Held several games, executions, and gladiators seen in a theatrical way
Covered in awning to prevent people from getting wet
Netting at bottom to protect the emperor
Called Colossoeum during teh Middle Ages because of the colossal statue next to it
Emperor Hadrian moved an 100 ft tall sun god next to it

Young Flavian Woman
Visual
Made of marble
Idealized face and hair
Hair pulled forward & upwards into ringlets
Iconographic
Most likely a woman sculpted in the Flavian style
Drillwork used to make ringlets
Hair was very fashionable during teh Flavian era and probably popularized by a woman of teh Emperor’s court
Owned by Fonseca, who owned it in the 18th century and gave it to the Capitoline Museum
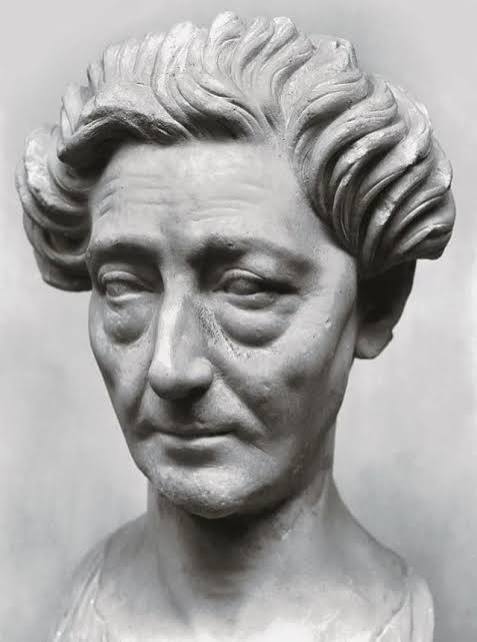

Middle-Aged Flavian Woman
Visual
More veristic than idealized
Hair is stylized
Has baggy eyes and wrinkles
Iconographic
Eyes and wrinkles show old age
Due to age, she would’ve been revered and looked up to when this bust was made

Arch of Titus
Visual
Made of concrete and marble
Is a freestanding gateway
Inscription reads “The Senate and Roman people dedicate this to Titus”
Iconographic
Concrete created by Romans
Made to commemorate Titus and his borhter, Domitian, in their victory in the Jewish war
Was once topped with a Bronze Titus on a horse
Inscription represents propaganda by Emperor Domitian
Sought to gain favorable public opinion as he rose to power
Concrete made by mixing lime, pozzolona, and water, then adding rock fragments
Cladded the concrete with thin marble panels to use less, showing that Rome was on a budget
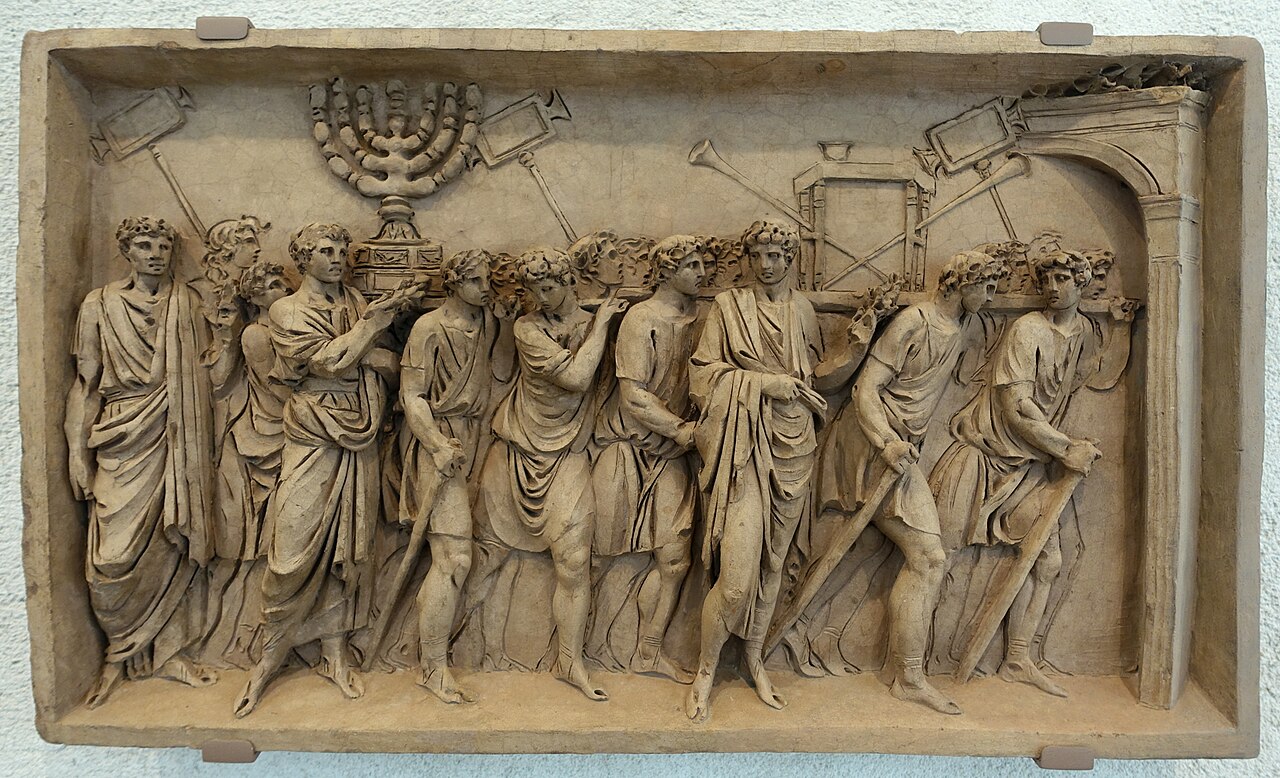

Spoils from Temple of Jerusalem
Visual
Depicts spoils of Jerusalem being brought to Rome in a triumphal parade honoring Titus
Figures are natualistic with an illusion of space as soldiers carry treasure
Figure on monument is Josephus
Iconographic
On the Arch of Titus
Triumphal archs are where emperors would enter with treasure, attendants, soldiers, and prisoners of war
The general of the losing army would be ceremonially murdered
Josephus was a Judean general who switched sides during the war
Spoils were considered holy objects
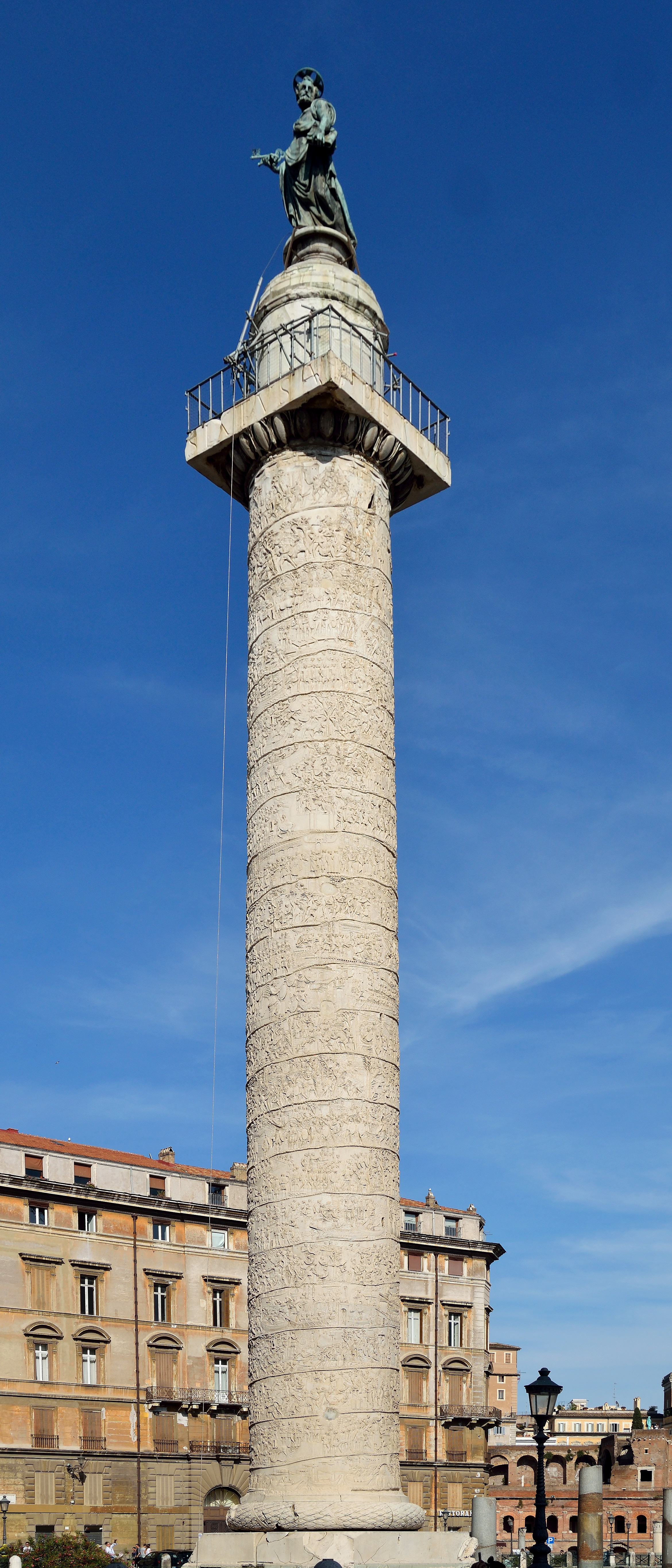

Column of Trajan
Visual
Made of marble
Is a column meant to be on its own
Is 125 ft tall
Covered in spiraled relief decoration
Depicts Trajan victories
Iconographic
Commissioned by Domitian
Emperors left their successes to able ministers instead of heirs to ensure continued stability
Spiraled relief decorations are a reference to scrolls
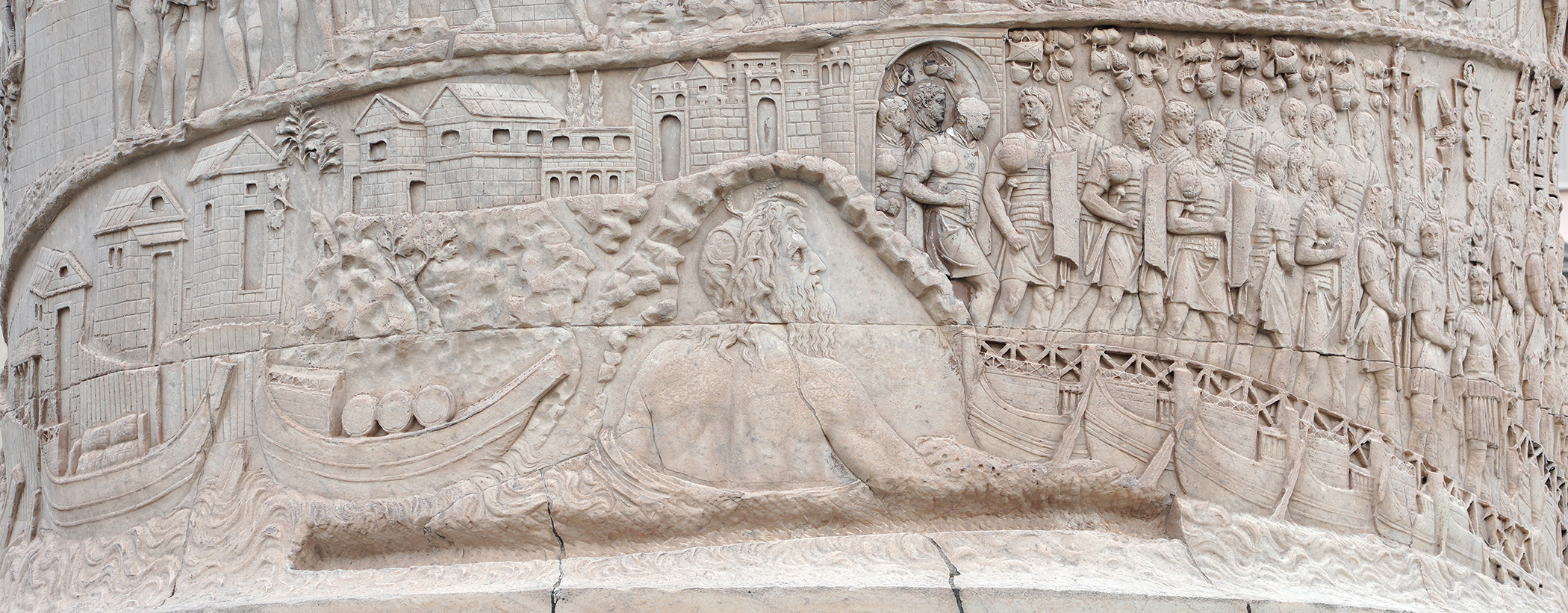

Romans Crossing the Danube and Building Fort
Visual
Made of marble
Depicts Romans crossing the Danube river in the first Dacian War
Depicts Roman army building a fort
Figure seen inside the water as Romans cross
Iconographic
Is the lower band of the Column of Trajan
Figure is personified version of Dabune (Danubus) to represent the river
Buildings were solid and well designed, showing how they’re disciplined and accomplished
Would also clear forests and build roads
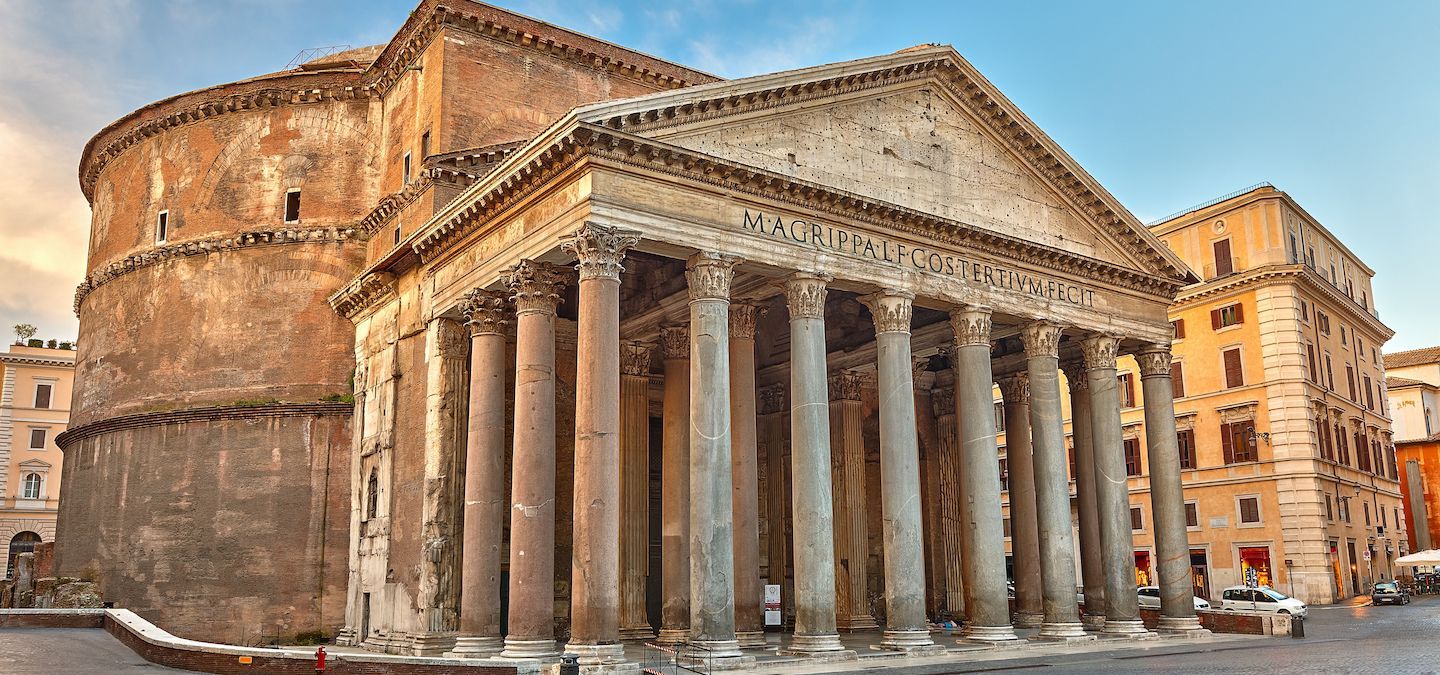

Pantheon
Visual
Made of concrete
Framed by a colonnade supported by marble bases & has Corithian capitals
Inside consists of ideal geometric shapes, friezes of false windows, coffers, and an oculus on the dome
Iconographic
Original bronze fittings are ripped off
Originally a temple to the gods, then made into a church
Imported from Egypt, a symbol of Rome’s power over the Mediterranean
Emperor Hadrian ordered construction of this building
Coffers used to reduce the dome’s weight for stability
Originally contained sculptures of gods and dietized emperors, symbolizing the earthly sphere meeting the heavenly sphere
Oculus represents advanced Roman engineering and architecture, as it’s the perfect circle
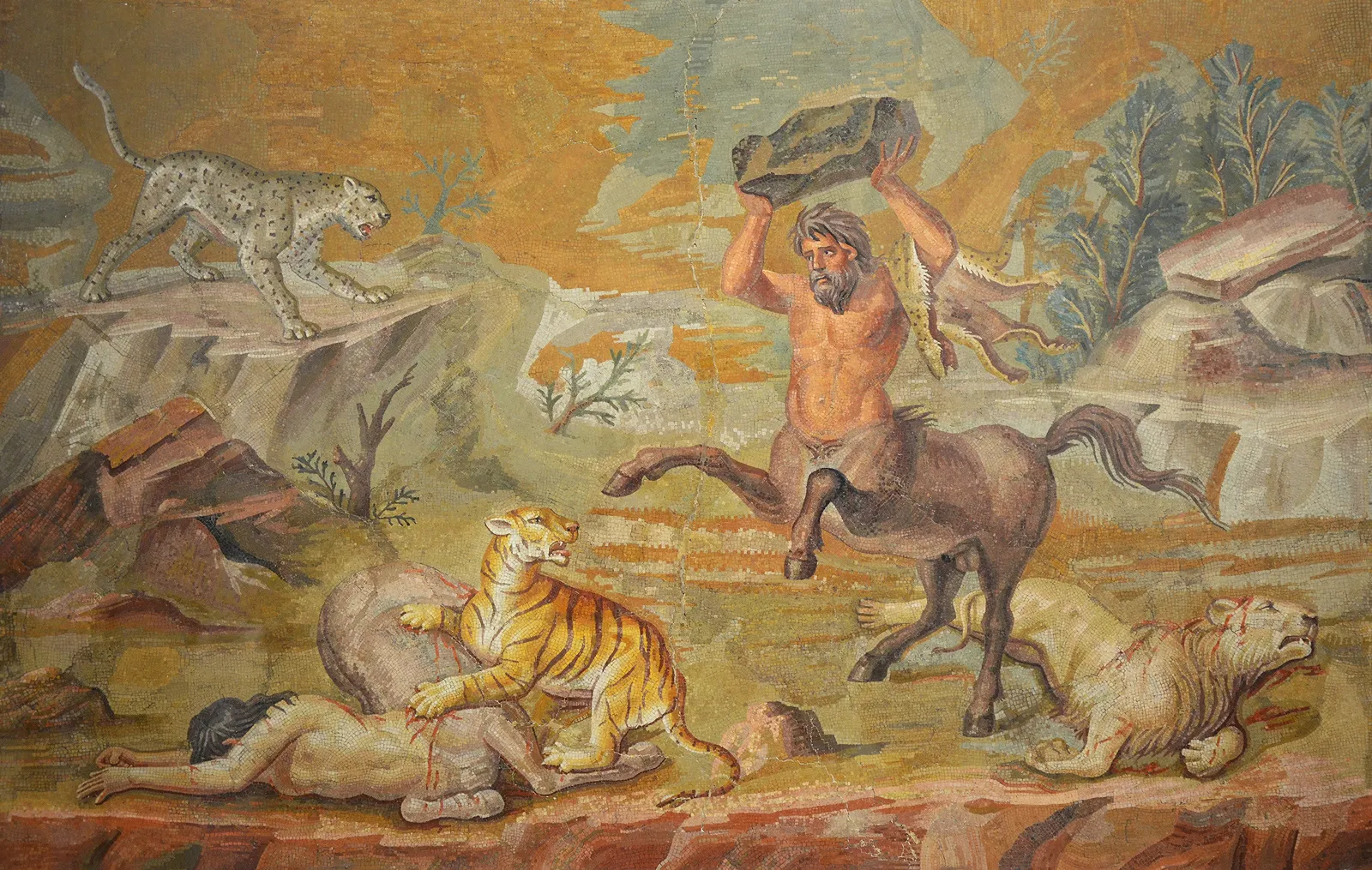

Pair of Centaurs Fighting Cats of Prey
Visual
Made of mosaic, stone, and tesserae (small block of material used in mosacis)
Naturalistic figures with a sense of depth and foreshortening
Depicts centaurs fighting with beasts
Centaur has worried expression as he’s about to hit the tiger, while the animals lack expressions
Iconographic
Found in Hadrian’s villa as part of a floor mosaic
Wild beasts would be kept in cages under Colosseums for entertainment and public executions
Different animals show Rome’s outreach, as tigers, cheetahs, and leopards don’t live in the same area
Symbol of how Romans saw themselves as separate from the chaos of nature, as we’re made to feel sympathy for the centaur due to its human qualities
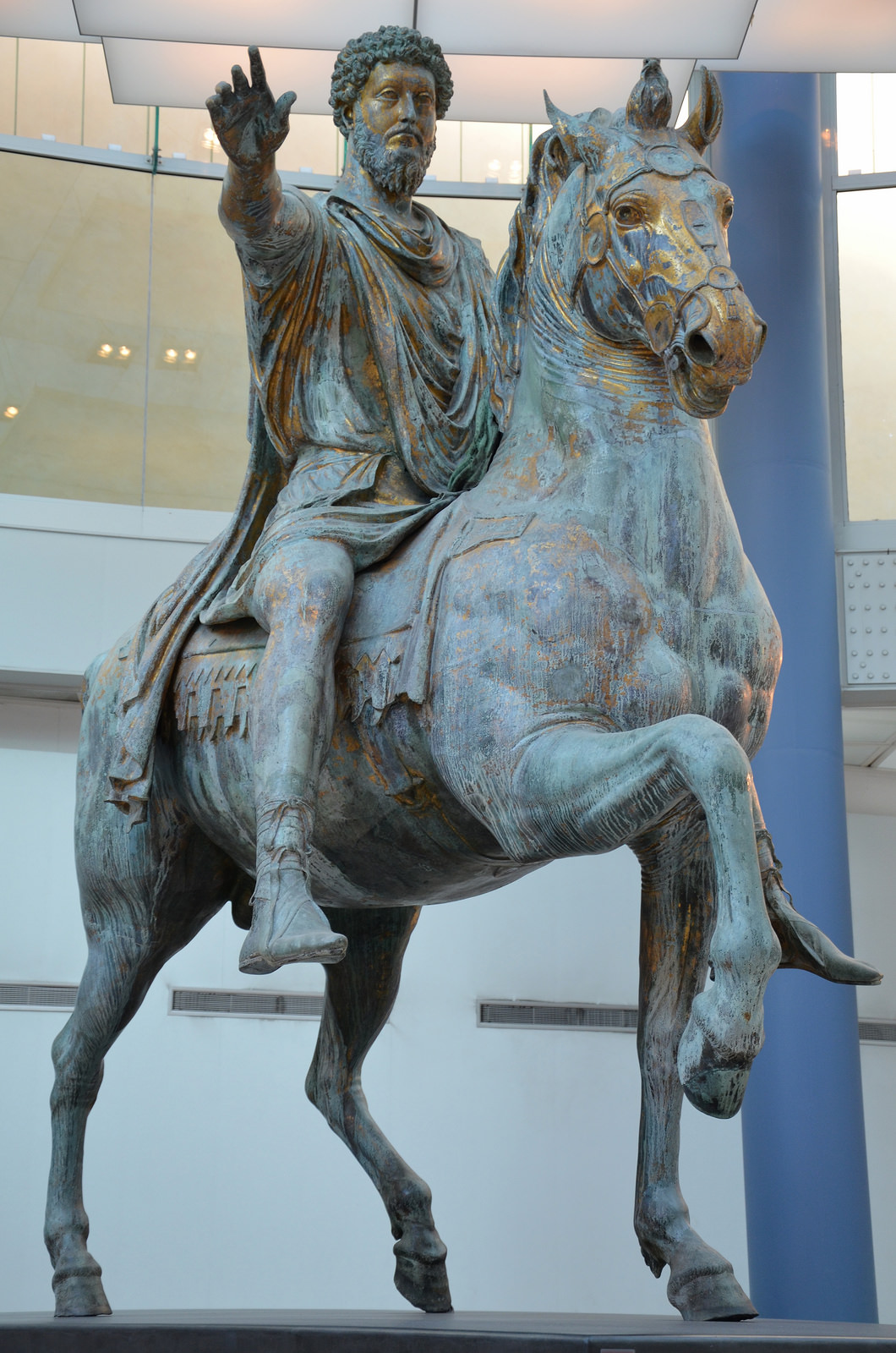

Equestrian Statue of Marcus Aurelius
Visual
Made of bronze
Depicts naturalistic and idealistic man with a Roman toga in Orater pose
Is a massive statue, but isn’t intimidating
Iconographic
Originally gilded
MA was the last good emperor before the Severan dynasty
Middle Ages assumed this was Constantine, so it wasn’t melted for armor
Pulled influence from Roman Republic, who prioritized political figures and military leaders
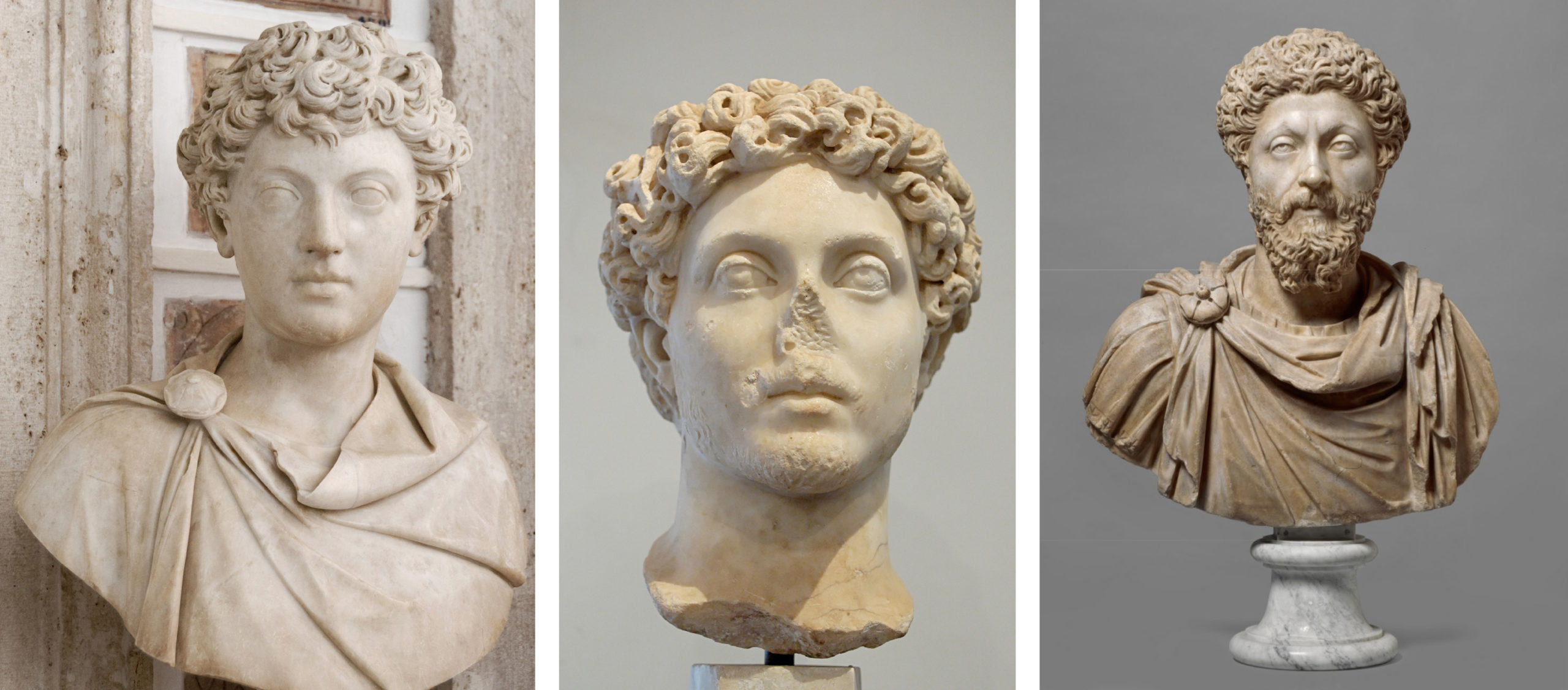

Marcus Aurelius Portraits
Visual
Made of marble
Are naturalistic and idealistic
Iconographic
Used as propaganda of a courageous and reliable leader
Unlike Augustus, these statues depict his age overtime
Became emperor at 40, so many depict him as 40 and up, with a beard
Severan Dynasty (193 - 235 AD)
Marcus Aurelius’ son, Commodus, took over and ensued chaos with his tyrannical rule
Assasination triggered war, which ended in Septimius Severus being the next emperor
Was an African emperor who strengthened infrastructure and maintained peace
Dynasty ends after last emperor is assasinated
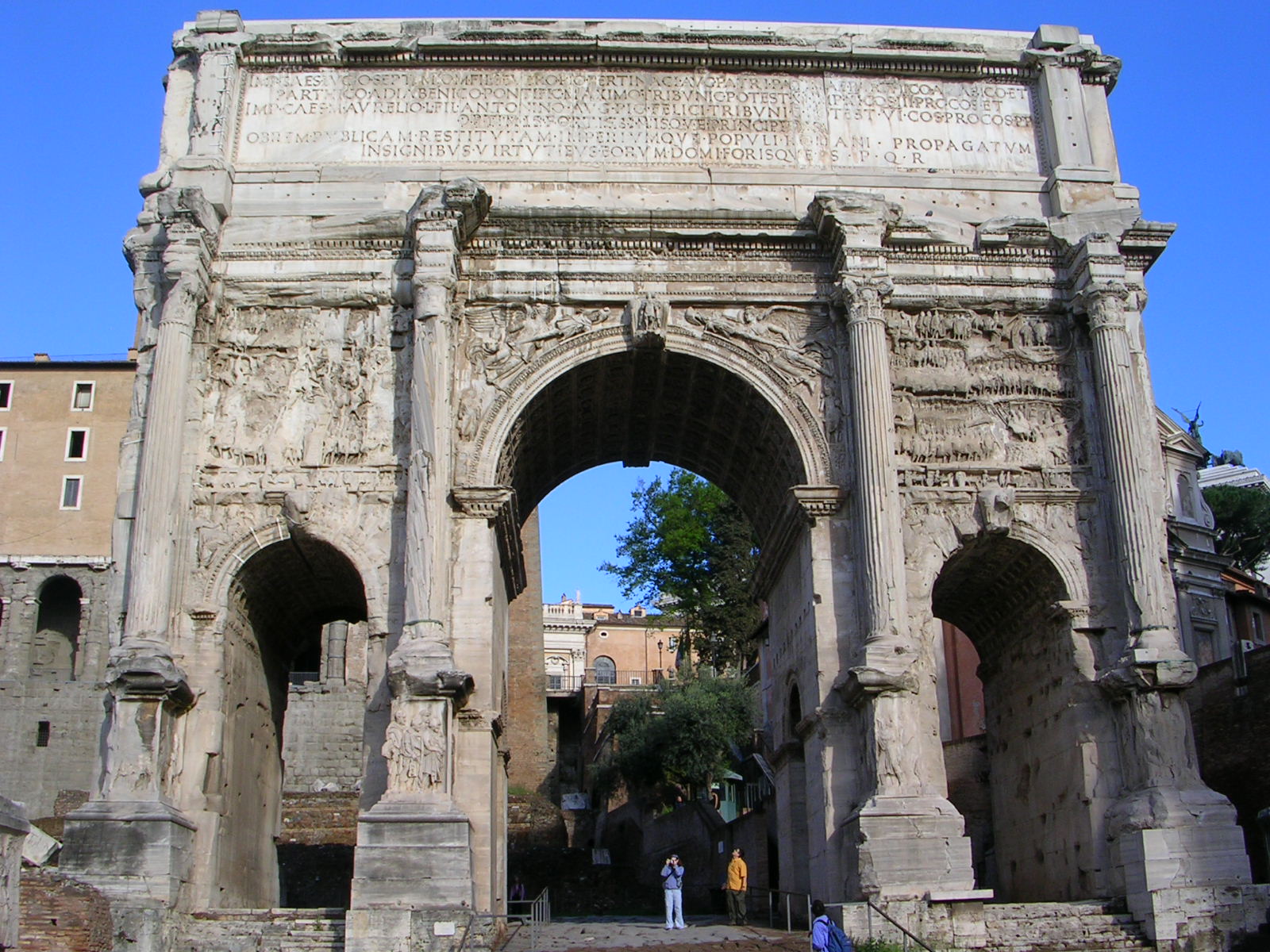

Arch of Septimius
Visual
Made of marble above a tavertine base
Is a triumphal arch ‘Consists of three bays with coffered barrel vaults
Forum side has massive freestanding columns with coposite capitals
Spandrels contain figurative sculpture with military scenes
Panels narrate the battles and cities that were conquered by Septimius
Some panels also show emperors in frontal view infront of a crowd
Has inscription
Iconographic
I by the Dan Martine Church, the civic and religious center of the Empire
Arch celebrates the military victory against the Parthians
Septimius refused the offer of a triumph because he suffered from arthritis
Panels of emperors infront of crowds express leadership
Inscription was originally gilded bronze letters and symbolized the power of the Emperor
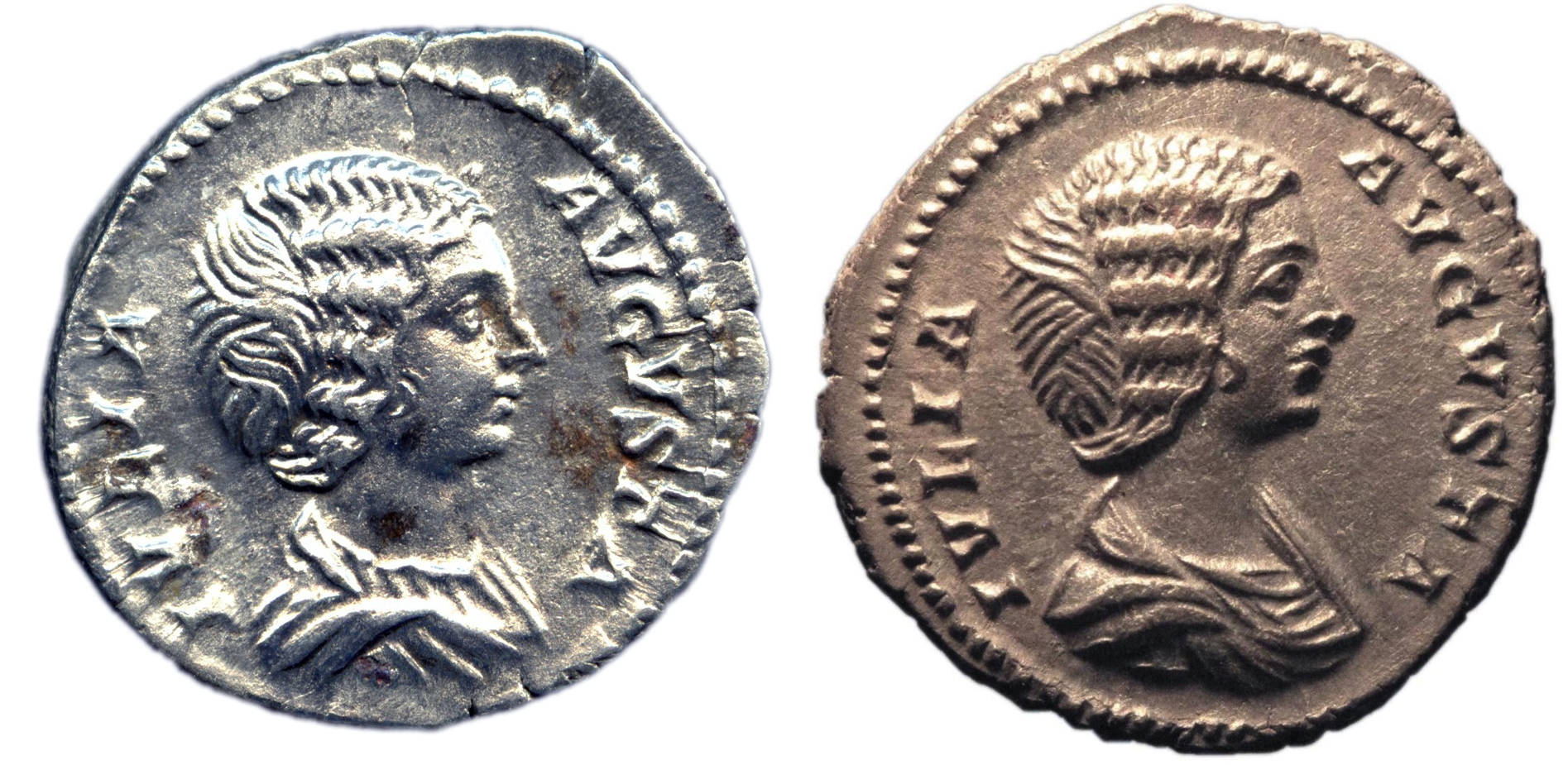

Severan Coin
Visual
Made of silver
Depicts woman with stylized hair consisting of a chignon, ridged waves, and small curl on the cheek
Is in relief
Iconographic
Depicts Julia Domna, the wife of MA
Married while he was a general
Became first empress of Asia
Used as propaganda to promote the Severan dynasty and her power as an Empress
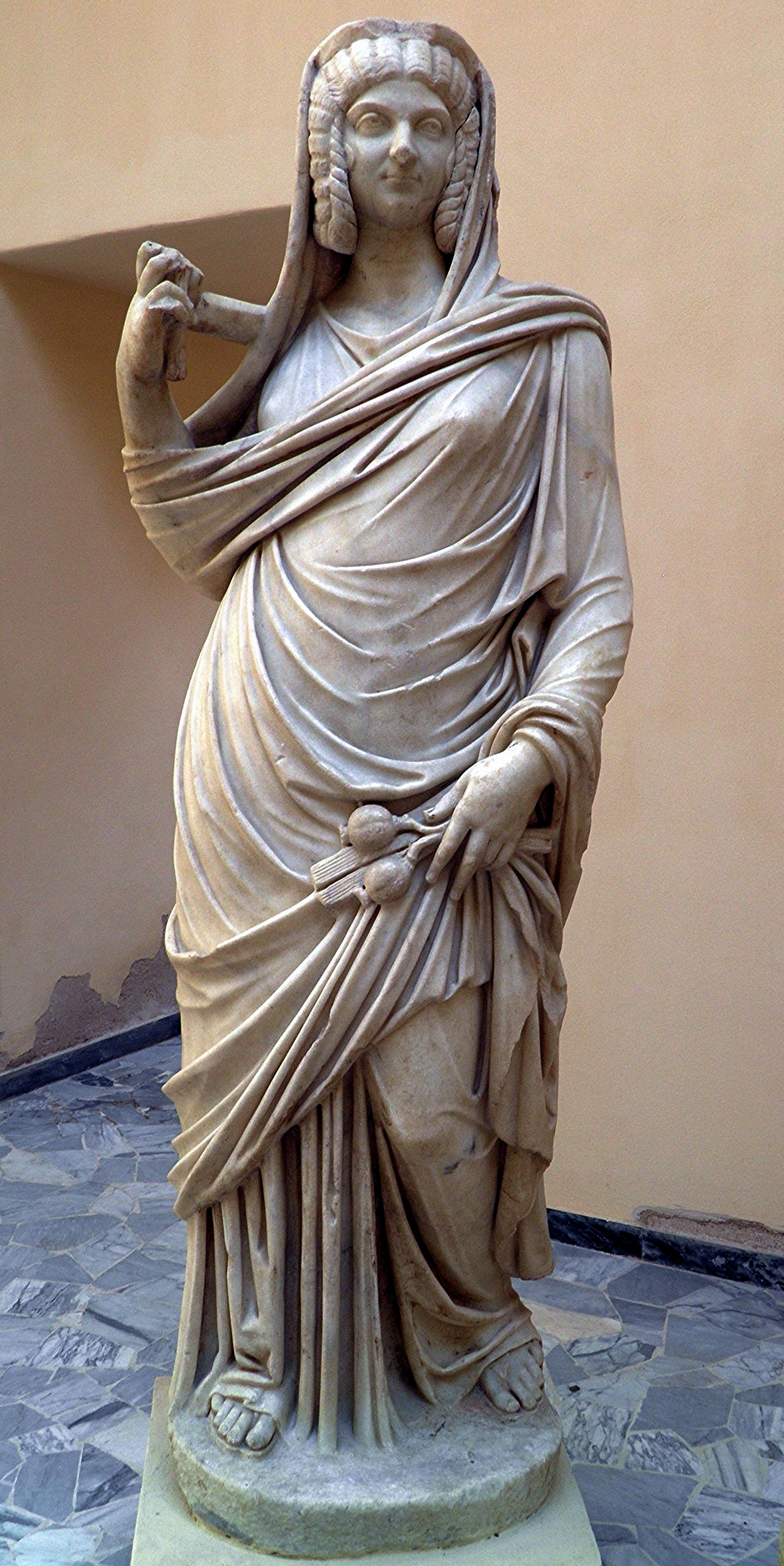

Julia Domna
Visual
Made of marble
Idealistic and realistic
Is in exaggerated contraposto stance
Has wrinkles, a broad forehead, smooth skin, and slight smile
Visible broken diadem on head
Holding wheat
Has a head covering
Iconographic
Forehead, skin, and smile were the ideal Roman beauty
Wigs were commonly worn in Rome
The crimped and braided sections are a way while the curls on teh cheek are natural
Broken diadem signals divinity
Wheat associated with Ceres, goddess of agriculture
Head covering is a sign of piety in religious ceremonies
Overall symbolizes a goddess essential for Roman prosperity and the feminine virtue of fertility
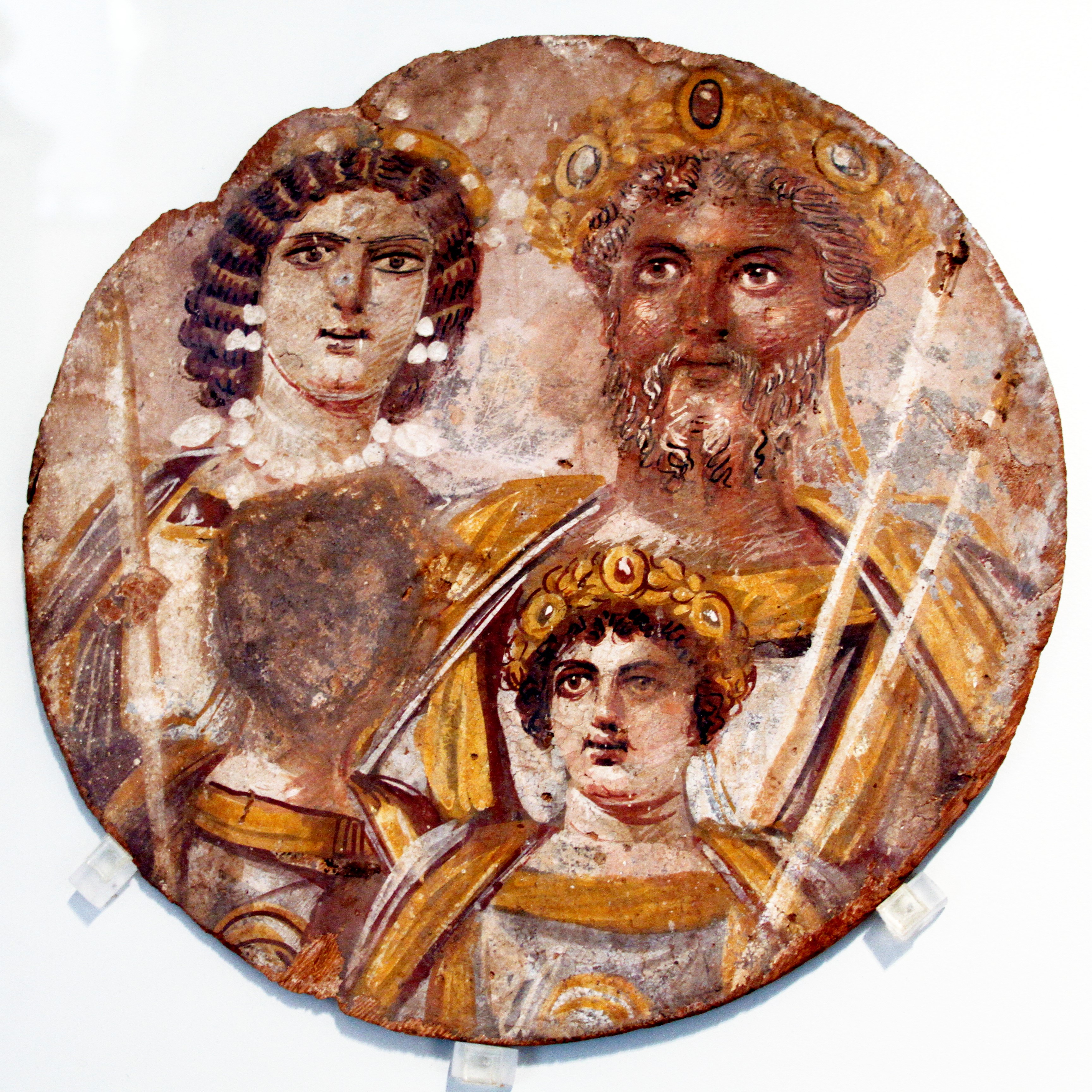

The Severan Tondo
Visual
Is tempera on wood
Depicts naturalistic figures in a family portrait
Upper right is is Septimius, with long hair and beard
Upper left is his wife, with pearls around neck and on ears
Bottom right is Caracalla and left is Geta
Iconographic
Rare example of the early use of tempera
Family protraits were a way to project their identity throughout the empire
Beard and hair are symbol of MA, as Septimius identifies with and calls himself MA’s son
Geta’s face is scraped away purposfeully
Due to having Geta murdered and passing laws to erase his memory, as Caracalla waned full power
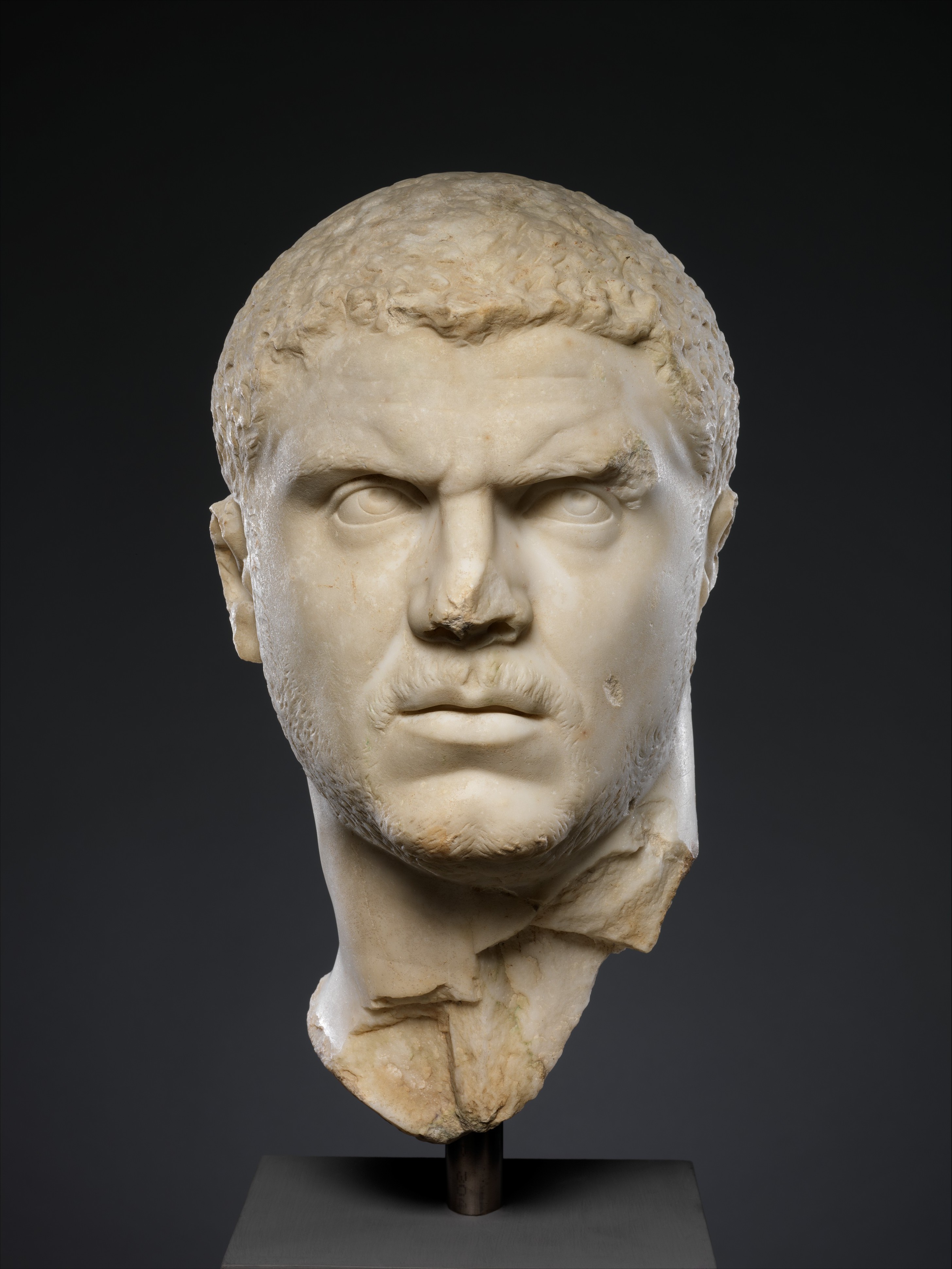

Caracalla Portrait
Visual
Made of marble
Is realistic with furrowed brows and wrinkles
Has drilled pupils to give more realism
Has a stern, wary look on his face that gives off paranoia
Iconographic
Depicts Caracalla
Became emperor but was later assasinated
Augustae & Caesars
Generals try to rule with little success
Diocletian, a politician, establishes peace in 284 AD
Divides Rome in two parts, each having a co-emperor, to make ruling manageable
East ruled by Diocletian Augustus and Galerius Caesar
West is ruled by Maximum Augustus and Constantius Caesar
Caesars were successors to the Augustae
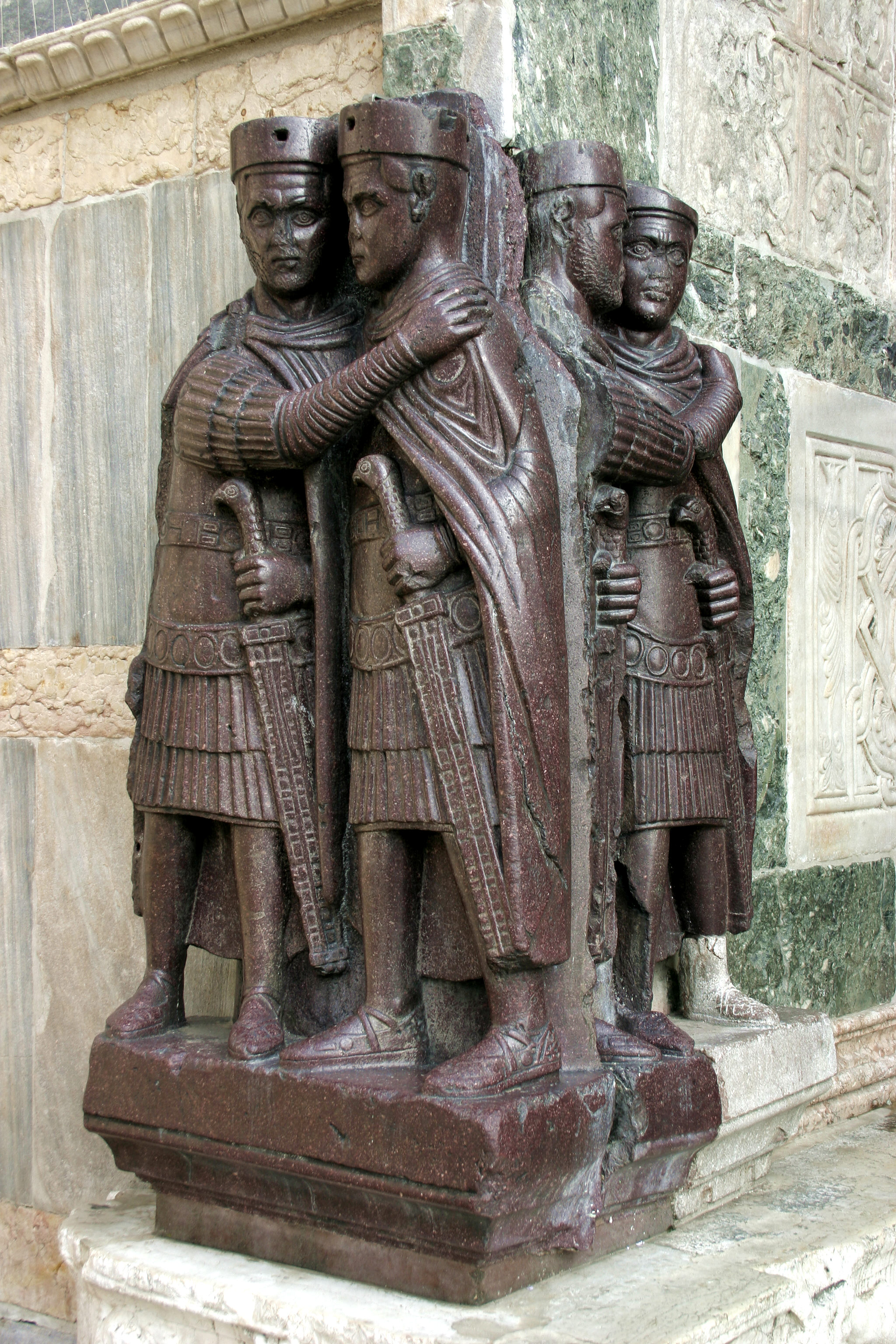

Portraits of Four Tetrachs
Visual
Made of porphyry (hard purple stone from Egypt)
Abstract and stylized
Depicts four figures clutching each other, possibly afraid
Have similar, almost identical faces
Iconographic
Unknown where style came from
Augustaes have bears, while Caesars don’t, so these are most likely Caesars

Constantine the Great Coin
Visual
Made of bronze
Front is naturalistic portrait of Constantine
Back is chi (x) rho (p) symbol
Iconographic
Constantine becomes emperor after Caesars take over and fight for power
Had a vision of the Chi Rho symbol, believing it to be a symbol from teh Christian god
Ordered it to be put on his soldier’s shields
Helped to recognize freedom to all religous groups
Likely used exucse of vision for political move, as he’s well revered by many
Didn’t convert ot Christianity until deathbed, as Emperors were the head priests and oversaw the state religion
Died in 337 AD
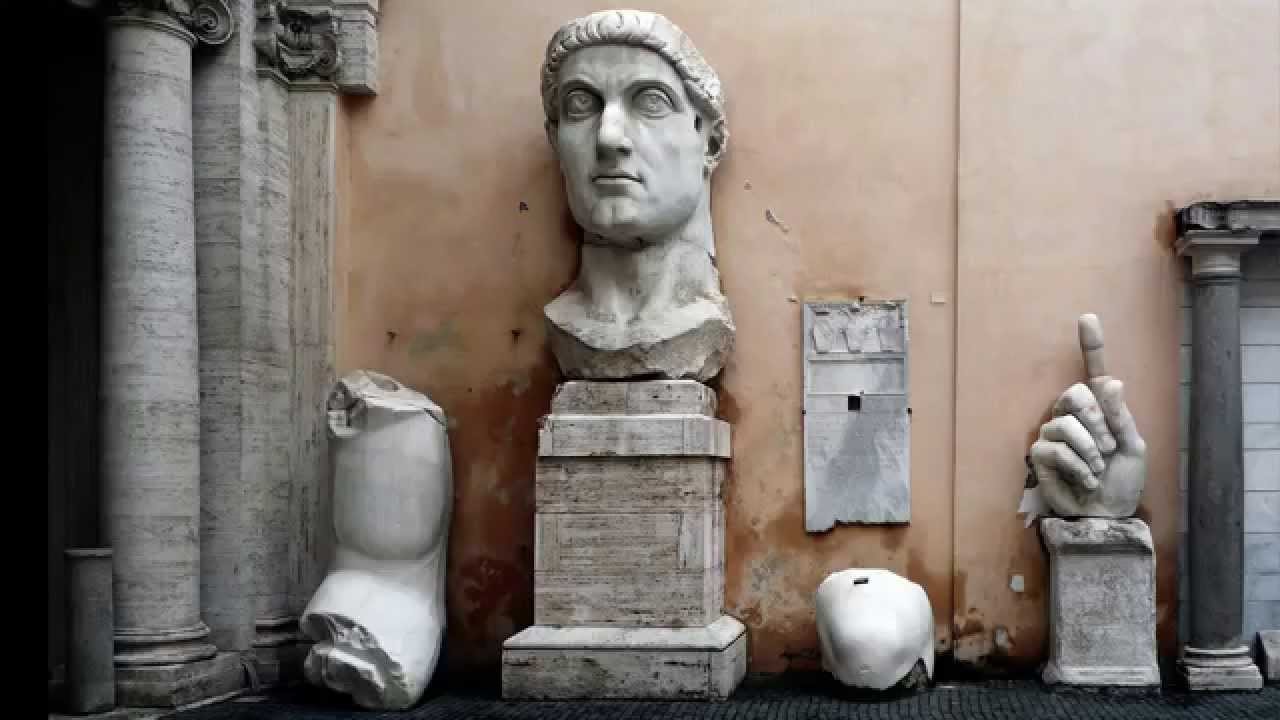

Colossals of Constantine
Visual
Made of marble
An individualized portrait
Realistic and idealistic with large eyes and stylized hair
Iconographic
Is now in fragments
Originally 30 ft tall
Size and figure are a symbol of power
Influenced by Egyptian colossal sculptures
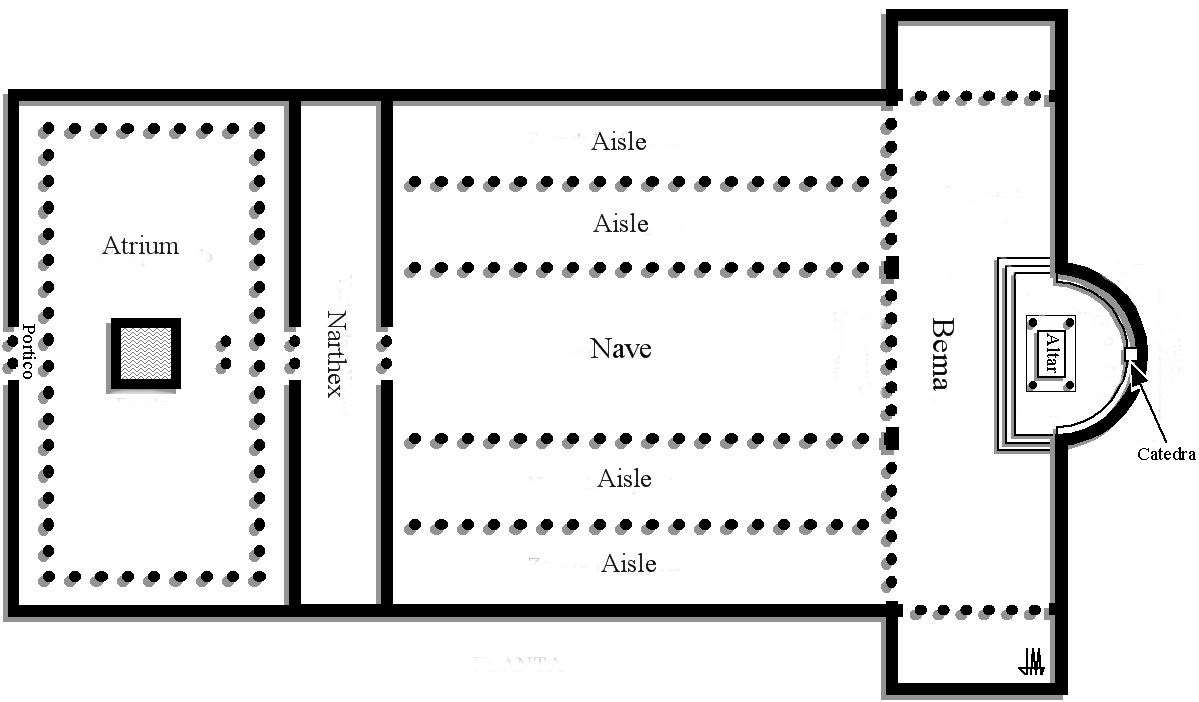
Old St. Peters
Visual
Made of brick, wood, and marble
Is a Basilica floor plan
Consist of a nave, aisles, apse, transept, narthax, and atrium
Has a clerestory
Iconographic
Commissioned by Constantine
Clerestory contained a row of windows to let in light
Was falling apart, so a new on was ordered to be builtUsed spoila, reusing older columns with various marble for new construction